Cardiovascular System Overview and Cardiac Cycle- Phys Worksheet Practice
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
The circuit that connects the heart and lungs, carrying blood to the lungs for gas exchange and returning it to the heart.
Pulmonary Circuit
The circuit that connects the heart to the rest of the body, supplying oxygenated blood to tissues and returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Systemic Circuit
The chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
Right Atrium
The valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle that prevents backflow of blood.
Tricuspid Valve
The chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Right Ventricle
The valve located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk.
Pulmonary Valve
The vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Pulmonary Trunk
The vessels that transport deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Pulmonary Arteries
The vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
Pulmonary Veins
The chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Left Atrium
The valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Mitral Valve
The chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
Left Ventricle
The valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Aortic Valve
The largest artery in the body that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
Aorta
The large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart.
Superior Vena Cava
The large vein that returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava
The tough outer layer of the pericardium that protects the heart.
Fibrous Pericardium
The inner layer of the pericardium that produces serous fluid to reduce friction.
Serous Pericardium
The outer layer of the heart wall, also known as the visceral layer of the serous pericardium.
Epicardium
The thick, muscular middle layer of the heart wall responsible for contraction.
Myocardium
The inner layer of the heart wall that lines the chambers and valves.
Endocardium
Internal ridges of myocardium in the right atrium and auricles that allow for stretch and increased volume.
Pectinate Muscles
Tough, tendinous strands that hold the AV valves in place during heart contraction.
Chordae Tendineae
Muscles located in the ventricles that attach to the AV valves via chordae tendineae and prevent valve prolapse.
Papillary Muscles
Internal ridges in the ventricles that prevent the walls from sticking together after contraction.
Trabeculae Carneae
The pathway of blood as it circulates through the heart, including the sequence from the atria to the ventricles and out to the lungs and body.
Blood Flow Through the Heart
The phase when ventricles decrease in pressure and volume after ejecting blood, allowing for filling from the atria.
Ventricular Relaxation
Valves located at the exit of the ventricles that prevent backflow into the ventricles when they relax.
Semilunar Valves
Valves between the atria and ventricles that open to allow blood flow into the ventricles during filling.
AV Valves
The phase when the atria contract to push blood into the ventricles, increasing pressure in the atria.
Atrial Contraction
The phase when ventricles contract to eject blood into the aorta and pulmonary trunk, increasing pressure in the ventricles.
Ventricular Contraction
The inverse relationship where an increase in volume leads to a decrease in pressure within the heart chambers.
Pressure-Volume Relationship
The flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart, supplying it with oxygen and nutrients.
Coronary Circulation
An artery supplying blood to the left atrium, left ventricle, and interventricular septum.
Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
A branch of the LCA that supplies blood to both ventricles and the anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum.
Anterior Interventricular Branch (LAD)
An artery supplying blood to the right atrium, SA node, AV node, and posterior part of the interventricular septum.
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
A condition often involving blockage of the LAD, leading to damage of the heart muscle due to lack of blood supply.
Myocardial Infarction
A large vein that collects blood from the heart muscle and drains it into the right atrium.
Coronary Sinus
Heart muscle cells that are striated, short, thick, branched, and typically contain one nucleus.
Cardiomyocytes
Specialized structures that connect cardiomyocytes, allowing for synchronized contraction.
Intercalated Discs
Folds in the plasma membrane of cardiomyocytes that increase surface area and interlock cells.
Interdigitating Folds
Structures that tightly join cardiomyocytes, including fascia adherens and desmosomes.
Mechanical Junctions
Gap junctions that allow for the flow of ions between cardiomyocytes, facilitating electrical signaling.
Electrical Junctions
The natural pacemaker of the heart located in the right atrium that initiates depolarization of atrial cardiomyocytes.
SA Node
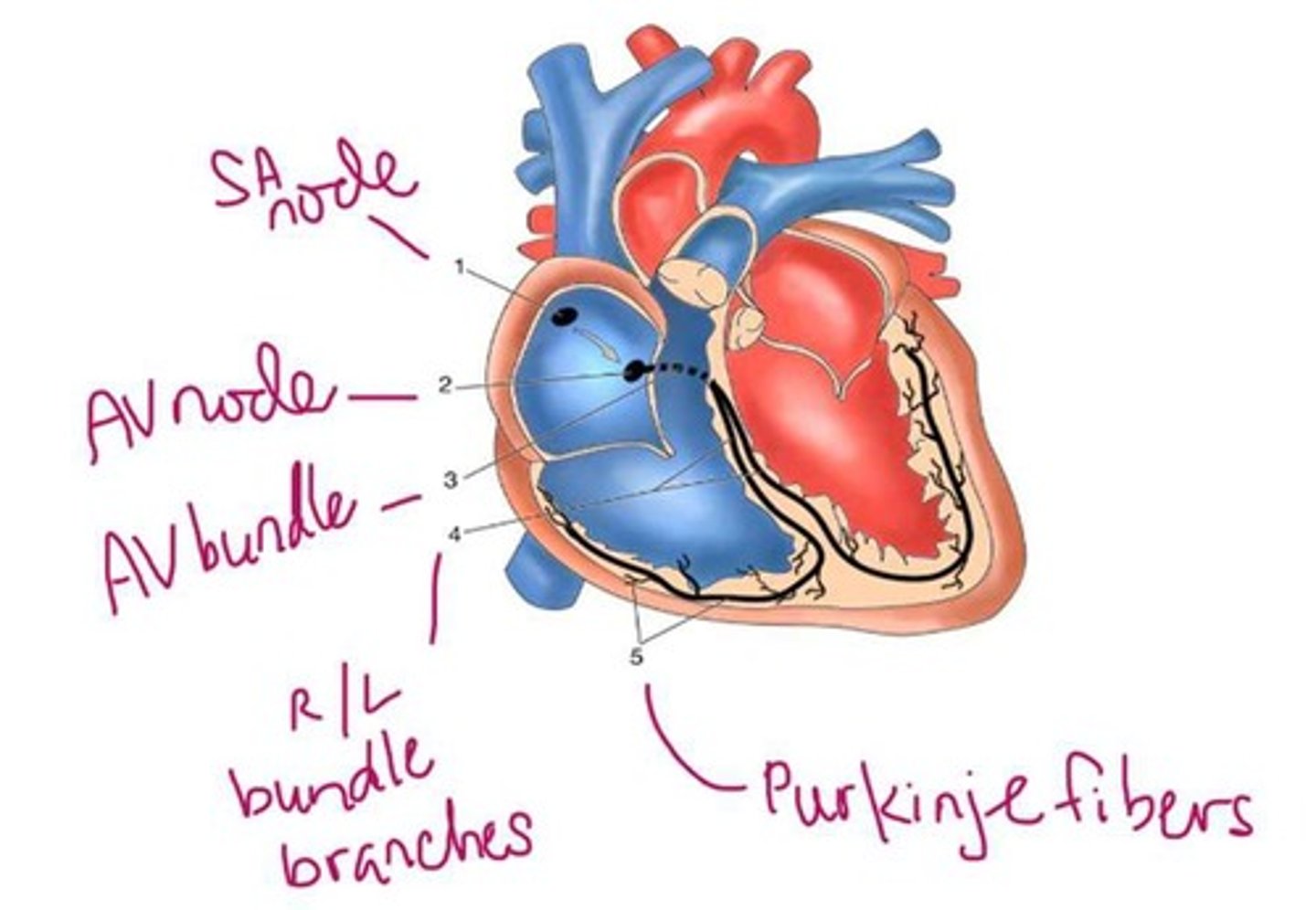
A node located at the lower end of the interatrial septum that delays the conduction signal to allow for ventricular filling.
AV Node
The slowing of the electrical signal through the AV node to ensure proper timing of atrial and ventricular contractions.
Conduction Signal Delay
The period during which the ventricles are filled with blood before contraction.
Ventricular Filling Time
Part of the autonomic nervous system that increases heart rate and myocardial contraction strength.
Sympathetic Nervous System
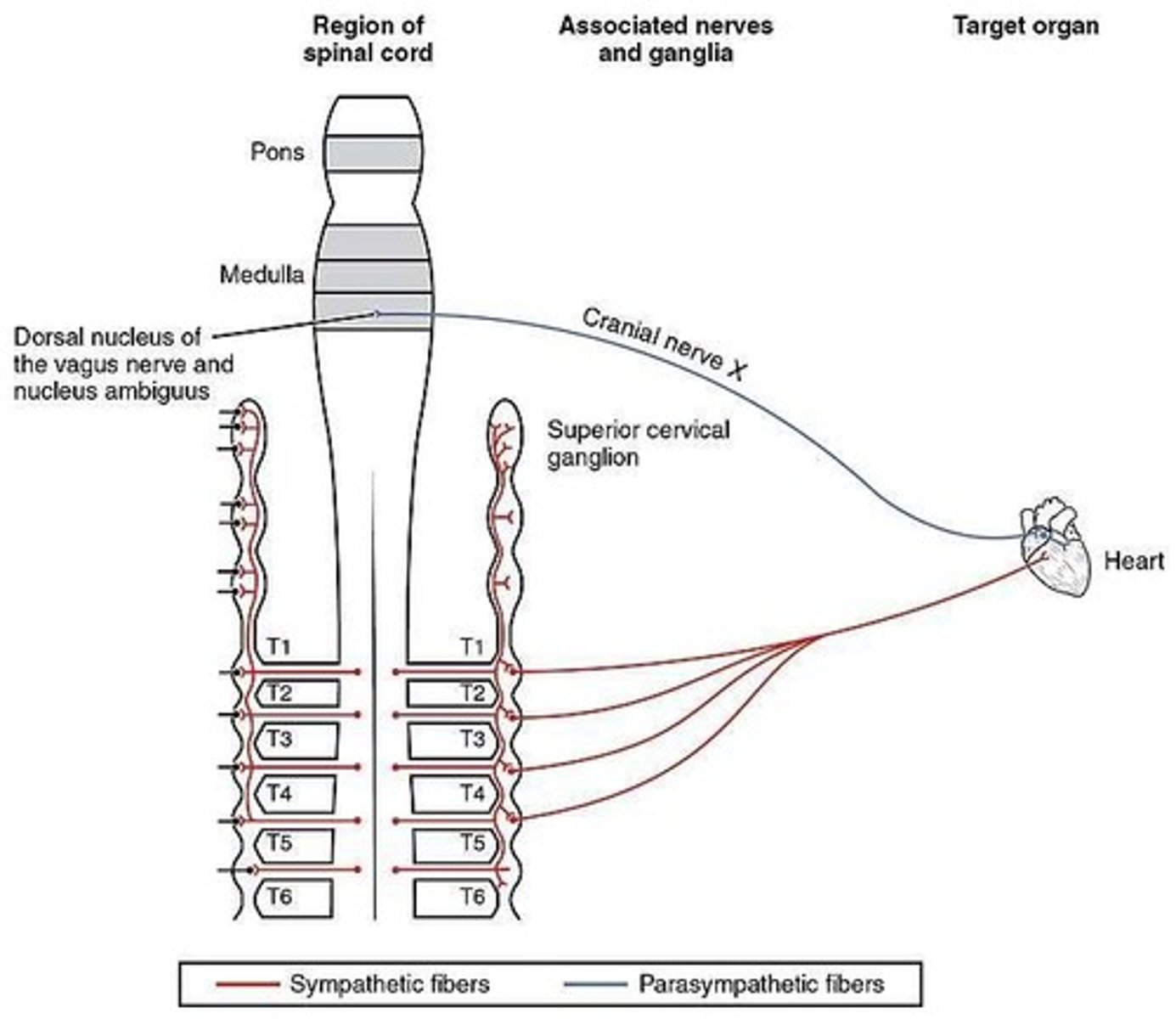
Part of the autonomic nervous system that decreases heart rate.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
An abnormal site within the heart that can initiate electrical impulses independently of the SA node.
Ectopic Focus
An abnormal heart rhythm originating from the AV node or bundle of His.
Junctional Rhythm
A recording of the electrical activity of the heart during the cardiac cycle.
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
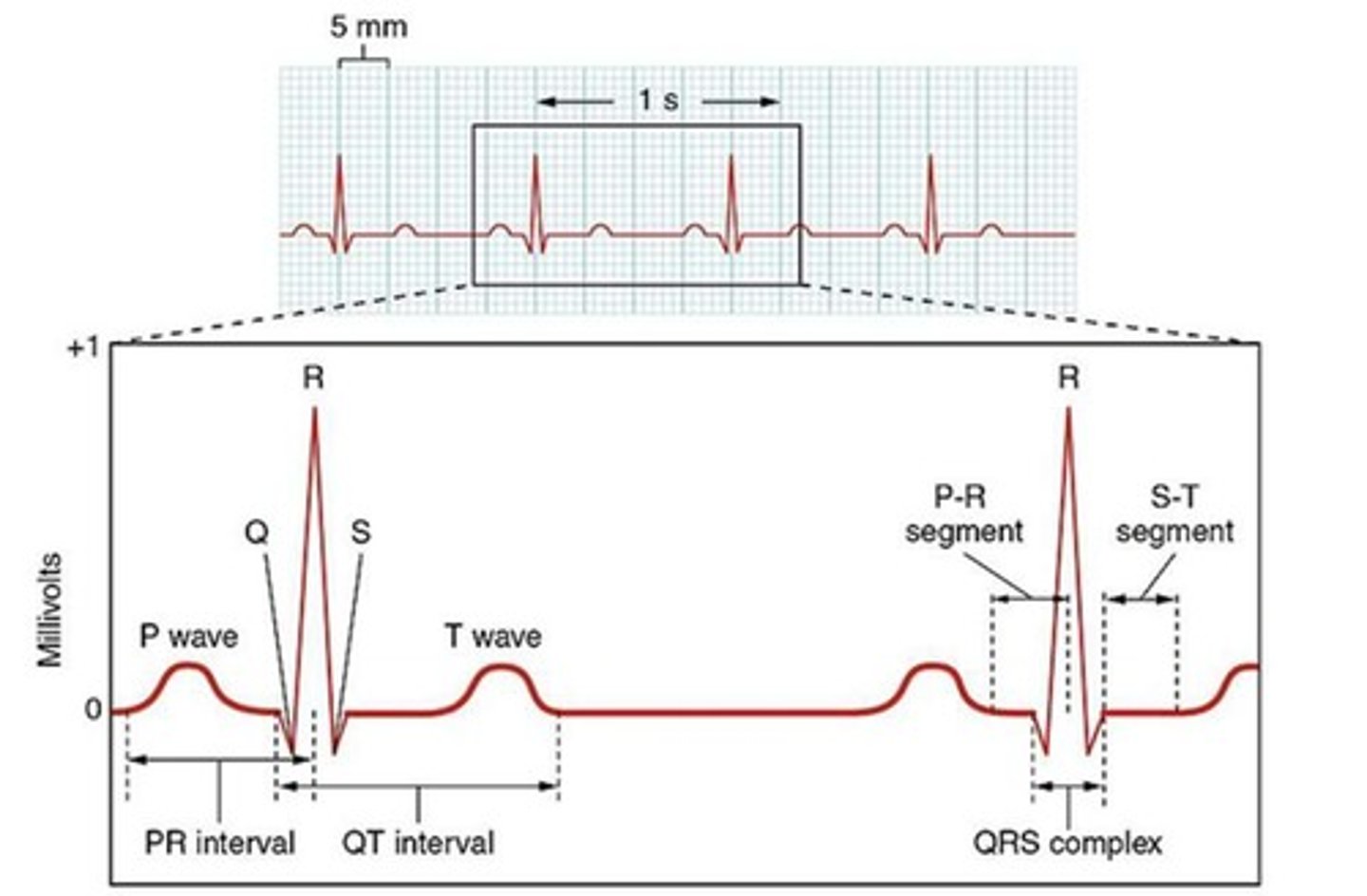
The wave on an ECG that represents atrial depolarization.
P-Wave
The flat line on an ECG between the P-wave and QRS complex, indicating the delay of the action potential through the AV node.
PR Segment
The part of the ECG that represents ventricular depolarization.
QRS Complex
The part of the ECG that indicates the period when the ventricles are in systole.
ST Segment
The wave on an ECG that represents ventricular repolarization.
T-Wave
An abnormal rhythm or rate of the heart due to issues in the conduction system.
Cardiac Arrhythmia
A condition where electrical signals cause the ventricles to contract rapidly and uncoordinatedly.
Ventricular Fibrillation
A condition characterized by uncoordinated contractions of the atria.
Atrial Fibrillation
A condition that obstructs the electrical pathway of the heart.
Heart Block
A condition where the signal from the SA node to the AV node is slowed, resulting in longer P-R intervals.
First Degree Heart Block
A condition where the electrical signal is progressively delayed until one signal is completely blocked.
Second Degree Type 1 Heart Block
A condition where some electrical signals do not reach the ventricles.
Second Degree Type 2 Heart Block
A condition where none of the electrical signals reach the ventricles.
Third Degree Heart Block
The two main factors that govern the movement of blood within the circulatory system.
Fluid Movement Variables
A condition where the electrical signals from the SA node to the AV node progressively lengthen until one signal is completely blocked, leading to a dropped beat.
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1
A type of heart block where some electrical signals fail to reach the ventricles, causing missed beats.
Second Degree Heart Block Type 2
The difference in pressure between two points that drives fluid movement from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
Pressure Gradient
The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, influencing blood flow and valve function.
Blood Pressure
The opposition to blood flow within the vessels, affecting how easily blood can move through the circulatory system.
Resistance
A phase of the cardiac cycle where the ventricles contract with no volume change, as all valves are closed.
Isovolumetric Contraction
A phase following ventricular contraction where the ventricles relax and all valves remain closed, leading to a decrease in pressure.
Isovolumetric Relaxation
The total volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of filling, typically measured at 151 ml.
End-Diastolic Volume (EDV)
The volume of blood remaining in the ventricles after contraction, typically measured at 59 ml.
End-Systolic Volume (ESV)
The amount of blood ejected from the ventricles with each heartbeat, calculated as the difference between EDV and ESV.
Stroke Volume
Stroke volume is calculated as EDV (151 ml) minus ESV (59 ml), resulting in a stroke volume of 92 ml.
Stroke Volume Calculation
The volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle of the heart with each heartbeat.
Stroke Volume (SV)
A measurement of the percentage of blood that is ejected from the heart during each contraction.
Ejection Fraction (EF)
The volume of blood the heart pumps per minute, calculated as stroke volume multiplied by heart rate.
Cardiac Output (CO)
The phase of the cardiac cycle where blood flows from the atria into the ventricles, increasing ventricular volume.
Ventricular Filling
The phase where blood is expelled from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Ventricular Ejection
The sound produced by the closure of the atrioventricular (AV) valves at the beginning of ventricular contraction.
First Heart Sound (S1)
The sound produced by the closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular relaxation.
Second Heart Sound (S2)
A condition characterized by the narrowing of a heart valve, which restricts blood flow.
Valvular Stenosis
A condition where a heart valve does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward.
Valvular Regurgitation
A condition in which the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs.
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
An abnormally high resting heart rate, typically above 100 beats per minute.
Tachycardia
An abnormally low resting heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute.
Bradycardia
Factors that influence heart rate; positive agents increase heart rate while negative agents decrease it.
Chronotropic Agents
The degree of stretch of the heart muscle fibers at the end of diastole, influencing stroke volume.
Preload
The intrinsic ability of cardiac muscle to contract, independent of preload and afterload.
Contractility
The resistance the ventricles must overcome to eject blood during systole.
Afterload
The principle stating that stroke volume increases with increased end-diastolic volume.
Frank-Starling Law
An elevated level of potassium in the blood, which can depress heart contraction strength.
Hyperkalemia
A low level of potassium in the blood, which can lead to irregular heart rhythms.
Hypokalemia
An elevated level of calcium in the blood, which increases the strength and duration of heart contractions.
Hypercalcemia
A low level of calcium in the blood, which decreases myocardial contraction strength but may increase heart rate.
Hypocalcemia