Exam #6 Muskoskeletal & Trauma Unit
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is osteogenesis imperfecta and it’s key features?
genetic in origin
Key Features: Brittle bones, due to not enough collagen or abnormal collagen
Marked scoliosis of the spine
What resembles a cage?
external fixator
The difference between an advancement flap and free graft is:
Advancement flap is still attached and free graft is harvested
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?
congenital muscle disorder
It’s a delayed motor development and muscle weakness
Deficiency of a muscle protein called dystrophin
Present in both skeletal & cardiac muscles
What is Paget’s disease and it’s key features?
osteitis deformans
acquired bone disorder
Rapid regeneration of bone in which the bone remains immature while entering the normal degeneration process
Immature bone is crudely structured and weak
Osteoarthritis (OA), heart problems, bone cancer
Treatment: Bisphosphonates
What is osteoporosis?
“lacy bones”; genetic
Progressive loss of bone mass
The greatest impact is on the spine
No cure; focuses on prevention
X-Ray, bone density scans (low dose), hips/spine
Osteoporosis causing reduced spinal bone density can result in
a compression fracture
a loss of height
a stooped posture
What is the treatment for osteoporosis?
Oral drugs to increase bone density to slow bone loss (bisphosphonates)
Fosamax
Boniva
Prolia
What is gout?
Acute inflammation of joints caused by kidney dysfunction or too much uric acid is produced by the body
Hot, red, and tender
Affects the big toe, can also affect ankles, wrist & hands
Diagnosis: blood for increased uric acid and creatinine
What’s the medication to treat gout?
allopurinol; change of diet from the eating of meats, fructose, beer, etc
What could be some dietary reasons someone get’s gout?
too much red meat, fructose, and beer
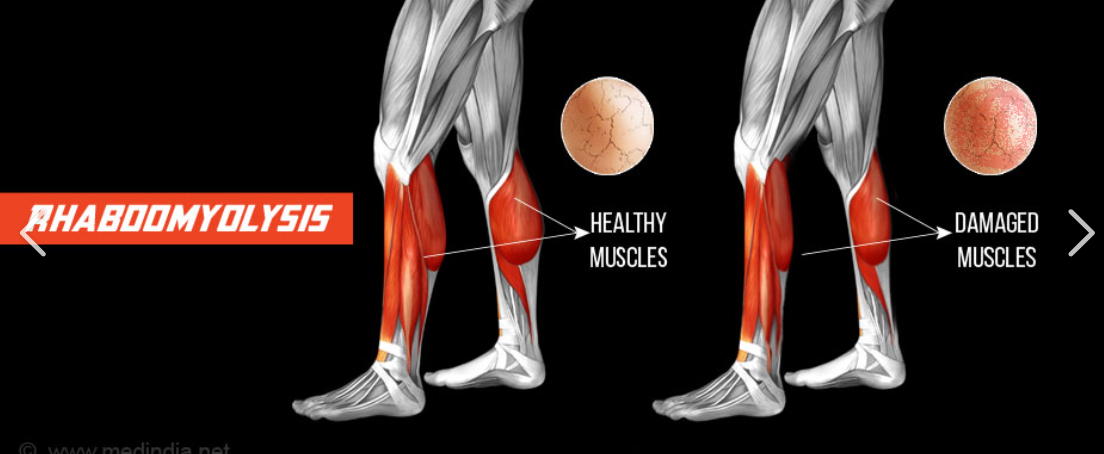
what is rhabdomyolysis?
(rhabdo) - acute muscle damage (can be life-threatening)
A release of protein byproduct of muscle damage is called
myoglobin
What are the causes and symptoms of rhabdomyolysis?
Causes
High-intensity exercise and trauma
Medications and illegal drugs/alcohol
Snakebites
Dehydration
Symptoms
Muscle weakness and soreness
Dark red urine
Nausea & vomiting
How is rhabdomyolysis diagnosed & treated?
Diagnosed
Lab test (urine) for myoglobin
Lab test (blood) for creatinine
Can look like coco-Cola
Treatment
IV fluid resuscitation
Dialysis
What can rhabdomyolysis result in?
acute renal failure, possibly leading to death
What is osteomyelitis?
Infection in the bone that travels through the bloodstream or spreads from nearby tissue
It can also begin in the bone itself if an injury exposes the bone to germs
What is osteomyelitis associated with?
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Surgical infection
Fistula (postoperative)
What is the post-operative complication that could be described as an abnormal connection between 2 body parts?
fistula
Why might a burn victim suffer form hypothermia?
skin is no longer able to hold in heat or fluid which can cause evaporation
What’s the surgical treatment for osteomyelitis?
Antibiotics (IV and oral)
Surgical debridement to clear necrotic tissue down to the viable bone
Use of rongeur and a curette
A large amount of hemorrhaging could be expected during what?
Joint replacements or amputations
Open heart surgery
thyroid procedures
What is osteoarthritis and it’s causes?
degenerative condition of the joint from wear & tear
Cartilage between the joints breaks down causing loss of lubrication and rubbing of bones together
Causes
Weight gain
Injury
Genetics
Not “cracking” or “popping” joints
A hematoma or seroma of an operative site wound
evacuation & drainage
What are some symptomatic treatments for osteoarthritis?
Weight loss/exercise
Oral medications
NSAIDS
Opioid pain meds: Vicodin
Steroid injections into the joint
Physical Therapy
What material is used in a hip prosthesis?
Polyethylene (plastic polymer)
Ceramics
Metals
What are neurostimulator devices?
failed back surgery syndrome
directs mild electrical impulses with pain messages to the brain
Spinal array and generator device
cervical nerve compression
More common in herniation and spondylosis
C4-C5 (shoulder and neck pain; loss of mobility, hurts bending head forward or to side)
C5-C6 (bicep, wrist, and thumb weakness and tingling)
C6-C7 (triceps, forearm, and fingers weakness and tingling)
C7-T1 (hand grip weakness, little finger tingling)
A collection fluid other than blood or pus in a wound
seroma
A collection of blood and clot in a wound
hematoma
The primary concern with a blow out fracture of the orbital floor
herniation of the eyeball or other tissues
thoracic nerve compression
Upper back pain, abdominal pain, chest pain, lower body dysfunction
Can affect your breathing
Common in scoliosis and kyphosis
lumbar nerve compression
sciatica/foot drop
L1-L2 (most often anterior thigh and increase cases of cauda equina)
L2-L3 (pain in the anterior thigh)
L3-L4 (posterior thigh pain, lack of patellar reflex)
L4-L5 (sciatica; numbess on top of foot drop
L5-S1 (inability to stand on toes; ankle can’t support weight)
What are some chiropractic treatments to treat spinal disorders?
Adjustments
Decompression
Heat therapy
Exercises
laminectomy
Creates space by removing the lamina or back part of the vertebra
Spinal decompression surgery, usually for stenosis and spondylosis
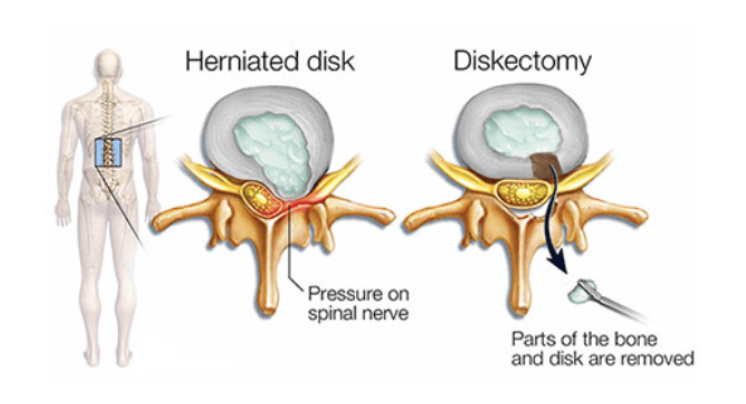
diskectomy
Removes a portion of a herniated disk material which is pressuring the nerve root
spinal fusion
Fusing vertebral levels, so they form one bone
Loss of flexibility of the spine
Interbody cages, pedicle screws, and plating systems are instruments that can be used for this procedure
spinal fusion

open (compound)
a fracture when the bone protrudes from the skin (penetration or laceration)
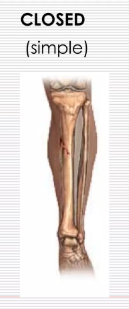
closed (simple)
the bone is broken; the skin is intact
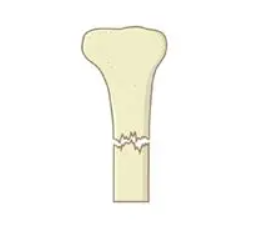
transverse
a fracture straight across the bone shaft
oblique
a fracture at an angle to the bone shaft
spiral
a fracture that twists around the bone shaft
displaced
a fracture when the bone is out of alignment
comminuted
a fracture when the bone is broken into 3 or more parts
greenstick
an incomplete fracture in which the bone is bent and only the outer curve of the bend is broken
compression
a fracture in which the bone is crushed or collapses into small pieces
intra-articular
a fracture that crosses a joint surface
A nasal fracture is accompanied by:
a deviated septum
nasal airway obstruction
Open or closed reduction/repositioning
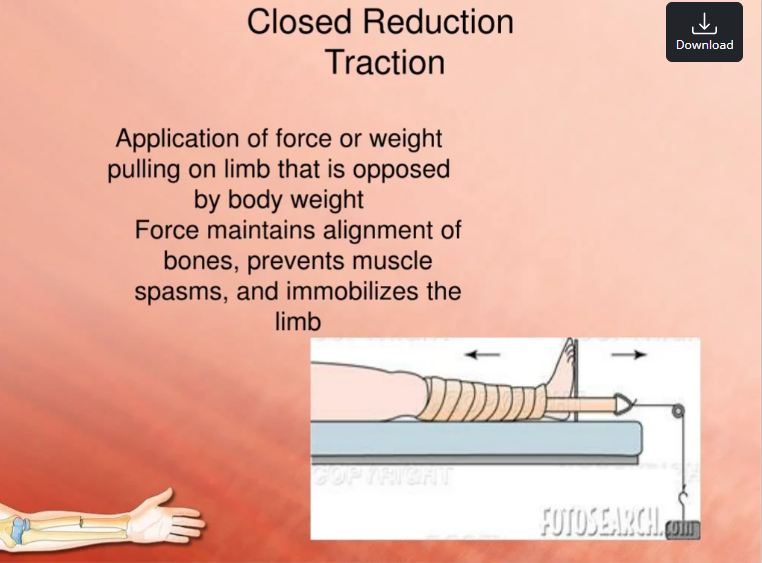
closed reduction
Reposition & manipulate the bone to put it in a cast or splint
Kirschner/K-wire is used for:
flexibility for holding broken bones in place
ORIF (Open Reduction Internal Fixation)
treatment for fractures
A doctor creates an incision to gain access to the fracture site, to reposition the bone
Applying hardware to secure the bone
Such as: Rods, plates, screws, nails
What is blunt force trauma and it’s treatment?
The force of impact containing damage where the hemorrhage damages critical organs, determining mortality
Treatment: symptomatic or surgical, blood transfusions
How is blunt force trauma diagnosed?
x-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, CBC, examining body fluids for blood
Blood loss and organ dysfunction may be immediate or delayed
Signs may be not visible
Morality due to penetrating injuries is determined by:
blood loss and vital organ damage
laparotomy
surgical treatment for internal injuries
surgically opening the abdomen
thoracotomy
surgical treatment opening the chest cavity for internal injuries
craniotomy
surgically opening the skull for internal injury treatment
amputation
Partial or complete separation of a limb
Damage to the bone, nerves, blood vessels, tissue, and skin of the stump
Reattachment (replantation) viability depends on time and the extent of damage
avulsion
a forcible separation or detachment, such as a tearing away of a body part
What are the treatments of amputations?
Treatment
Freshening of the amputation stump
Sealing off blood vessels and preparing the stump for grafting
What are the complications of amputation?
Infections of the amputation stump
Non-healing graft due to comorbid conditions
Phantom limb syndrome
When an amputee feels like a limb is still attached
phantom limb syndrome
What is the cause of post-laminectomy syndrome?
scar tissue
The main concerns after an amputation due to an animal bite
blood loss and infection
What happens to tissues to cause compartment syndrome?
pressure & swelling damage tissues
Fascia does NOT allow for tissues to expand
may be a result of trauma, especially in crush injuries or higher energy BFT (blunt force trauma)
What are lacerations?
Open wounds
Full thickness disruption through the skin & deeper tissues underneath
Evidence of nerve and tendon damage
Mortality depends on degree of blood loss from lacerated blood vessels
Risk of infection and development of cellulitis and gangrene
What is degrees of burns?
classified by the extent and severity of damage caused of the layers of skin affected
1st degree (superficial) burns
Affects only the outer layer of skin - epidermis.
The burn site is red, painful, dry, and with no blisters.
Mild sunburn is an example.

Second-degree (partial thickness) burns
Involve the epidermis and part of the lower layer of skin, the dermis. The burn site looks red, blistered, and may be swollen and painful

third-degree (full thickness) burns
Full thickness - destroys the epidermis and dermis.
They may go into the innermost layer of skin, the subcutaneous tissue.
The burn site may look white or blackened and charred
fourth-degree (underlying tissue) burns
Go through both layers of the skin and underlying tissue as well as deeper tissue, possibly involving muscle, tendons, ligaments, and bone.
There is no feeling in the area since the nerve endings are destroyed
What are the body parts for rule of 9’s?
EMTs use this method of quickly estimate the body surface area of a burn
Head and Neck:
Upper Extremities: arm, forearm, hand
Torso: anterior and posterior
Lower Extremities: leg, thigh, lower leg, foot
Genital or Perineal Region: private areas
The complications and treatments for a 3rd degree burn?
Treatment
Surgical debridement of necrotic tissue down to granulation tissue
Pealing or sloughing at a burn center
Skin grafting
Xenografts - fish skin
Complications
Dehydration
Hypothermia
Thrombosis
contusions
Bruising caused by broken capillaries
Blood may gravitate to other areas, turn purple and yellow as blood is absorbed
Treatment: Tylenol, nothing with bleeding properties, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE)
“I’ve fallen and I can’t get up”
Cause of friction burns/abrasions include:
Rubs off the skin due to direct contact with rough surface
Skinned knee (“raspberries”)
Grazing an object
Continued rubbing or scratching
Friction burns
Floor/rug/carpet burn
Rope burn
Road rash
Treadmills
Minimal bleeding, but area scabs over and may form a scar
Treatment is topical
Covered with breathable gauze or non-stick bandage
Ointments to minimize risk of infection
major sprain & its complications
acute inflammatory response, swelling pain
Rest, Ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and immobility/NSAIDS
Complications
Tearing, permanent weakening, arthritis
May require surgical intervention later
deep scar
scar formation
fibrotic area under the skin (bumpy) or depressed area
massage area to break up fibrotic tissue, so it can be absorbed
Can take months
May need dermatologist intervention
superficial
scar formation
keep soft with creams
massage area to prevent scar contracture
can take months to go away or may leave a permanent scar due to the destruction of pigment producing cells
dermatologist intervention
chemical peel
radiofrequency and ultrasonic directed therapies
A closed wound that comes apart
dehiscence
separation of wound edges (internal or external)
Resection (removal of whole) and excision (removal of part) end in this suffix
ectomy
What practice is an operating room can help prevent a retained foreign body?
pre and post count
Mechanical complications that could occur due to an implanted device in the body
Displacement and obstruction
Erosion and leakage
Breakage and protrusion
What are two anatomical components of a prosthesis in a total hip arthroplasty?
acetabulum and femoral head
Long periods of immobility, especially for the elderly, could lead to:
deconditioning
Bone harvested (grafting) in an autograft for spinal fusion is likely to come from these places
iliac crest & vertebra