AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY ULTIMATE REVIEW FLASHCARDS
1/384
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Incoming Freshman!!!! You are welcome!!!! I GOT A 5!!!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
385 Terms
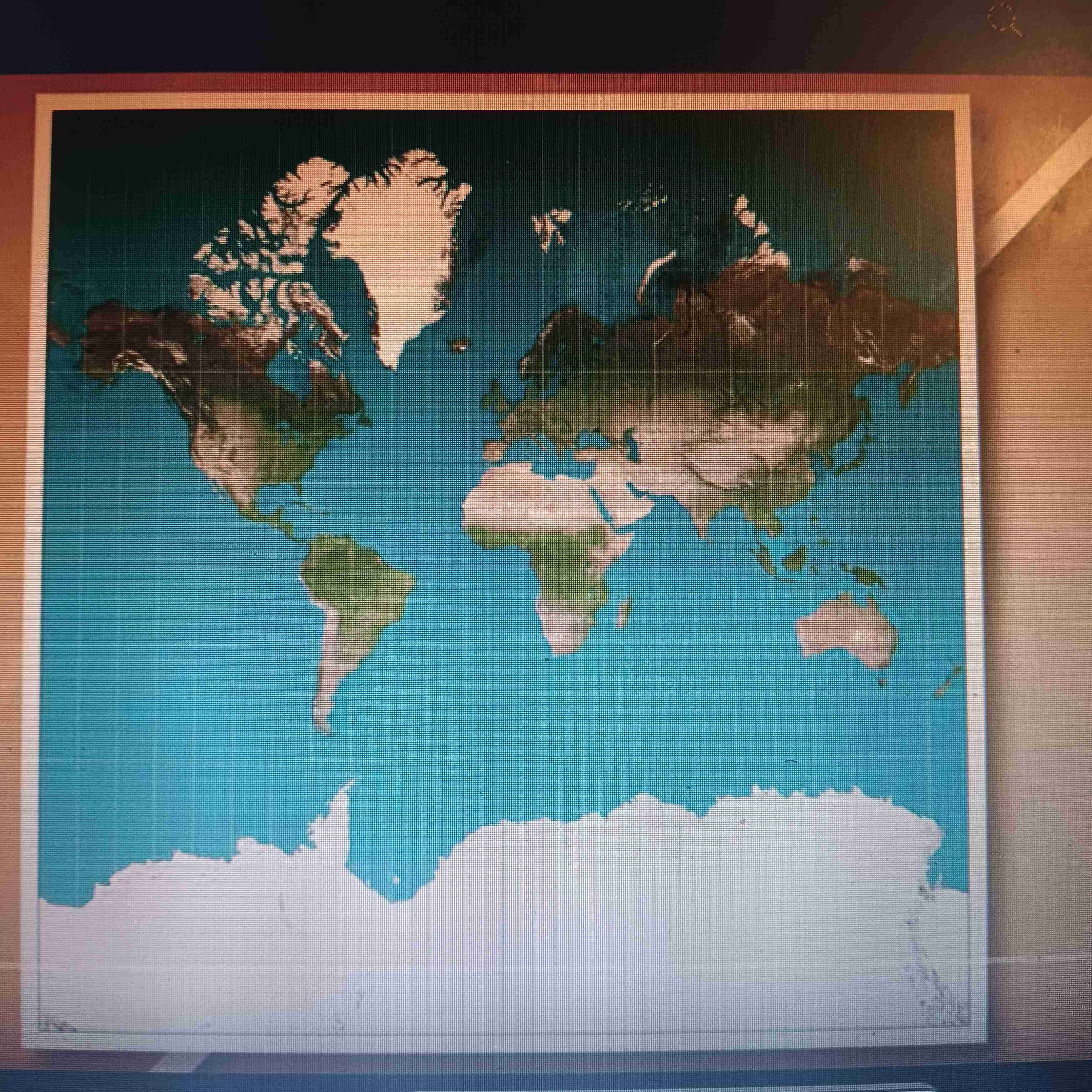
Mercator Projection
Accurate direction;distorts size and shape
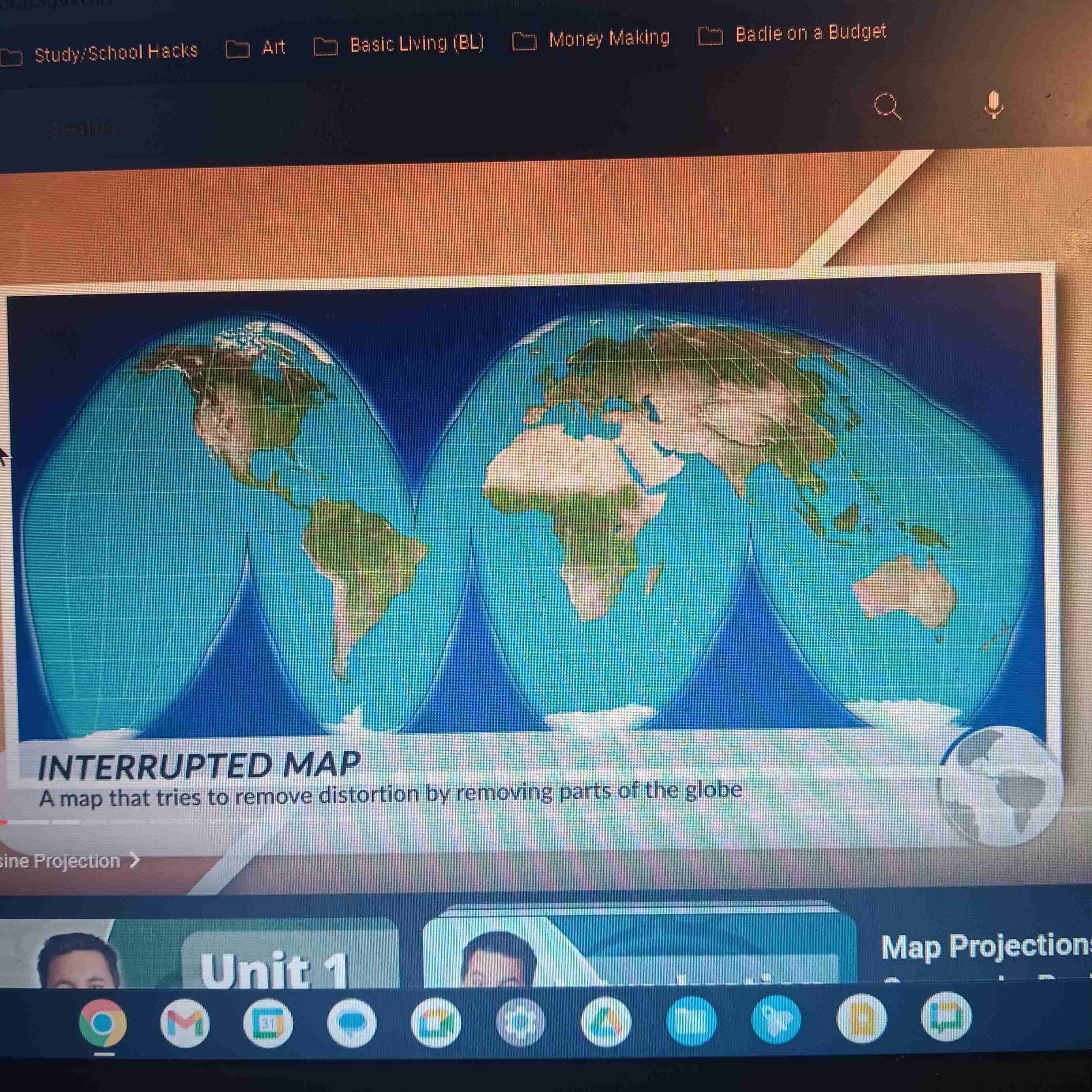
Goode Homolosine
Accurate size & shape; distorts distance
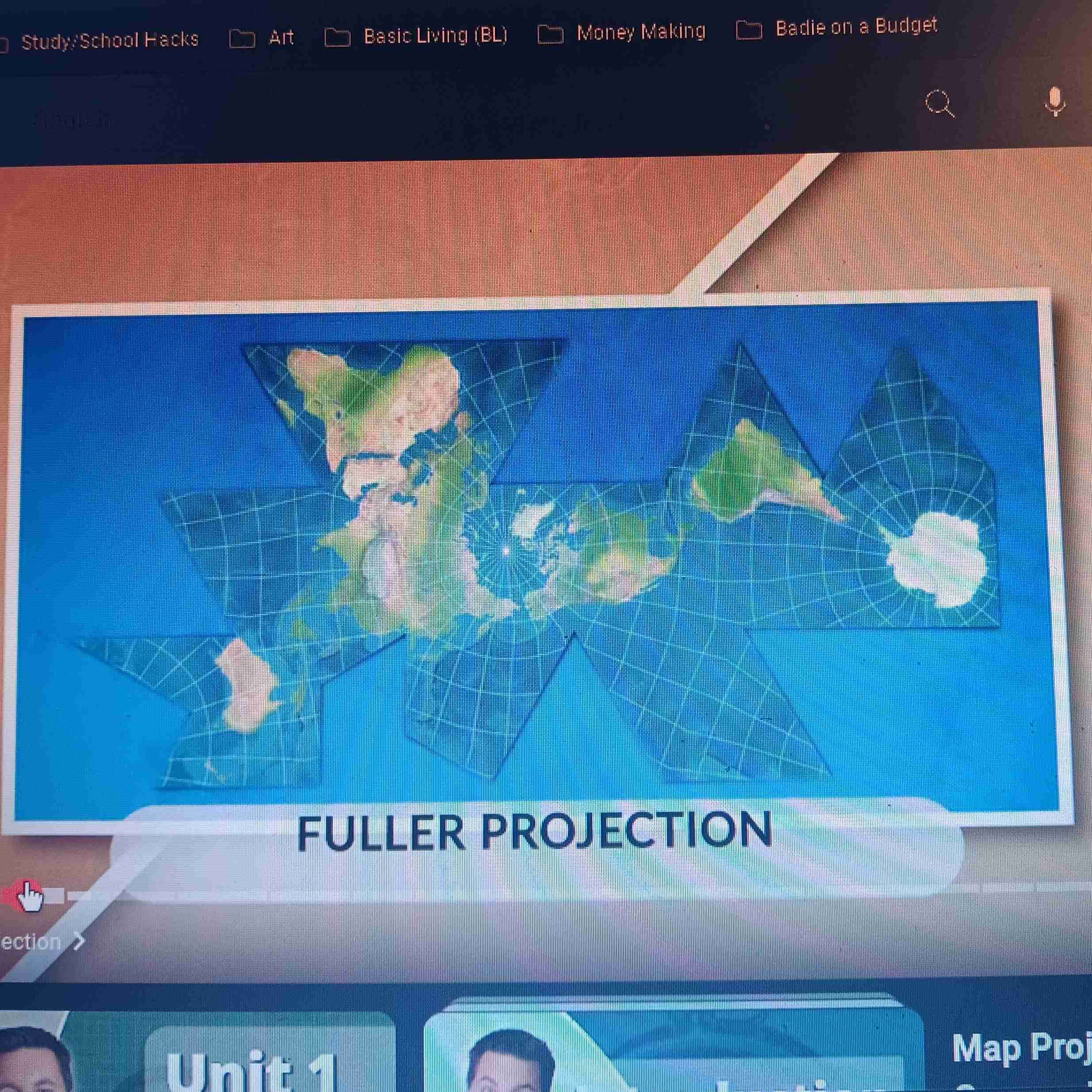
Fuller Projection
Accurate size & shape; difficult to read
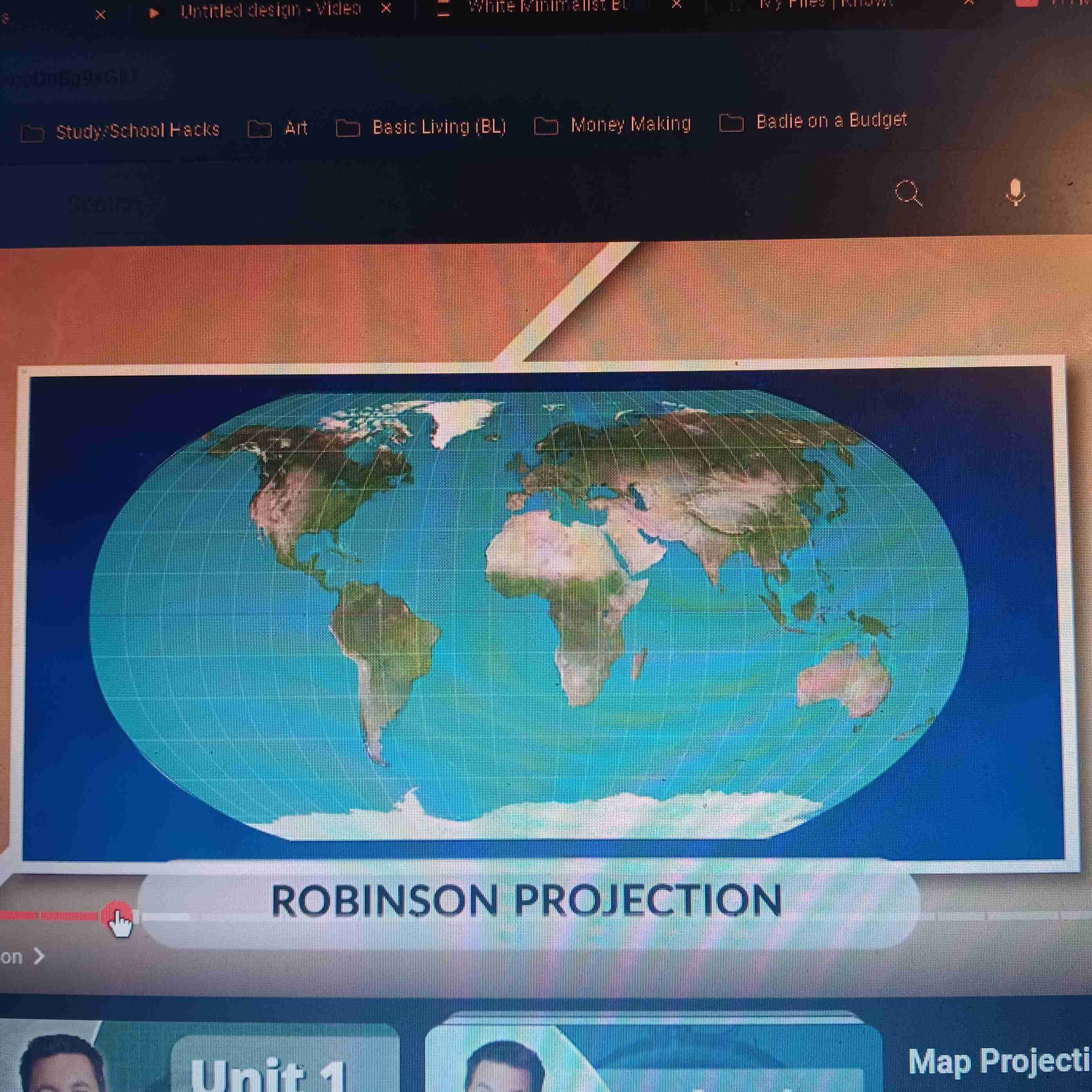
Robinson Projection
Accurate size and shape; distorts near N. and S. Poles

Winked Projection
Accurate size and shape; distorts near N. and S. Poles
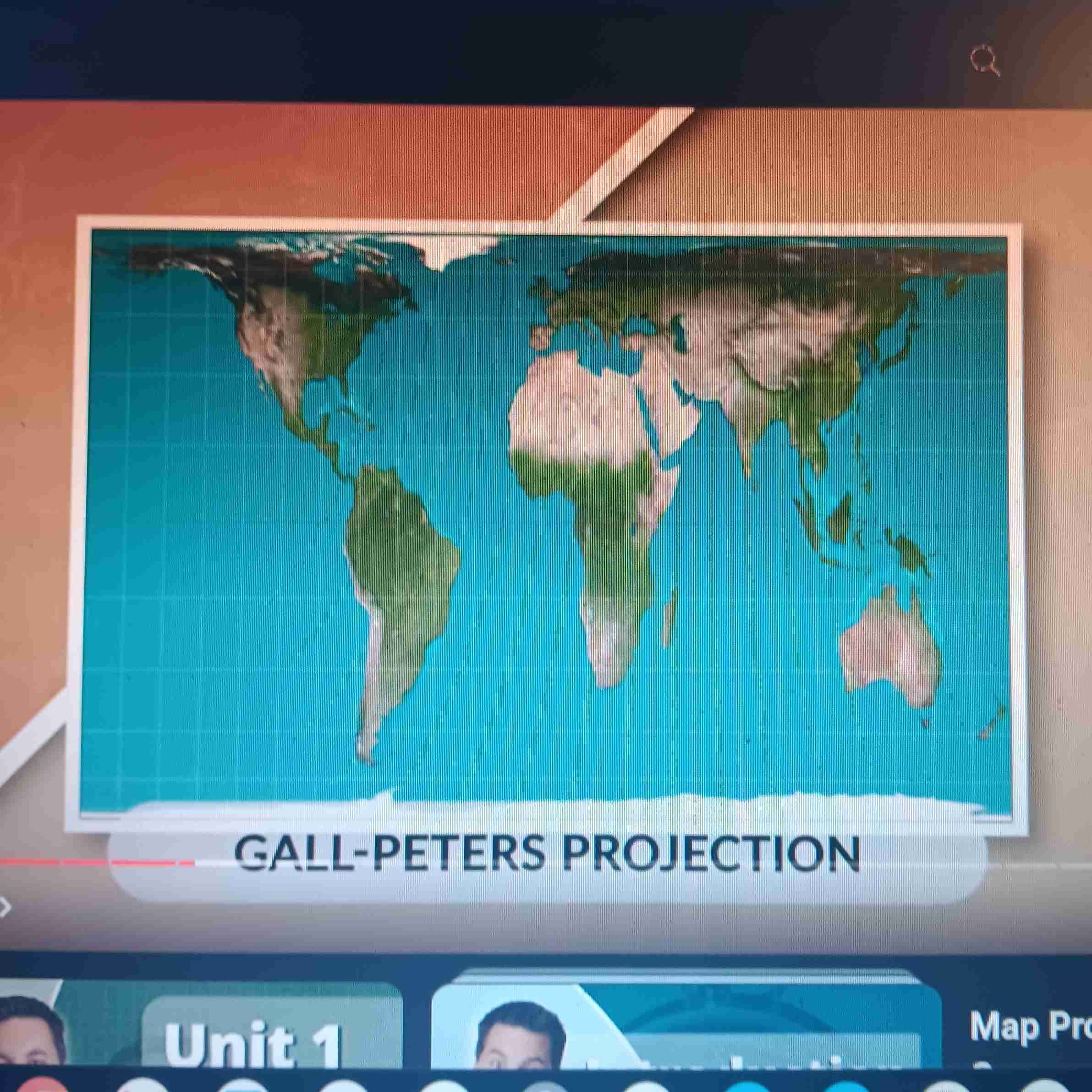
Gall-Peters Projection
Most accurate in size and shape; distorts near N. and S. Poles
Reference Maps
Info map- shows boundaries, name of cities, and geographic features
Thematic Maps
Displays spatial patterns of places using data of different topics
Choropleth Map
Uses different colors to show data
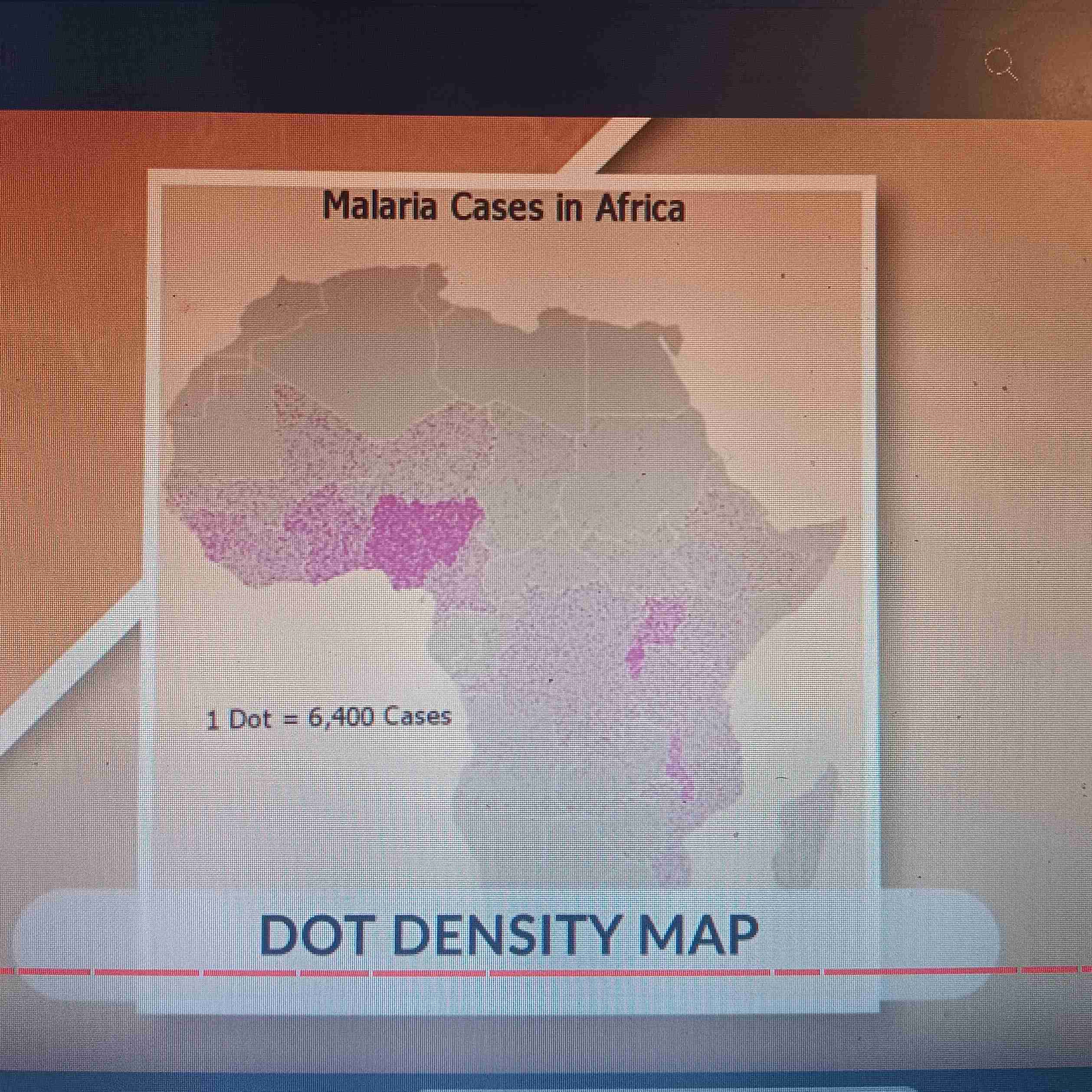
Dot Map
Uses dots to show data
Graduated Symbol Map
Uses shapes, items, or symbols to show data
Isoline Map
Uses lines to show data; ex: weather maps
Cartogram Map
Greatest value represented by largest are; distorts shape and size
Small Scale Map
Large area, less detailed
Large Scale
Less area, more details
Clustered
Close together
Dispersed
Spread out
Remote Sensing
Info collected by satellites
Used during: determining land cover and use, monitoring weather, and monitoring environmental changes
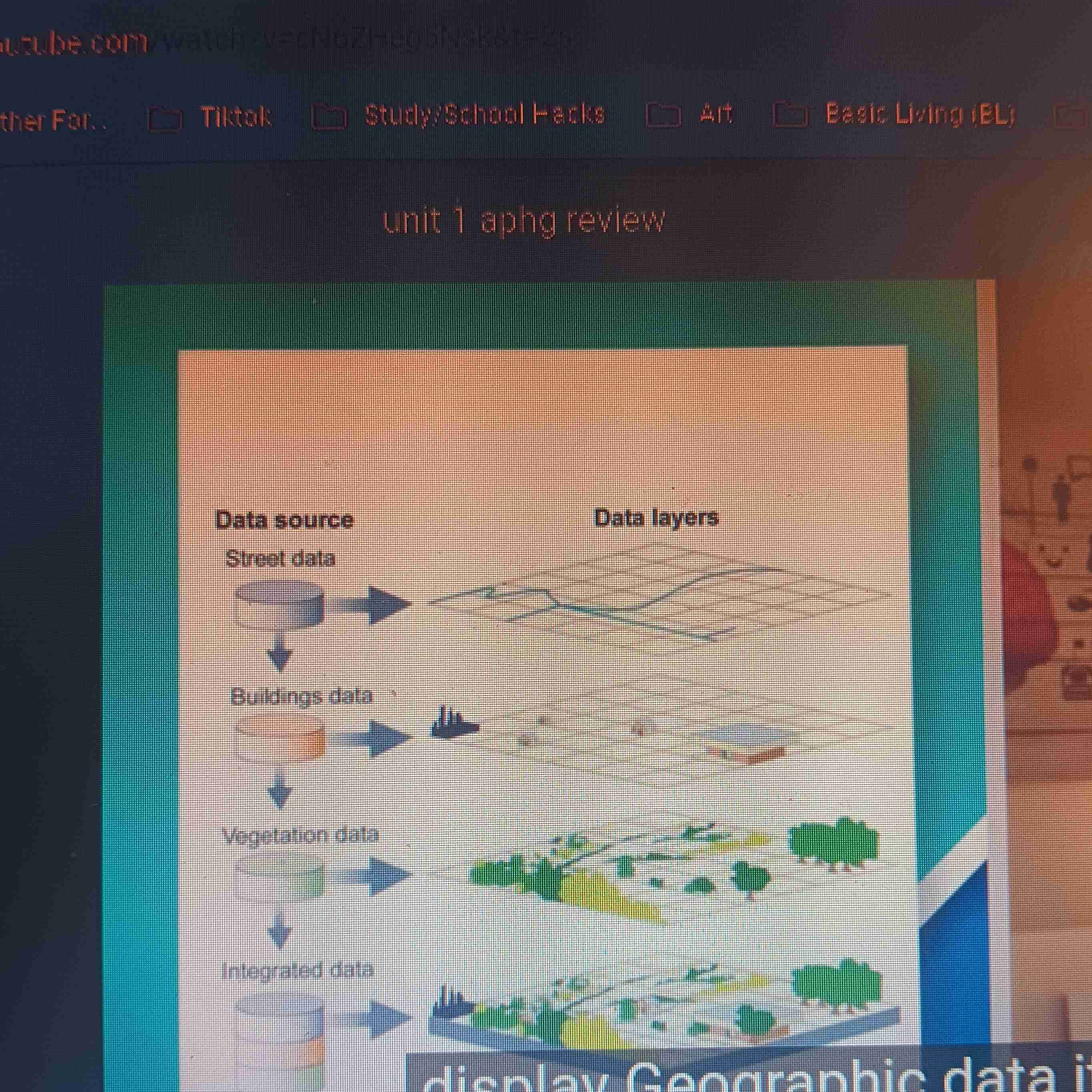
GIS (geographic information system)
Computer system that collects, analyzes, and display geographic data
GPS (global positioning system)
Network of satellites Used to determine absolute location
Used: navigation
Geospatial Technologies
Remote sensing, GIS, and GPS
Field Observations
Data that is observed “in the field”
Quantitative Data
Info that’s measured and recorded using numbera
Qualitative Data
Collected as interviews, document archives, descriptions, and visual observations
Absolute Location
Exact spot where something is located; longitude and latitude
Absolute Distance
Exact distance from 2 places; measured in miles and kilometers
Ex:”Chipotle is 2.5 miles from here”
Absolute Direction
Exact direction you're heading
Ex: East
Relative Location
Description of location using landmarks
Relative Distance
Approximate measurement between two places; measured through time or direction
Ex: “Chipotle is about 6 minutes away from here”
Relative Direction
Direction depends on surrounding area
Ex: “North of you right now”
Place
Specific point on Earth with on or more unique characteristics
Physical characteristics + Human Characteristics
Physical characteristics
climate, rivers, mountains, vegetation
Human characteristics
Language, religion, amount of people living in a place, culture present
Sense of Place
Site (physical characteristics) + Situation (human characteristics)
Toponym
Name given to a place on Earth (can be named after person, religion, resources, or physical features of the environment)
Placelessness
A location lacks identity; could be uniform to society.
Ex: Cities in America
Concentration
Clustered or dispersed
Density
Amount of objects or people in an area
Ex: urban areas are more densely populatedsince more people live there
Distance Decay
How a relationship between 2 or more things breaks down as distance increases
Time-Space Compression (
Reductionof time it takes for something to reach another place
Counters Diatance Decay
Thanks to social media, internet, emails, etc
Sustainability
Development that serves current need of people without compromising the needs of future generations
Environmental Determinism
The environment sets the possibilities for human and society
Ex: a society near a lake only fish
Environmental Possibilism
Acknowledges limits on the effects of the natural environment and focuses more on the role that human culture plays.
Ex: Building land on water
Land Use
Land is used for Recreational, Agricultural, transportation, residential, industrial, and commercial
Natural resources
Resources produced in nature
Renewable Resources
Natural resources that can be used multiple times without running out
Ex: Crops
Non-renewable Resources
Natural resources that can only be used once
Ex: Oil and natural gas
Scale
The ratio between the size of things in real life and size on the map
Geographic Scale
Refers to the area being studied
Types of Scale
(From large scale ➡ small scale)
Local/City➡County➡State➡National/Subanational➡Regional➡Global

Scale of Analysis
Observation of data at the global, national, regional, and/or local scale
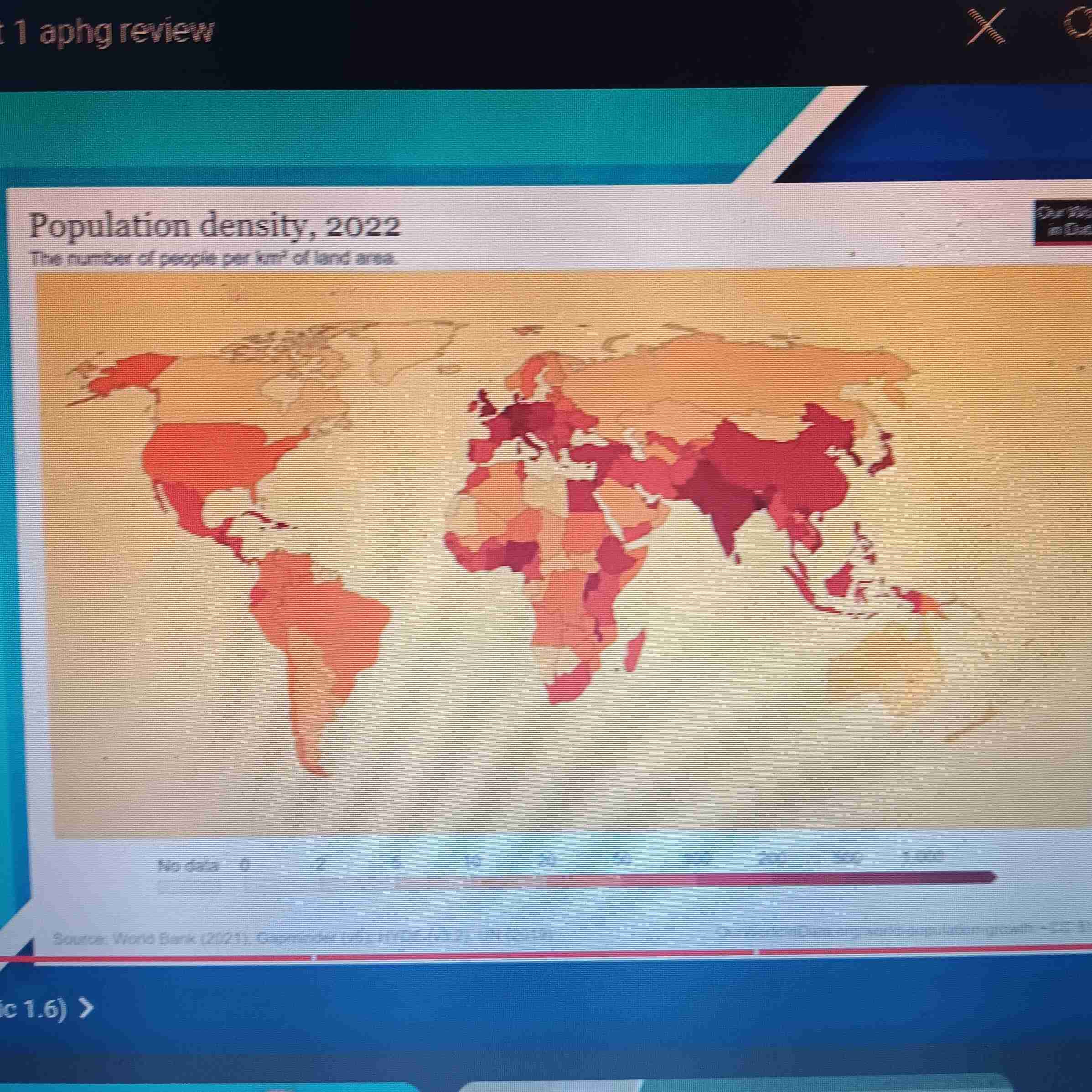
Ex. of Image-
Geographic Scale: Global
Scale of Analysis: National
Region
A geographic area that’s defined be common characteristics and/or patterns of activity
Formal Regions (uniform regions)
Defined by economic, political, social, or environmental characteristics
Functional Regions (AKA Nodal Regions)
Characterized by a hub/central place/node through communication or transportation
Ex: Highway Systems, newspaper circulation area, subway systems
Perceptual Regions (AKA Vernacular Regions)
Linked be people's shared opinions, attitudes, feelings, or beliefs on the region.
Ex: “The South”
Spatial Distribution
How resources, activities, and human demographic features are arranged across Earth
Space
Physical gap between two places
Pattern
Arragment of objects in space
(Linear pattern, centralized pattern, random pattern)
Population Distribution
The pattern of human settlement
Population density
How clustered or dispersed a population is
Physical factors
Climate, landforms, water bodies
Human Factors
Culture, economics, history
Ecumene
Inhabited places on Earth
Arithmetic density
Total #of people to the total land area
Assumes everyone is evenly distributed
Total population/ total amount of land
Physiological Density
The # of people to the arable, or farmable land of a certain area
Total population/total amount of arable land
Agricultural Density
The # of farmers to the arable land of a certain area
Amount of farmers by are/ total amount of arable land
Cohorts
An age group (y-axis)
Dependency Ratio
Ratio of the number of dependents (0-14 and 65+) to the working-age population in a country or area
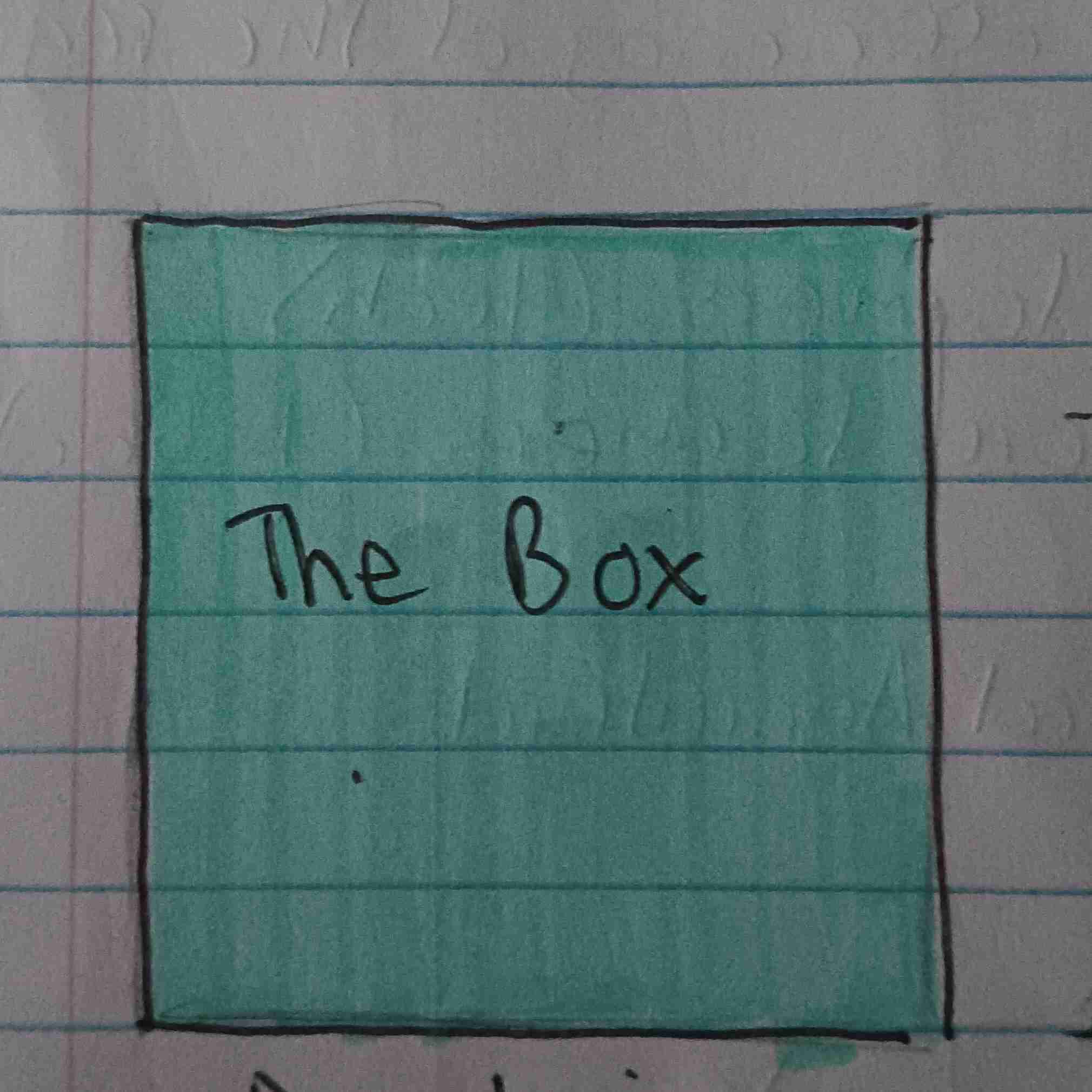
Box Pyramid
Developing or more Developing
Slow growth
Christmas Tree Pyramid
Less developed
Rapid growth

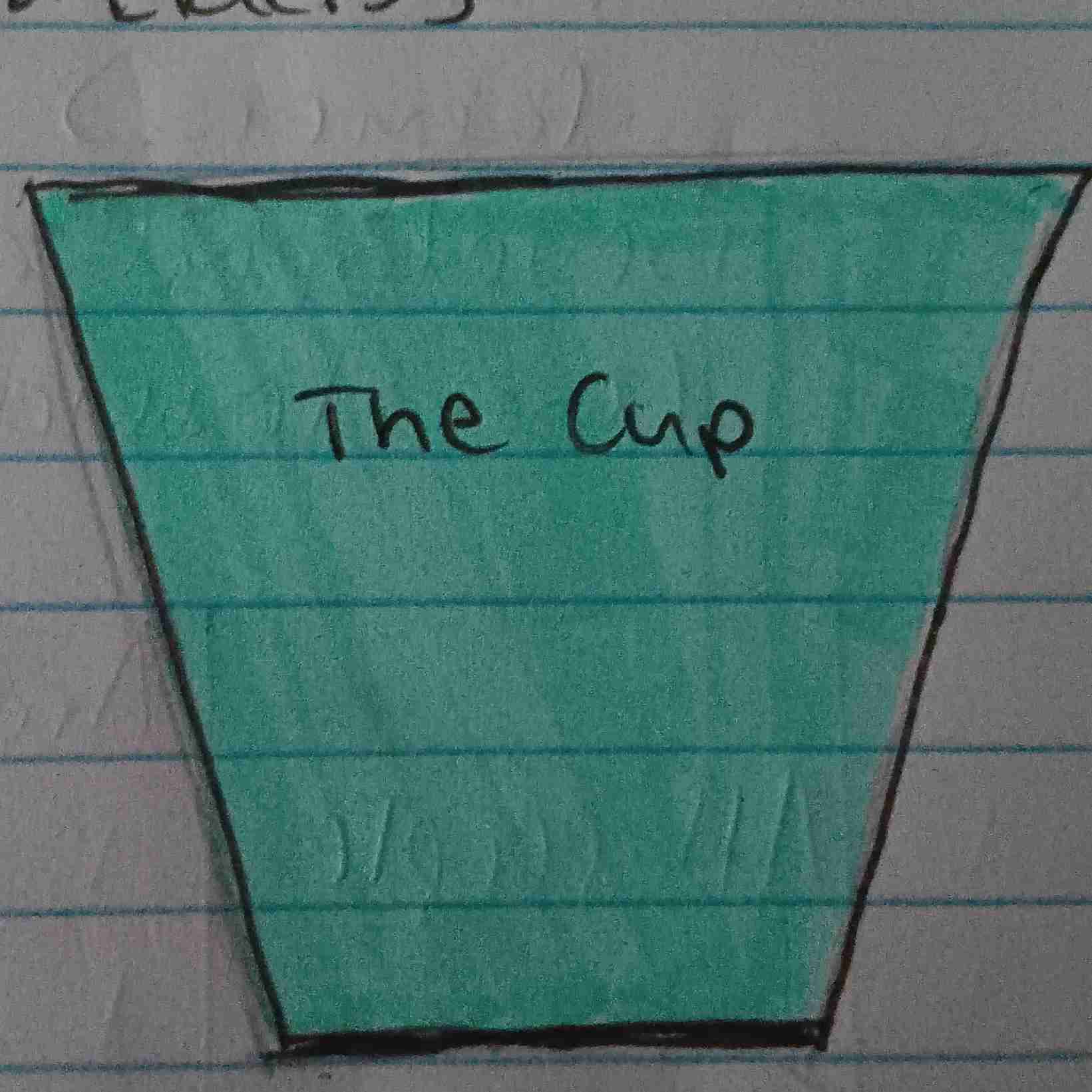
Cup Pyramid
Negative Growth
MDC
Less people have kids
Aging population
Carrying Capacity
Ability of an area to sustain its people with the resources and tech available (without environmental degradation)
Urbanization
Movement into cities
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
Total # of live births in a year for every 1,000 people
Crude Death Rate
Total #of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
CBR - CDR = NIR
Doubling Time
Amount of time it takes for a population to double in size
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
Average number of children a women will have
Replacement Rate
2.1
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
Total # of deaths in a year among infants under 1 years old for every 1,000 live births in a society
Child Mortality Rate (CMR)
Total #of deaths in a year among children between 1-5 years old
Demographic Transition Model
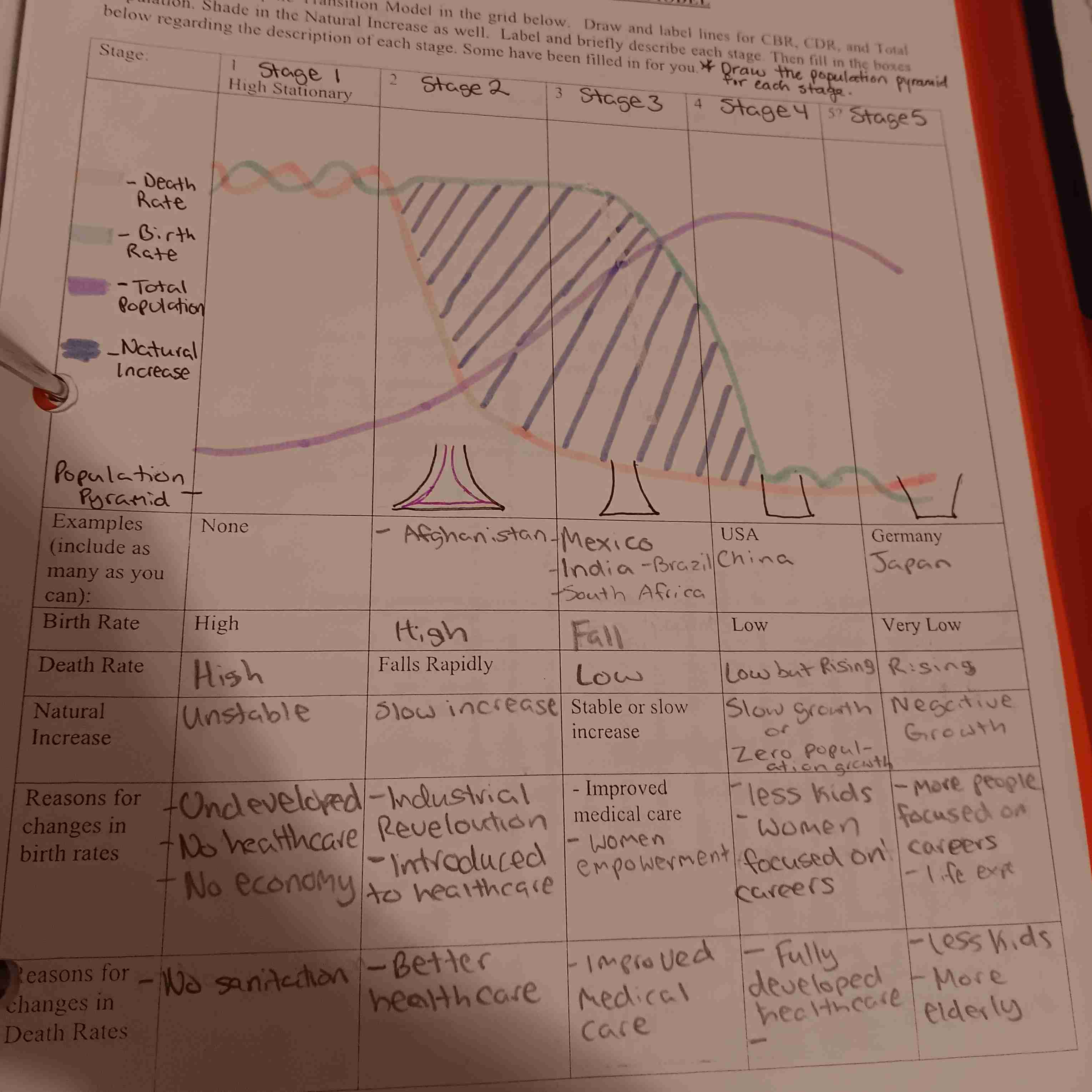
DTM Stage 1
High CBR and CDR
Agriculture
No stage or healthcare
No longer any countries in stage 1
DTM Stage 2
Trigger: Industrial Revolution
Increased Urbanization
CDR decreases
More medicine
Better sanitation
More Immigration and emigration
Ex: Afghanistan
DTM Stage 3
Higher life expectancy
Better medicine
Women's empowerment: Better education
Women no longer have domestic role
CBR decreases
Ex: Mexico
DTM Stage 4
Zero population growth (ZPG)
More economic growth
Higher education for women
Less families
Cost of living increases
Ex: USA & China
DTM Stage 5
Older population
Very developed
CBR decreases
Negative Growth
Ex: Germany and Japan
Immigration
Moving in
Emigration
Moving out
Demographic Momentum
Tendency for growing populations to continue to grow after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution
Doubling Time
Projected amount of time it will take for a given population to double
Epidemiological Transition
Focuses on the causes of death for each stage of the DTM
Epidemiological Transition Stage 1
(Pestilence, Famine, and Death)
Epidemics
Famine
Parasitic Diseases
Dirty water
Infectious Diseases
Animal att
Epidemiological Transition Stage 2
(Intro to Medicine and Sanitation)
Fewer deaths and reduction in pandemics
Increased standard of living
Epidemiological Transition Stage 3
(Degenerative Diseases)
Disease that continue to worsen over time
Heart attacks
Cancer
Epidemiological Transition Stage 4
(Fighting Degenerative Diseases)
Medical advances delay degenerative diseases
Longer life expectancy
Improved diets and lifestyle
Epidemiological Transition Stage 5
(Reemergences of Infectious Diseases)
Causes:
Evolution of diseases
Increased poverty
Increased Urbanization
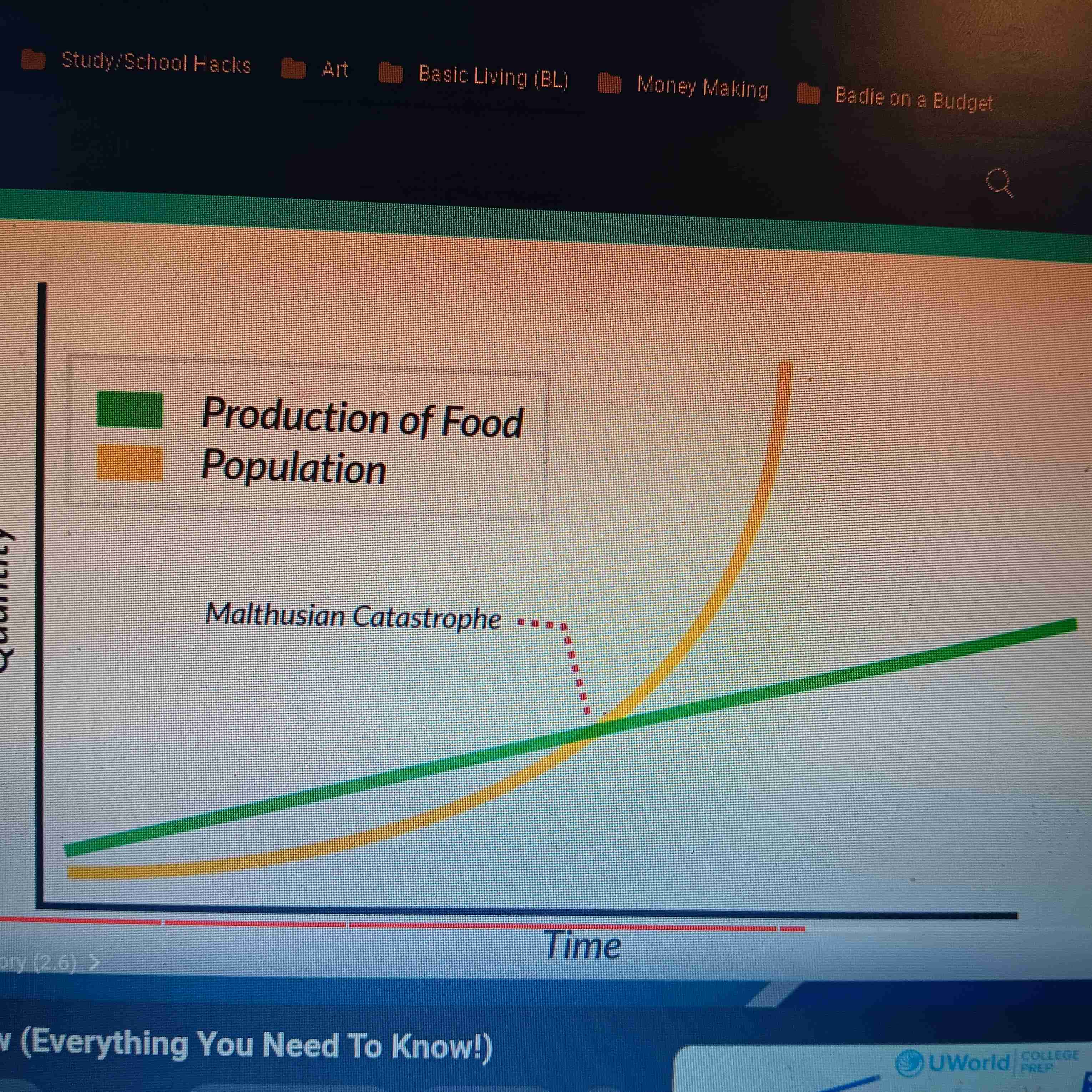
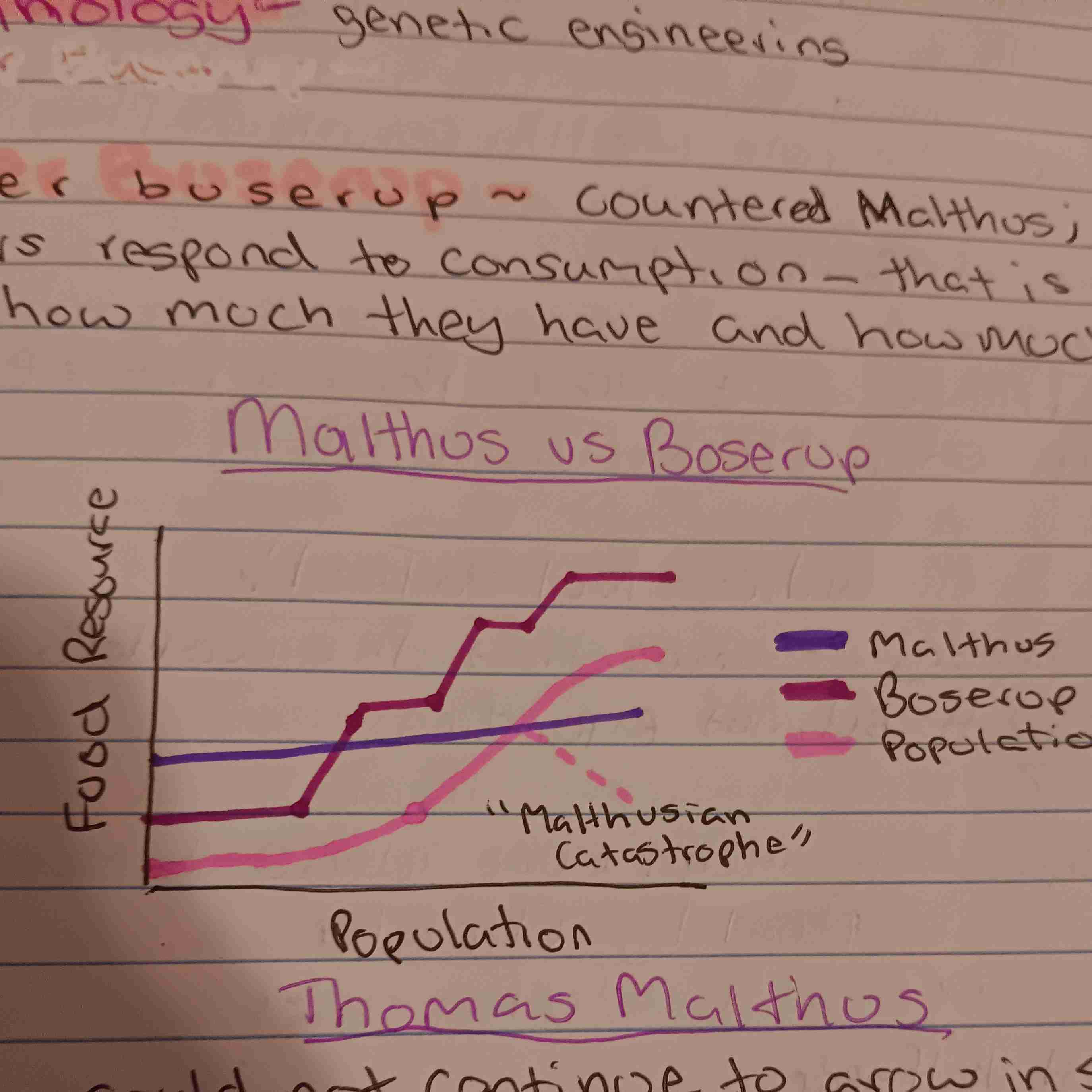
Malthusian Theory
Theory that population grows exponentially (increases one top of one another), it's ability to producefood would only increase arithmetically (increase in uniform amount). Leading to Famine, war, disease outbreaks
Ester Buserup
Countered Malthus; said subsistence farmers respond to consumption-Thai is farmers know how much they have and how much the need.
Neo-Malthusians
Believed Malthus was right, but mostly focus on the damage done to the environment by having to many people. i.e Clean air