PS371: Behavioral Medicine/Health Psychology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Behavioral Medicine
Knowledge from behavioral science applied to …
development …
diagnosis …
prevention …
treatment of medical problems
Interdisciplinary
Health psychology
Sub-field of Behavioral Medicine
Focus: factors that promote & maintain health
Assist formulation of …
improvements to health care systems
health care policy
Psychological, social impact on health
May adversely impact health:
Psychological factors lead to biological processes, which lead to illness, disease
Long-standing behavioral patterns increase risk for physical disorders
May also positively impact health
Examples: Exercise … yoga … relaxation training
Effects of acute or prolonged stress primary interest
Other potential focal interests include:
inequity in healthcare decisions
risk factors for significant medical conditions
interpersonal factors affecting prevention, treatment, outcome
Psychophysiological disorders
Best known:
Ulcers … asthma … insomnia … headache … coronary heart disease … hypertension
To this list you may add:
Ulcerative colitis … fibromyalgia … irritable bowel syndrome … chronic fatigue syndrome (among others)
Hans Selye
Study of effects of chemicals on health of lab rats
Test rats injected with chemical extracts
“Control” rats injected with saline
Test animals developed ulcers, other physiological problems
So did animals injected with saline!
Selye concluded that experimental procedures, conditions → adverse outcomes
Underlying cause … stress
Defined stress as …
biological syndrome
reaction to some physiological shock to organism’s system
disruption of stable, internal balance (organismic homeostasis)
General Adaptation Syndrome
Body goes through several stages in response to chronic stress
alarm reaction … body prepares to fight or flee
resistance … mobilize coping mechanisms to respond to the stress
exhaustion … resulting in illness, even death
Stress
Brief exposure to stressors may enhance functioning
Immediate response to virus is an enhancement in immunity
Long-lasting exposure may lead to deterioration
Biological … Psychological … Social stressors have similar effects
Make a person more susceptible to illness, alter course of disease
More recent definitions include:
Condition where expectations do not match perceptions of internal or external environment
Stress: operates at unconscious level
Distress: conscious awareness of impact
Biological cost of adapting to stress = allostatic load
Represents physiological consequences of chronic exposure
May have implications for physical or mental health functioning
Sympathetic nervous system
Mobilizes resources during times of threat / danger
With activation …:
heart beats faster
blood flow increases
respiration increases
adrenal glands stimulated
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis
Hypothalamus → pituitary
stimulate adrenal glands
produce surge of epinephrine, cortisol
Also note … hippocampus sensitive to cortisol …
helps turn off stress response
Emotional memories
Higher cortisol levels may harm hippocampus, have adverse effects on cognitive abilities
Cardiovascular disease
Hypertension (HTN)
Secondary: known biological cause (e.g., excess dietary salt)
Essential: no verifiable physiological cause; assumed due to physiological and psychological factors
> 33% population > 20 y/o have HTN
Majority (~90%) have no verifiable physiological cause
20-64 y/o: male ≥ female 65+ y/o: female ≥ male
Hypertension (HTN) & psychosocial factors
Association with personality factors:
negative emotions (e.g., anger, hostility), their suppression
more likely in African Americans
Culturally mediated
Personality association stronger with increasing age, accumulation over time, body’s ability to adjust to suppressed anger
Association with social factors: loneliness, depression, uncontrollability
Levels of social support and blood pressure associated
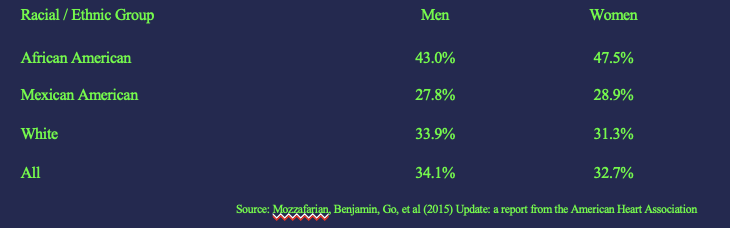
Hypertension (HTN) & Genetics
HTN runs in families
those with family history show grerater reactivity
offspring twice as likely to develop HTN
elevated blood pressure evident during first weeks of life
Hypertension (HTN) & Stress
Stress and heart attack
long-term survival related to subsequent stress
high stress without treatment leads to higher risk for later heart attack, 3 times more likely to die during 5-year follow-up
Men at greater risk for heart attack
Treatment of hypertension
Impact of cognitive-behavioral therapy, other non-drug therapies consistent with drug treatment effects
Mediation
Psychological sequelae of physical illness
Some infected with COVID-19 experience long-term effects
post-COVID conditions (PCC) or long-COVID
Symptoms last much longer than usually expected / persist despite recovery from acute infection … may include:
Tiredness that interferes with daily life
Difficulty breathing / shortness of breath
Chest pain
Headache
Sleep problems
Changes in smell or taste
… and many more
Long COVID
Many report variety of neurological/neuropsychiatric symptoms/disorders
Such symptoms of neuro-COVID may include:
fatigue
brain fog
memory issues
attention difficulties
sleep disturbance
anxiety
dysphoria
Severity of initial illness predicts probability of presence/severity of long-COVID, but not necessarily the experience of neuro-COVID symptoms
World Health Organization reported that anxiety and depressive disorders increased by 25% worldwide during first year of COVID-19 pandemic
disproportionately seen in women
young people more likely to present with suicidal / self-harming behavior
Still, COVID not necessarily responsible for this dramatic increase
Must recognize wide-ranging stressors, including but not limited to
health risks / illness
changes in work / school-based activities
loss of family members / friends due to death / isolation
social isolation / withdrawal
financial strain
social / political discord …
Increased availability of services (e.g., telehealth) insufficient to meet need
Reactions to traumatic stressors
Do adverse consequences necessarily follow from exposure to biological and/or psychological stressors?
George Bonanno and colleagues studied this relationship for many years. Argue that four distinct trajectories of response follow exposure to potentially traumatic events:
Chronic distress
Delayed reaction
Recovery
Resilience
Resilience
Definition: Process and outcome of successfully adapting to difficult or challenging life experiences, especially through mental, emotional, and behavioral flexibility and adjustment to external and internal demands.
Many previously saw this as rare (reflecting exceptional emotional strength) or as representing denial (illusory mental health)
Resilience now recognized as more common than other three types of responses combined
Most common outcome following traumatic experience is stable trajectory of healthy functioning!
Unfortunately, attempts to predict resilience reveal a paradox:
Correlates of resilient outcomes are (statistically) modest, so it is not possible to accurately identify who will be resilient to potentially traumatizing experiences
Among most consistently reported predictors:
Personality variables
Financial / educational assets
Coping/ emotional regulation strategies
Experience and expression of positive emotions
Demographics factors (e.g., male gender, greater educational attainment)
Exercise
Psychological treatment of physical disorders
Unlike with exposure therapy (e.g., for Specific Phobia), when may not want to use such techniques …
Relaxation training, biofeedback, meditation, hypnosis, others beneficial against hypertension
Alone and in combination these may also help with:
Headaches, insomnia, asthma, diabetes, chronic pain, irregular heartbeat, and others