Catabolism Part 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Catabolism
Breakdown of molecules to release energy and building blocks
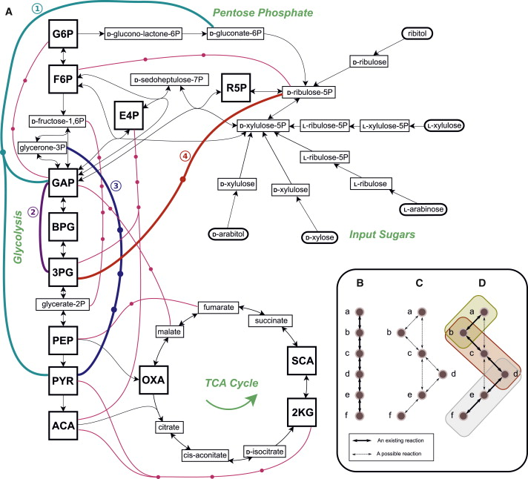
Central metabolism
Conserved pathways converting substrates into energy and precursors
CMP
Central metabolic pathways shared among microbes
Heterotroph
Consumes organic substrates for energy and carbon
Conservation
CMPs like glycolysis conserved across life forms
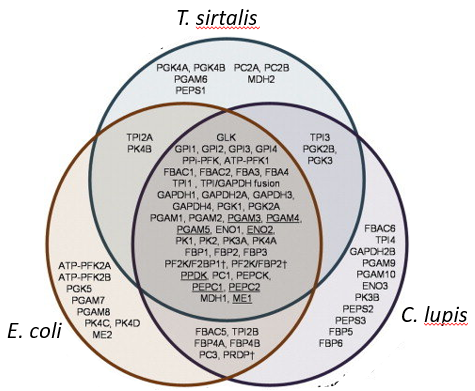
Pathways
EMP, PP, TCA, and ED are main metabolic routes
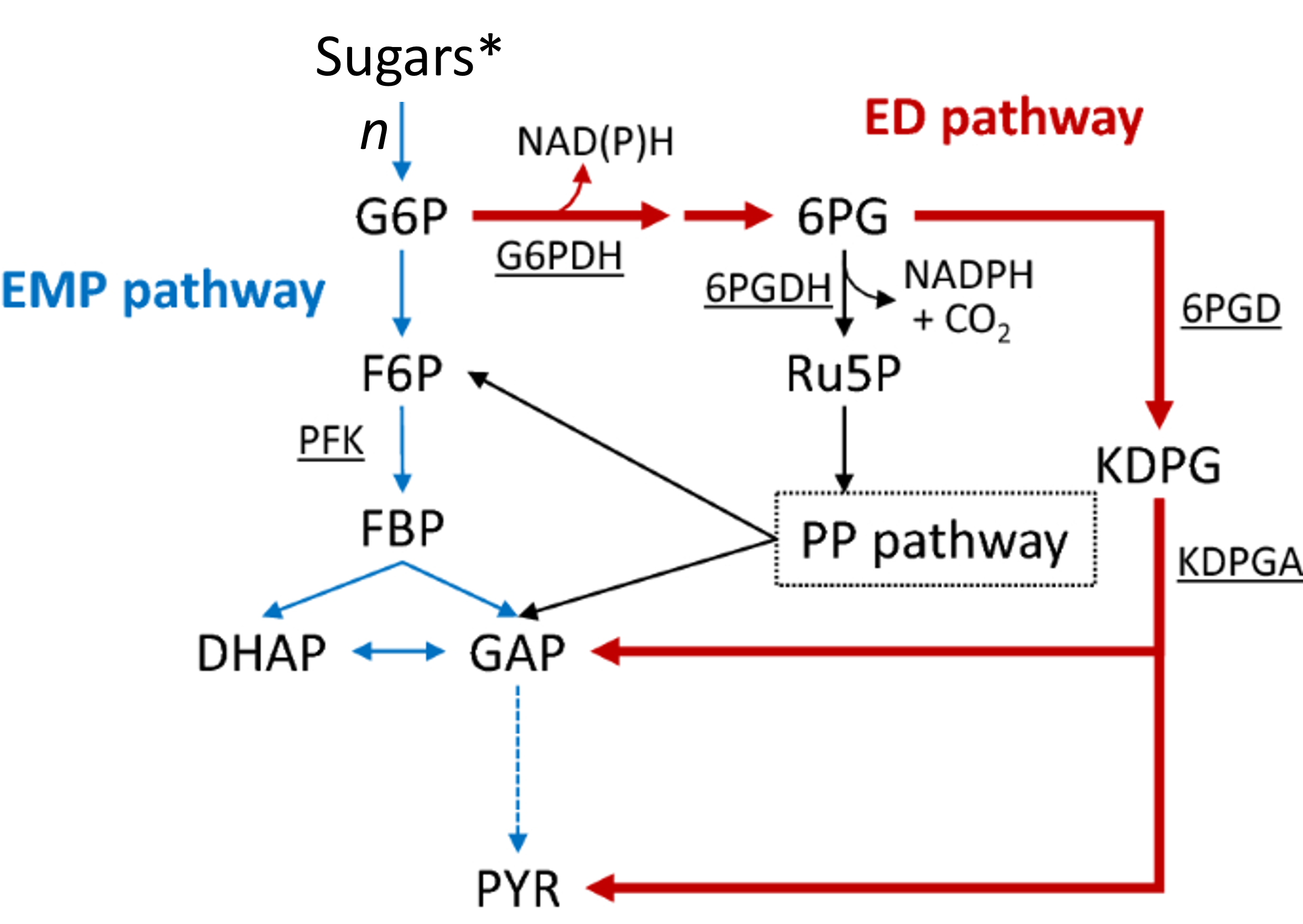
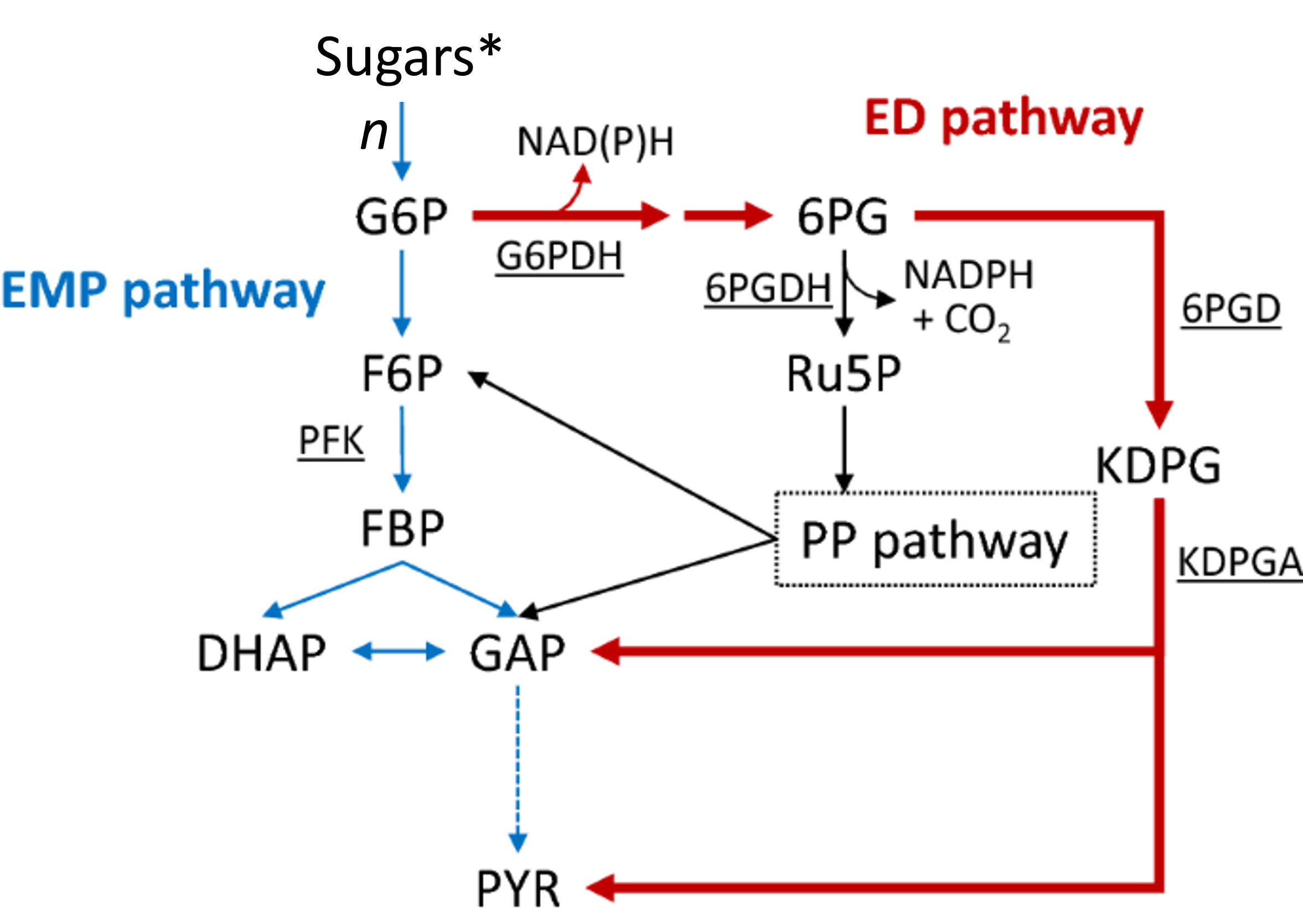
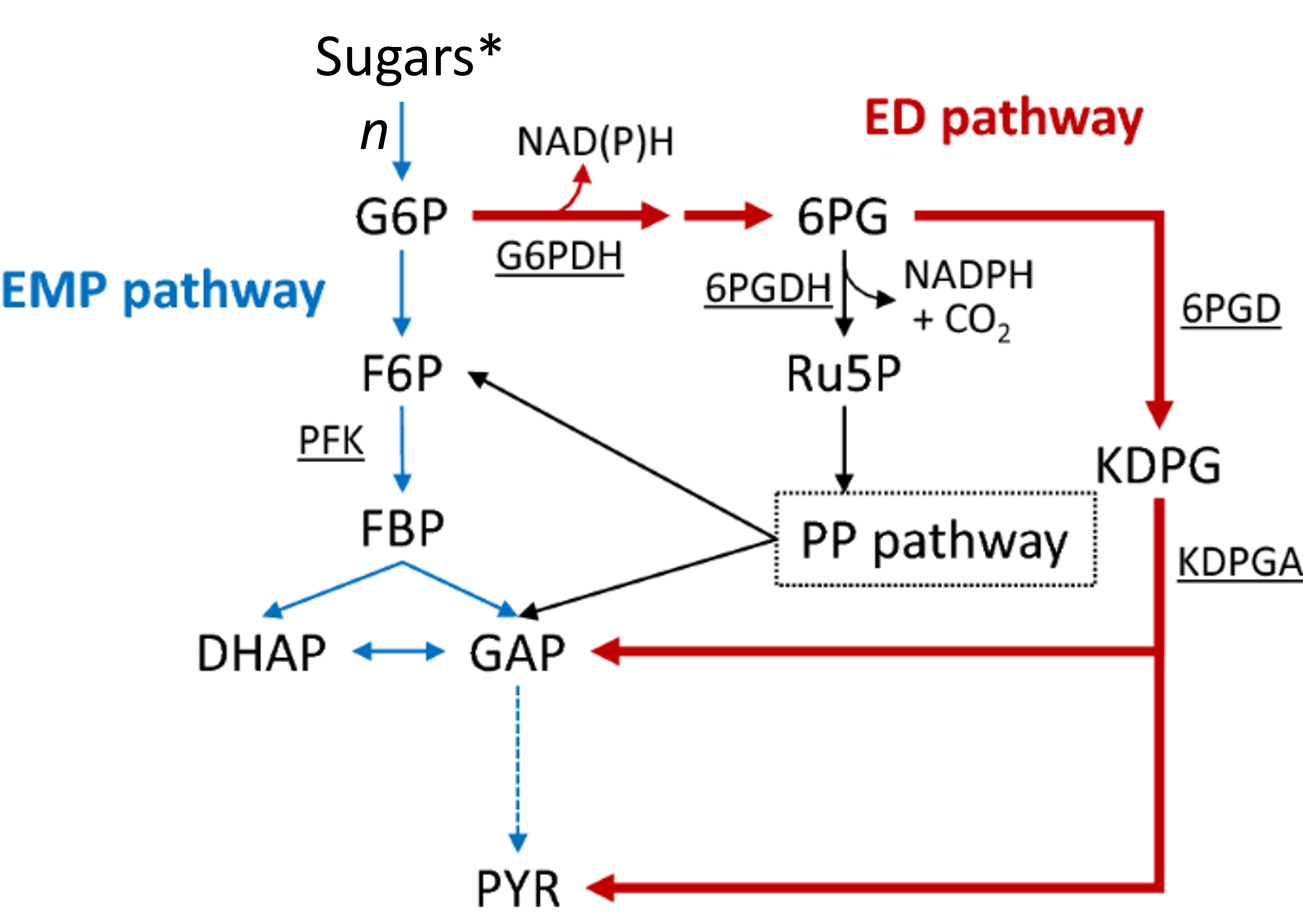
Glycolysis
EMP pathway for sugar catabolism and energy production
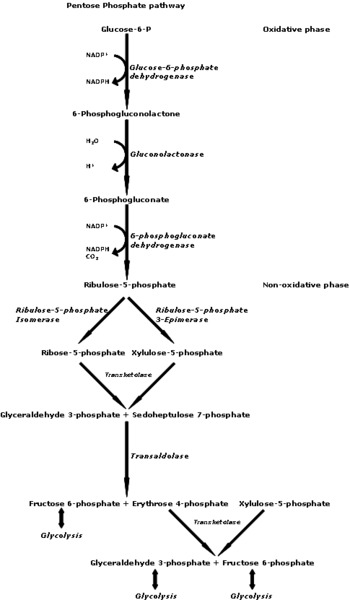
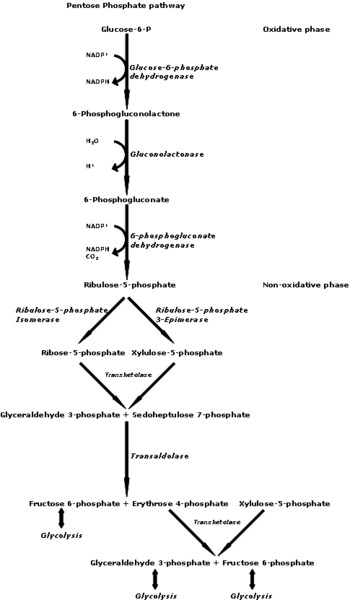
Pentose phosphate
PP pathway producing NADPH and biosynthetic precursors
TCA cycle
Citric acid cycle generating NADH, FADH2, and CO2
Entner-Doudoroff
ED pathway alternative to EMP in many bacteria
Substrates
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and aromatics
Gustav Embden
Contributed to glycolysis pathway discovery

Otto Meyerhof
Elucidated steps in glycolysis (1930s)

Jakub Parnas
Collaborated on glycolysis research

EMP
Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway for carbohydrate catabolism
Non-glucose sugars
Converted to glucose-6-phosphate for glycolysis
G6P
Glucose-6-phosphate; entry compound into glycolysis
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis used in TCA cycle
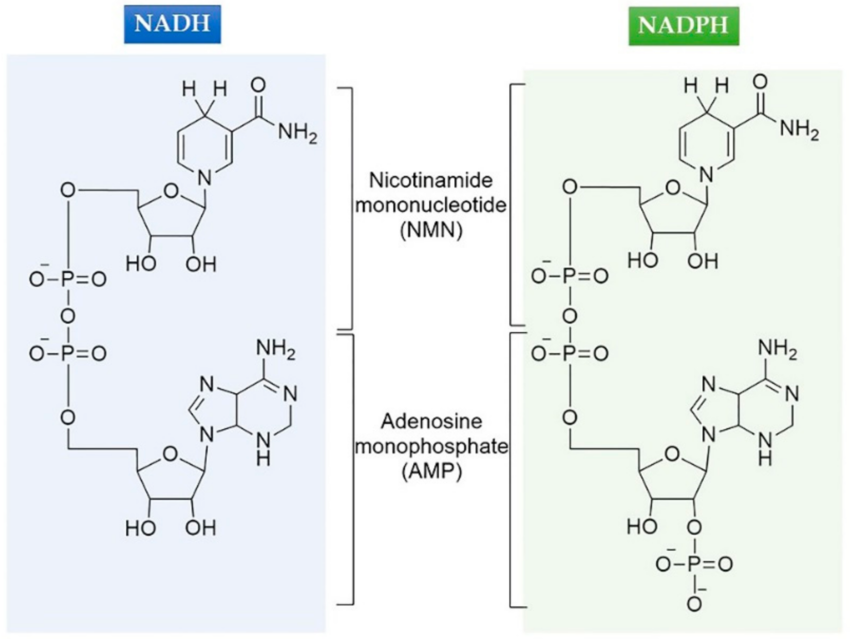
NADH
Energy carrier produced during glycolysis
ATP
Energy molecule produced by substrate-level phosphorylation
Pentose
Five-carbon sugar metabolized in PP pathway
Ribulose-5P
Intermediate in pentose phosphate pathway

NADPH
Energy carrier for biosynthesis and ROS detoxification
ROS
Reactive oxygen species; can damage microbial cells
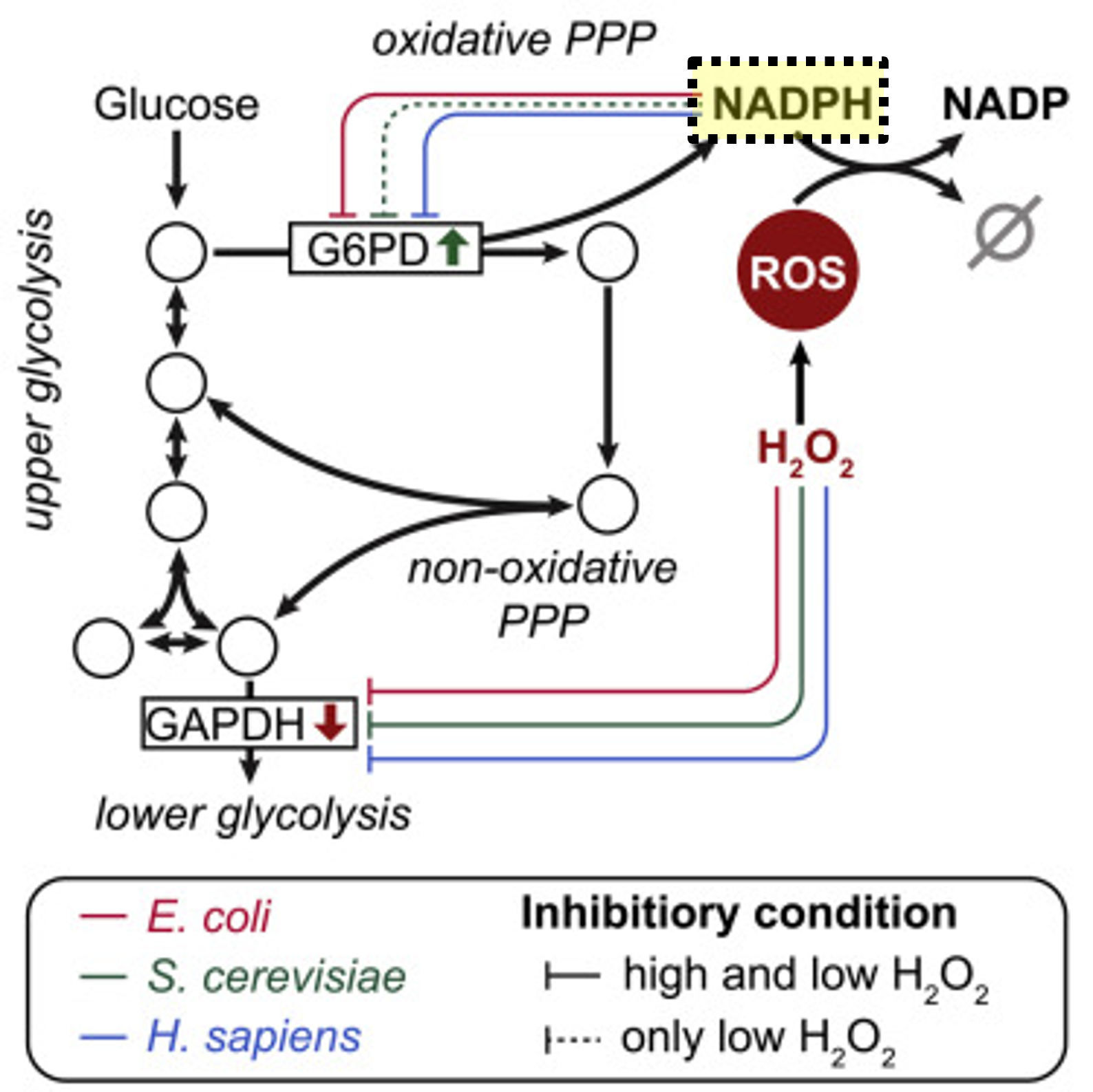
Detoxification
NADPH neutralizes ROS in microbes
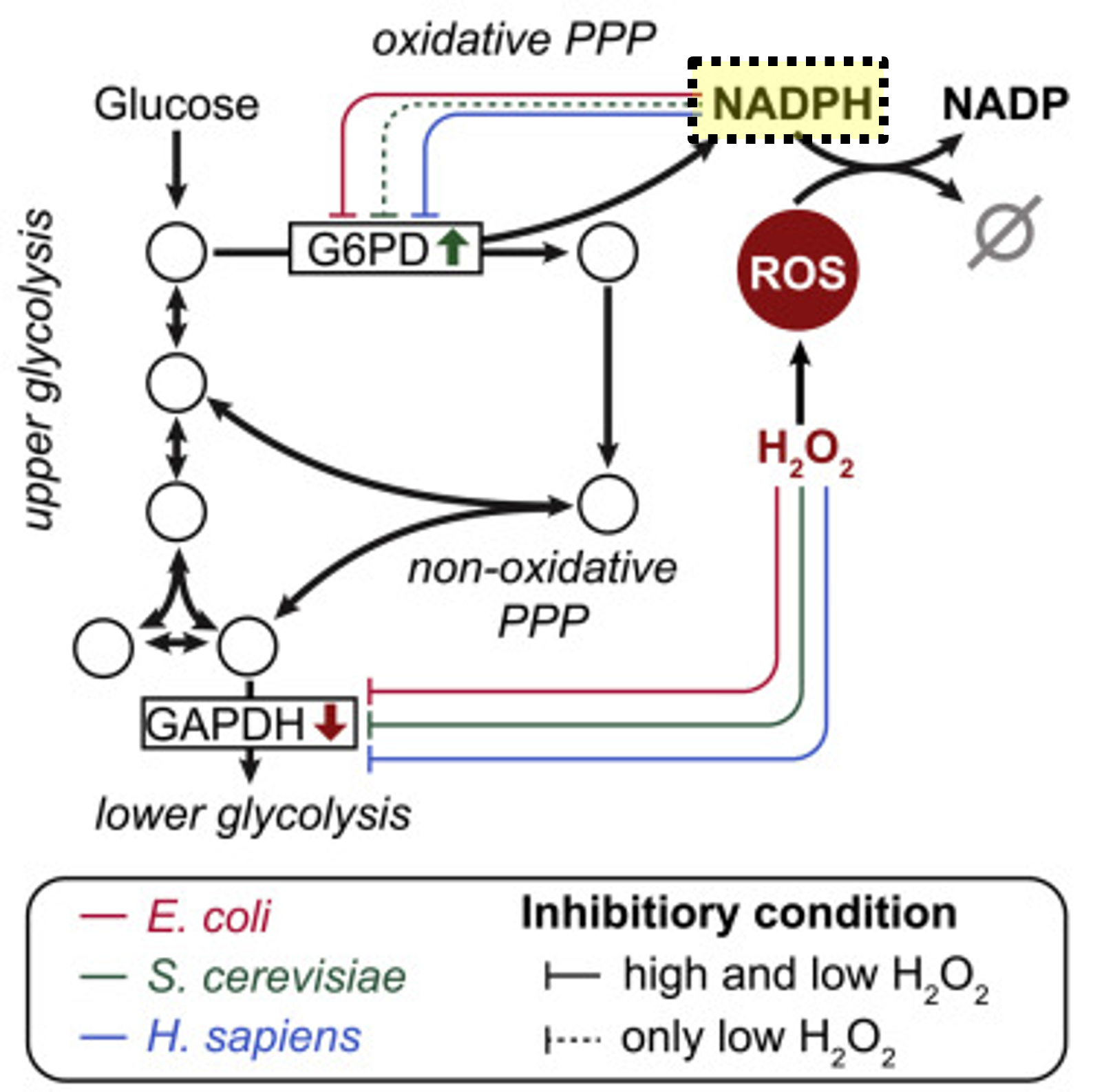
Ru5P
Ribulose-5-phosphate, precursor for nucleotides

Oxidative branch
PP pathway variant for energy generation
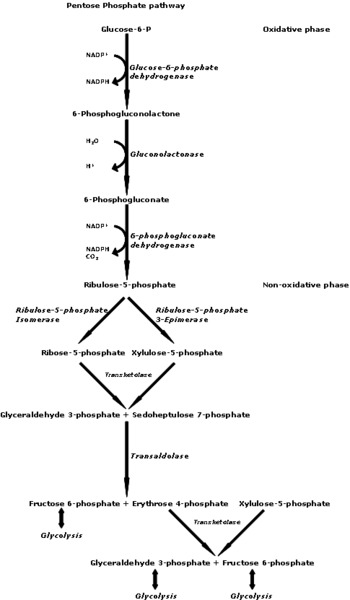
Reductive branch
PP pathway variant for biosynthesis
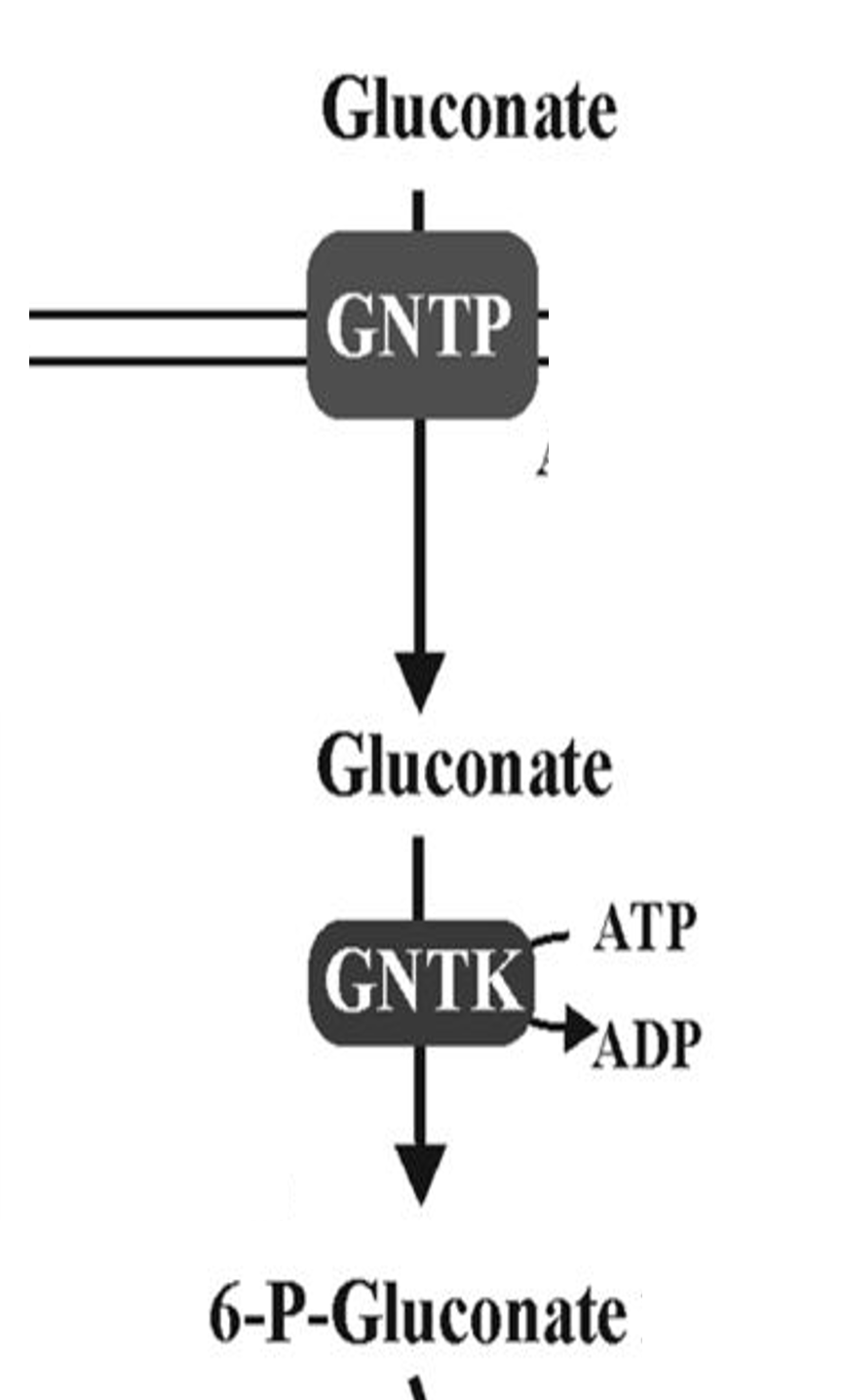
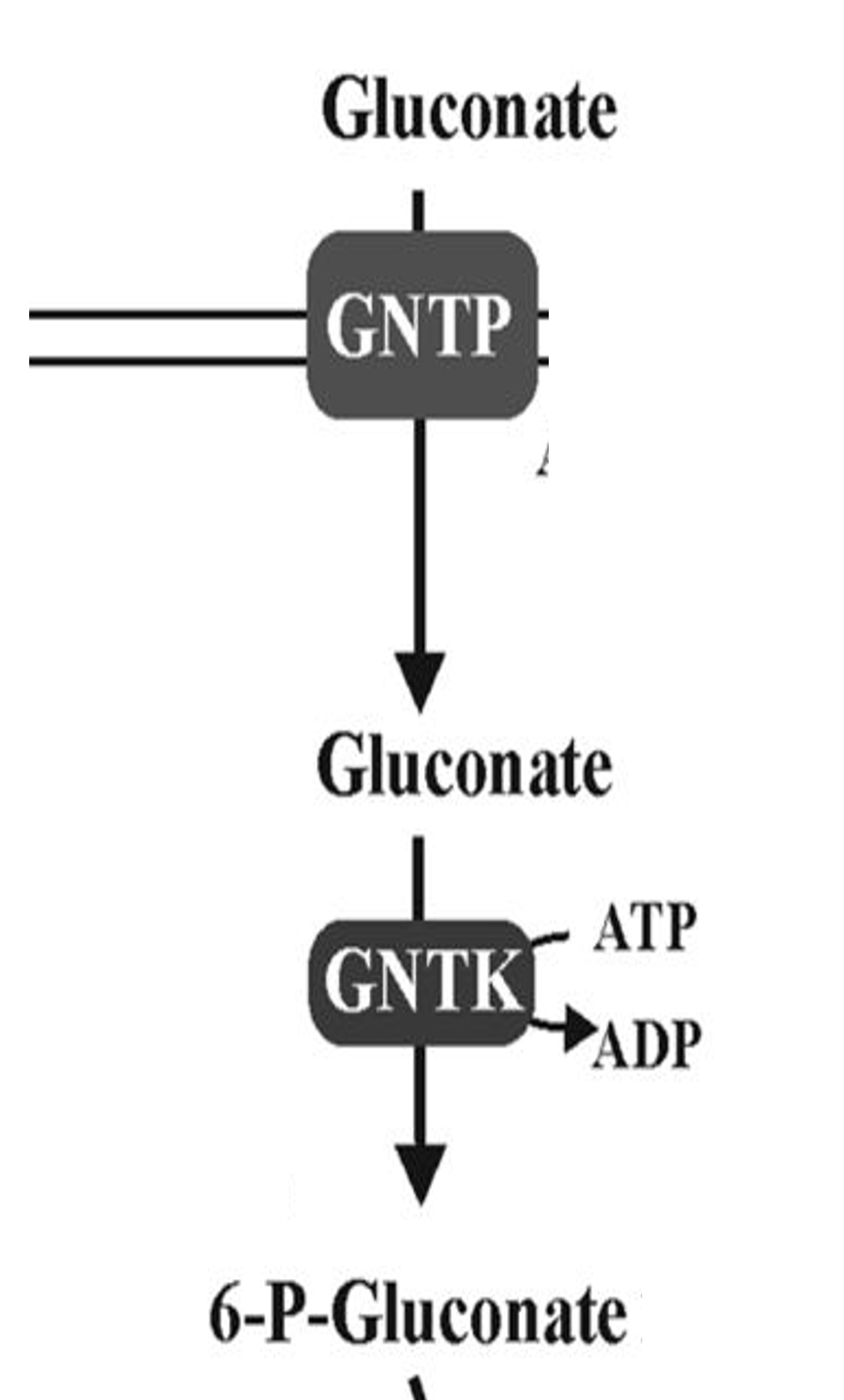
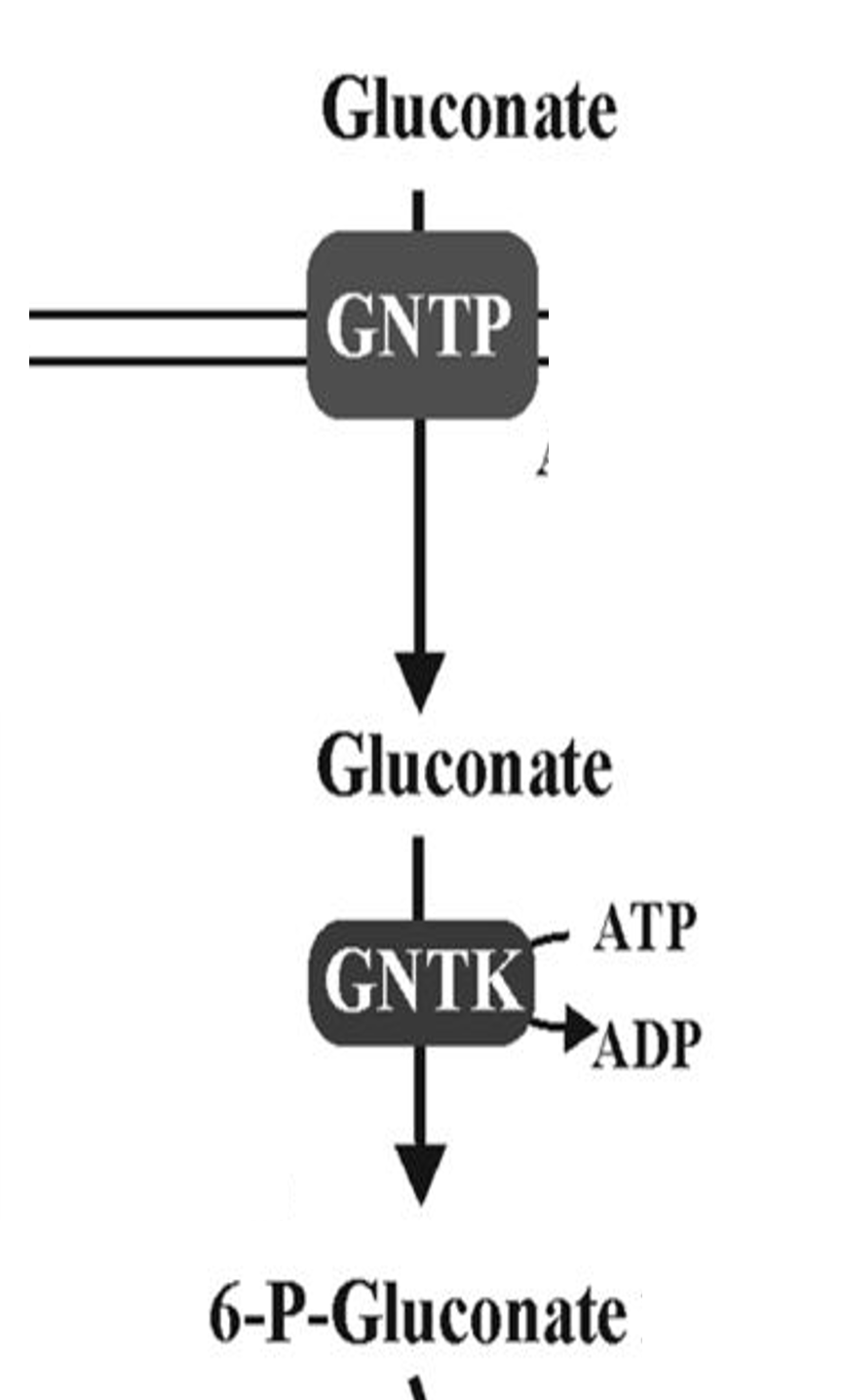
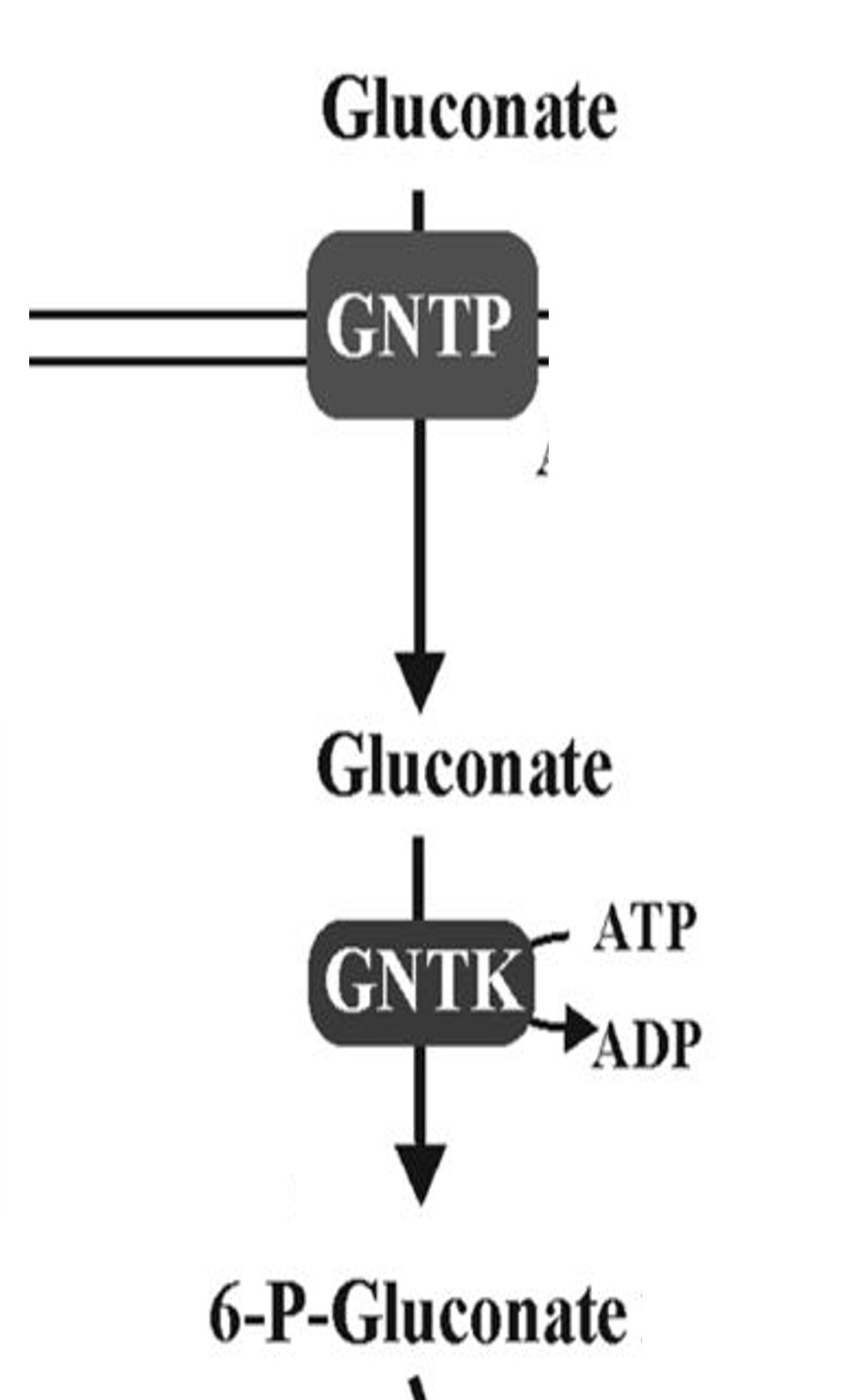
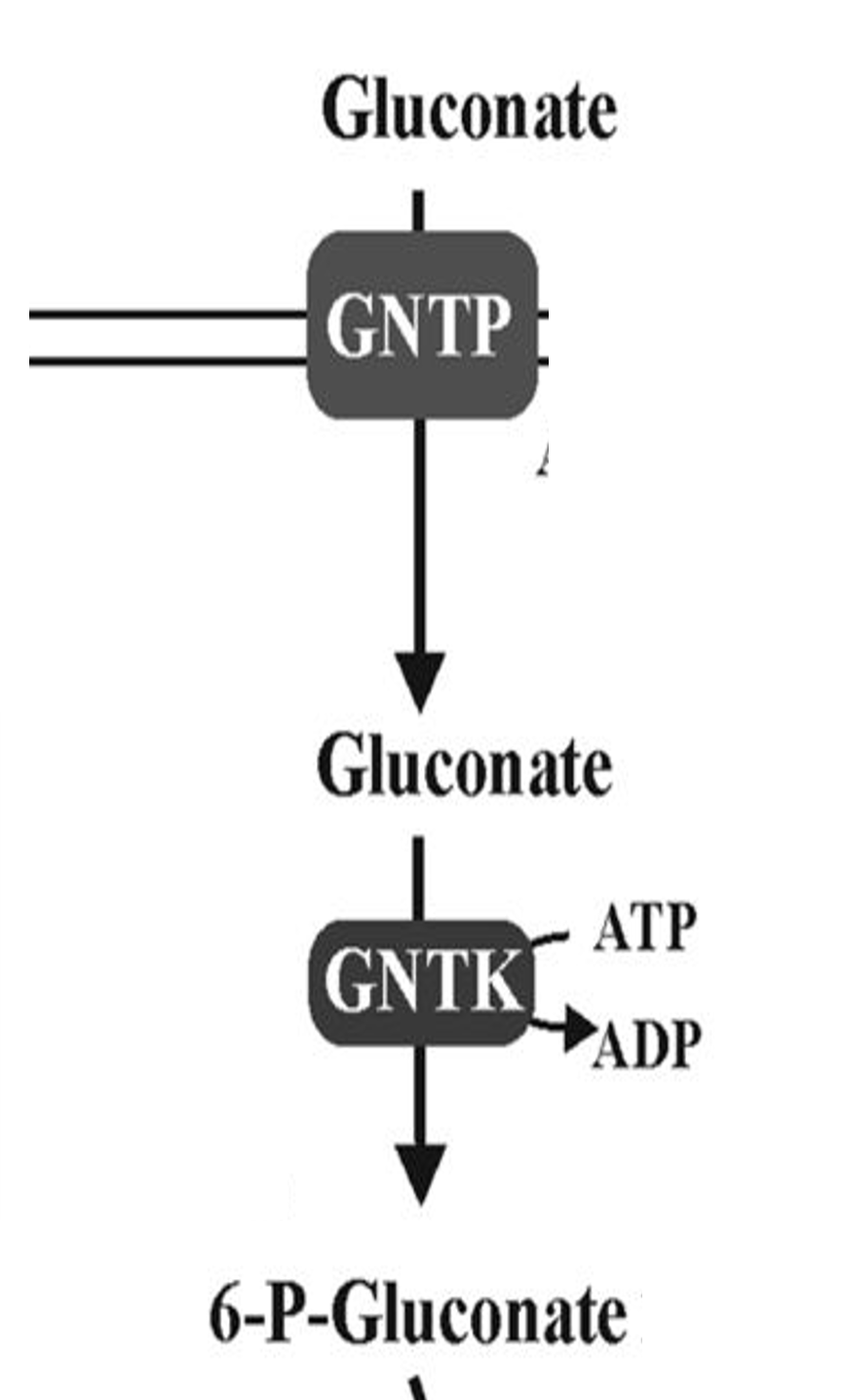
Gluconate
Sugar acid metabolized via ED pathway
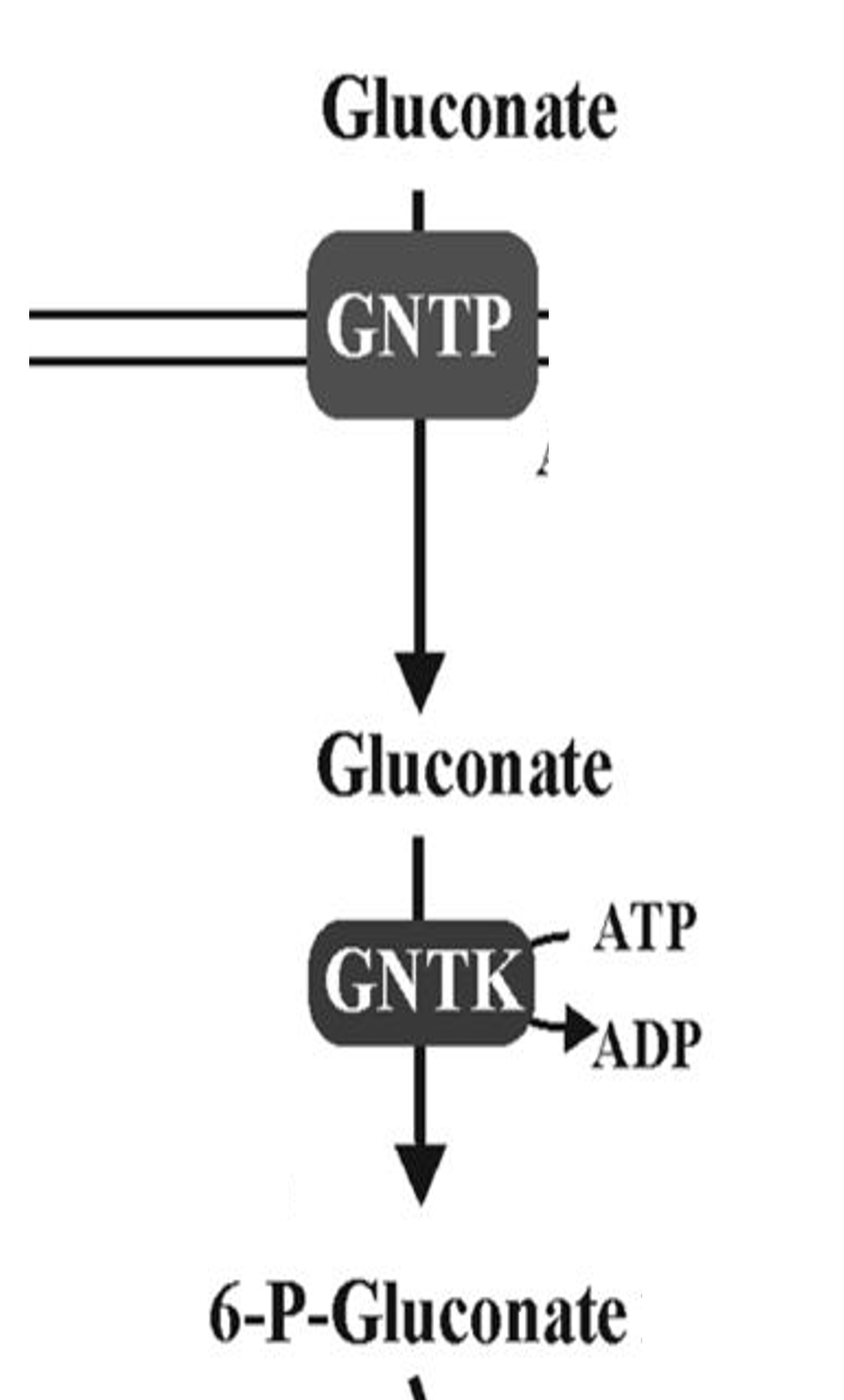
GntP
Symporter that imports gluconate into cells
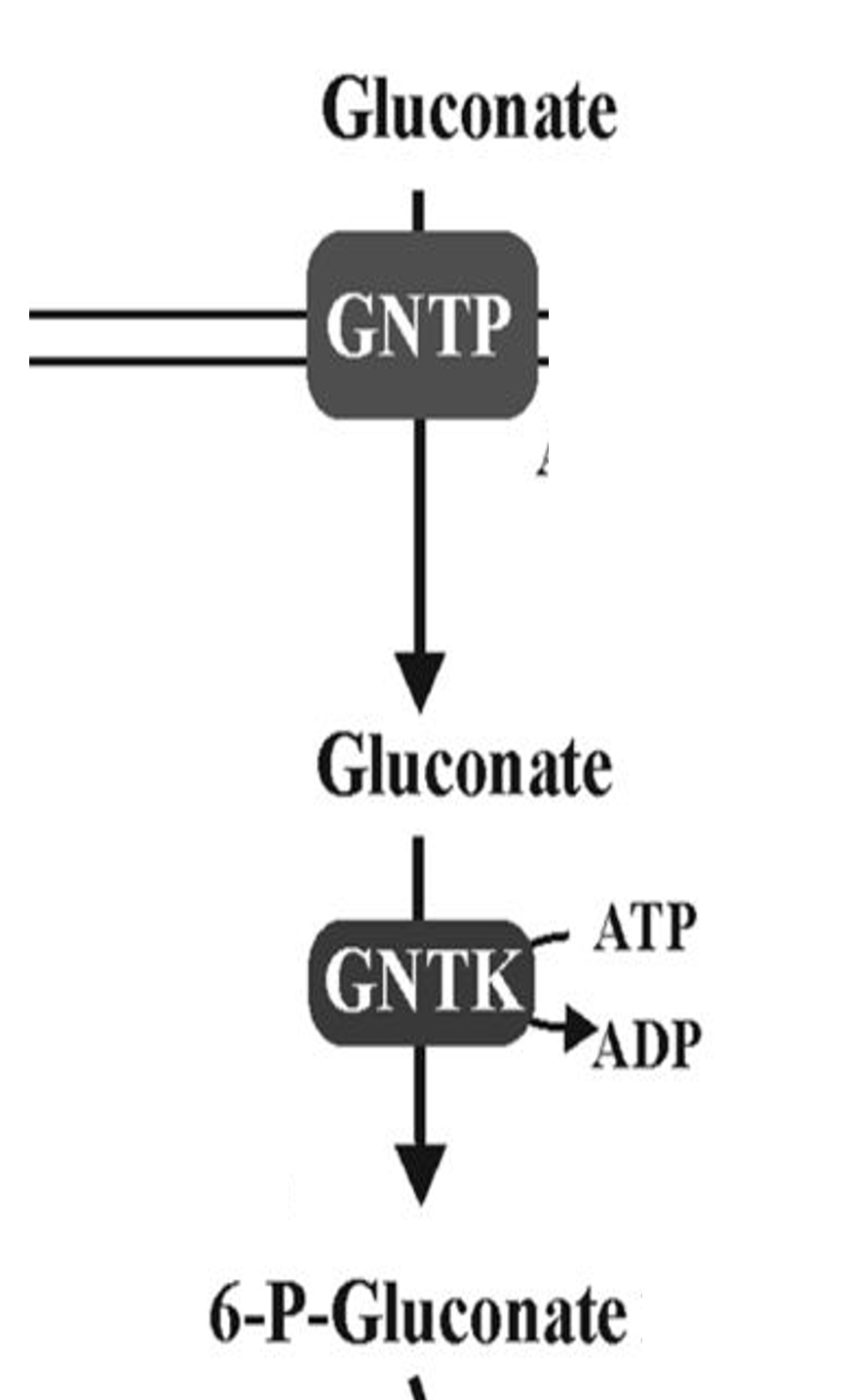
GntK
Kinase phosphorylating gluconate for metabolism
G6PDH
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in ED pathway
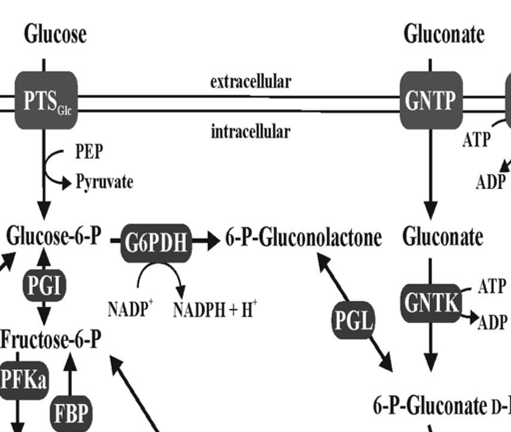
Pgl
Lactonase enzyme in ED metabolism
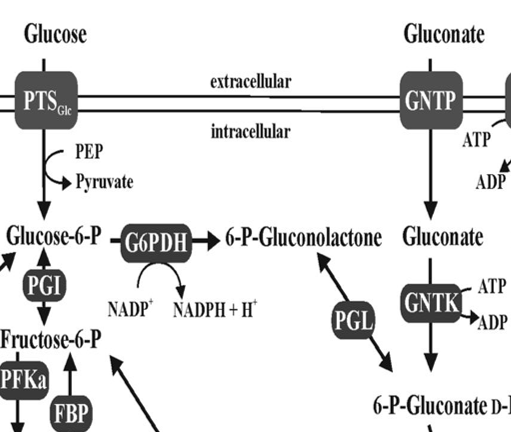
PTS
Phosphotransferase system transporting sugars into cells
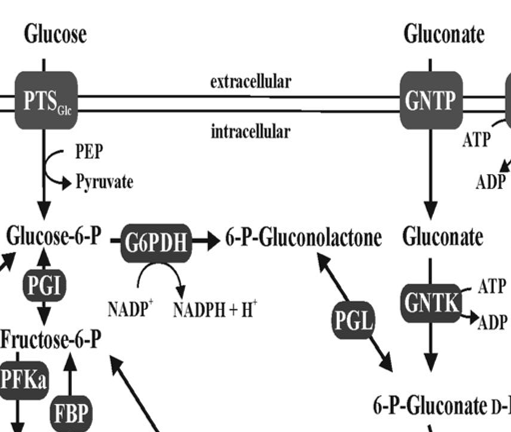
6PG
6-phosphogluconate metabolized via ED pathway
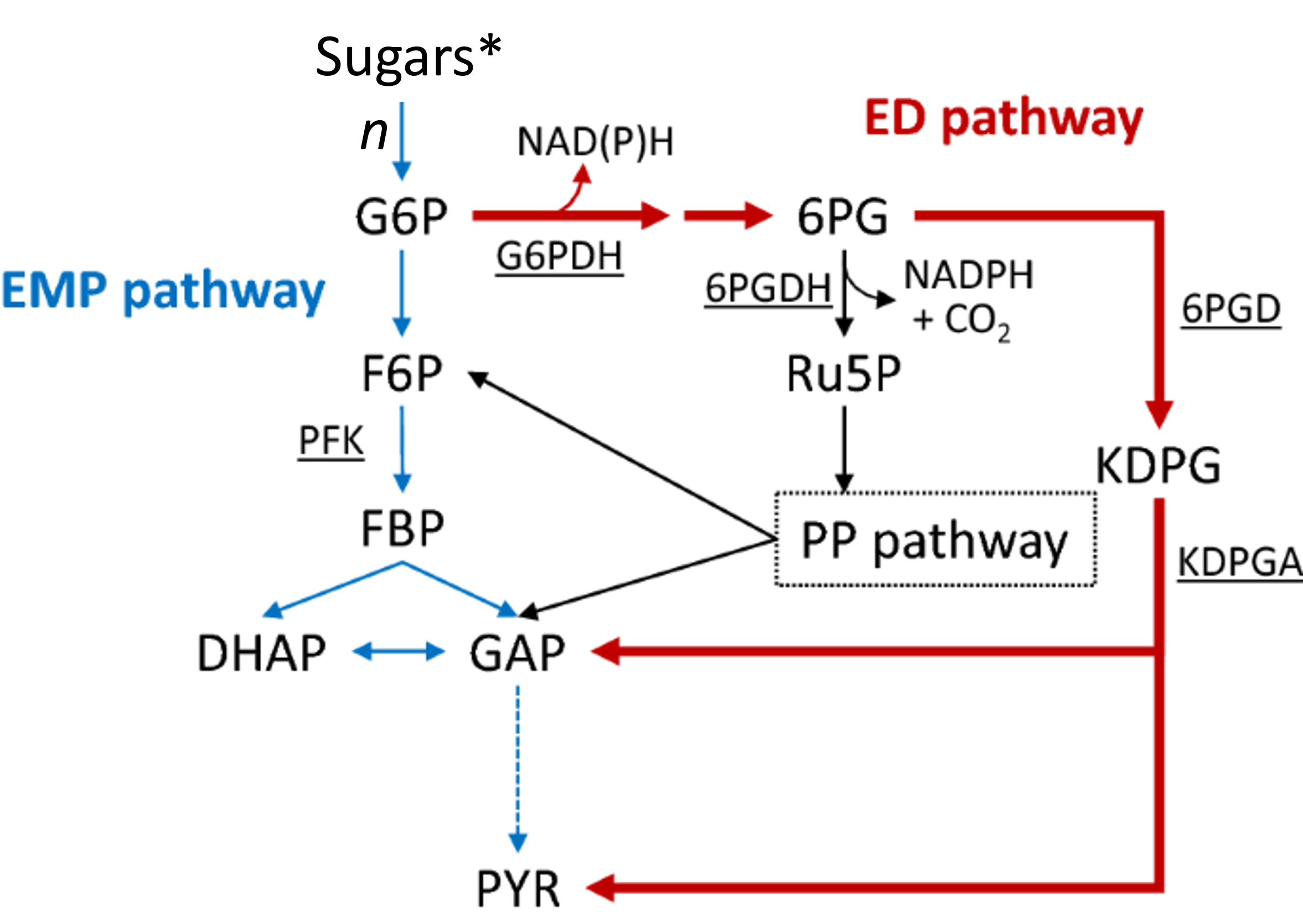
ED evolution
Entner-Doudoroff predates glycolysis evolutionarily
ED presence
Found in ~25% of named bacterial species
PP presence
Present in bacteria and eukarya; mostly absent in archaea
ED role
Used for sugar metabolism in intestines
Gluconic acid
Substrate commonly catabolized by ED pathway
Bacteria
Often combine EMP, PP, and ED for metabolism
Anabolism link
CMPs provide precursors for biosynthesis
Waste products
Generated alongside energy and precursors
Energy carriers
ATP, NADH, NADPH generated in CMPs
CMPs
Convert substrates into energy, waste, and building blocks
Carbon fate
Transformed into energy, CO2, or biosynthetic precursors
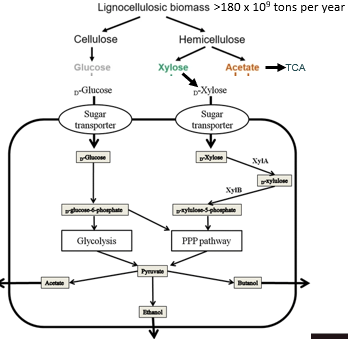
Ligninocellulose
Plant material metabolized using EMP and PP pathways
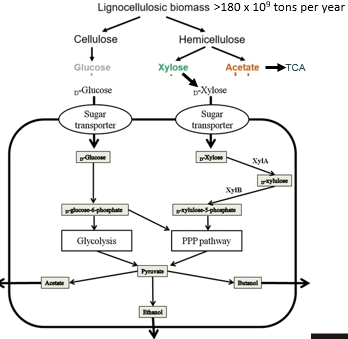
Ligninocellulose mass
180 billion tons metabolized yearly by microbes
TCA intermediates
Used for biosynthetic reactions in cells
Metabolic conservation
Shared across bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes
Archaea
Often lack full PP or use ED variants (spED, npED)
Haloferax volcanii
Archaeon with specialized ED pathway
Eukaryotes
Some diatoms and plants have ED enzymes
Rice
Plant example with partial EMP and ED components
Barley
Plant example with partial EMP/ED pathways
Energy conversion
CMPs convert carbon substrates into usable energy
Building blocks
CMPs supply metabolites for anabolism
Carbohydrates
Preferred substrates for microbial catabolism
CAZymes
Carbohydrate-active enzymes hydrolyzing polysaccharides
Aldehyde sugars
Products of glycosidase activity
Alcohol sugars
Intermediate metabolites in carbohydrate catabolism
Acid sugars
Oxidized carbohydrate derivatives
Microbial diversity
Different species use varying CMP entry points
EMP frequency
Occurs in over 90% of named microbes
PP frequency
Occurs in >90% of bacteria and eukarya
ED frequency
Occurs in ~25% of bacterial species
ROS role
Causes structural damage; mitigated by NADPH
Energy storage
CMPs generate ATP for later use
Work energy
ATP fuels cellular processes
Metabolic waste
Byproducts of catabolism
Pyruvate use
Feeds into TCA for further oxidation
CMP goal
Energy production and precursor formation
Metabolic branch
Oxidative vs reductive PP functions
Antimicrobials
None target EMP, ED, or PP pathways
ED discovery
1952; major bacterial sugar metabolism route
EMP discovery
1930s-40s; universal glycolytic pathway
PP discovery
1930s-50s; pathway for pentose metabolism
TCA discovery
1937; citric acid cycle by Krebs
E. coli
Model organism using EMP, PP, and ED pathways
T. sirtalis
Example organism showing metabolic conservation
C. lupis
Microbe with conserved central pathways
Noor et al 2011
Described conservation of microbial catabolism
Fabris 2012
Identified ED-like pathways in plants and diatoms
Rice et al 2000
Described ED variants in Haloferax volcanii
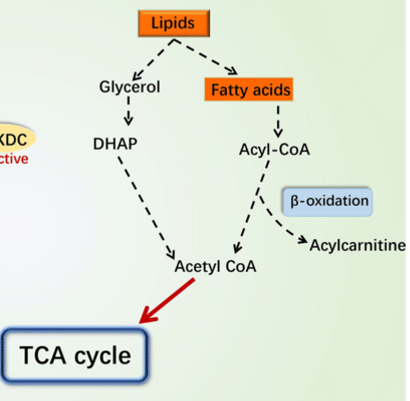
lipids
animal fats, dairy, plant fats, seeds & co.
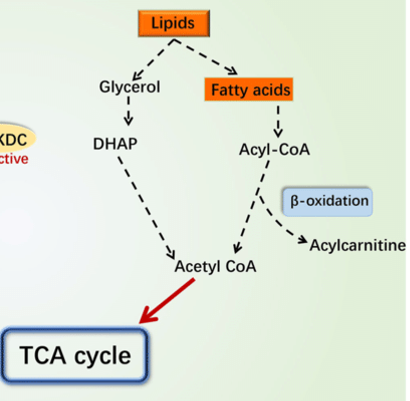
lipase
specialized hydrolase for assimilation of carbon from fats
Fat metabolism
___ by microbes is used commercially in the (1) food industry, (2) pharmaceuticals, (3) cosmetics, (4) medical diagnostics, and is central to (5) infectious disease
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
(TB) uses fats to survive for decades (aka latency) in its host in tubercle lesions
tubercles
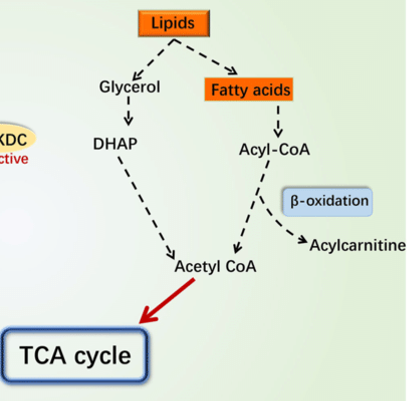
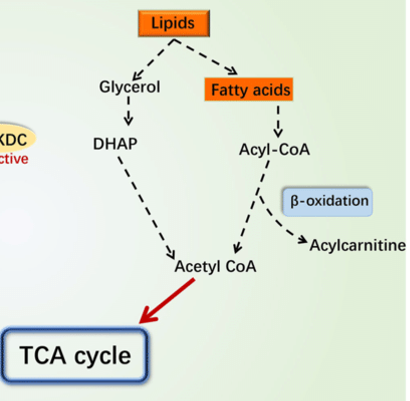
Latent TB hydrolyze stored lipids to glycerol, and fatty acids for food inside lesions
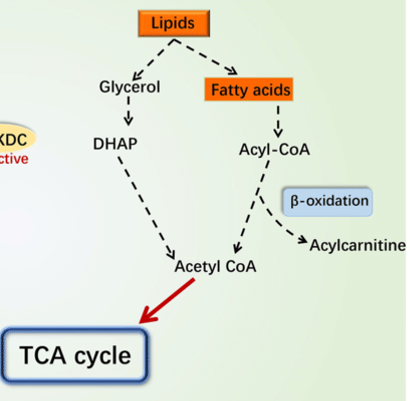
Glycerol
___ is metabolized by glycolysis to pyruvate, ATP and NADH
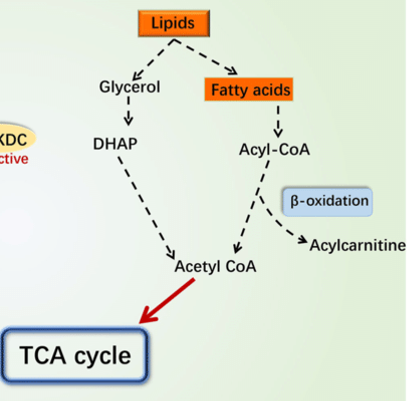
beta-oxidations
Fatty acids go through a series of ___
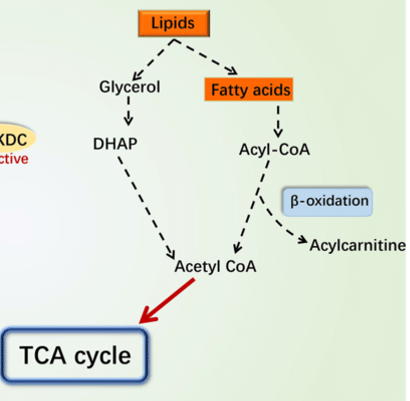
acetyl-CoA
products of beta-oxidations
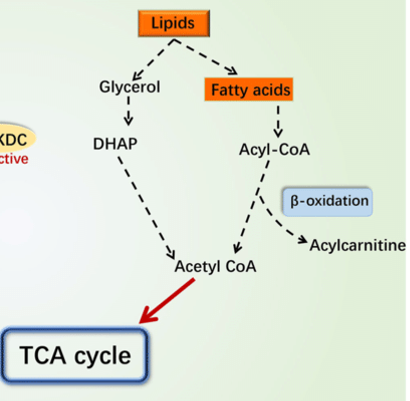
Krebs cycle
acetyl-CoA is further metabolized by ___
protease
hydrolase for proteins to become peptide amino acid
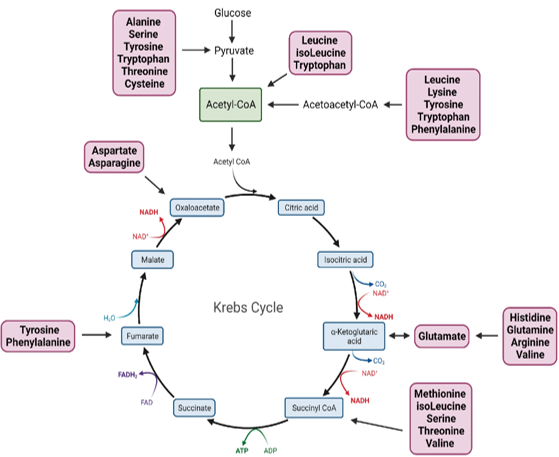
carboxylic acid intermediates
peptides are further deaminated to ___ of CMPs
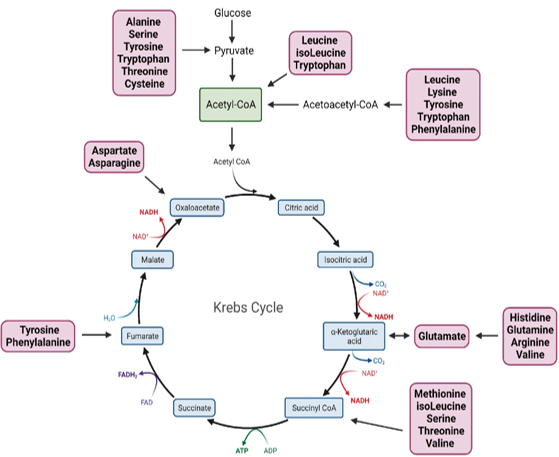
Kreb’s cycle
carboxylic acid intermediates are further catabolized via ___ ___