stupid baka quiz 4
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
retrieval models
provide a mathematical framework for defining search process
What is an in-memory index
it keeps entire vocabulary and posting lists in RAM during index construction
why is an in-memory index limited?
it cannot scale because it assumes entire index fits in memory (fails for large collections where postings/term dict > avail RAM)
why is random disk access a bottleneck?
they require disk seeks :((((( takes wayyy too long compared to RAM access
why build partial indexes?
because full inverted index cannot fit into RAM
how long would it take to read 1mb sequentially from MEMORY?
~3 nanoseconds
how long would it take to read 1mb sequentially from DISK?
825 nanoseconds
how long would it take to read 1mb sequentially from SSD?
49 microseconds
why sort partial indexes/lists before writing them onto the disk?
to make them easier to merge
you have two sorted partial indexes A and B and you want to merge them so that you can have one nice big index. HOWEVER, you do not have enough space to hold both in memory at the same time. You should….
Read the two files block by block and repeating until you have one sorted big index at the end (e.g., comparing block A1 to block B1 then comparing block A2 to block B2 etc etc)
Given partial indexes (A, B, C, D, E, ….) is it more efficient to read from two documents at a time or do a multi-way merge and read from all files simultaneously?
Read from all files simultaneously (as long as reading block sizes are big enough)
Given that postings are sorted by docID, if list lengths are x and y, then merge takes …
O(x + y) operations
Given x terms and their corresponding postings lists, what’s the best order for query processing?
Process them in order of INCREASING frequency (e.g. pair of words with least amount of postings » pair of words with greatest amount of postings)
Given the phrase “Friends, Romans, Countrymen”, what bi-grams are generated?
(friends romans) (romans countrymen)
Should n-grams be adopted for arbitrary sizes? (True/False)
False, they’re unfeasible
What’s some problems with n-grams?
False positives, indexes/dict too big
For phrase queries, we should use a merge algorithm _______ at the _____ level
recursively, document
A positional index ________ postings storage ______
expands, substantially
Are positional indexes in standard use now?
True
Positional indexes require an entry for each….
occurrence
What are some advantages of Boolean search?
all of the above
What are some drawbacks to boolean retrieval?
All of the above
With a large index that doesn’t fit in memory, scanning the file looking for query terms could take…
from O(n) to O(logN), depending on whether or not query terms are sorted
With a large index that doesn’t fit in memory, jumping to the right positions could take…
O(1)
In order to keep retrieval time quick, you should build a _______ for your index
index
MapReduce is…
a distributed programming tool designed for indexing and analysis tasks
A key benefit of MapReduce is that the multiple operations on the same input provides…
fault tolerance
Index merging is a good strategy when updates come in _______
large batches
Is index merging efficient at handling small updates? (True/False)
False
Why is multi-way merging more efficient?
Since it reads from all partial index files at once and avoids disk I/O
Why is sequential disk access faster than random access?
Sequential disk access avoids disk seeks
What do skip pointers do, and how do they help?
Allow the algorithm to jump ahead within long postings lists instead of advancing one docID at a time
What is the trade-off of adding more skip pointers?
Improves skipping ability but increases index size and overhead
How do skip pointers help?
reduce the number of comparisons needed during intersections
Why can’t we simply scan the entire inverted index file to find a term’s postings
Scanning is O(n), and the file may be gigabytes long
What does “indexing the index” accomplish?
It creates a RAM-resident table mapping terms → byte offsets in the on-disk index
Why is binary search NOT sufficient to search inside the inverted index file?
Records inside the index file have variable length, so you cannot jump to the middle.
What is stored in the secondary index (the lexicon)?
Term statistics, vocabulary, and byte offset pointers
Why does the secondary index likely fit in RAM?
It only stores metadata for terms, not the postings lists
What is the purpose of splitting the index into directories (a/, b/, c/, …)?
It keeps each index file smaller and easier to cache or load in parallel.
How does MapReduce support large-scale indexing?
It parallelizes indexing by mapping documents into (term, docID) pairs and reducing them by term
What happens during the Shuffle phase of MapReduce indexing?
Machines combine identical terms from all mappers so reducers receive all data for each term.
Boolean queries are good for …
Expert users with precise knowledge, applications
Boolean queries result in….(too few, too many, both) results
both (too few and too many)
In ranked retrieval, system returns
ordered list of top documents in collection for a query
Free text queries are queries wehre
user queries are just words in a human language
How can we rank-order the documents in the collection with respect to a query?
Assign a score that measures how well document and query “match” to each document
Jaccard coefficient
jaccard(A,B) = | intersection(A, B) | / | union(A, B) |
What are some good properties of Jaccard coefficient?
A, B don’t need to be same size
Always comes out to be in range [0, 1] inclusive
What are some issues with using Jaccard
Doesn’t consider term frequency, doesn’t consider IDF
Bag of words model
Vector representation that doesn’t consider the ordering of words in a document
Relevance (does/does not) increase proportionally with term frequency.
does not
Log frequency weight of term t in d is, (given term frequency > 0)
1 + log10*term freq
Given a query ‘kitty loaf’ and document: “fat cat loaf is the best loaf’, what is the Jaccard Coefficient?
1/7
Given a query ‘kitty loaf’ and document: “I like chonk chonk cute cat’, what is the Jaccard Coefficient?
0

What is the document frequency of cat given document corpus:
3

What is the inverse document frequency of cat given the following corpus
1
==> total # of docs = N = 3
document frequency = 3
log10(N/df) = log10(3/3) = 1
Rare terms are (more/less) informative than frequent terms
more
Document frequency captures….
number of documents that contain a word t
inverse measure of informativeness of t
idf (inverse document frequency) of t is calculated by doing
idf = log10(N / df)
where total # of docs = N
document frequency = # of docs term is in = df = (1 + log(tf))
Does idf have an effect on ranking for one-term queries? (True/False)
False
The collection frequency of t is ….
the number of occurrences of t in the collection, counting multiple occurrences.
tf-idf is calculated by ..
multiplying tf and idf together
= (1 + log(tf)) * log(N/df)
What are some benefits to using tf-idf?
Increases with the number of occurrences within a document
Increases with the rarity of the term in the collection
In the vector space model, _______ are the axes
terms
In the vector space model, _______ are the points/vectors
documents
In the vector space model, documents are ranked according to….
proximity to queries in this space
In the vector space model, proximity represents the…
similarities of vectors AND the inverse of distance
Why is Euclidean distance a bad idea for vector space proximity?
because Euclidean distance is large for vectors of different lengths, and queries and documents will (usually) have very different lengths...
In the vector space model, documents are ranked according to the _______- between documents and query
angles
After length-normalization, both long and short documents now have comparable…
weights
SMART Notation
denotes the combination in use in an engine, with the notation ddd.qqq
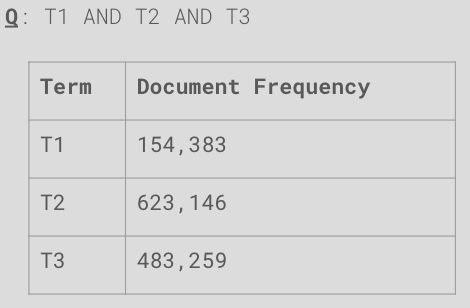
Determine the most efficient processing order, if any, for the Boolean query Q considering the document frequency information from the table →
(T1 AND T3) first, then merge with T2

What is the tf-idf of...the word loaf in S1?
2
(1+log(tf)) * log(N/df)
tf = 2 (occurs twice)
idf = log(N/df) = log(3/2)
(1 + log(2)) * log(3/2)
![<p>Using cosine similarity as the ranking formula, what is the relative ranking of these documents for a query with coordinates [1, 1, 1, 1]?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/76ba2a01-2c56-4fe9-849a-42a50bc260e3.png)
Using cosine similarity as the ranking formula, what is the relative ranking of these documents for a query with coordinates [1, 1, 1, 1]?
D2, D1
(there’s a lot of math involved, but for time purposes in quiz, just look and see that D2 more similar than D1)