BIO 269 Exam 4 -Casotti WCU
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
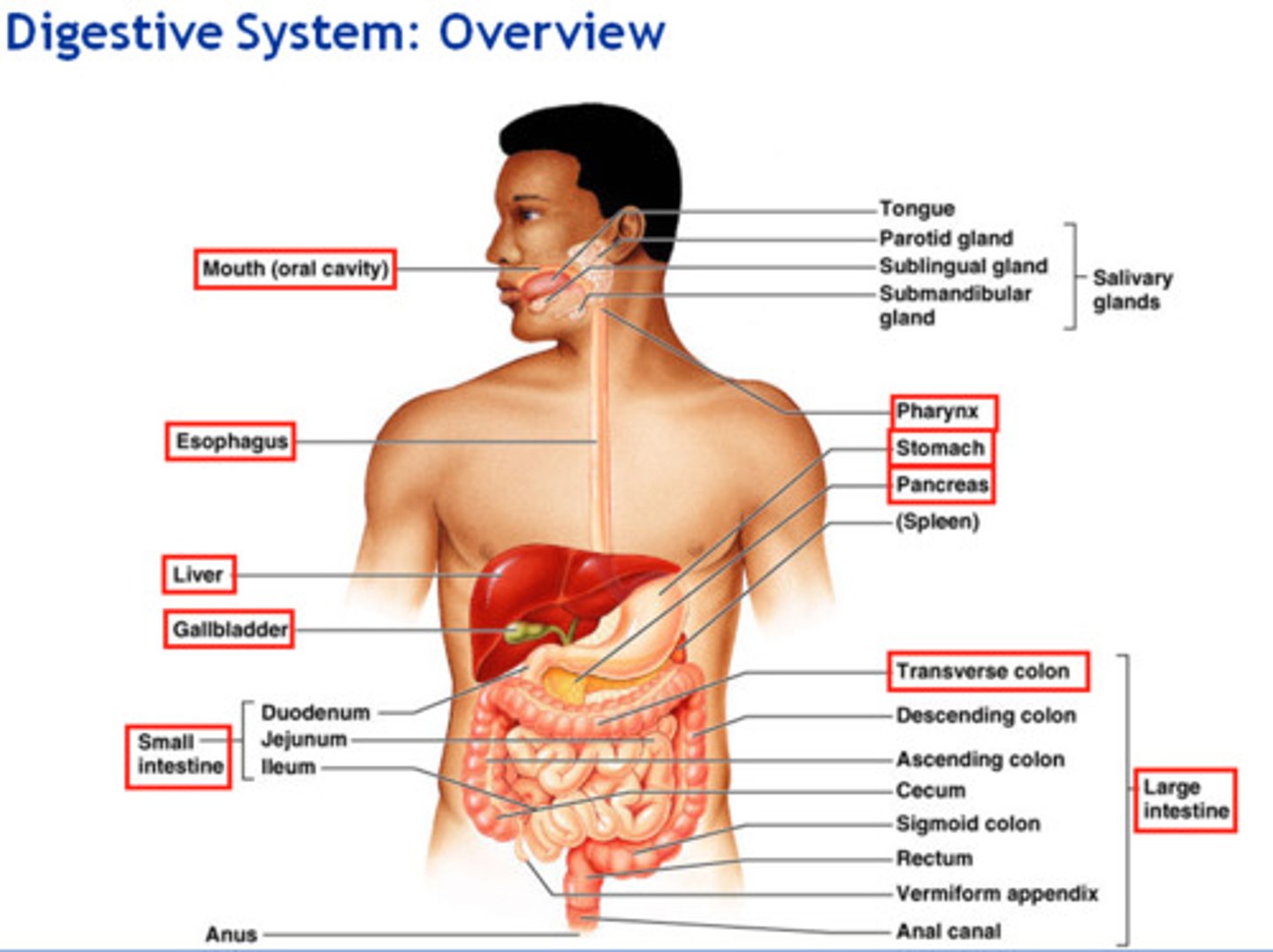
Digestion Overview
-Mouth: parotid, submandibular, sublingual glands release saliva
-Pharynx
-Esophagus
-Stomach: food stored and broken down here
-Small intestine: duodenum, jejunum, ileum, about 6 feet long with small diameter
-Pancreas and Liver: empty into duodenum
-Gallbladder: stores bile
-Large Intestine: cecum (appendix at end), ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon
-Rectum
-Anus
Functions of Digestive System
1) Ingestion
2) Motility
3) Mechanical and Chemical digestion
4) Secretion
5) Absorption
6) Elimination of waste
Ingestion (function)
Food entering the mouth
Motility (function)
-Slow waves: maintain muscle tone, gets stomach back to original size after overeating and stretching
-Propulsive movement: AKA peristalsis, unidirectional in esophagus and intestines
-Mixing movement: bidirectional in stomach and intestines
Digestion (function)
-Mechanical: chewing with teeth in mouth, churning in stomach, segmentation in small intestine
-Chemical: passage across plasma membrane, Carbs -tri-/di-saccharides to monosaccharides, Proteins -into amino acids, Fats -into monoglycerides and fatty acids
Secretion (function)
-Mouth: saliva
-Stomach: acid (HCl)
-Liver + Pancreas: into duodenum
-Small intestine
Absorption (function)
-80% in duodenum
-20% is remaining small intestine and large intestine
Elimination (function)
-eliminating waste
Alimentary Canal
Digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
4 Layers of the Alimentary Canal
-Mucosa
-Submucosa
-Muscularis externa
-Serosa
Layers of Mucosa
-Epithelium: single layer
-Lamina Propria: loose connective tissue, fenestrated capillaries, lacteals
-Muscularis Mucosae: layer of muscle
Layers of Submucosa
Just contains arteries and veins, lacteals, loose connective tissue to support vessels
Layers of Muscularis Externa
-Circular layer: inner
-Longitudinal layer: outer
Layers of Serosa
-Connective Tissue
-Epithelium (mesothelium)
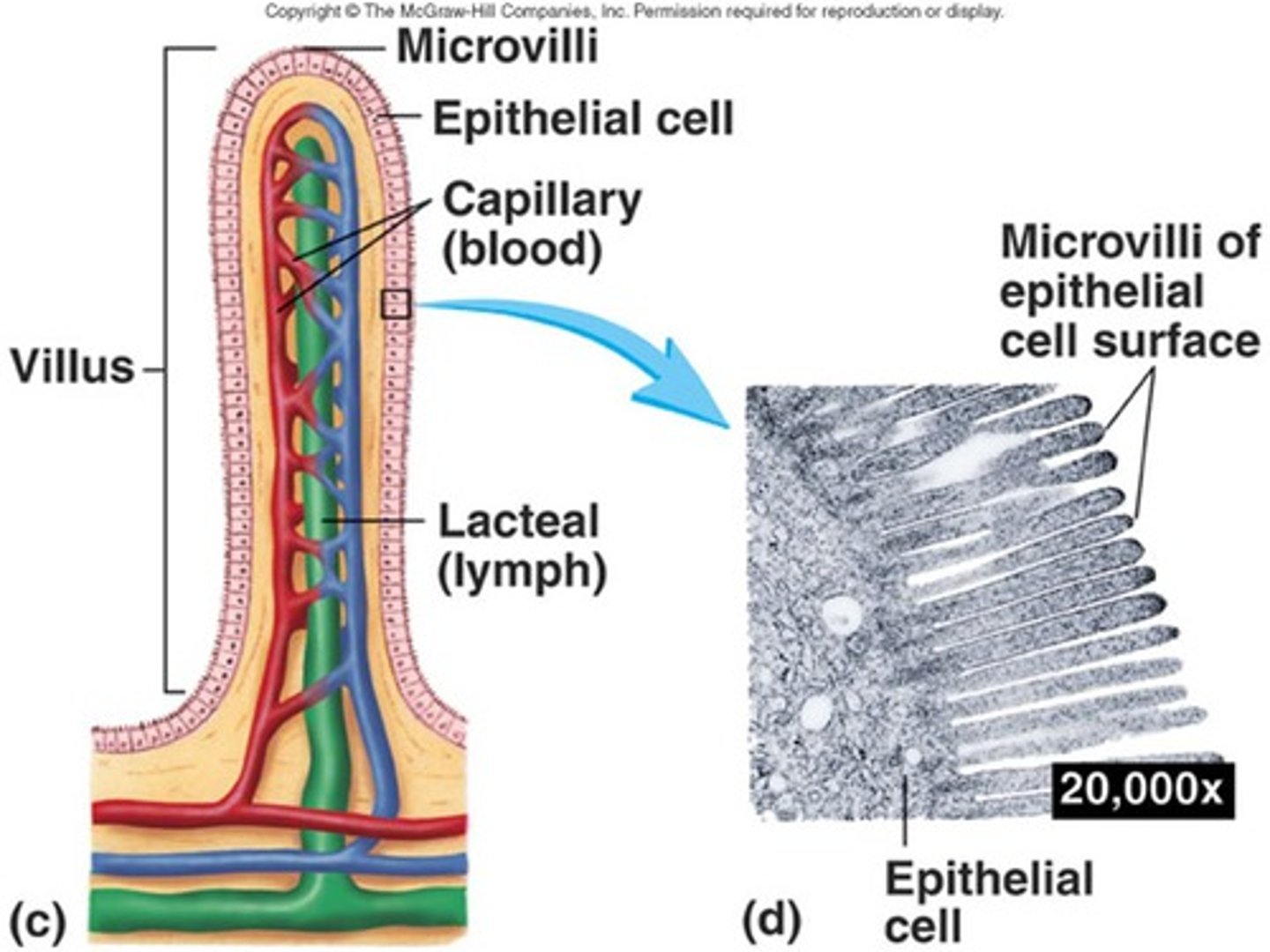
Intestinal villi and Microvilli
-increase surface area of the small intestine
-contains crypt in between villi
-contains enterocyte cells lining the villi that contain microvilli
-lacteals, arteries, and veins found inside villi
Absorption
-Esophagus: none -Stomach: none (exception is alcohol absorbed in stomach)
-Small Intestine: LOTS of absorption
-Large Intestine: only water and solute
Small vs Large intestine cells
-Small: projections outward
-Large: grooves sinking inward
Accessory Glands
-Salivary: moisten, lubricate, breakdown saccharides
-Pancreas: enzymes secreted into duodenum, neutralizes stomach acid
-Liver: breakdown fats, neutralize stomach acid
-Gall bladder: store bile that was made by liver
Mastification
-Grind and break down food
-Stimulate saliva production
-Mix food with saliva
Teeth and forces
-Premolars and molars: used to grind, 200 lb force on food
-Incisors, canines: used for cutting and tearing, 55 lb force on food
Deglutition meaning
The process of swallowing
3 Phases of Deglutition
-Buccal -mouth
-Pharyngeal -Pharynx
-Esophageal -esophagus
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering lungs
Upper Esophageal Sphincter open or closed during Buccal phase of deglutition?
-closed
-allows for breathing through nose when chewing food
Upper Esophageal Sphincter open or closed during Pharyngeal phase of deglutition?
-open
-cant breathe
Upper Esophageal Sphincter open or closed during Esophageal phase of deglutition?
-closed
-breathing continues
Upper Esophageal Sphincter
-muscular ring located at the top of the esophagus made of smooth muscle
-always closed unless food needs to pass through
-ensures breathing commences
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
-prevents acid reflux from stomach entering esophagus
-"heart burn"
-also always closed unless food needs to pass through to stomach from esophagus
How long does food passage take?
About 10 seconds
Stomach Anatomy
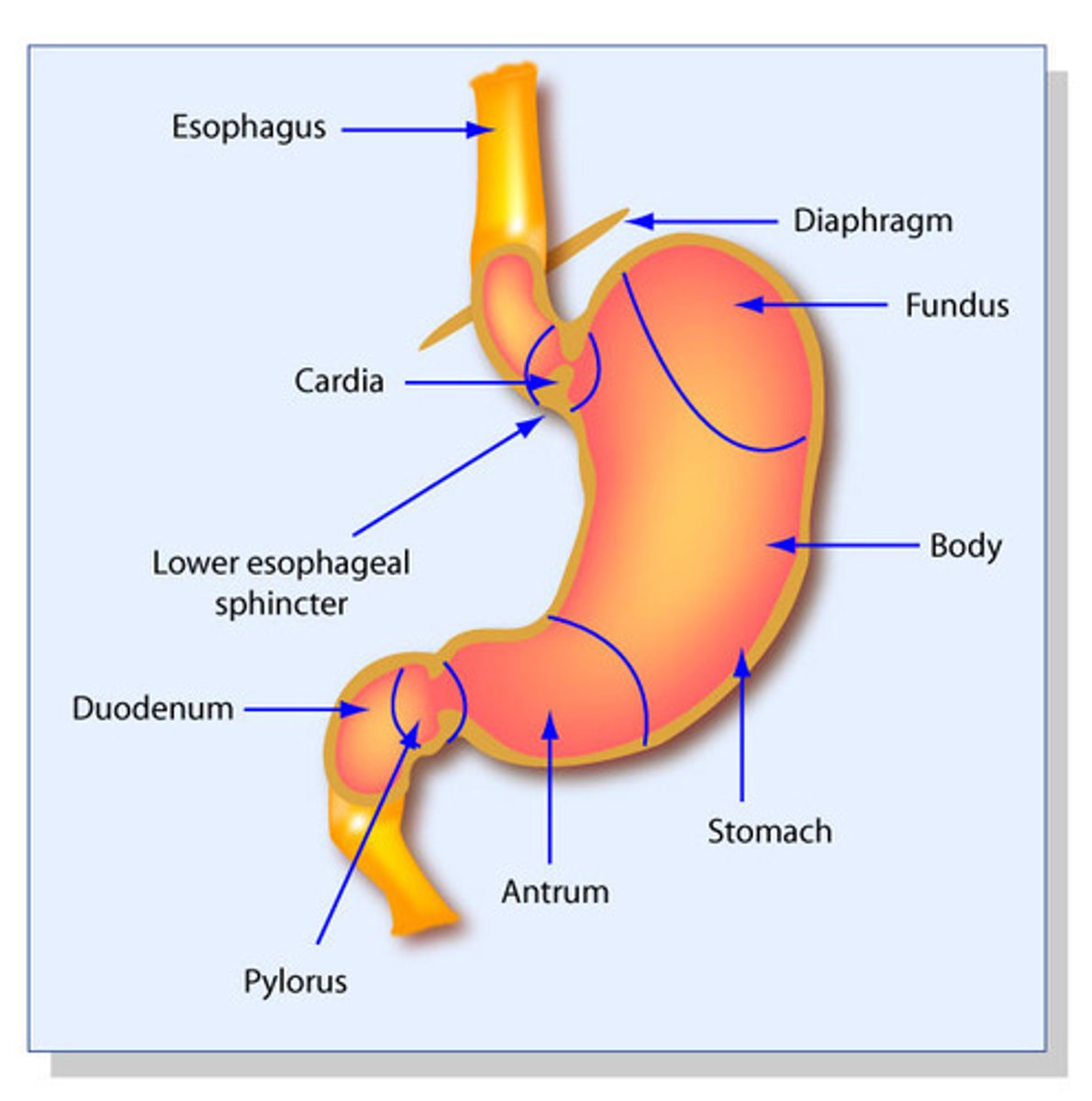
3 Sections of the stomach
-Fundus
-Body
-Antrum
Sphincter allowing passage from esophagus to stomach
Cardiac Sphincter
Sphincter allowing passage from stomach to duodenum
Pyloric sphincter
Motor Functions of the Stomach
-Receptive Relaxation: stomach relaxes to make room for incoming meal
-Gastric Peristalsis: wave of smooth muscle contractions for slow emptying and so that small amount of chyme leaves stomach at a time
How much can the stomach hold?
1.5 liters of chyme
Chyme
Partially digested food mixed with stomach secretions and saliva)
Why is only a small amount of food passed through the pyloric sphincter at once?
To ensure that the duodenum has time to release secretions and absorb the maximum amount of nutrients
3 phases of gastric motility
1) Slow waves to maintain muscle tone
2) Spike potentials upregulating stomach activity
3) Hyperpolarization when exercise and digestion pauses
What upregulates Gastric Motility?
Events in the stomach
-when volume of chyme increases
-when smooth muscle of stomach is excited
-prescence of protein bc antral muscose releases gastrin
Gastrin
Hormone released into blood stream by antral mucosa (in stomach) that targets the stomach to increase gastric peristalsis
What downregulates Gastric Motility?
Events in the duodenum
-decreasing distention (stretch) of duodenum
-lower pH (more acidic) of duodenum chyme
-Presence of protein, sugars and fats cause hormones to be released from duodenal mucosa (gastric inhibitory peptide GIP, secretin)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP)
Inhibits gastric motility and stomach secretions
Segmentation
Mixing and propulsive contractions combined in the small intestine
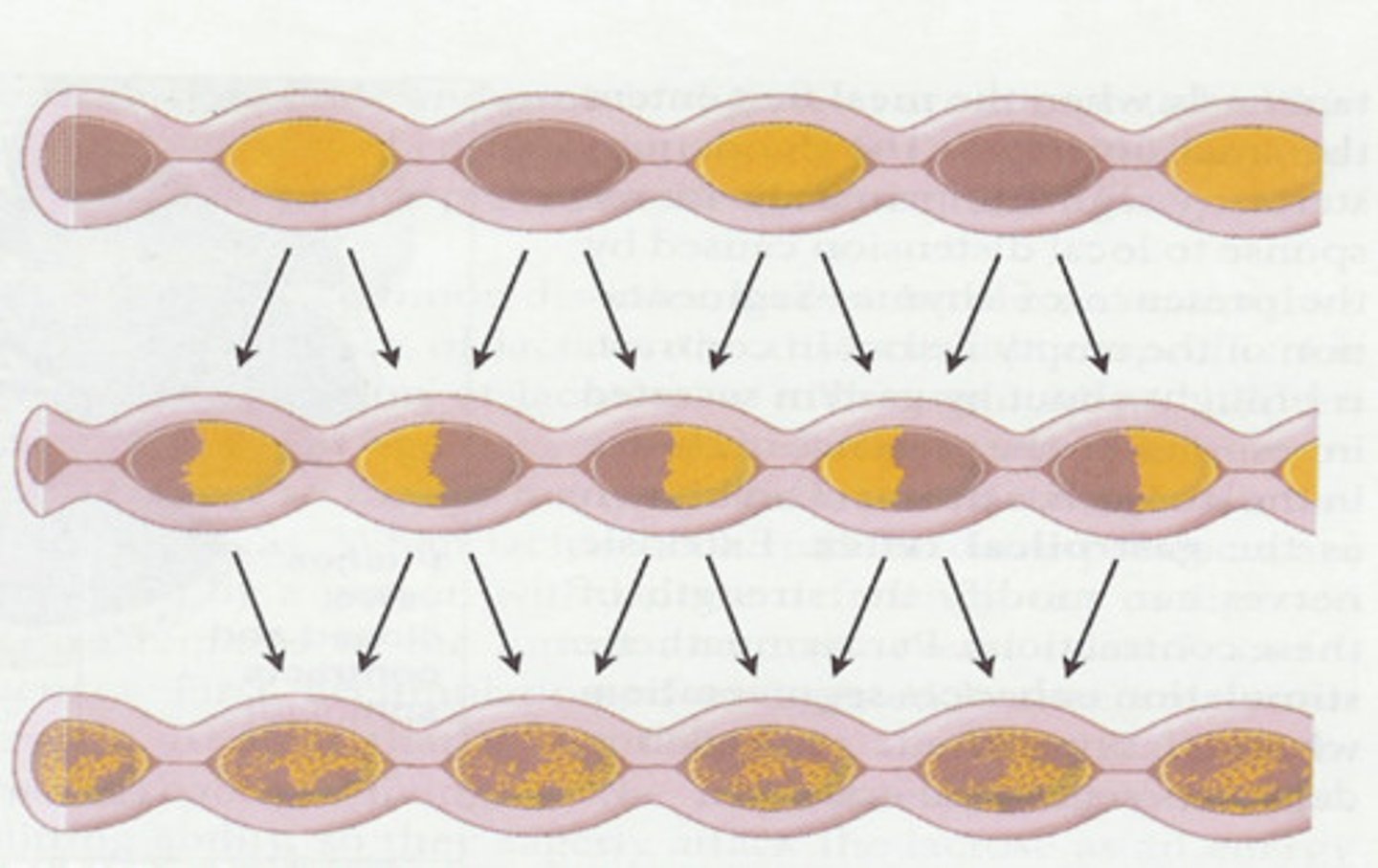
What controls small intestine motility?
-Neural: slow waves
-Hormonal: upregulation associated w gastrin, CCK, secretin, and insulin, downregulation associated with glucagon
When starving yourself, what hormone is high in the small intestine?
Glucagon
Ileocecal Junction
the end of the small intestine where the ileum joins the cecum of the large intestine
Function of Ileocecal valve
Prevent backflow of contents
Operation of ileocecal valve
-chyme backs up
-opens when pressure in ileum > cecal pressure
-closes when pressure is relieved
Large Intestine Motility
-rhythmical: every 30 minutes contraction occurs in slow waves to maintain muscle tone
-mass movement: coincides with ileum contraction, ~1 hour after a meal fecal matter emptied
Large Intestine Anatomy
-haustra: punches along large intestine, change location as fecal matter passes through
-teniae coli: smooth muscle down middle of the haustra
ANALOGY:
umbrella wires=teniae coli
umbrella fabric=haustra
Defecation
-contraction of abdominal wall musculature and lowering of diaphragm places pressure on colon wall
Defecation Process/Sphincter Function
Pressure of fecal matter on internal sphincter sends signals → sensory nerve fibers in spinal cord → cerebral cortex in brain →
IF NO BATHROOM inhibitory signals → external sphincter contractions
IF BATHROOM voluntary motor signals → external sphincter relaxes
3 Phases of Digestions
1) Cephalic
2) Gastric
3) Intestinal
Can be in multiple phases at once
What triggers saliva production?
An increase in parasympathetic stimulation
3 Salivary Glands
-parotid
-submandibular
-sublingual
Composition of saliva
-99.5 % water, 0.5 % protein (amylase, mucus, lysozyme) and electrolytes
Functions of Saliva
-water softens food
-amylase breaks down polysaccharides
-mucus lubricates
-lysozyme kills bacteria
Esophageal Secretion
-mucus provides for lubrication and takes 10 seconds transit time
3 Gastric Secretions
-HCl
-Pepsinogen
-Mucus
HCl secretion
-by parietal cells
-in Cephalic Phase: secreted along w gastrin
-in Gastric Phase: breakdown of proteins to peptides, more stretch=more HCl release, Protein + HCl =gastrin release, gastrin increase HCl release, BENEFICIAL positive feedback (more your eat, more stomach stretches, more gastrin released)
Pepsinogen Secretion
-In Gastric Phase: chief cells release zymogen granules and they hit low pH in stomach, breakdown, and release pepsinogen
-IN STOMACH: pepsinogen + HCl in stomach =pepsin (active form)
-IN SMALL INTESTINE: pepsin + HCO3 = affect nulified because of the high pH so pepsin doesnt work
Mucus Secretion
-release by goblet cells
-prevents mechanical injury of friction
-HCl + pepsin break down protein so protects cell membranes in stomach from being broken down
Intestinal Phase of gastric secretions
inhibits gastric secretions by:
1) decreasing parasympathetic stimulation
2) local reflex vis enteric NS
3) release of secretin, GIP, and CCK
Enteric Nervous System
-nerve fibers from duodenum to stomach
-send local reflex to decrease smooth muscle activity
Inhibitors of the Stomach
1) Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP): released from duodenal mucosa, stimulus is fat and sugars in duodenum, decreases gastric motility and secretions
2) Secretin: released from duodenal mucosa, stimulus is high acidity in duodenum, decreases gastric motility and secretions, upregulates pancreas secretions
3) CCK: released from duodenal mucosa, stimulus is prescence of lipid and protein, decreases gastric motility, *upregulates pancreas secretions and gall bladder emptying
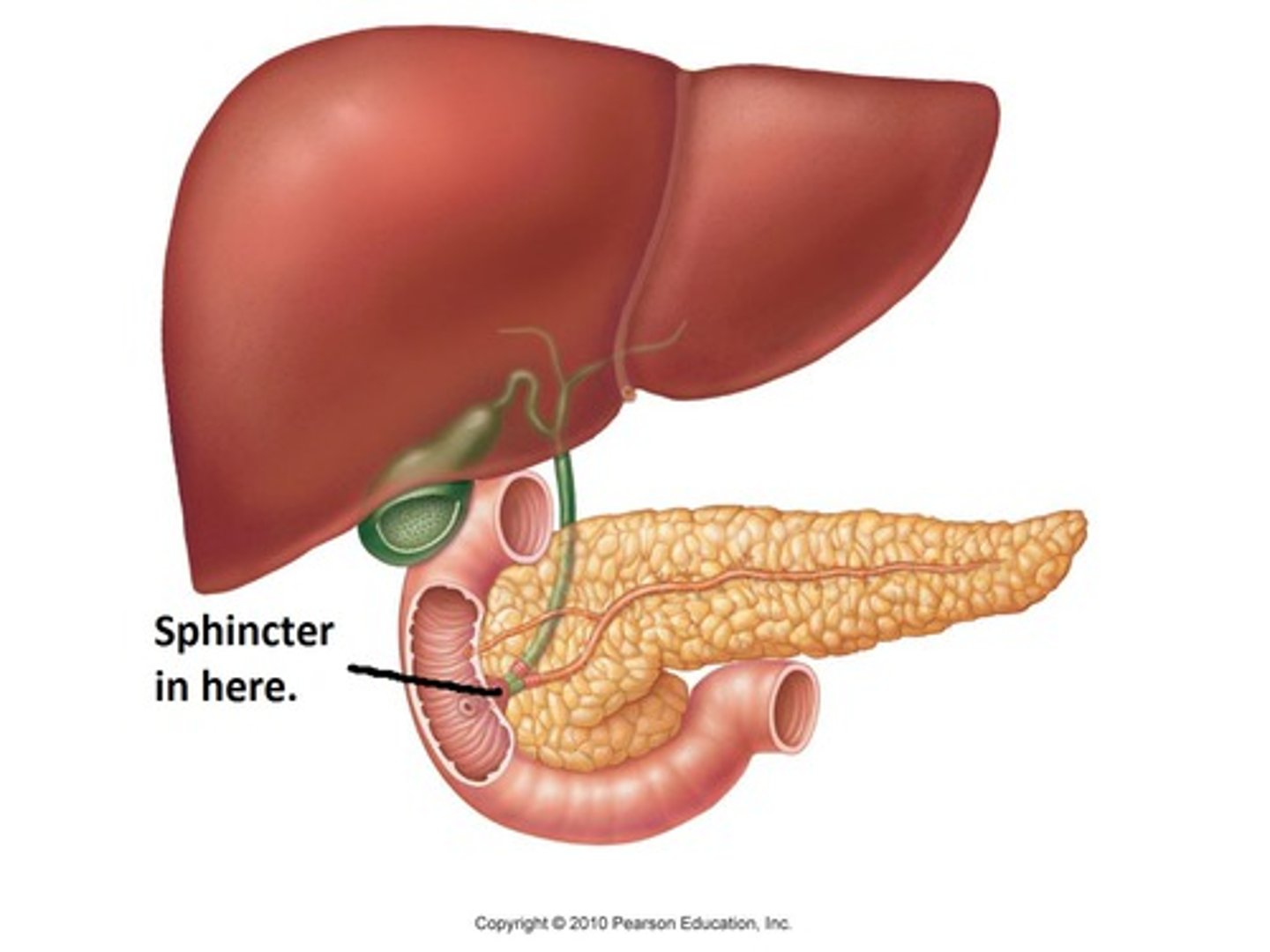
Pancreas Anatomy
-inferior to stomach, squeezed between stomach and small intestine
-contains a pancreatic duct that runs through the pancreas, splits into many acinus (bubbles) lines with duct cells and acinar cells
Acinar Cell Secretions
-proteolytic enzymes: (trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase) breaks down proteins to peptides
-lipase: breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides
-amylase: breaks down poly to disaccharides lactose and maltose
Duct Epithelial Cell Secretion
-bicarbonate ions to neutralize the stomach acidity (bc enzymes only work at a specific pH)
Pancreatic Hormone Secretions
1) Secretin: targets duct cells, secreted by duodenal mucosa in response to high [H+], increases sodium bicarbonate secretion
2) CCK: targets acinar cells, secreted by duodenal mucosa in response to fat and protein, increases total amount of enzymes secreted
3) Acetylcholine: targets both acinar and ducts cells, neurotransmitter releases from parasympathetic influence
What does bile contain?
Bile salts, bicarbonate, and water
Liver Contents Functions
-Bile salt + water: emulsifies lipid
-Bile salt prevent reaggregation of emulsification (fat droplets going back together)
-Bicarbonate: neutralizes gastric HCl
-Bile salts also have hydrophobic and hydrophillic sides to prevent fat droplets from binding again, fat droplets increase surface area of triglycerides then lipase breaks triglycerides into monoglyceride and fatty acids
How bile is released
CCK causes smooth muscle on gallbladder to contract, sphincter of oddi relaxes and enters into duodenum
Small Intestine Secretions
-crypts of Lieberkuhn release mucus (from Brunner's glands) and aqueous salt (slat and water)
Function of Small Intestine Secretion
-lubication and protection from acidic stomach acid
-aid in enzyme breakdown of chyme
-salt keeps fecal matter soft and maintains osmolality
What are bronner's glands
-located in crypts of Lieberkuhn
-made up of mucous goblet cells
Large Intestine Secretions
-Crypts of Lieberkühn without villi secretes mucus
Function of Large Intestine Secretions
-protection against abrasion
-holds feces together
-protection against bacterial activity (which keeps pH low)
Hydrolysis Reaction
The addition of water in order to split up a large molecule
EX tri+disaccharides into monosaccharides
Condensation/Dehydration Reaction
The subtraction of water to build two molecules into one large molecule
EX Monosaccharides into tri+disaccharides
What are saccharides made of
carbon rings
Examples of disaccharides
sucrose
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose + fructose
Sources of Carbs
-sucrose (table sugar)
-lactose (milk)
-starches (non-animal products)
Digestion of Carbs
-fiber not digested by humans bc contains cellulose and we do not make cellulase in our bodies
-starts in mouth by salivary amylase
-in duodenum by pancreatic amylase
-in intestine by enterocytes -lactase, sucrase, maltase and alpha dextrinase)
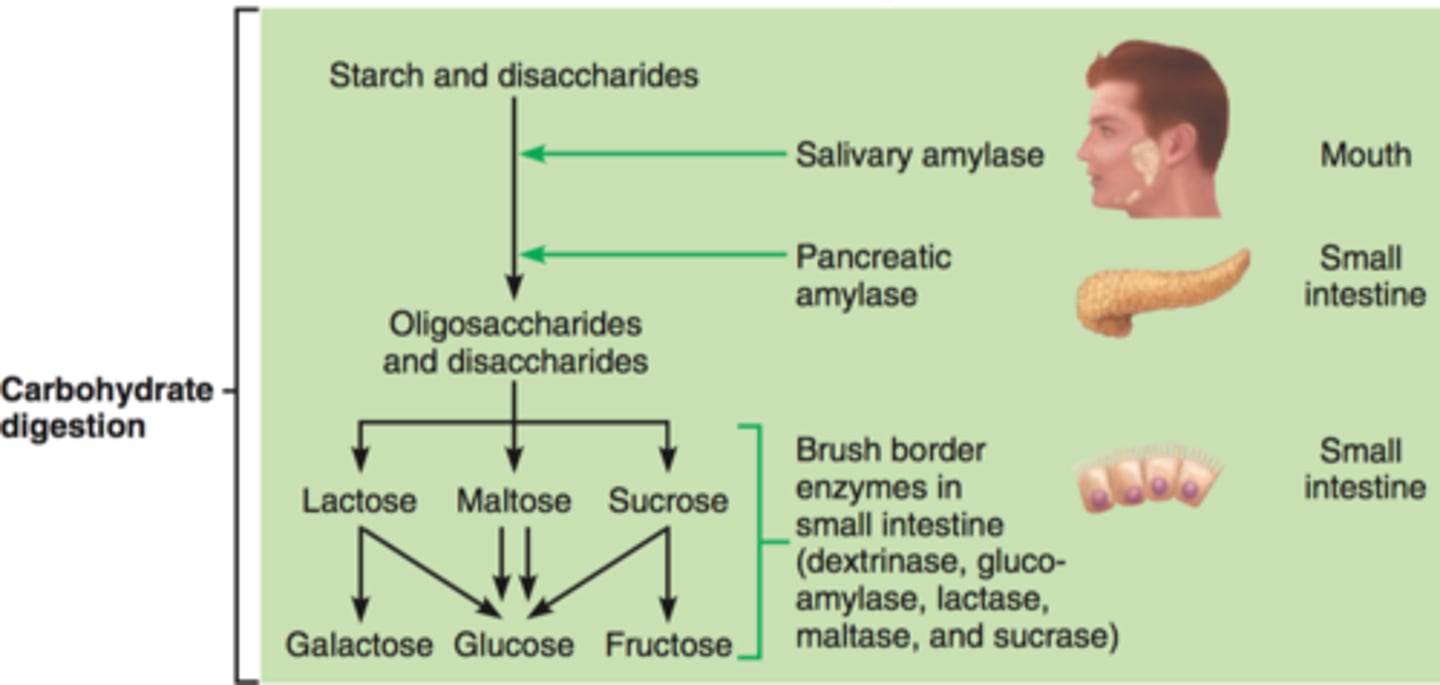
Are carbs digested in the stomach?
NOOOO
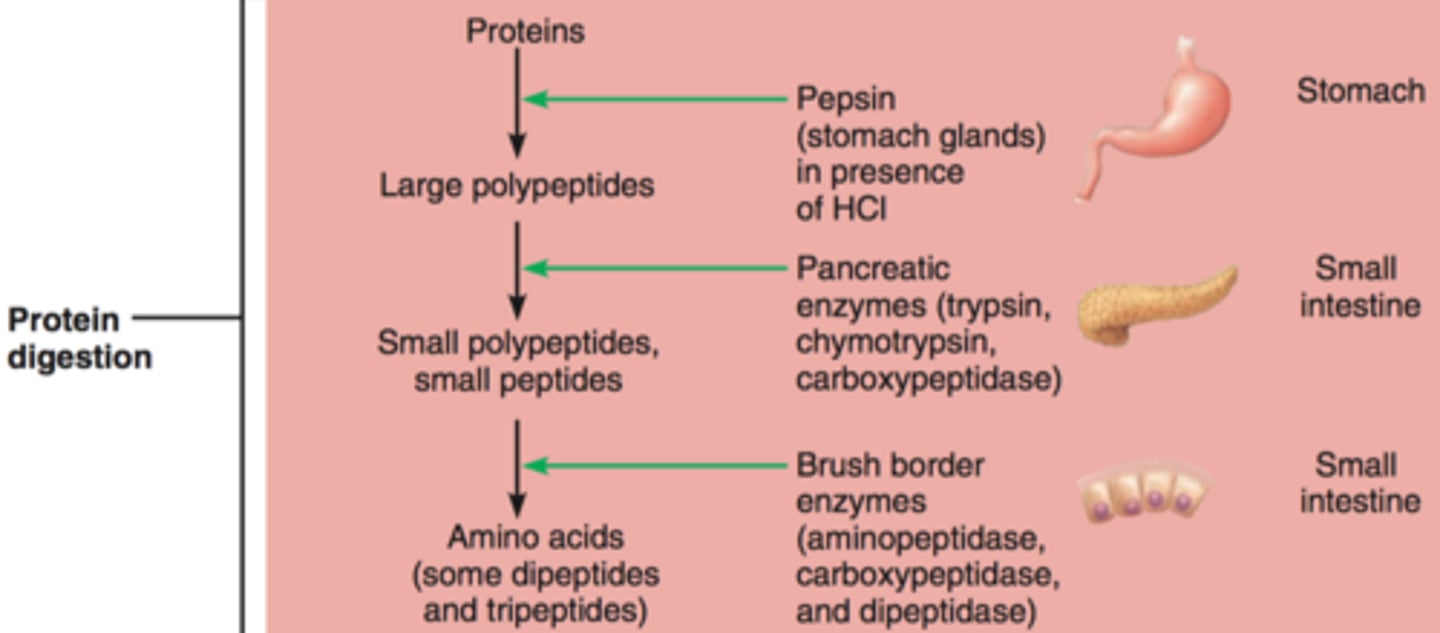
Digestion of proteins
-proteins to peptides to amino acids
-sources: dietary, endogenous -w/in body (enzymes, hormones, dead cell membranes)
-from protein to peptides: stomach (pepsin), duodenum (pancreatic secretions)
-from peptides to amino acids: intestine (enterocytes -peptidases)
Digestion of fats
-occurs twice
-once in intestine: triglycerides → 2 fatty acids + 1 monoglyceride
-once in blood stream: triglycerides → 3 fatty acids + glycerol
-sources: dietary
-mechanical disruption in stomach
-small intestine (bile emulsifies triglycerides, lipase converts it into fatty acid and monoglycerides)
-bile salts prevent aggregation
-digestion of triglycerides by pancreatic lipase
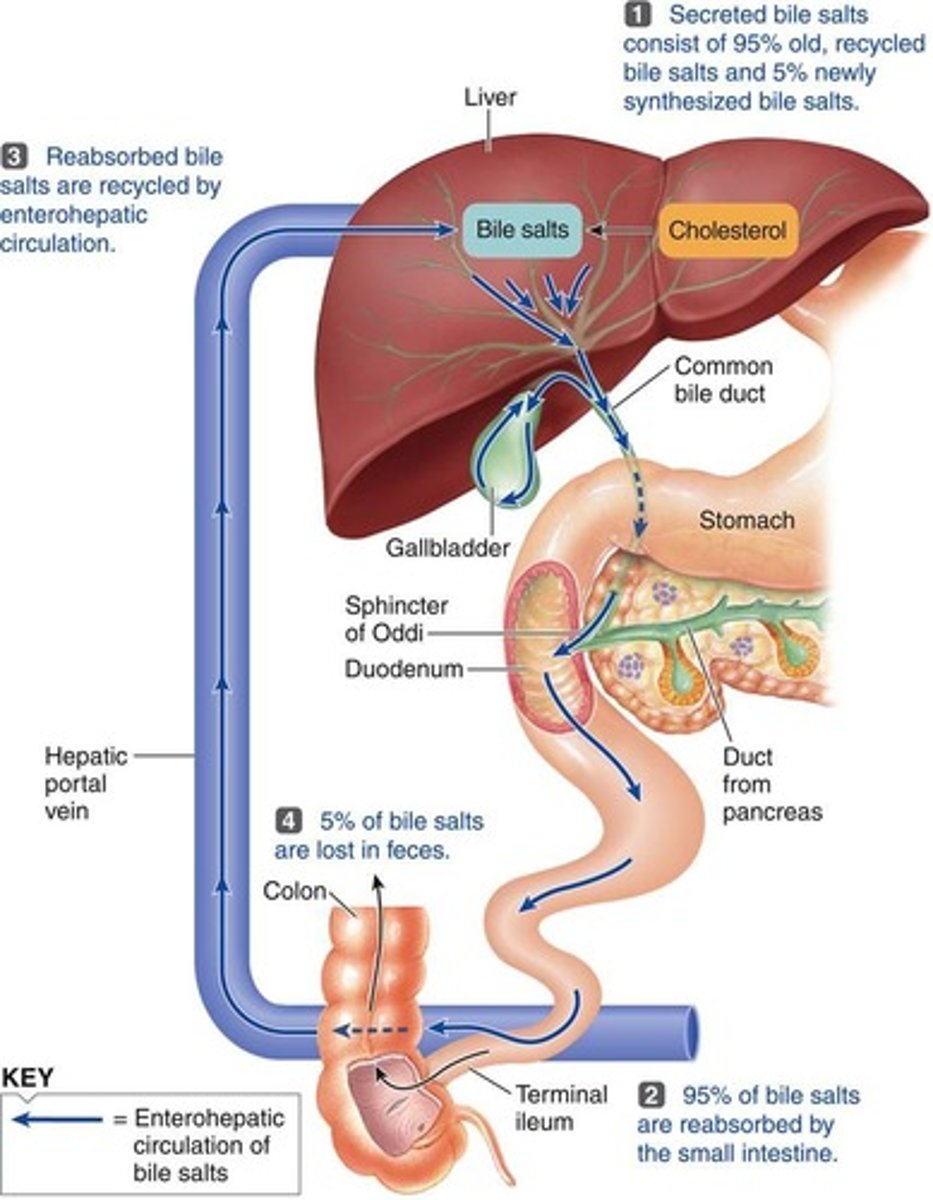
Enterohepatic Circulation
-bile is recycled and goes back to the liver
-from the liver through the common hepatic duct to the gall bladder for storage
-95% is absorbed into the hepatic portal vein and transported to the liver
Fluid absorption
-8.2 L of fluid in tract
-98.5% is absorbed
-input by salivary glands, stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, colon
-7.2 L absorbed in small intestine, 0.85 L in colom
-0.15 L excreted through feces
Carbohydrate Absorption
-co-transported with Na+ by protein transporters
-facilitative diffusion into blood
Protein Absorption
-co-transported with Na+ by protein transporters
-facilitative diffusion into blood
Absorption of Lipids
-Fatty acids and monoglycerides diffuse into cell
-Converted to triglyceride
-Enter ER and come out as triglyceride again
- enter Golgi and then form into chylomicron
-Exocytosis into lacteal
-Eventually empty into neck veins
*all bc fenestrations too small to absorb triglyceride into blood stream soooo lymphatic system*
Absorption in the Colon
-Proximal: Na+ actively absorbed
-Distal: secretion of bicarbonate (neutralizes the by-product of carb breakdown which is acid from bacterial action -which break down carbs in the large intestine)
-resultant gradient allows passive water absorption leading to dry feces
Disorders of Colon
-constipation: decreased colon motility, colon distention with fiber, laxatives decrease water absorption
-Diarrhea: increased colon motility, irritants, decrease in water absorption, or water secretion into the tract
Lactose Intolerance
-decreased lactase in body results in more lactose present
-osmotic gradient creates less water absorption and more water secretion
-results in distention, cramps, and diarrhea
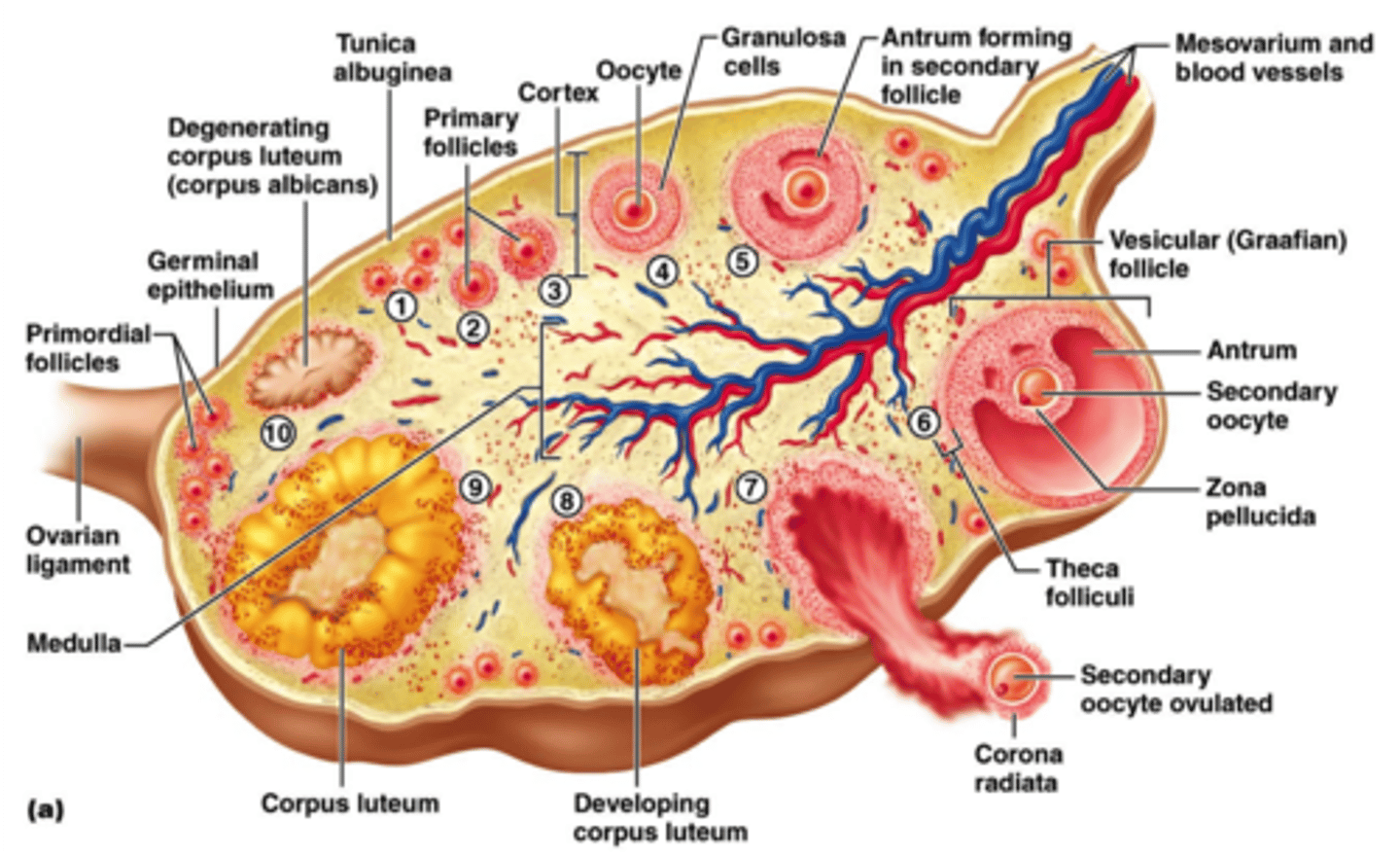
Female Reproduction Overview
-Production of egg and nutrition of embryo
-Hormones: estrogen (estradiol), progesterone, gonadotropic hormones
-2M eggs at birth, 3 - 400,000 left at puberty and 400 released during lifetime
-Menopause - follicles degenerate
OOgenesis
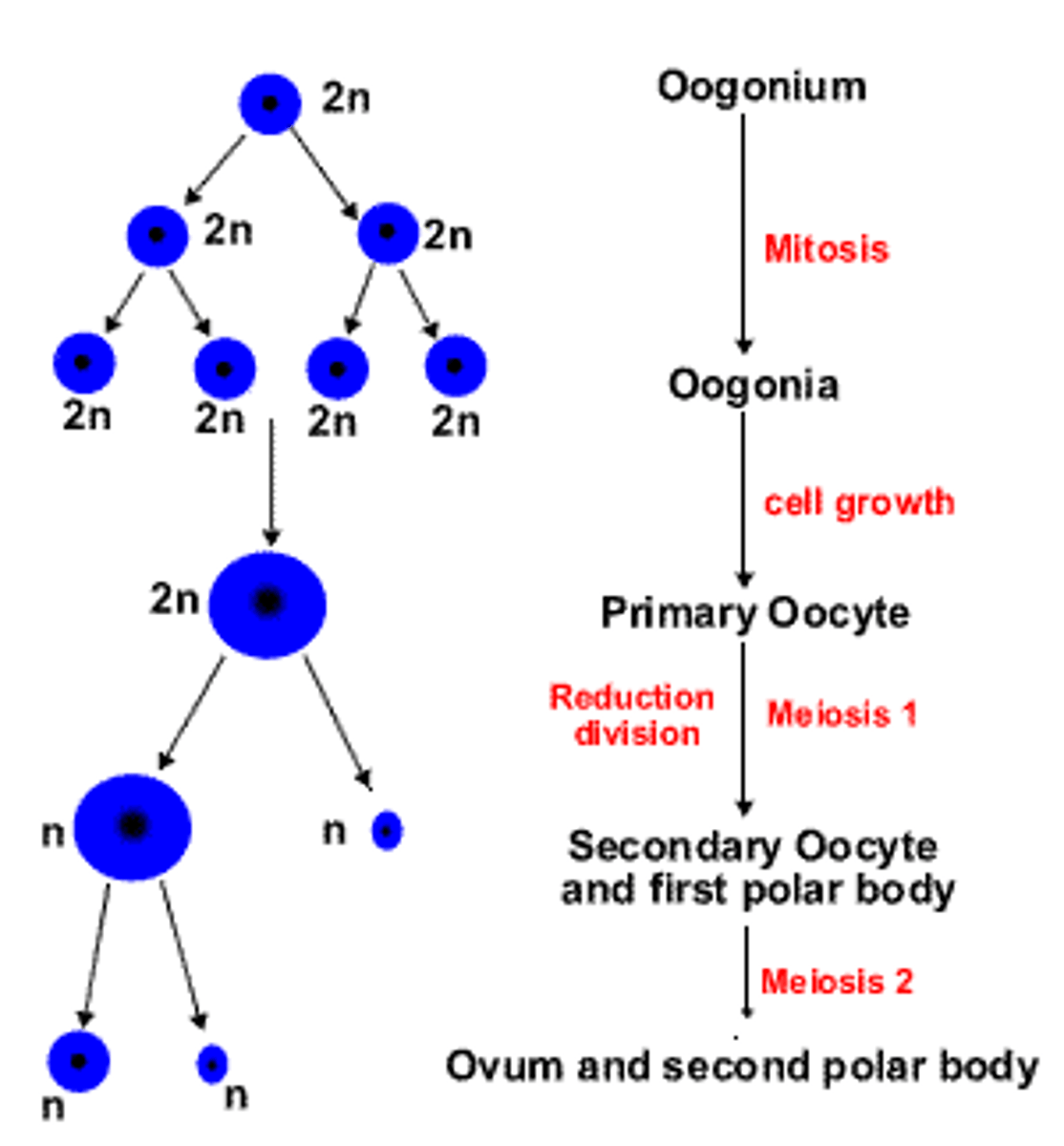
Ovarian Cycle
Primordial follicle (1)
Primary follicle (2)
Secondary follicle (3-5)
Vesicular follicle (6)
Secondary oocyterelease (7)
Corpus luteum (8)
Corpus albicans (9