***FINAL EXAM: Chapter 24 The Respiratory System単語カード | Quizlet
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
provides gas exchange
supplies body with O2 and disposes CO2
provides protection against pathogens
provides ability for speech
helps regulate blood volume, blood pressure and body fluid pH
Functions of the Respiratory System
conducting zone
from nose to terminal bronchioles
functions to filter, moisten and warm incoming air
respiratory zone
from respiratory bronchioles to alveoli
actual site of gas exchange in lungs
Parasnasal sinuses
act as resonance chambers in speech
pharynx
throat
funnel-shaped
serves as common passageway for food and air
mostly skeletal muscle
within mucosa are tonsils - destroy pathogens
nasopharynx (air), oropharynx (food and air), laryngopharynx (food and air)
What are the 3 pharyngeal regions from superior to inferior?
larynx
voice box
superiorly attaches to the hyoid bone and opens into the laryngopharynx; inferiorly, it continues with the trachea
voice production
provides an open airway
act as a switching mechanism to route air and food into proper channels
functions of the layrnx
9 laryngeal cartilages connected by membranes and ligaments
structure of the larynx
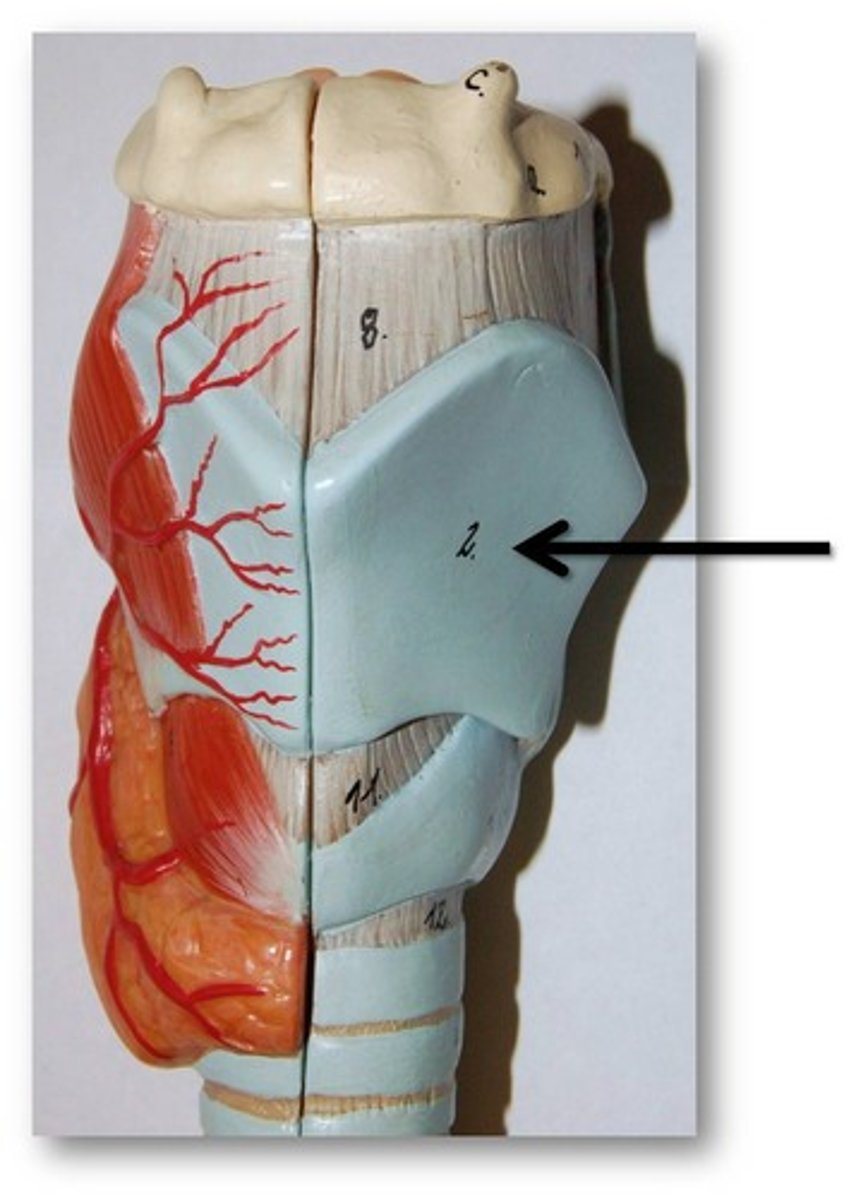
thyroid cartilage
shaped like an upright open book or shield
largest laryngeal cartilage
forms most of anterior and lateral walls of larynx
adam's apple in males
hyaline cartilage
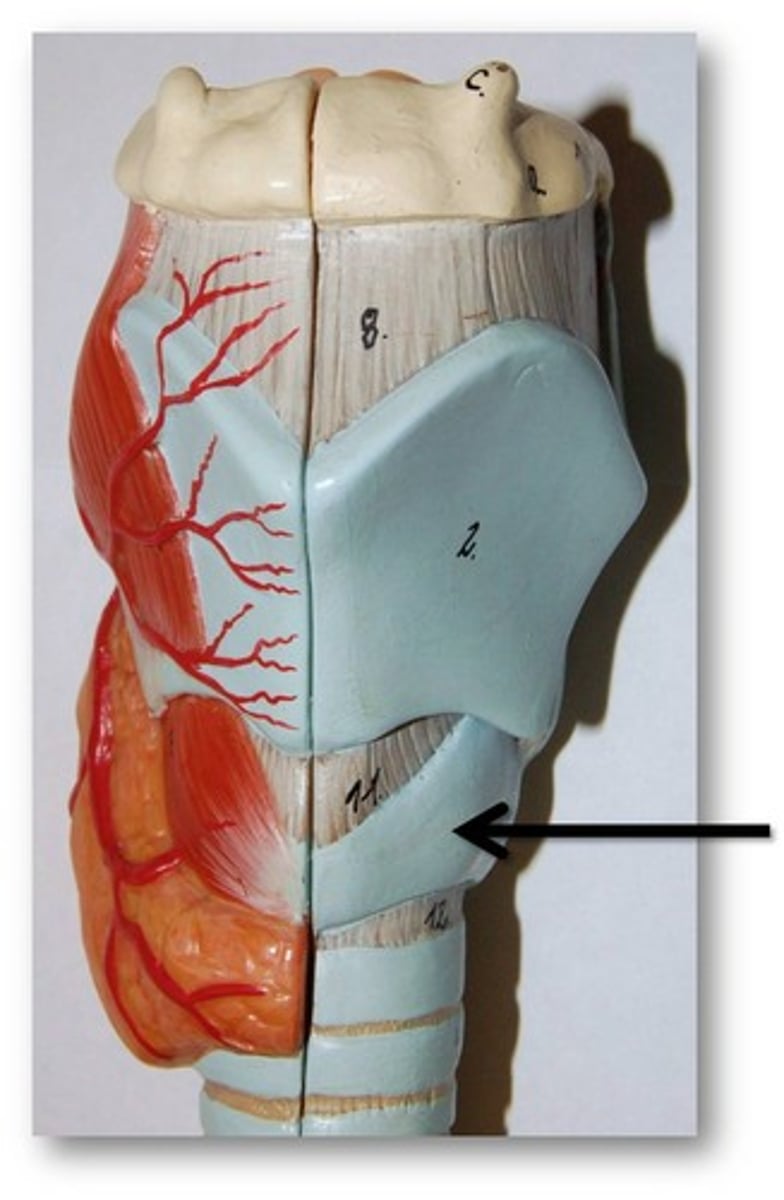
cricoid cartilage
signet-ring-shaped cartilage that forms a complete ring of cartilage with greatly expanded posterior portion
located inferior to thyroid cartilage, on top of trachea
protects the glottis
hyaline cartilage
Epiglottis
shoehorned shaped laryngeal cartilage
comprised of ELASTIC cartilage
almost entirely covered in mucosa
functions in cough reflex
trachea
The windpipe; a passage through which air moves in the respiratory system.
ends by branching into the two main bronchi
tracheal wall
16-20 C-shaped rings of hyaline tracheal cartilage joined by one another via annular ligaments
protects airway
provides flexibility
mucous membrane or mucosa
Which layer is ciliated pseudostraitified columnar epithelium found in the tracheal wall?
submucosa
Which layer are seromucous galnds found in the tracheal wall?
carina - where the last tracheal cartilage ends and trachea branches into main bronchi
Where is the cough reflex often initiated in the trachea?
bronchial tree
a system of respiratory passages that branches extensively within the lungs
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli
The respiratory zone consists of structures decreasing in size:
trachialis muscle
functions in decreasing the diameter of trachea
elastin
Irregular plates of cartilage replaces cartilage rings as each main bronchi enters lung. cartilage is absent in bronchioles but what is present instead?
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
to simple columnar
to simple cuboidal
What are the epithelial changes of the trachea leading into the bronchioles?
alveoli ducts
microscopic air-exchange chambers of the lungs
surrounded by a delicate network of pulmonary capillaries and fine elastic fibers
Type I cells in alveoli
single layer of squamous epithelial cells, which lines the walls of alveoli; surrounded by delicate basal lamina
Type II cells in alveoli
cuboidal epithelial cells, which secrete a fluid that coats the internal alveolar surfaces and contains SURFACTANT - prevents alveolar walls from sticking together during exhalation
Alveolar macrophages (dust cells)
exist in the air space of alveoli and remove the tiniest inhaled particles that are not trapped by the nasal mucosa
the pleurae
double-layered flattened sacs around each lung, whose walls consists of serous membranes
parietal and visceral pleura`
What are the 2 layers that cover the lungs?
parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall
visceral pleura
inner layer of pleura that covers the external surface of the lungs
pleural cavity
potential space (between the parietal and visceral pleurae) filled with pleural fluid, which decreases friction between the lungs and the thoracic wall during breathing
stroma
the lungs consist mainly of air tubes and spaces and the balance of the tissues called ________, which is a framework of connective tissue containing many elastic fibers
results in light, soft, spongy, elastic organs (lungs)
apex
superior, rounded tip of lungs
base
concave inferior surface that rests on the diaphragm
hilus
indentation on medial surface of each lung through which blood vessels, bronchi, lymph vessels and nerves enter and exit the lung
left lung
somewhat small lung
contains the cardiac notch
has only 2 lobes divided by the oblique fissure
right long
lung
has 3 lobes divided by the oblique fissure and horizontal fissure
pulmonary arteries
deliver oxygen-poor blood to the lungs, from heart for oxygenation
pulmonary capillaries
network surrounds the alveoli
pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood form alveoli of lungs to the heart