RadTech Bootcamp Image Quality (Shape Distortion Quiz)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
1
New cards
Shape Distortion includes which specific types of distortion?
Elongation and foreshortening
\
(Shape Distortion is described as a misrepresentation of the shape of the anatomy being imaged, and the two possible forms are described as elongation and foreshortening. Elongation would result in an image appearing longer than normal size. Foreshortening would result in an image shorter than normal size. Size distortion includes magnification and minification)
\
(Shape Distortion is described as a misrepresentation of the shape of the anatomy being imaged, and the two possible forms are described as elongation and foreshortening. Elongation would result in an image appearing longer than normal size. Foreshortening would result in an image shorter than normal size. Size distortion includes magnification and minification)
2
New cards
Shape distortion is related to a misalignment of, or angle present, on which three?
X-ray tube, Anatomy being Imaged, IR
\
(Shape distortion is created when any of these three components of the exposure, x-ray tube, anatomy of interest, or image receptor (IR), is situated at an angle related to the others. An angle on the tube, anatomy positioned at an angle, or an angled image receptor will all result in some form of shape distortion. Focused grids filter out some of the photons in the beam, but won’t distort the image. Source-to-image distance (SID) controls size distortion which includes magnification of the part controls the size distortion which includes magnification of the part. Increasing object-to-image distance (OID) will magnify the object causing size distortion. SID will decrease magnification reducing size distortion.)
\
(Shape distortion is created when any of these three components of the exposure, x-ray tube, anatomy of interest, or image receptor (IR), is situated at an angle related to the others. An angle on the tube, anatomy positioned at an angle, or an angled image receptor will all result in some form of shape distortion. Focused grids filter out some of the photons in the beam, but won’t distort the image. Source-to-image distance (SID) controls size distortion which includes magnification of the part controls the size distortion which includes magnification of the part. Increasing object-to-image distance (OID) will magnify the object causing size distortion. SID will decrease magnification reducing size distortion.)
3
New cards
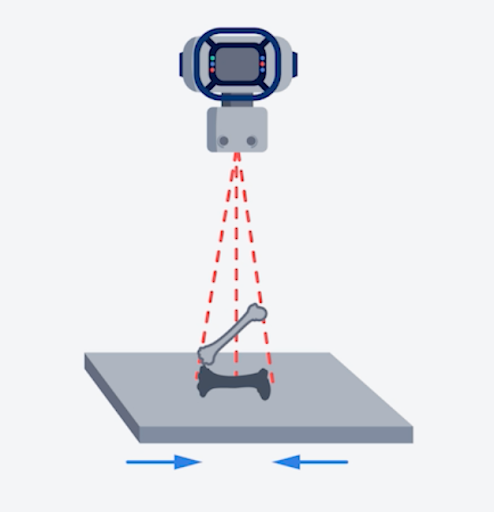
Which type of shape distortion is represented in the following illustration?
Foreshortening
\
(When the anatomical part is angled, but the x-ray beam is directed perpendicularly to the receptor, foreshortening of the object being imaged will result. In this illustration, foreshortening is evident by the projected shadow, which is shorter than the actual image. The Moire pattern is a wave-like artifact.)
\
(When the anatomical part is angled, but the x-ray beam is directed perpendicularly to the receptor, foreshortening of the object being imaged will result. In this illustration, foreshortening is evident by the projected shadow, which is shorter than the actual image. The Moire pattern is a wave-like artifact.)
4
New cards
When the anatomy being imaged is parallel to the image receptor (IR) and the x-ray beam is angled, what type of shape distortion will result?
Elongation
\
(Elongation occurs when the beam is misaligned, or angled, in relation to the part and image receptor (IR). If the anatomy described as parallel to the IR, then no angle on either of those components is present. Foreshortening is the result of misalignment of the anatomical part. Magnification is size distortion caused most often by a large object-to-image distance (OID))
\
(Elongation occurs when the beam is misaligned, or angled, in relation to the part and image receptor (IR). If the anatomy described as parallel to the IR, then no angle on either of those components is present. Foreshortening is the result of misalignment of the anatomical part. Magnification is size distortion caused most often by a large object-to-image distance (OID))
5
New cards
Which of the following projections would result in foreshortening of the anatomy being imaged?
Anteroposterior (AP) Lordotic Chest
\
(For an anteroposterior (AP) lordotic chest radiograph, the patient is required to lean back against the upright image receptor, placing the thorax at an angle to the image receptor (IR). The x-ray beam is directed perpendicularly to the receptor. Since the part is angled in relation to the beam and receptor, foreshortening of the thoracic cavity will result, with the lungs appearing much shorter than in a routine posteroanterior (PA) chest radiograph.)
\
(For an anteroposterior (AP) lordotic chest radiograph, the patient is required to lean back against the upright image receptor, placing the thorax at an angle to the image receptor (IR). The x-ray beam is directed perpendicularly to the receptor. Since the part is angled in relation to the beam and receptor, foreshortening of the thoracic cavity will result, with the lungs appearing much shorter than in a routine posteroanterior (PA) chest radiograph.)
6
New cards
Which of the following cranium projections would result in elongation of the anatomy being imaged?
Anteroposterior (AP) axial (Towne) skull with a 37-degree tube angle
\
(The Towne’s projection will result in elongation due to the angled tube. The PA and lateral skull projections will not have shape distortion since no angled is involved. The Parietoacanthial (Waters) projection will have foreshortening because the part is angled in the beam.)
\
(The Towne’s projection will result in elongation due to the angled tube. The PA and lateral skull projections will not have shape distortion since no angled is involved. The Parietoacanthial (Waters) projection will have foreshortening because the part is angled in the beam.)
7
New cards
Which of the following projections use shape distortion to cause elongation providing better visualization of the anatomical area?
Axial Projection of the calcaneus with 40-degree tube angle and AP axial (Towne) Skull projection with a 37-degree tube angle
\
(Shape distortion is often purposely created so that parts of anatomical structures can be seen from different perspectives, or without superimposition by other structures. For example, many projections of the skull involve angles of the beam or the part in order to demonstrate specific cranial of facial structures not otherwise demonstrated. The axial projection of the calcaneus uses a 40-degree tube angle to elongate the part to better visualize it. AP axial (Towne) Skull projection with a 37-degree tube angle to elongate the skull to better visualize the occipital bone. The lateral calcaneus with a 0-degree tube angle would not result in any distortion. The oblique elbow projection would not result in elongation since there is no tube angle present).
\
(Shape distortion is often purposely created so that parts of anatomical structures can be seen from different perspectives, or without superimposition by other structures. For example, many projections of the skull involve angles of the beam or the part in order to demonstrate specific cranial of facial structures not otherwise demonstrated. The axial projection of the calcaneus uses a 40-degree tube angle to elongate the part to better visualize it. AP axial (Towne) Skull projection with a 37-degree tube angle to elongate the skull to better visualize the occipital bone. The lateral calcaneus with a 0-degree tube angle would not result in any distortion. The oblique elbow projection would not result in elongation since there is no tube angle present).
8
New cards
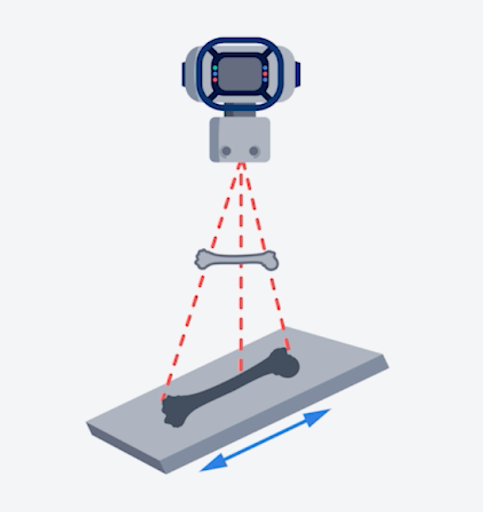
What type of distortion is represented in the following illustration?
Elongation
\
(Since the shadow of the anatomical part appears longer, shape distortion is present, specifically elongation. Elongation results in an increase in the length of the object of the image. In the image, the image receptor is angled causing elongation. Elongation is caused by either an angulation of the x-ray tube or angulation of the image receptor. Foreshortening is caused by the misalignment of the anatomical part to the image receptor. In this image, the part has an increased object-to-image distance (OID) which would not allow for minification to occur. Oblique would not allow for minification to occur. Oblique would indicate that the anatomical part is positioned at an angle.)
\
(Since the shadow of the anatomical part appears longer, shape distortion is present, specifically elongation. Elongation results in an increase in the length of the object of the image. In the image, the image receptor is angled causing elongation. Elongation is caused by either an angulation of the x-ray tube or angulation of the image receptor. Foreshortening is caused by the misalignment of the anatomical part to the image receptor. In this image, the part has an increased object-to-image distance (OID) which would not allow for minification to occur. Oblique would not allow for minification to occur. Oblique would indicate that the anatomical part is positioned at an angle.)
9
New cards
What type of shape distortion is present when there is angulation on an image receptor?
Elongation
\
(An angled image receptor will result in the same type of shape distortion as an angled x-ray beam, which is elongation. Magnification is primarily caused by increased object-to-image distance (OID))
\
(An angled image receptor will result in the same type of shape distortion as an angled x-ray beam, which is elongation. Magnification is primarily caused by increased object-to-image distance (OID))
10
New cards
Which of the following situations will result in the greatest amount of shape distortion?
X-ray beam angled 45 degrees to anatomy that is parallel to the IR
\
(All shape distortion is caused by an angle of one of the three components of the exposure, beam, anatomical part, or receptor. As the angle of any of these parts increases, the amount of shape distortion created also increase. Therefore, an angle on the tube of 45 degrees would result in more shape distortion than the other choices provided).
\
(All shape distortion is caused by an angle of one of the three components of the exposure, beam, anatomical part, or receptor. As the angle of any of these parts increases, the amount of shape distortion created also increase. Therefore, an angle on the tube of 45 degrees would result in more shape distortion than the other choices provided).