APHG 7: Industrial and Economic Development
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Agglomeration
CLUSTERING of like businesses for mutual benefit like reducing transportation expenses (competition)

Deglomeration
The exodus of business from a crowded area or business district of like businesses.

Basic jobs
Jobs that produce goods that will consumed outside the local community (non-local), brings money into the area

Non-Basic Jobs
Jobs within and for the local community, these do not bring more money into the area

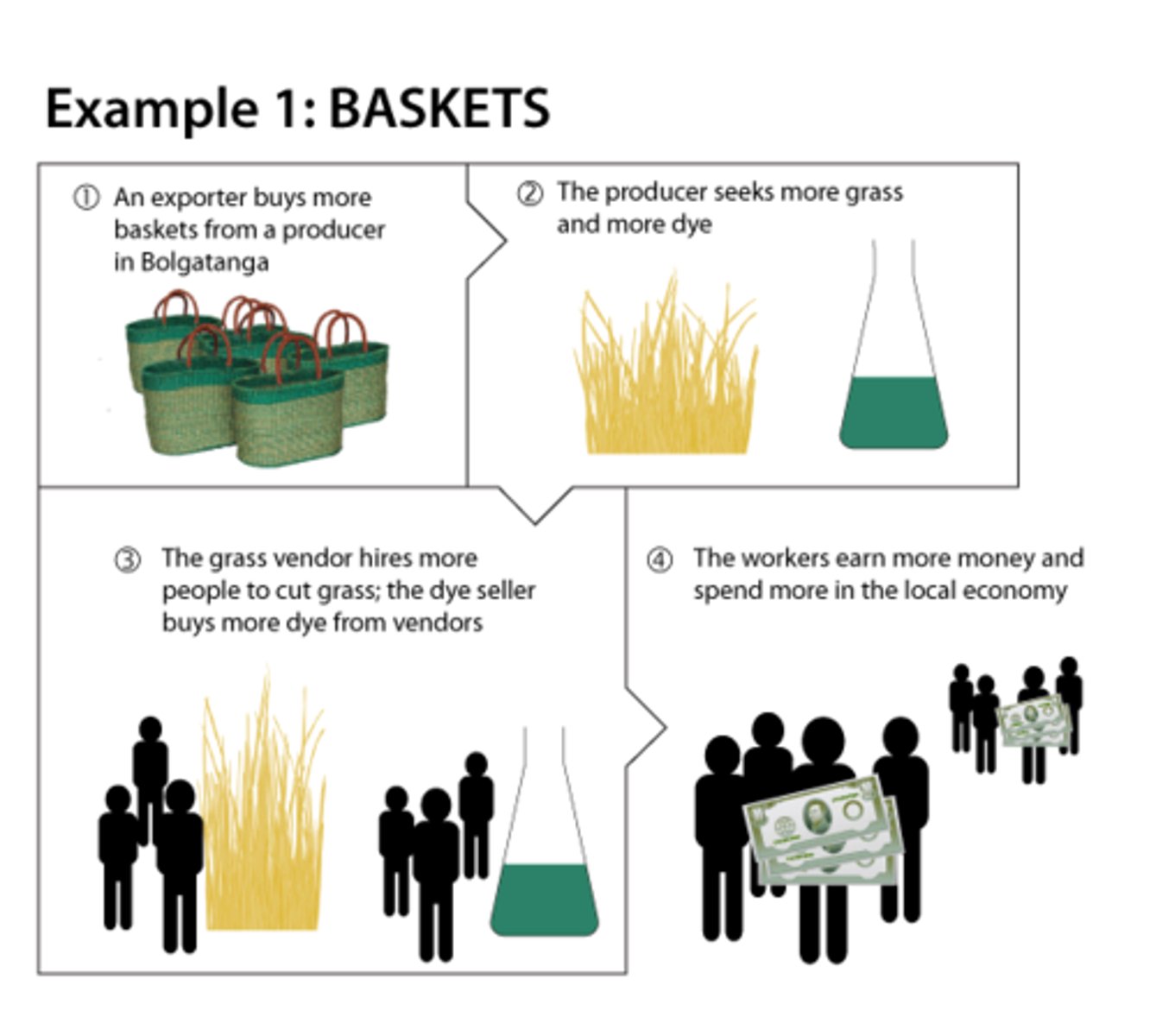
Multiplier Effect
The increase in non-basic, local jobs because new basic, non-local jobs. Ex: Factory hires 500 workers... now they need haircuts, floral shops, car washes, move theatres, etc.
Break-of-bulk point
A location where transfer among transportation modes is possible. (aka intermodal; ships, trains, trucks)

Bulk-Gaining Industry
An industry that makes something that gains volume or weight during production. (Market oriented)

Bulk-Reducing Industry
An industry in which the inputs weigh more than the final products. (Resource oriented)

Comparative Advantage
The ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than other producers.
Complementarity
Two regions through trade that specifically satisfy each others demands.

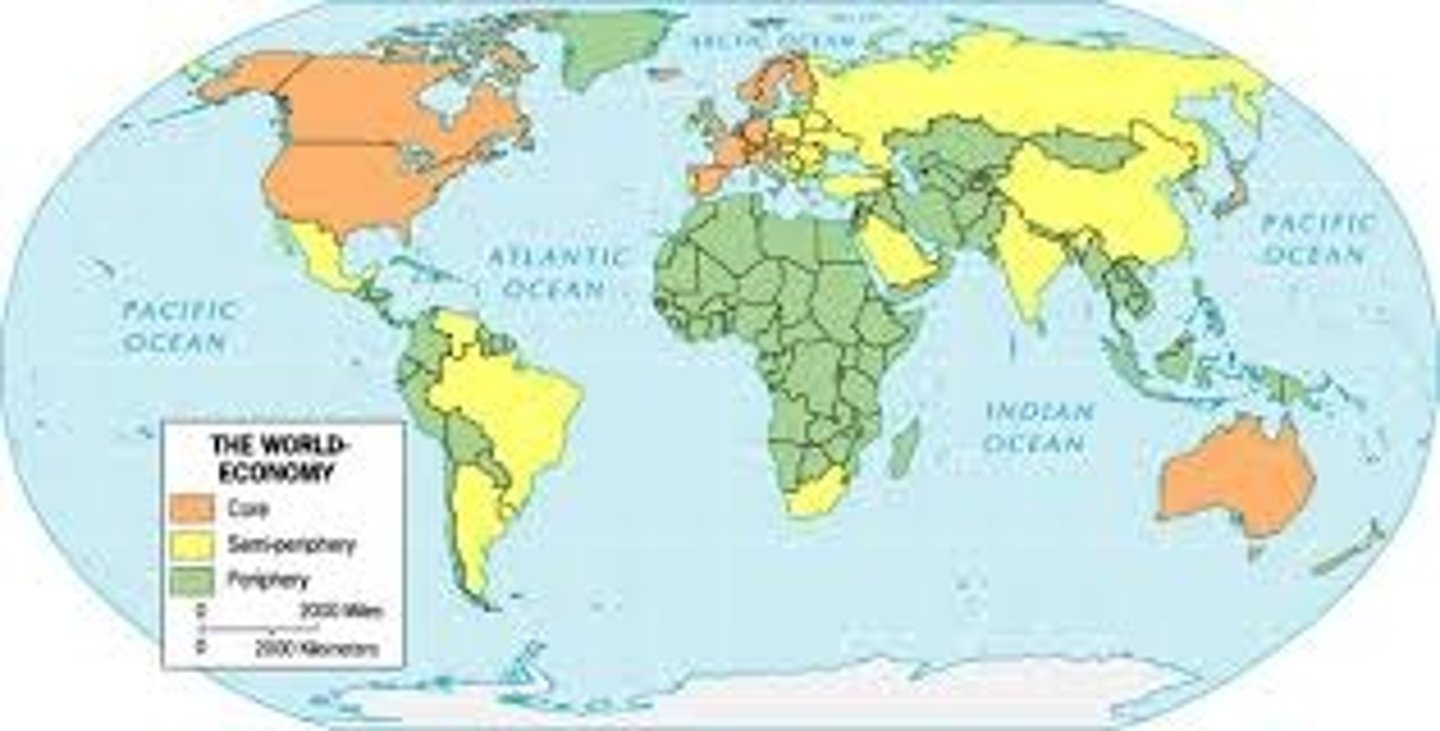
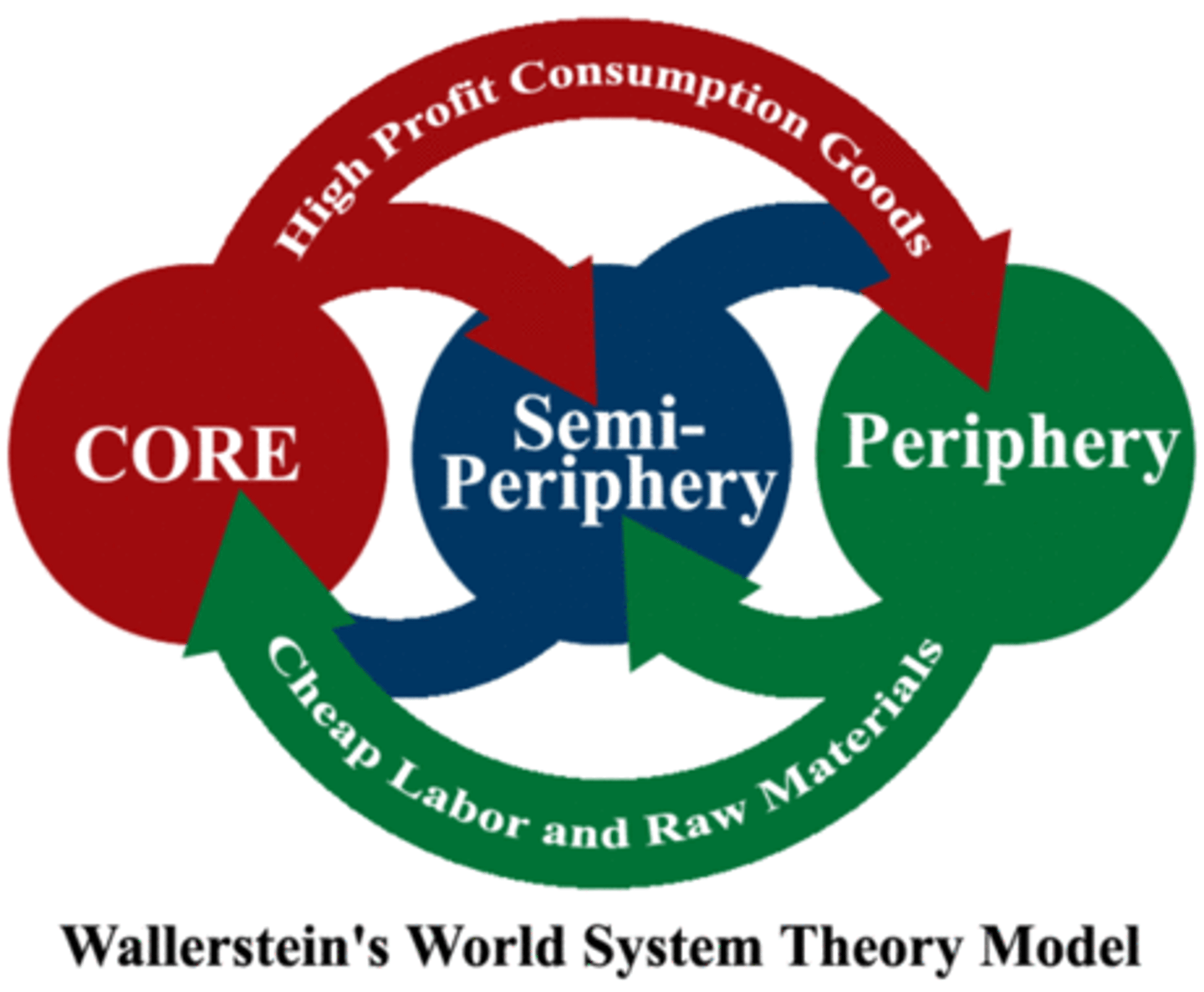
Core
The centers of economic, political, and/or cultural power within a given territorial entity. Can be used at local, national, regional or global scale of analysis
Semi-Periphery
Intermediary regions in terms of the hierarchy of power between core and periphery regions.
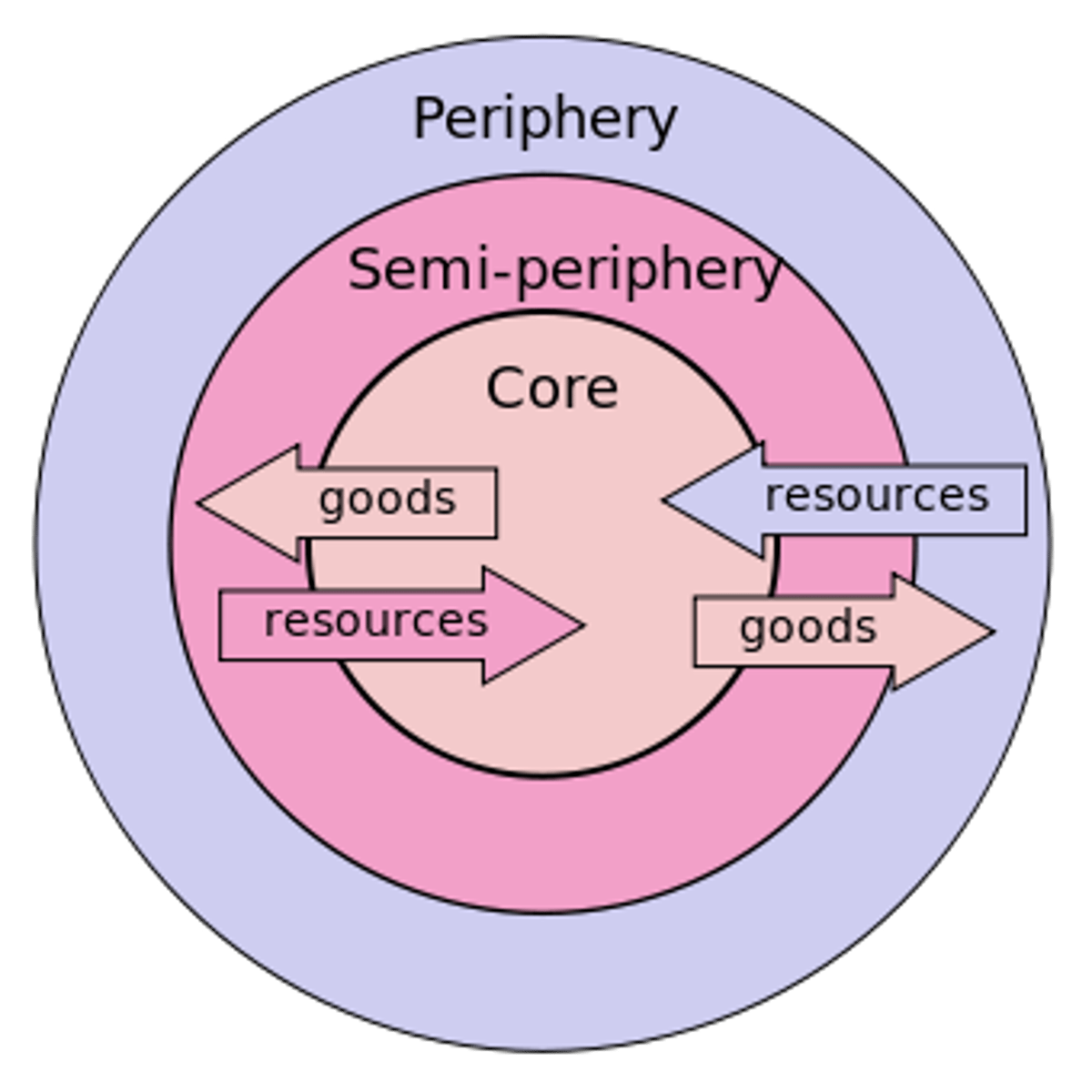
Periphery
The economically and politically least powerful regions and therefore, are often marginalized of under the control of both semi-peripheral and core regions.
Ecotourism
A form of tourism that appeals to the ecologically and socially conscious individuals. Often used by LDCs to spur development.

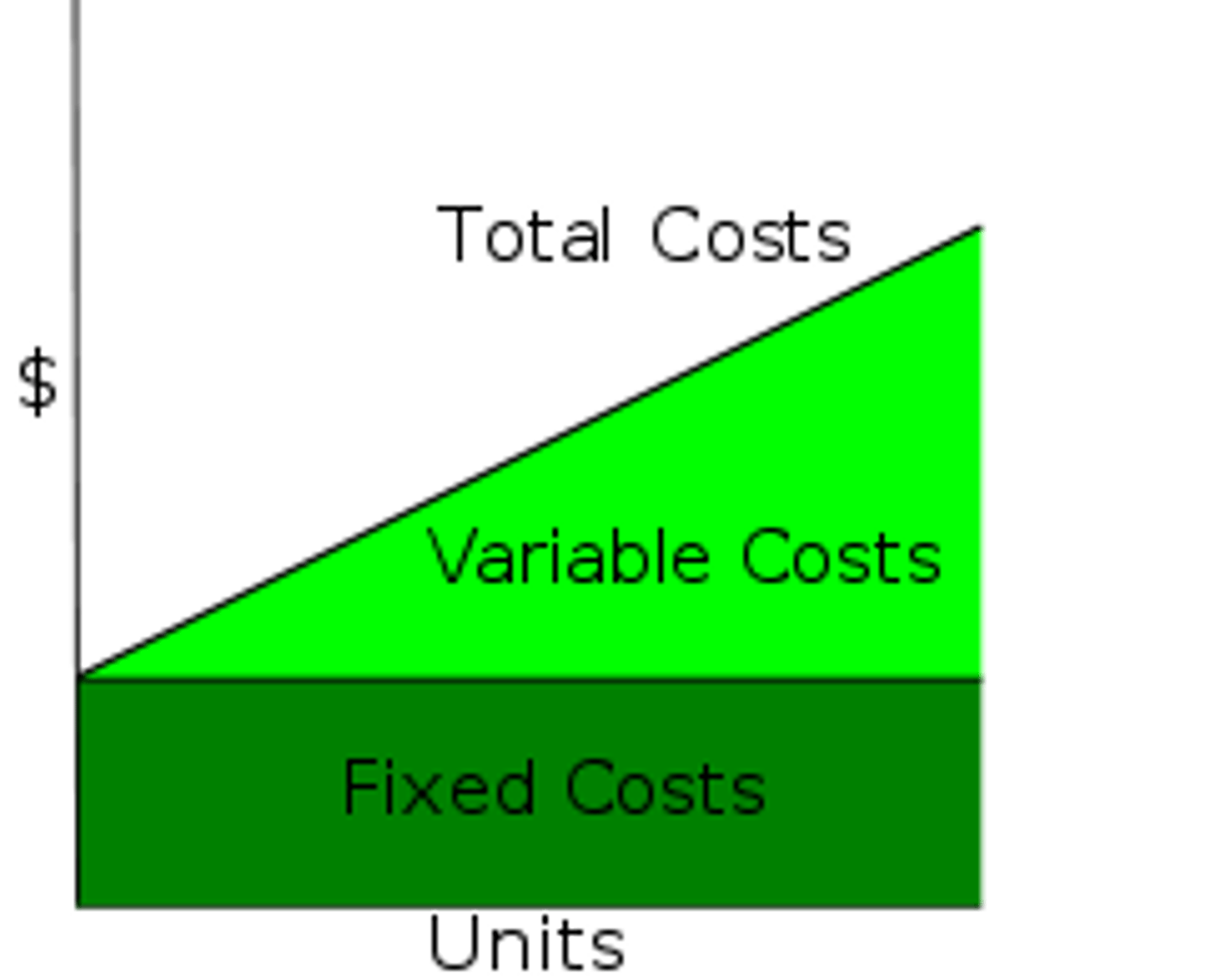
Fixed Costs
Expenses that do not change in proportion to the activity of a business (taxes, rent)

Variable Costs
costs that change as output changes (raw materials)
Footloose
When an industry is neither resource nor market orientated. Can be easily moved.

Fordism
A highly organized and specialized system for organizing industrial production and labor. (Mass production)

Post-Fordism
modern industrial production has moved away from mass production in huge factories towards specialized markets based on small flexible manufacturing units often using automation to replace human labor

Foreign Direct Investment
Investment in the economies of LDC's by transnational corporations based on MDC's.

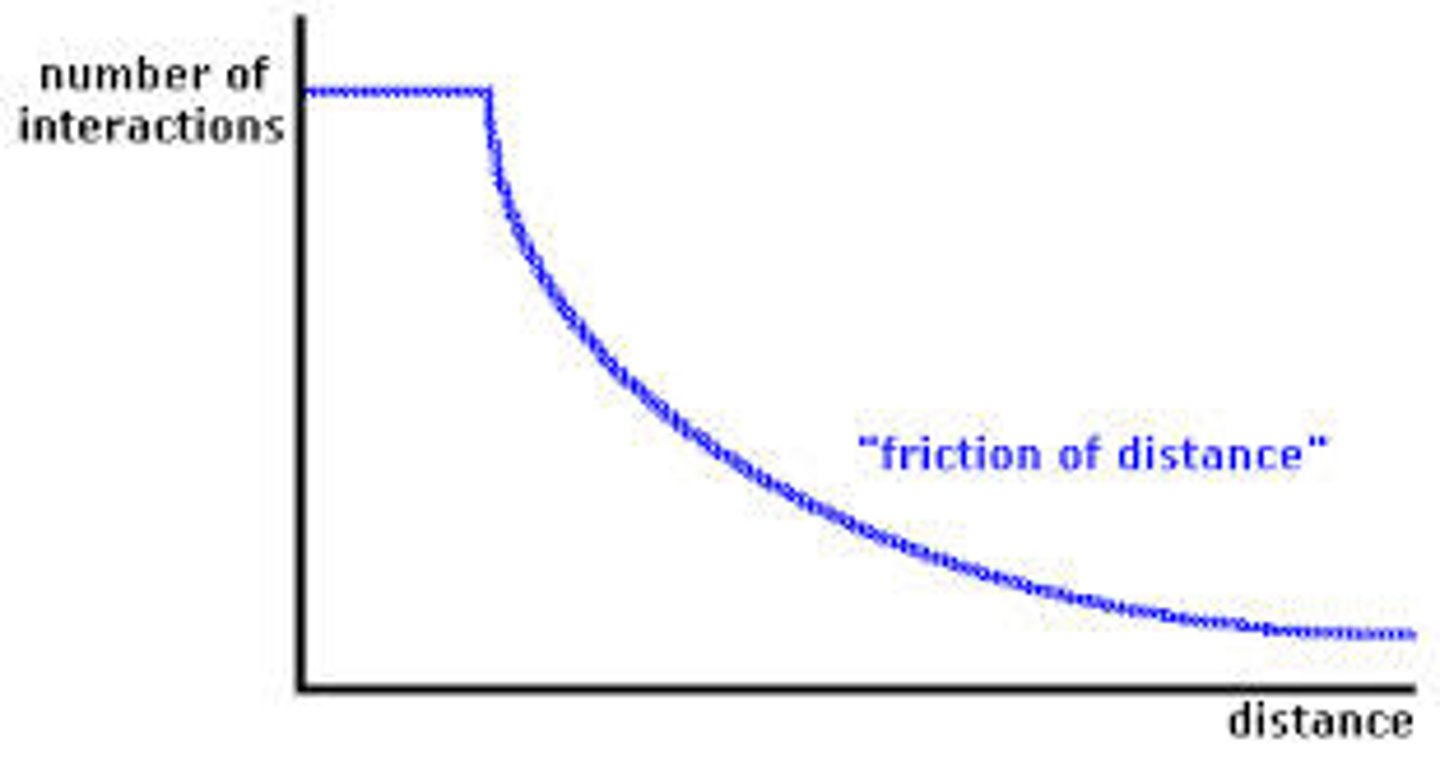
Friction of Distance
Based on the notion that the time and cost increase with the increase in distance. (NOT the same as distance decay!)
Gross National Income per capita (GNI)
The value of the output of goods and services produced by a country in a year divided by the number of people that live in the country.

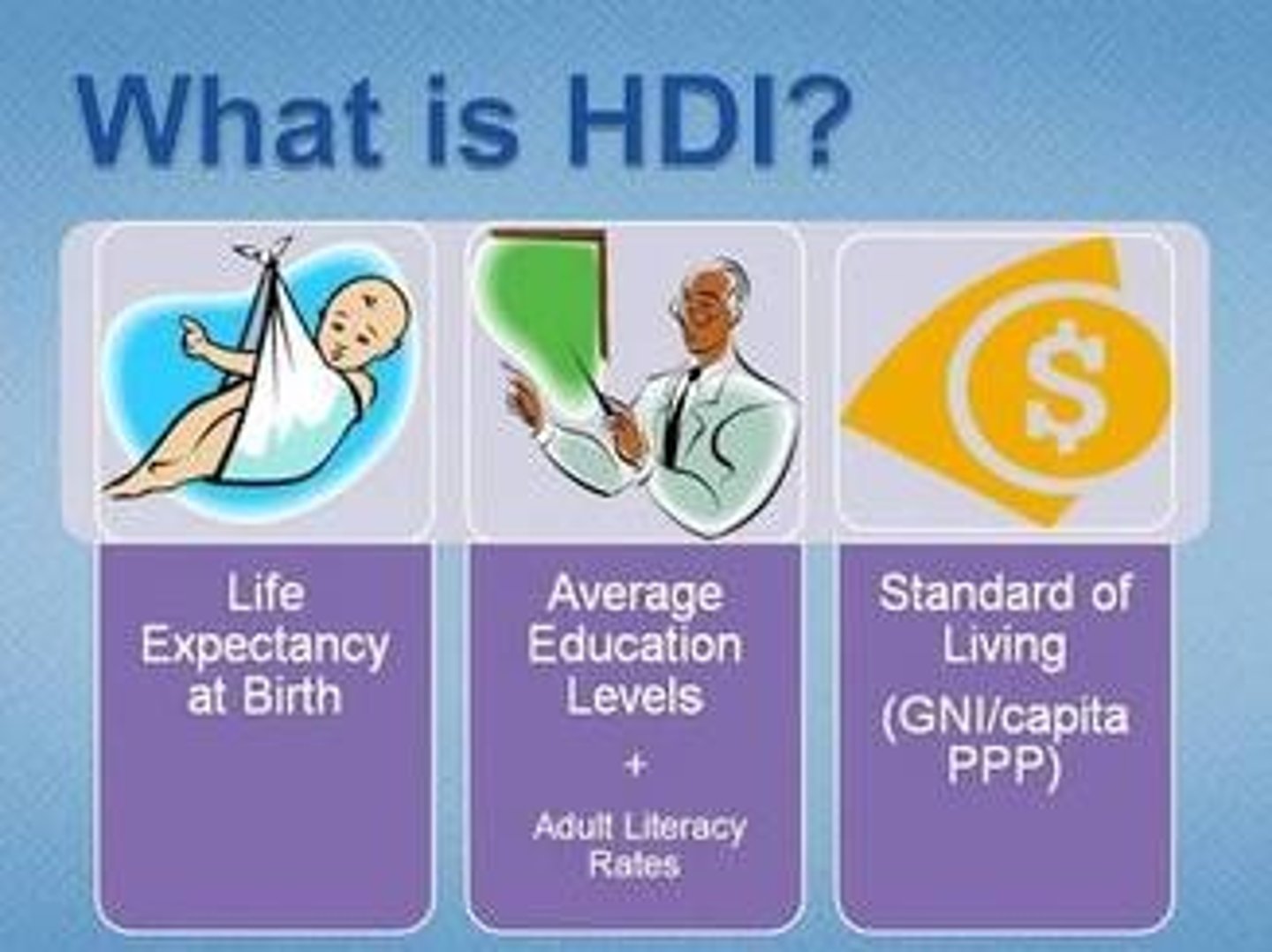
HDI
Human Development Index: Measures a country's level of development by looking at demographic info based on health, wealth and education
International/Global Division of Labor
In which some components of products are made in one country and others in another. Brains and decision making in MDCs, low cost labor in LDCs

Investment Capital
The total amount of money that was endowed into a company by the shareholders, bondholders, and all other interested parties.

Just in Time Production
Shipment of parts and materials to arrive at a factory moments before they are needed. Diffusion from Toyota in Japan

Export Processing Zones (EPZ)
Areas where governments create favorable investments and trading conditions to attract export-oriented industries.

Free Trade Zones
A geographic are where goods may be landed, handled, manufactured or reconfigured, and reexported without intervention of the customs authorities.
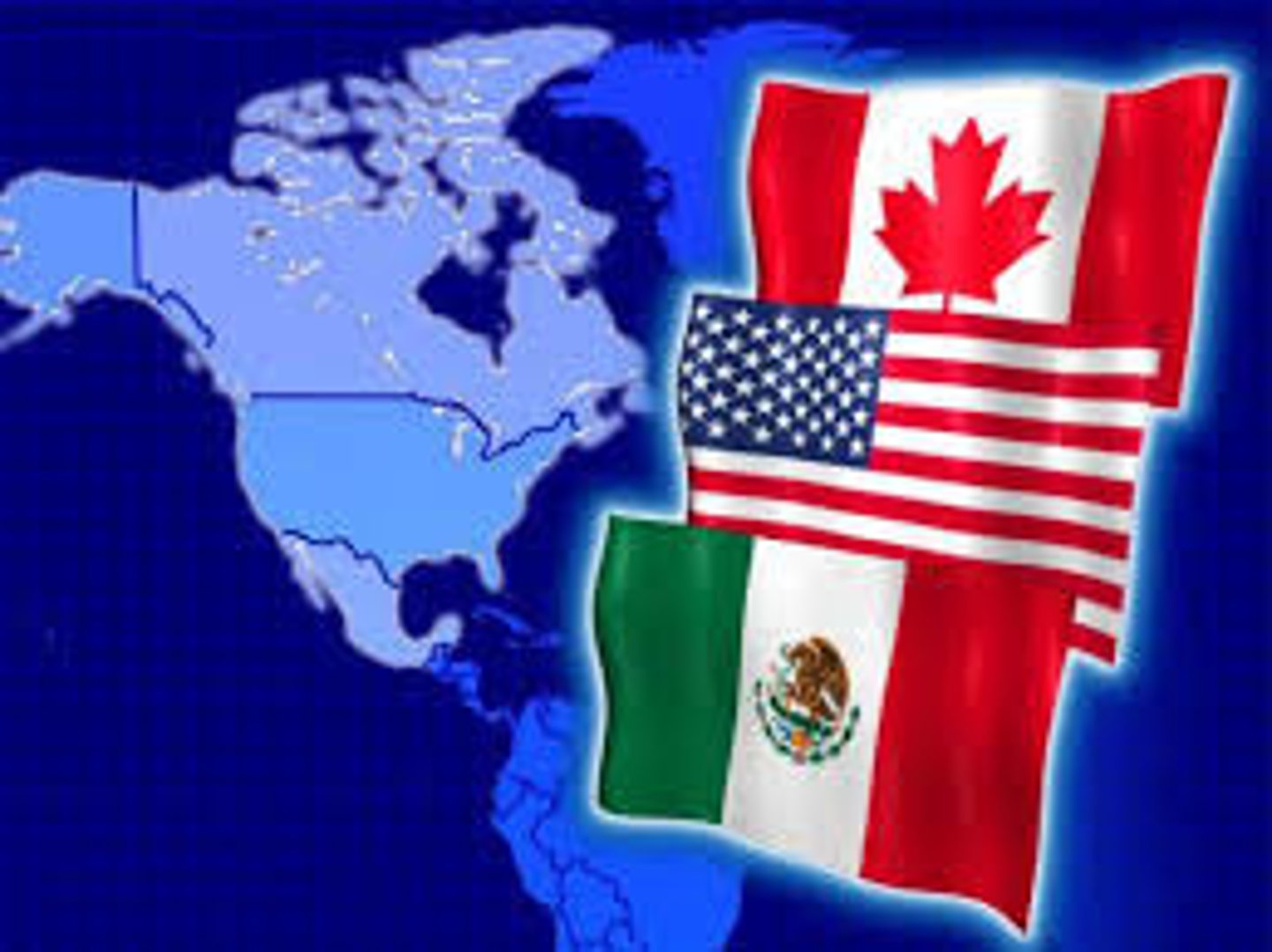
Maquiladoras
Factories built by US companies in Mexico near the US border to take advantage of much cheaper labor costs in Mexico and close proximity to US markets.

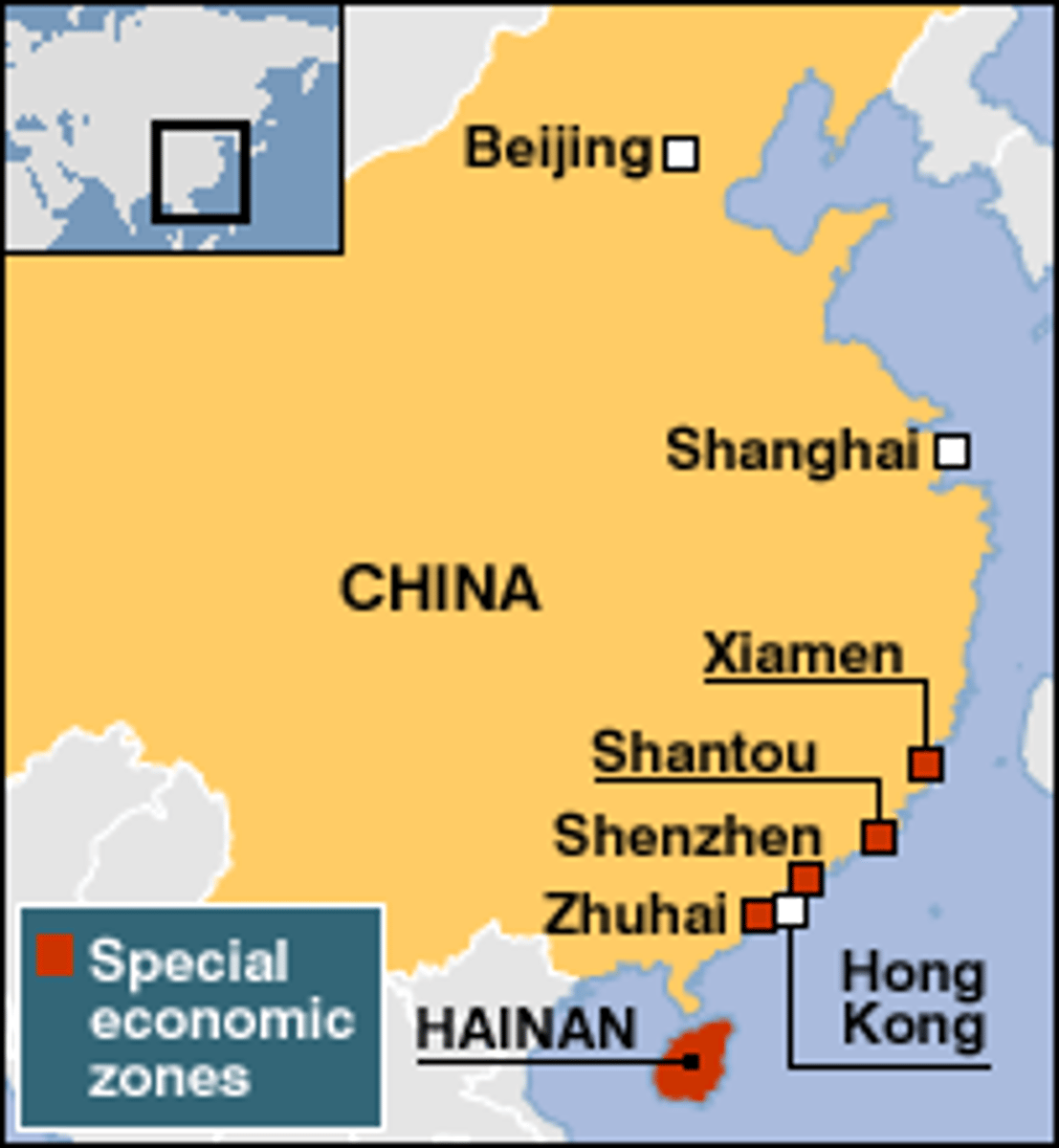
Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
specific area within a country in which tax incentives and less stringent environmental regulations are implemented to attract foreign business and investment
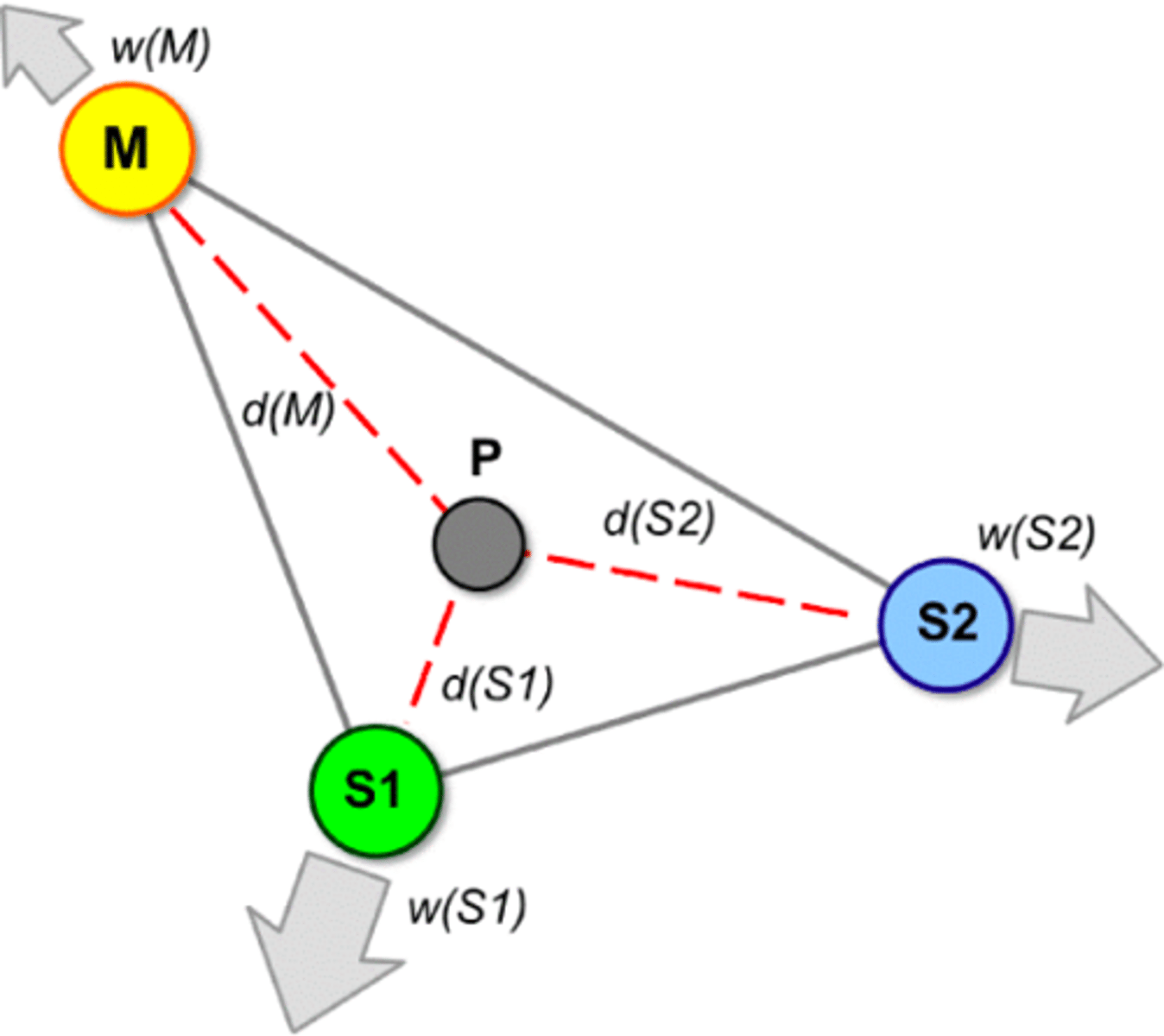
Market Orientation
The tendency of an economic activity to locate close to its market to limit transportation costs because it is a bulk gaining activity
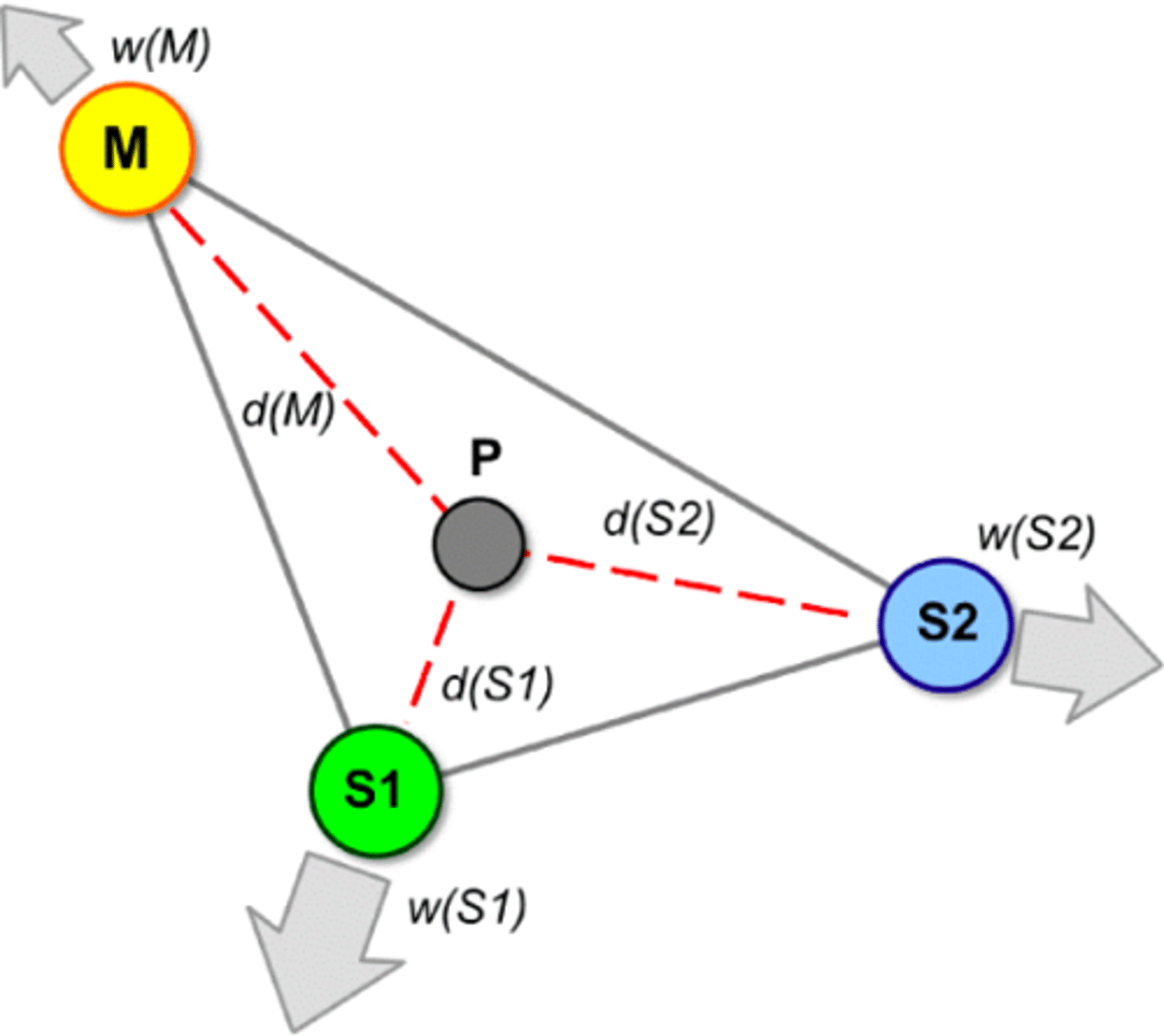
Resource Orientation
The tendency of an economic activity to locate close to its resources to limit transportation costs because it is a bulk reducing activity
Microloans
The practice of loaning people in poverty small amounts of money, in order for people to start their own small business. Often loans to women in LDCs

Multinational Corporations (MNC)
A business that has its facilities and other assets in at least one country other than its home country.

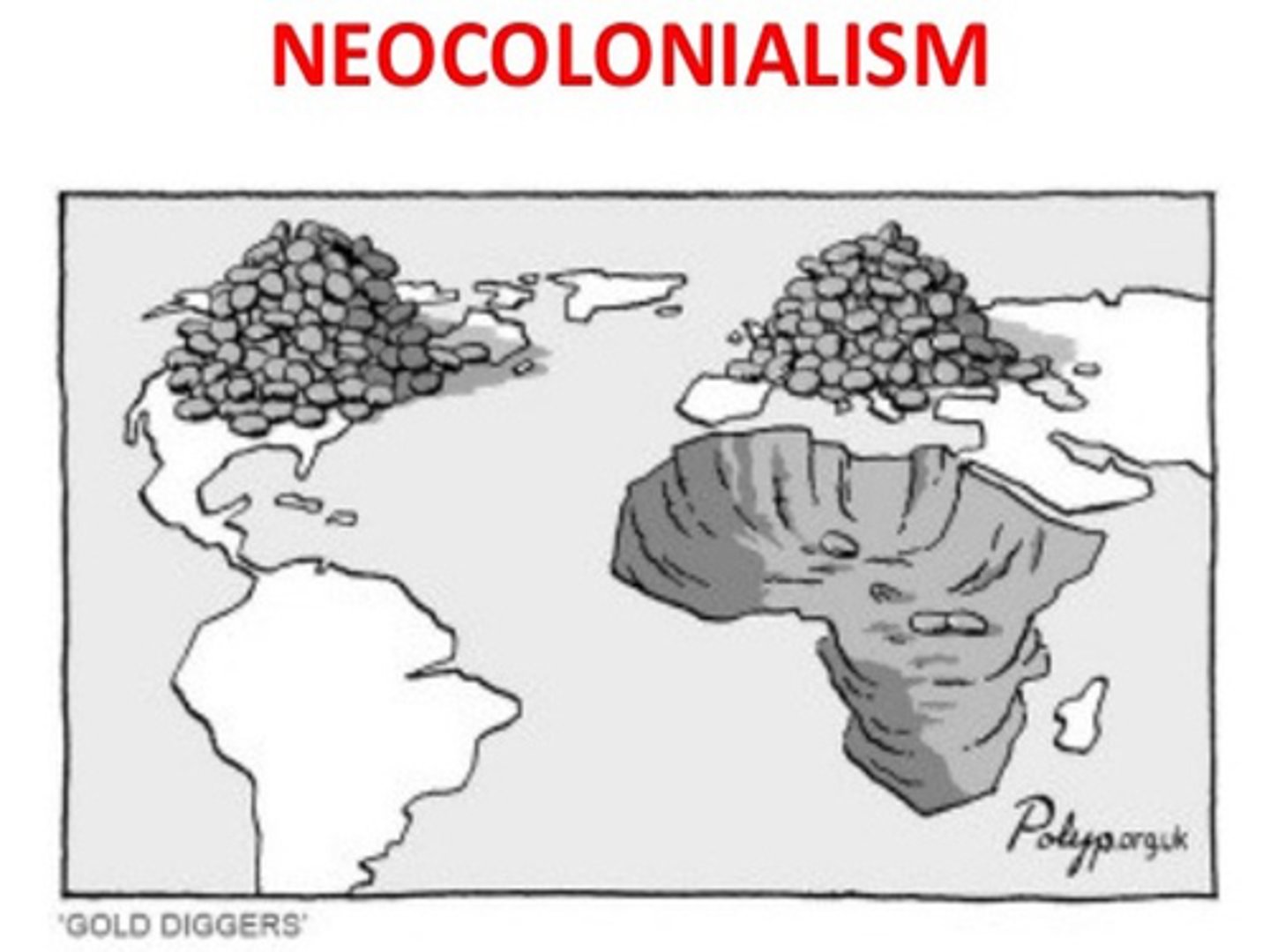
Neocolonialism
International economic arrangements where colonial power maintains control of colonies and dependencies after WWII.
Outsourcing
A decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers (usually out of the country) for cheaper labor costs

Postindustrial
Economic transition from a manufacturing based economy to a service based economy.

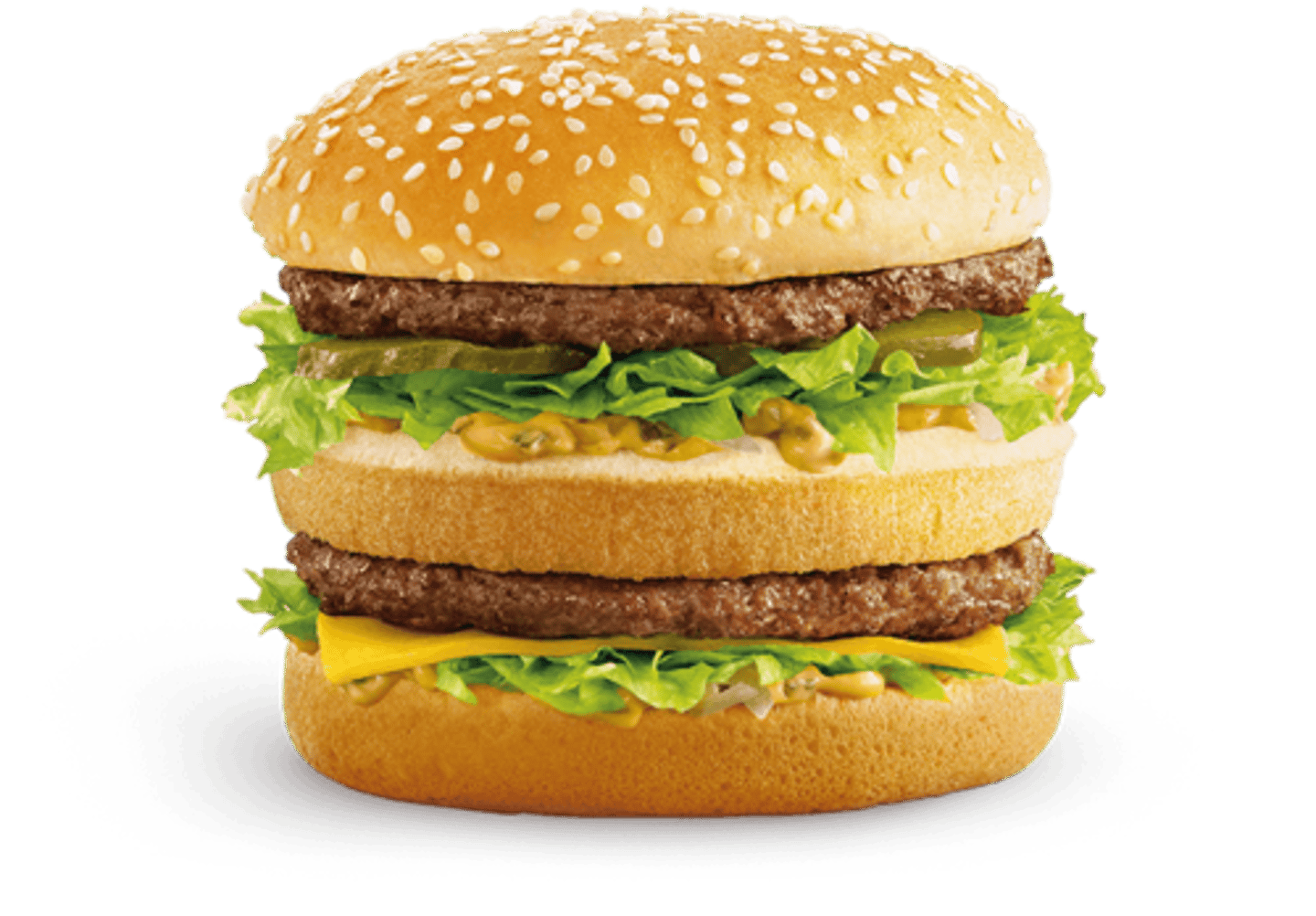
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Equilibrium exchange rate between currencies to equalize their purchasing power. The Big Mac index is an example.

Substitution Principle
Substitution of a product, service, or process to another that is more efficient and beneficial while retaining the same functionality, such as bettering the environment.
Technology Transfer
Already existing knowledge, facilities, or capabilities developed with money from the government and can be used for a number of things rather than a particular group.

Technopole
Centers or nodes of high technology research and activity around which a high-tech corridor is sometimes established.

High-Tech Corridors
Place where technology and computer industries agglomerate.

Growth-Pole
An urban center with certain attributes that will stimulate regional economic development and its hinterland.

Value Added
Gross value of the product minus the cost of raw materials and energy

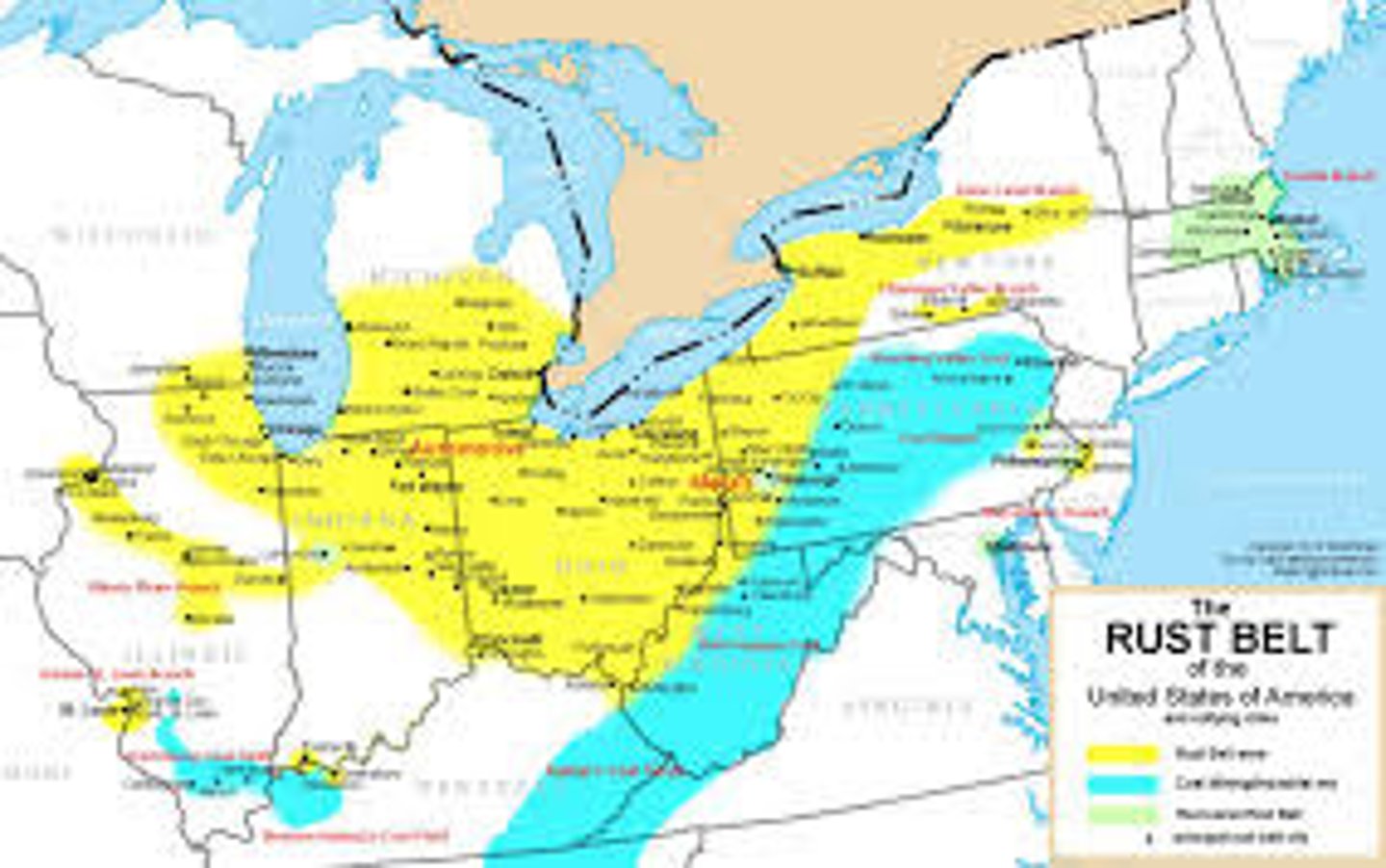
deindustrialization
Jobs shift from secondary to tertiary sector; leading to Rust Belt phenomenon in the US Midwest
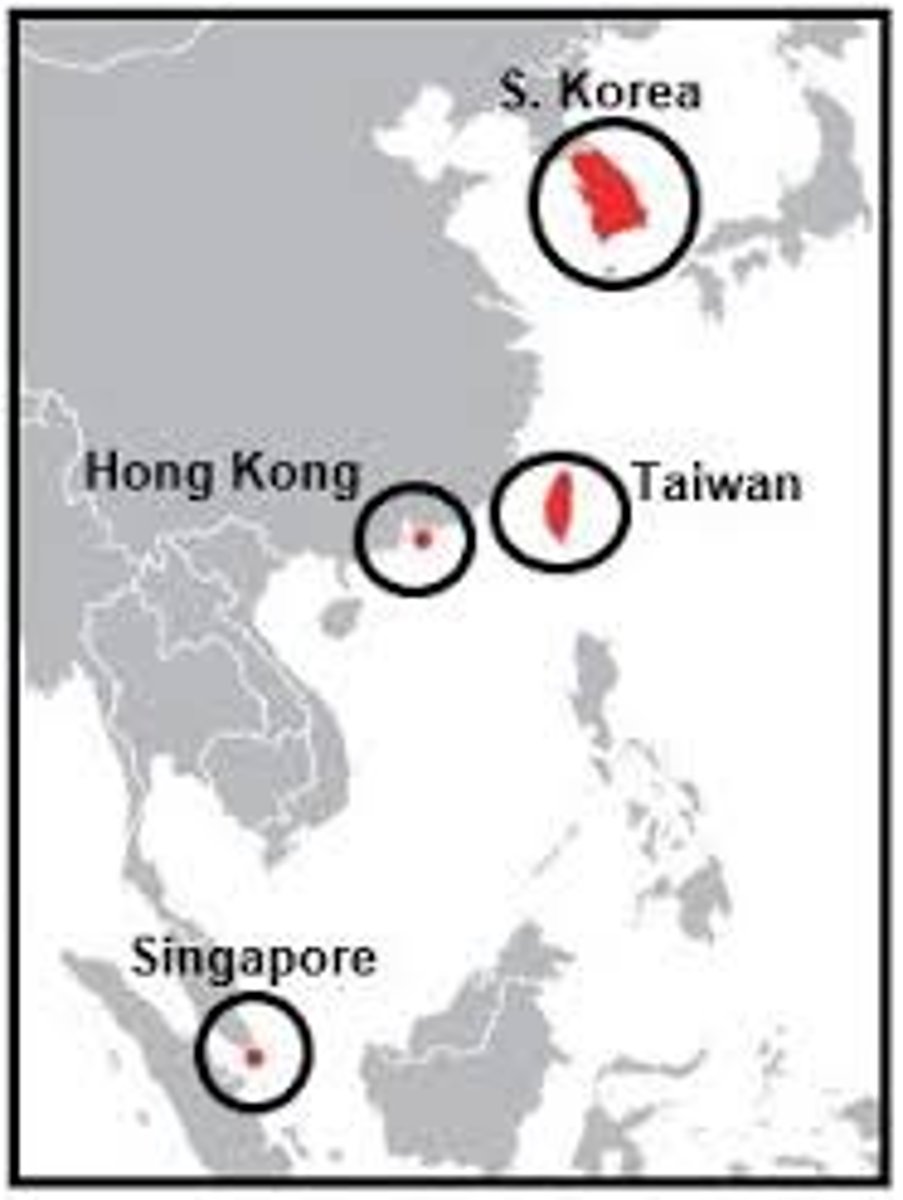
Asian Tigers
(S Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, Hong Kong) Succeeded Japan as leading Asian manufacturers in 1980s
BRICs
(Brazil, Russia, India, China) predicted economic growth with sizable domestic economies, predicted to dominate world economy by 2050

NICs
Newly Industrialized Countries
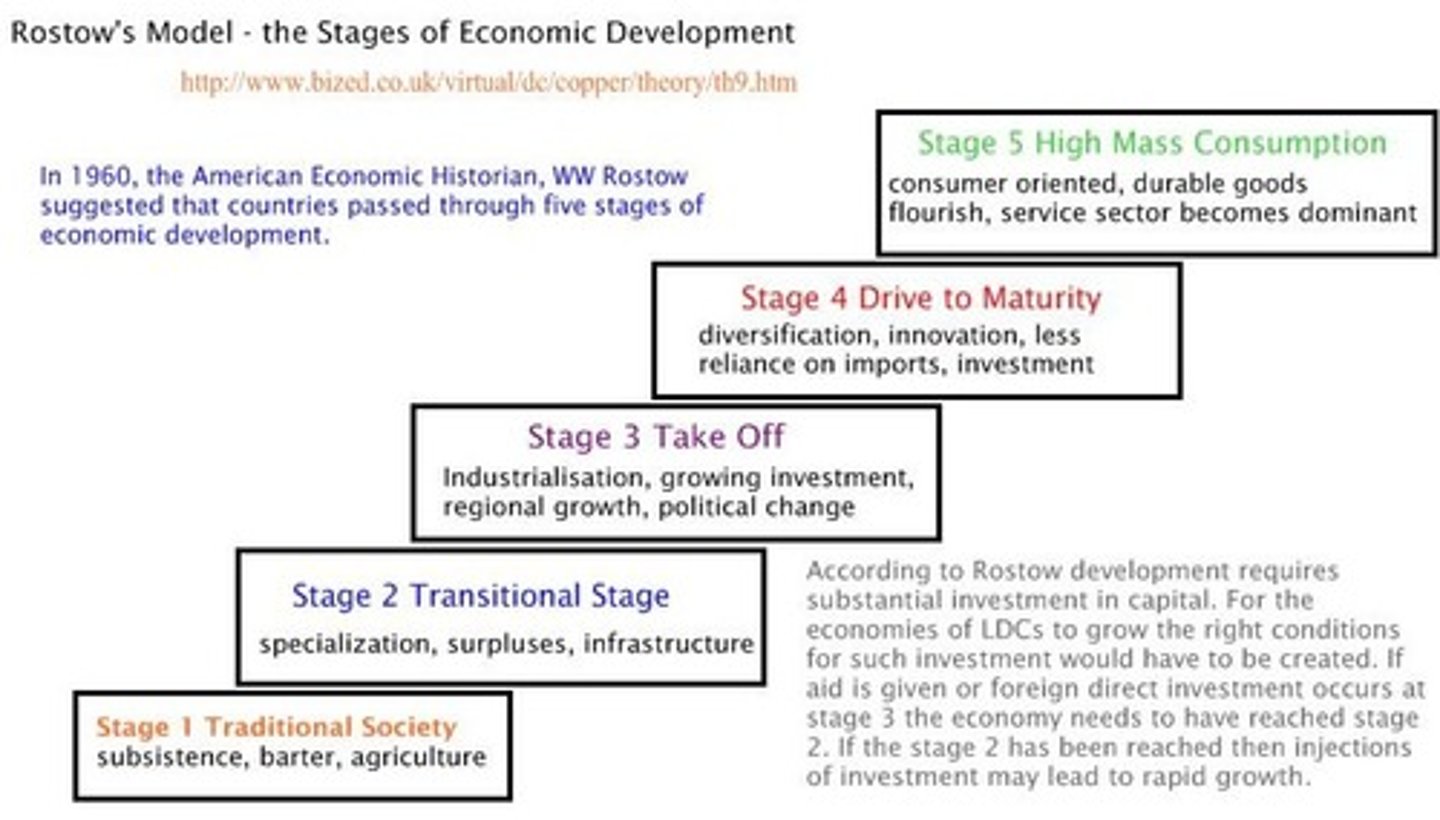
Rostows Five Stages of Development
a liberal developmental model showing traditional society, pre-conditions for take-off, take-off, drive to maturity, age of mass consumption
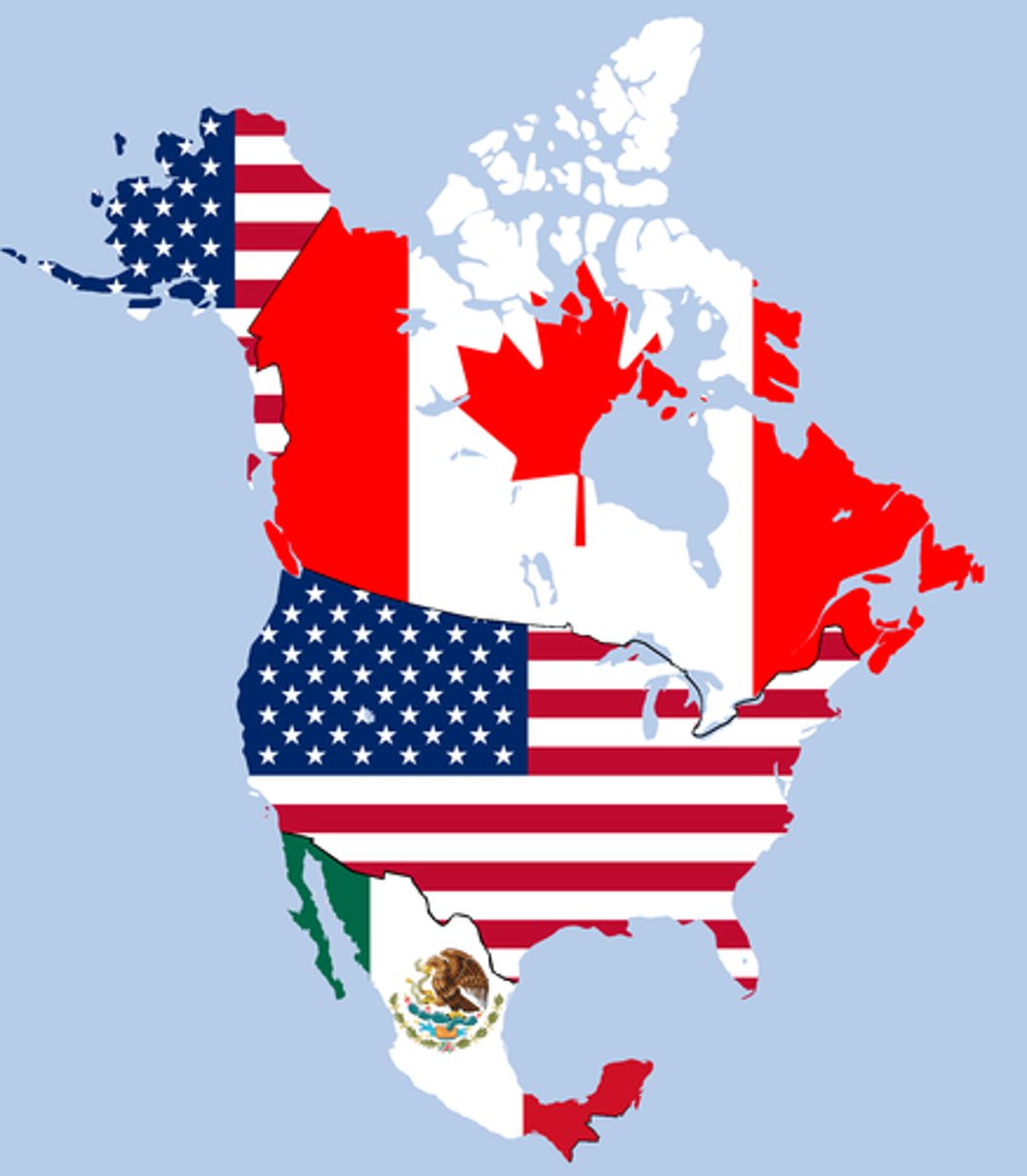
United States Mexico Canada Agreement
replaced NAFTA, Canada, US and Mexico free trade agreement
WTO
The World Trade Organization - an international body that enforces agreements that reduce barriers to international trade; successor to the GATT

OPEC
An international oil cartel originally formed in 1960; attempts to limit production and raise prices. (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries)

UN SDGs
17 UN goals to end poverty and hunger while increasing education and healthcare and ensuring gender equality

Weber's Least Cost Theory (Location Theory)
Explains and predicts the precise location of industry; emphasizing that firms seek a site of minimum transport and labor cost.
Wallerstein's World Systems Theory
Since 1450, the world has been divided into core, periphery, and semi-periphery regions. Core countries are dominant capitalist countries that exploit peripheral countries for labor and raw materials.
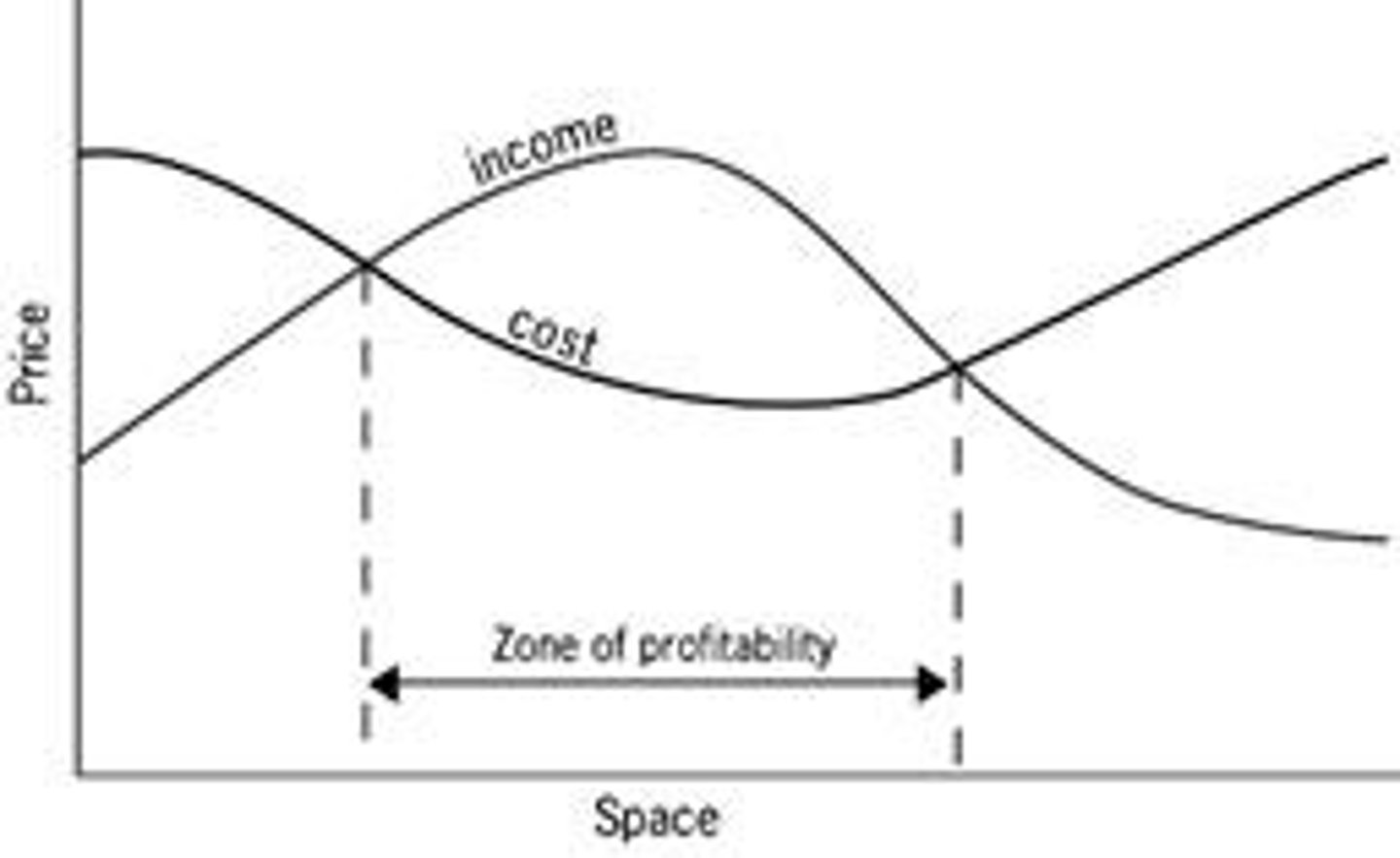
Losch's Model (Zone of Profitability)
zone of profitability; firms will identify a zone of profitability (not just a point) where income will outpace costs
ex: A place w/ low labor costs, easy travel, and resources.
MINTs
Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey

Pacific Rim
Japan, China, Vietnam, Thailand, & includes Tigers
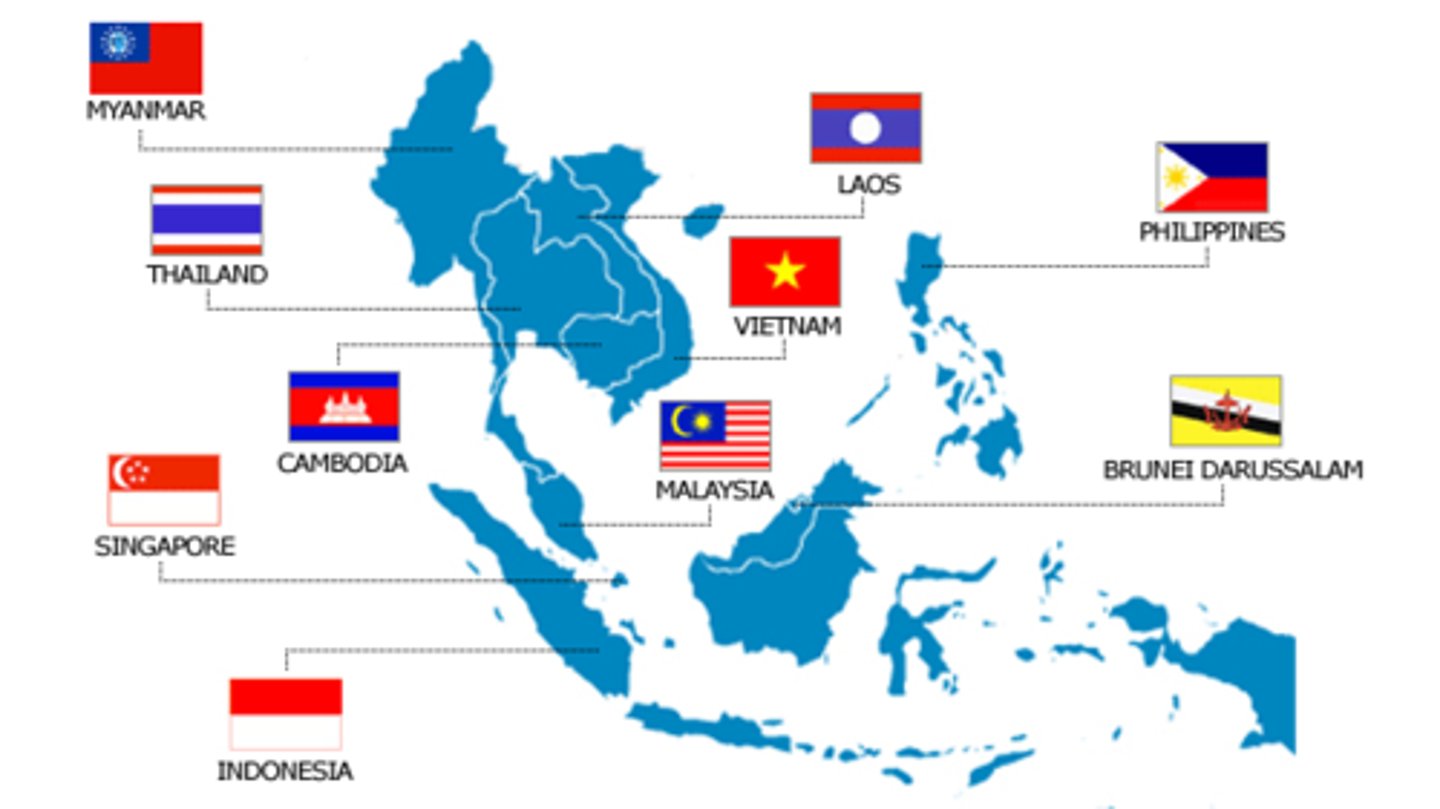
ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations
GII
Gender Inequality Index: index for measurement of gender disparity that considers women's access to reproductive services, empowerment, and labor participation of women to determine a country's composite score.

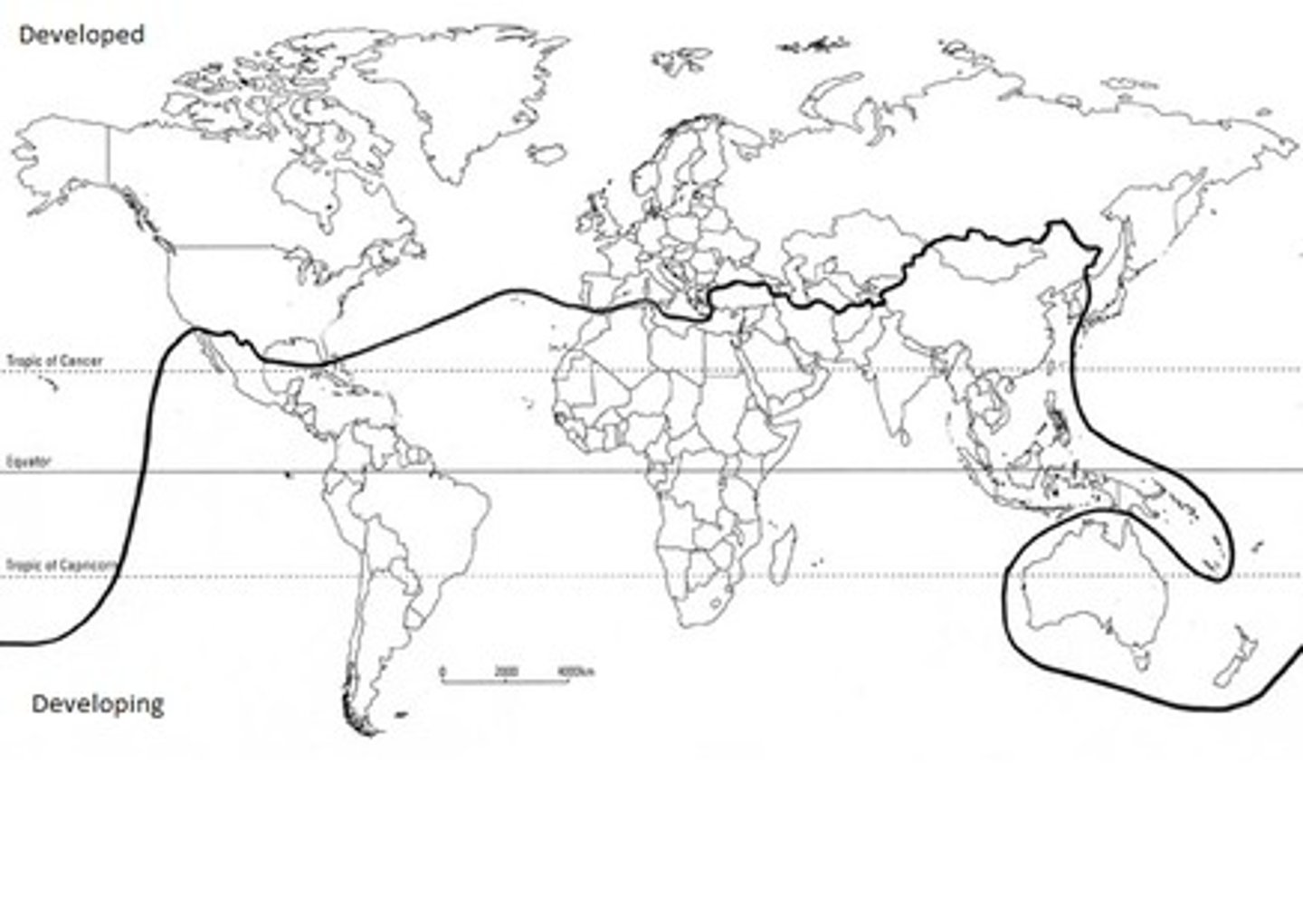
Brandt Line (North/South)
invisible line across the world that divides the rich north from the poor south
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods.

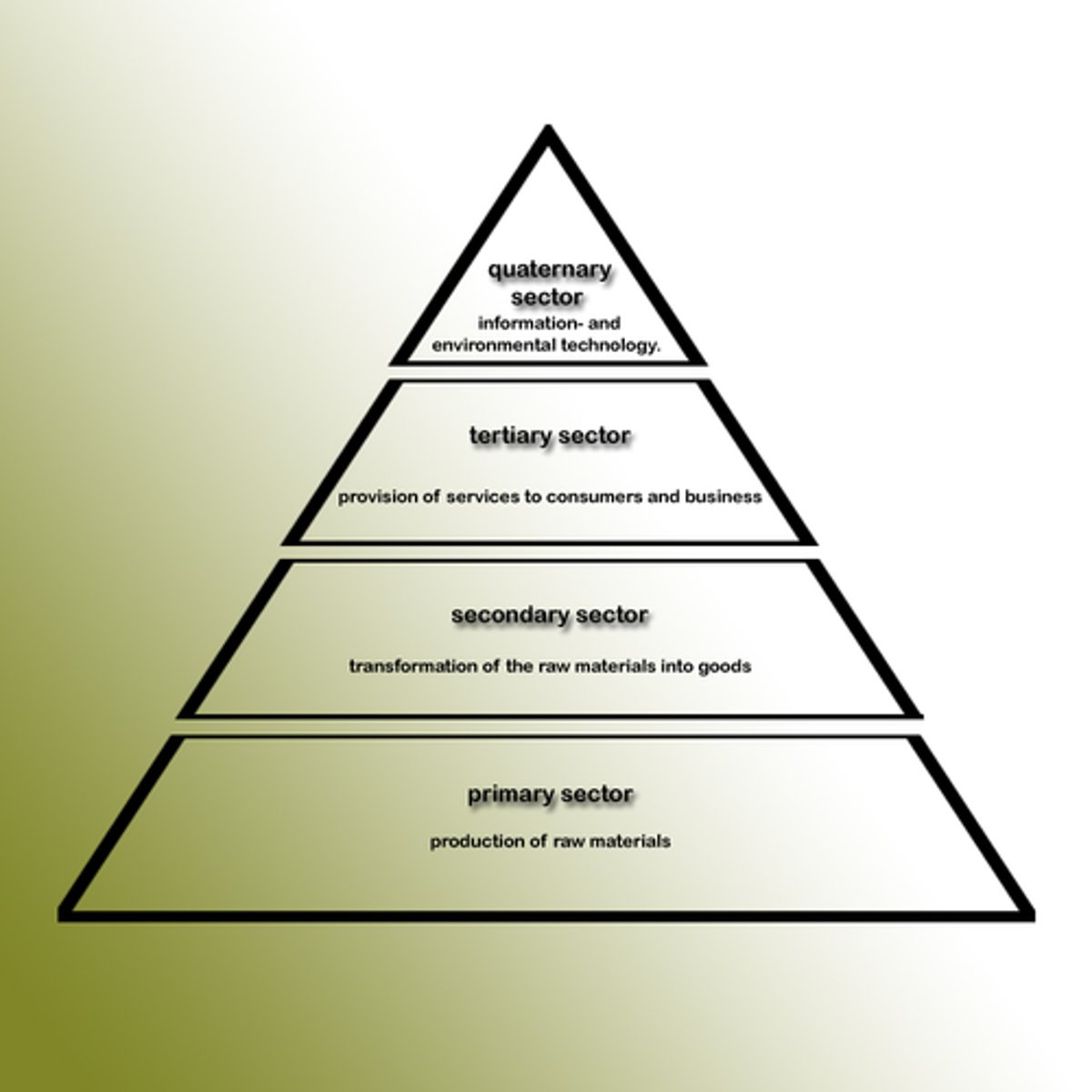
Economic Sectors
primary (taking raw materials from earth - agriculture, mining), secondary (manufacturing - textile or auto industries), tertiary (providing goods or services), quaternary (information and technology), quinary (leadership and executive decision making)
Dependency Theory
a model of economic and social development that explains global inequality in terms of the historical exploitation of poor nations by rich ones
Neoliberalism
A strategy for economic development that calls for free markets, balanced budgets, privatization, free trade, and minimal government intervention in the economy.
European Union (EU)
(syn Common Market) an economic association established in 1957 by a number of Western European countries to promote free trade among its members

MERCOSUR (Southern Common Market)
An alliance that promotes the free circulation of goods, services, and production factors, and has a common external tariff and commercial policy among member nations in South America
IMF (International Monetary Fund)
part of the UN; makes loans to countries to finance development

economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises

sustainable development
economic development that is conducted without depletion of natural resources.

GDP/ GDP per capita
Gross Domestic Product (total value of all goods and services) divided by the population

informal economy
Economic activity that is neither taxed nor monitored by a government; and is not included in that government's Gross National Product; as opposed to a formal economy

Primary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with the direct extraction of materials from Earth's surface, generally through agriculture, although sometimes by mining, fishing, and forestry.
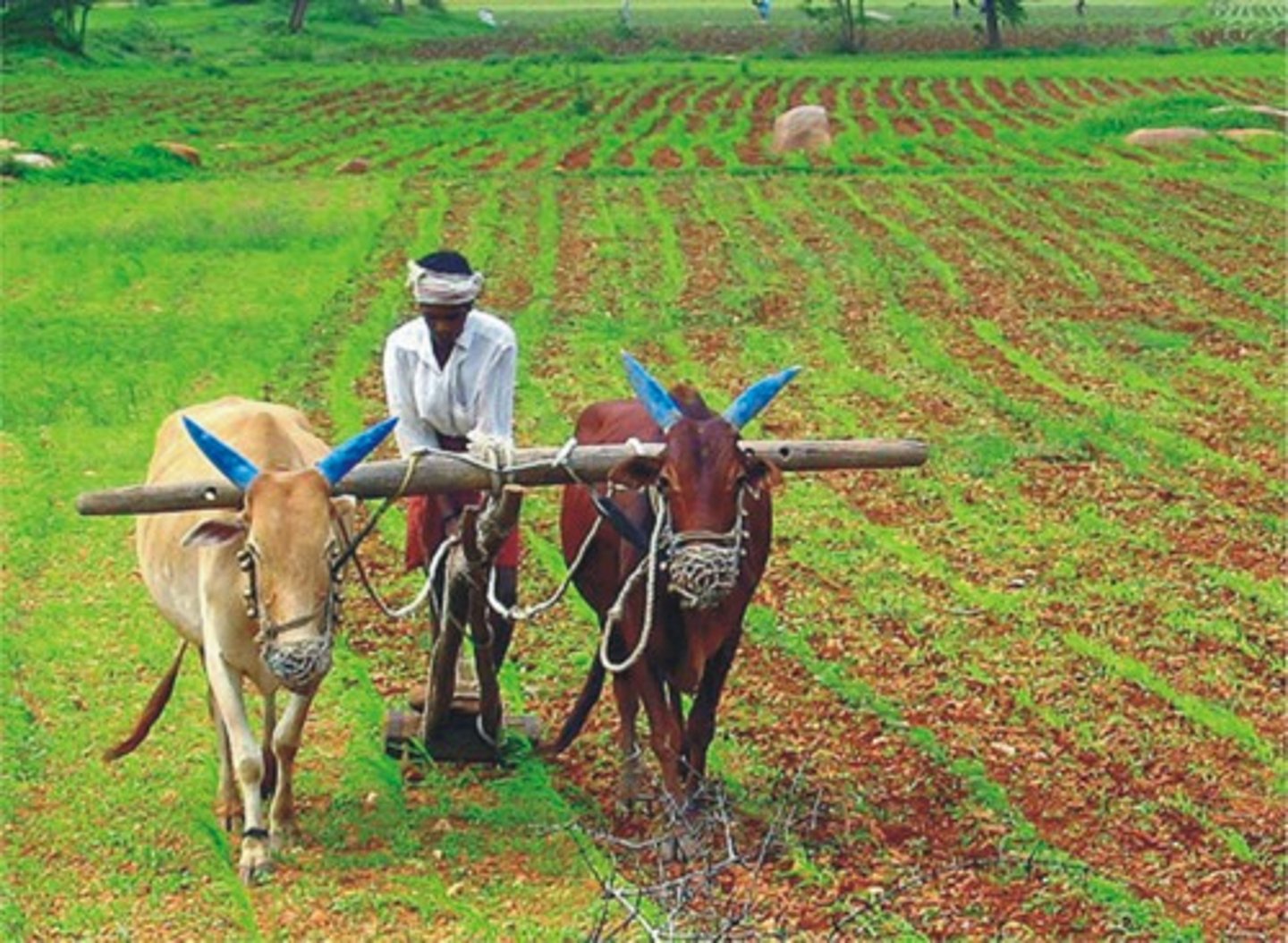

Secondary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with manufacturing useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials.
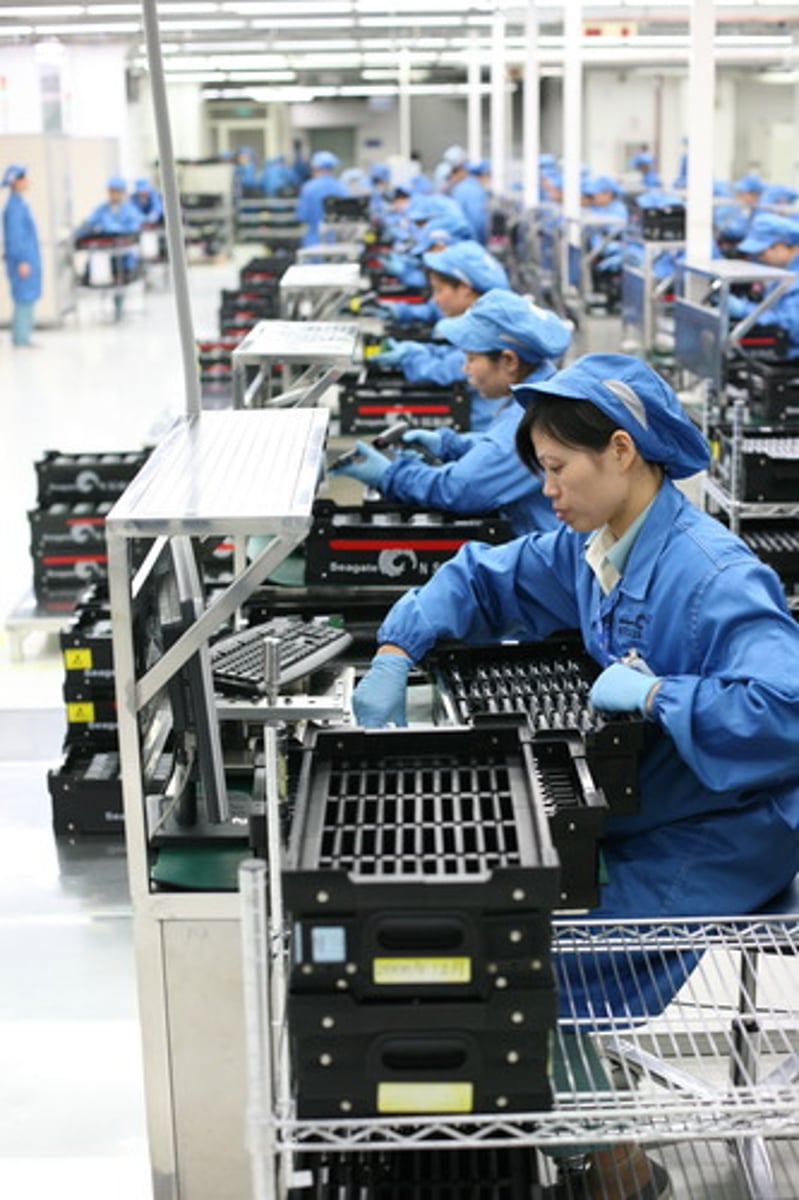

Tertiary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with transportation, communications, and utilities, sometimes extended to the provision of all goods and services to people in exchange for payment.

Quaternary Sector
a way to describe a knowledge-based part of the economy which typically includes services such as information generation and sharing, information technology, consultation, education, research and development, financial planning, and other knowledge-based services.

Quinary Sector
The most advanced form of Quaternary activities consisting of high-level decision making for large corporations or high-level scientific research.

Formal Economy
The legal economy that is taxed and monitored by a government and is included in a government's Gross National Product; as opposed to an informal economy

income distribution
The way the national income is divided into "shares" ranging from the poor to the rich.

TFR
(total fertility rate) The number of births that 1,000 women would have if the current year's age-specific birth rate remained constant throughout their childbearing years

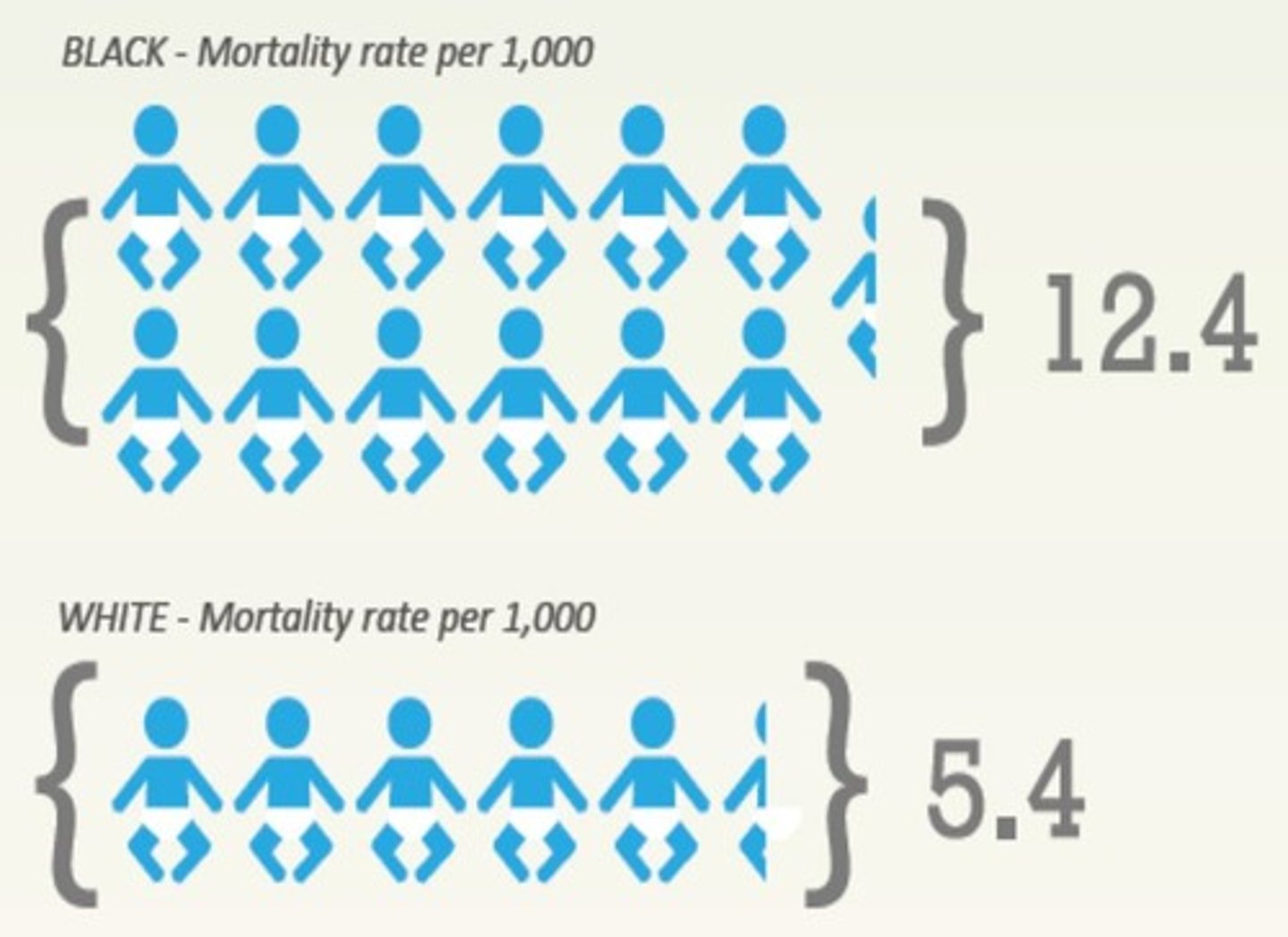
IMR
Infant Mortality Rate: The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
Access to health care
access to hospitals, doctors, essential medicine and preventative health care

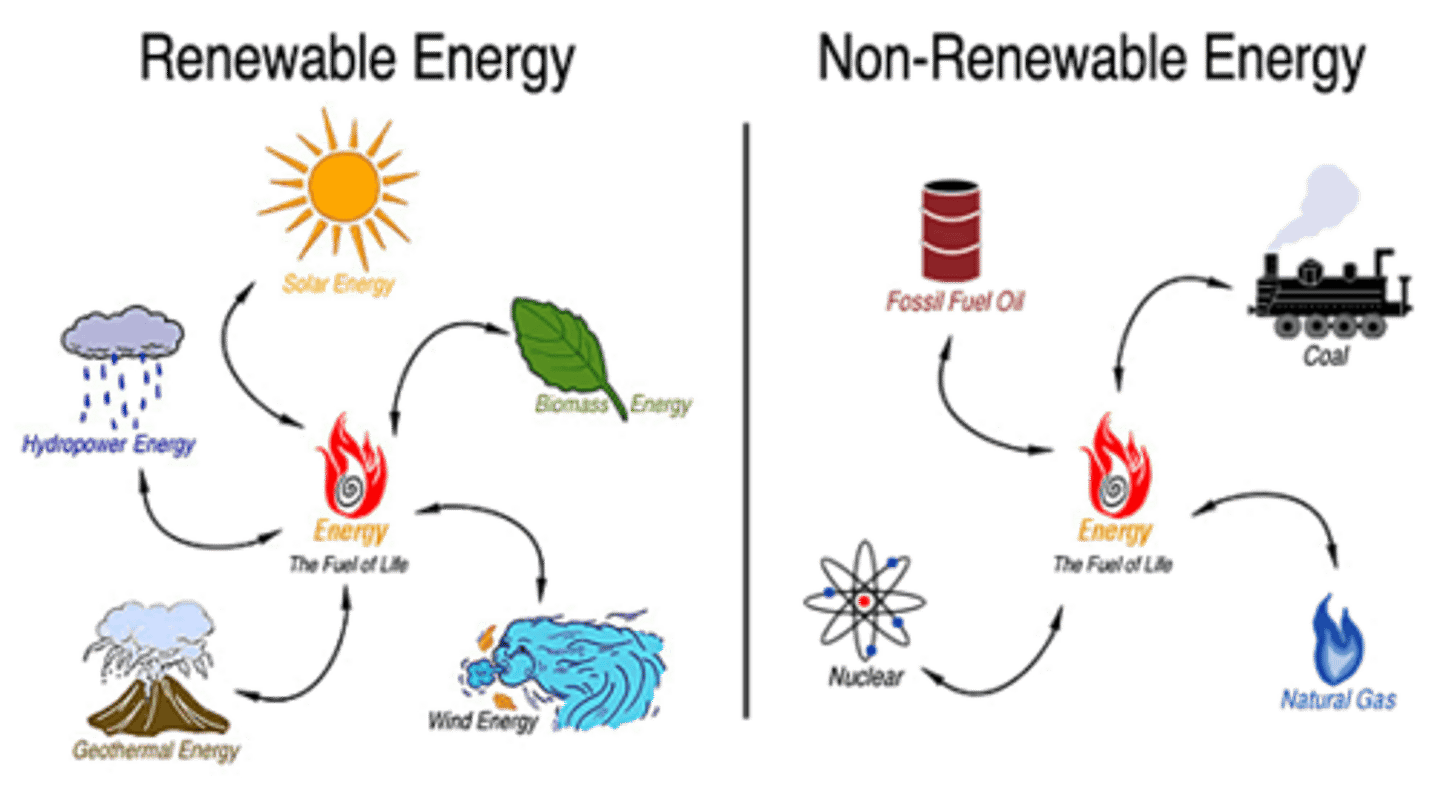
renewable energy
energy from a source that is not depleted when used, such as wind or solar power.
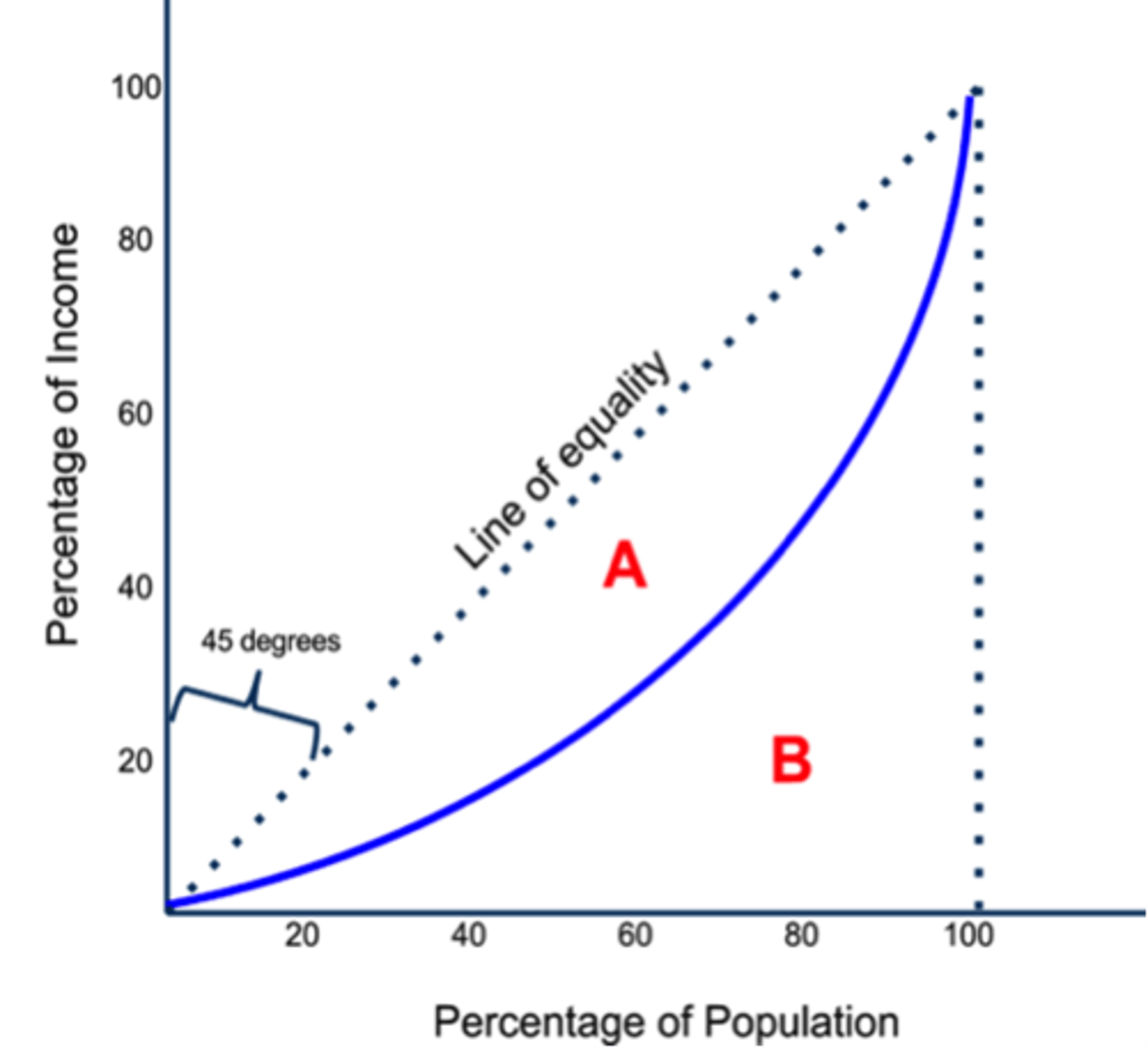
Gini Coefficient
a number that summarizes a country's level of income inequality based on how unequally income is distributed across quintiles
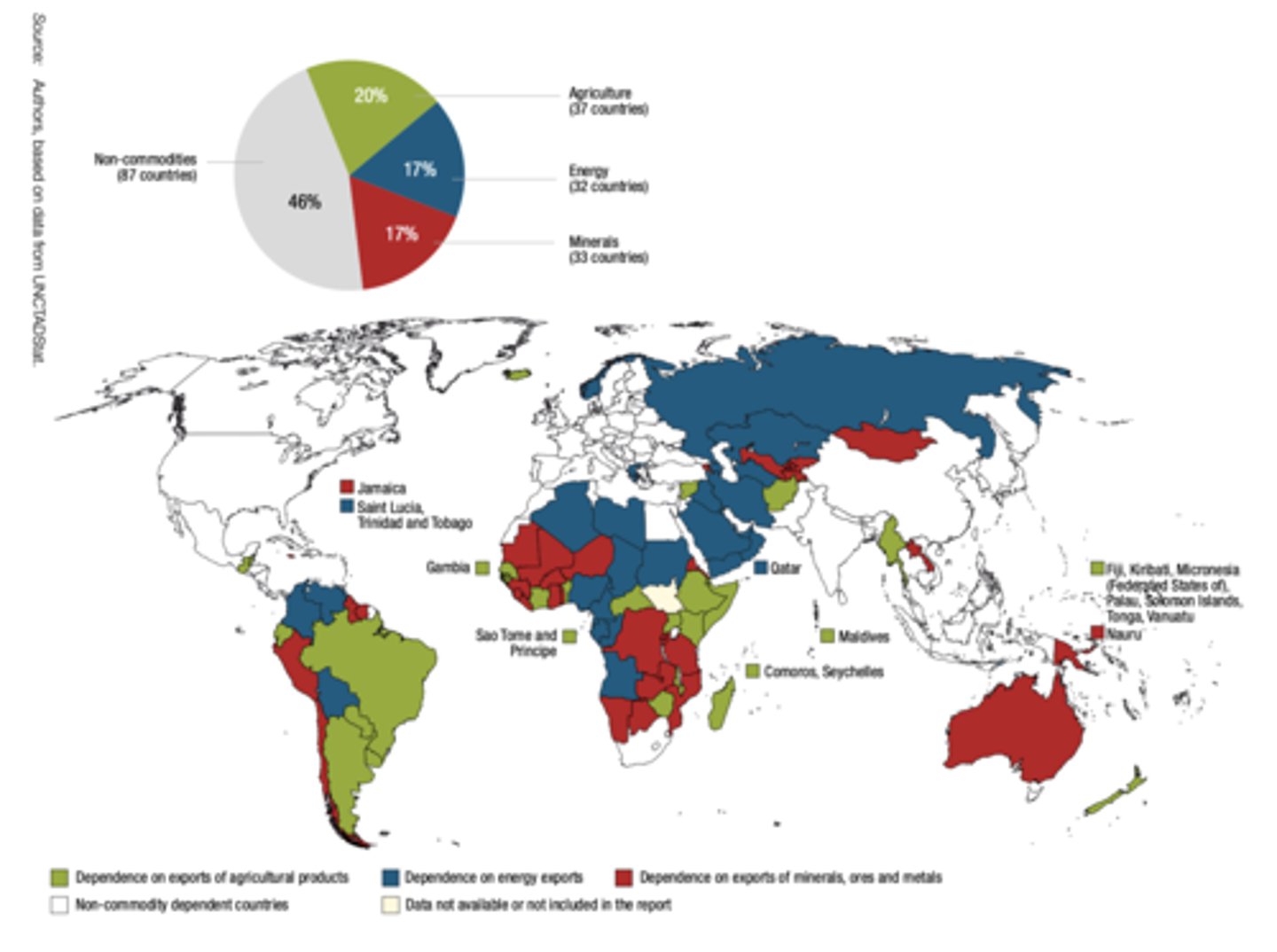
commodity dependence
An economy that relies on the export of primary commodities for a large share of its export earnings and hence economic growth
free trade agreement
Trade between nations that is not hindered by tariffs or other obstacles. On January 1, 1989, a free trade agreement between Canada and the United States came into effect.
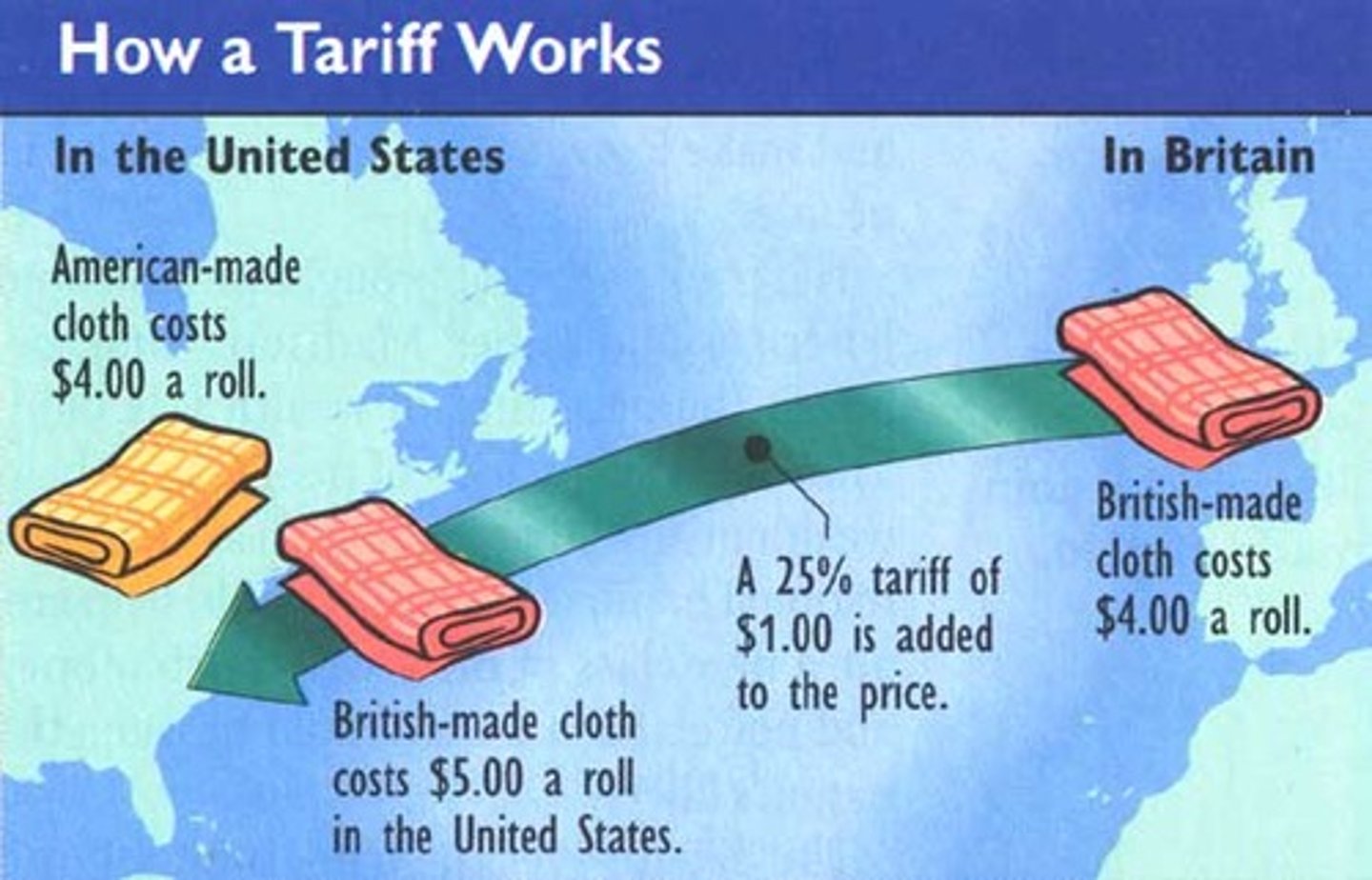
Tariff
A tax on imported goods
Global Financial Crisis (Debt Crisis)
The economic crashes that happened internationally due to the globalization of the world's economy. Problems in some countries (Europe and the United States), caused financial problems in countries that trade with them.
international division of labor
The process where the assembing procedures for a product are spread out through different parts of the world

Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Goals resulting from a UN-led effort to end extreme poverty by focusing on 17 key indicators, the top five of which are no poverty, zero hunger, good health, quality education, and gender equality, with key benchmarks for 2030.
