NSG 501 Exam 3: Medication Dosage Calculations MASTERY – NCLEX-Aligned Practice, IV Drip Rates & Expert Strategies (Instant Download)"with complete verified solutions 2025
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
medication math
converting and doing math to get the right dose for a patient
key points to medication math
>>Always double-check your work
>>Make sure you have the right units
>>Know your conversion factors
>>You are the final check before the patient*!!*
as nurses we need to know how to:
-do basic math
-need to check EPIC, MAR and what the pt dose is
should there be a trailing 0 after a decimal?
no!
No trailing zero after a decimal point or a whole number
1 mg (not 1.0 mg)
should there be a "naked" decimal point ( .4) ?
no!
No naked decimal point
0.5 ml (not .5 ml)
should there be a terminal period after units are listed?
no!
Use mg, ml, g, without a terminal period.
->Period could be mistaken as number 1 if written poorly.
mg (not mg.)
should there be a space between the number and the units? (10mg or 10 mg)
Numerical dose and unit of measure
>> Place adequate space between the dose and the unit of measure
10 mg (not 10mg)
should commas be used for # above 1,000?
yes, Use commas for dosing units at or above 1,000
can you use abbreviations?
Use only approved abbreviations
>do not want to confuse others
>we want to speak in a common language
unsafe abbreviations
many abbreviations you should NOT use
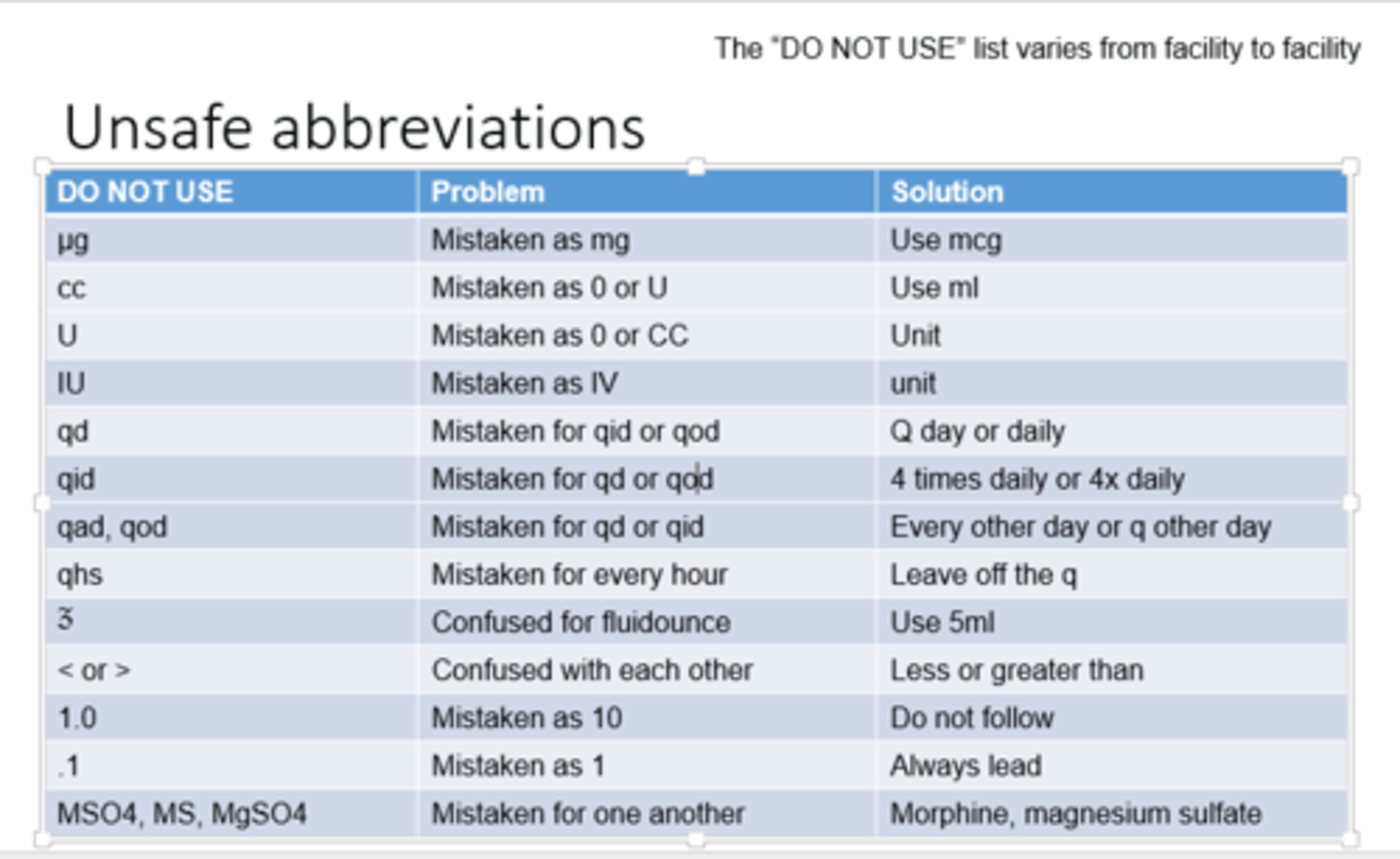
rules of rounding
> or = to 5 round up
<5 round down
Never round up medication in tablet form
--> 1.5 tablets remains as is; not 2 tablets
Each step of calculation must be carried out to at least the hundredth place
>aka do not round as you go, you can only round the final answer
->The final step or "final answer" is to be rounded:
>Tenths if greater than 1 (1.56 = 1.6)
>Hundredths is less than 1 (0.422 = 0.42)
medication math is all about getting the right answer of math problem T/F
no because it hold more value than just the right answer to the problem
-yes we need right answer
-but we also need to understand the importance of the correct dose!
dosage calculation conversions
you need to know/memorize these conversions

1 mg
1000 mcg
1g
1000 mg
1L
1000 mL
1 mL
1 cc
5 mL
1 Tsp
3 Tsp
1 tbsp
15 mL
1 tbsp
30 mL
1 oz
1 oz
2 tbsp
8 oz
1 cup
1kg
1000 grams (g) (gm)
1 kg
2.2 lbs
unit conversion
The process of changing a measure to an equivalent measure that has different units.
example: 1kg = 2.2 lbs
to convert from pounds to kg
# pounds / 2.2 = # of kg
To convert kilograms to pounds:
# of kg. x 2.2 = # of lbs.
If your patient weighs 140 lbs., how many kg. does he weigh?
140/2.2 = 63.63 kg (rounded to 63.6 kg)
If your patient weighs 92.4 kg., how many pounds does he weigh?
92.4 kg. x 2.2 = 203.28 lbs. (rounded to 203.3)
3 methods to med math
Formula method
Ratio proportion method
Dimensional analysis
formula method
Dose ordered x Quantity on hand /
Dose on Hand = amount to administer
Example: Patient to be given 60 mg of toradol IM. The vial of toradol contains 30mg/1mL. How many mililiters will you administer?
Dose ordered: 60mg
Quantity on hand: 1mL
Dose on Hand: 30mg
60mg x 1mL = 2 mL to be administered
30mg
ratio proportion method
Set up ratios that are equal to one another and cross-multiply to solve
dose ordered / amt to administer = dose on hand / quantity on hand
Ex: Example: Patient to be given 60 mg of toradol IM. The vial of toradol contains 30mg/1mL. How many milliliters will you administer?
Dose ordered: 60mg
Quantity on hand: 1mL
Dose on Hand: 30mg
60mg/ x mL = 30 mg / 1 mL = 30x =60 = x= 2 mL

dimensional analysis method
a method of problem solving whereby problems are set up so that unwanted units cancel
Dose ordered x concentration on hand
Allows for all math to be completed in one linear setup by matching up units to cancel out
Example: Patient to be given 60 mg of toradol IM. The vial of toradol contains 30mg/1mL. How many mililiters will you administer?
Dose ordered: 60mg
Concentration: 30mg/1mL
60mg x 1mL/30mg= 2 mL
A client is ordered 50 mg of gentamicin (Garamycin) by IM injection. The drug is available in 20 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer?
Answer: 12.5 mL
The doctor has ordered Solu-Medrol, 30mg IVP q8h for a patient with a COPD exacerbation. The vial comes as 150mg/2ml. How many ml will you give over 24 hours?
1.2 mL over 24 hours
Physician orders lasix 4mg/kg/day to be given q6 hours. Patient weighs 22 lbs and lasix comes in vials as 5mg/2mL. How many mL will you administer per dose?
4 mL/dose
infusion rates
formula:
total volume in mL / # of hours
ml per hour
example:
1000ml / 8 hrs
= 125 ml / hr
A doctor has ordered a 1.5L NS bolus to infuse over 2hours. What ml/hr will you set the pump to infuse this fluid?
750 ml/hour
for all these problems , where can i see the work?
the work for these problems is in the med math lecture
>lists steps for each method on solving!