Biotechnology: Cell Structure, Molecules, and Genetic Engineering
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
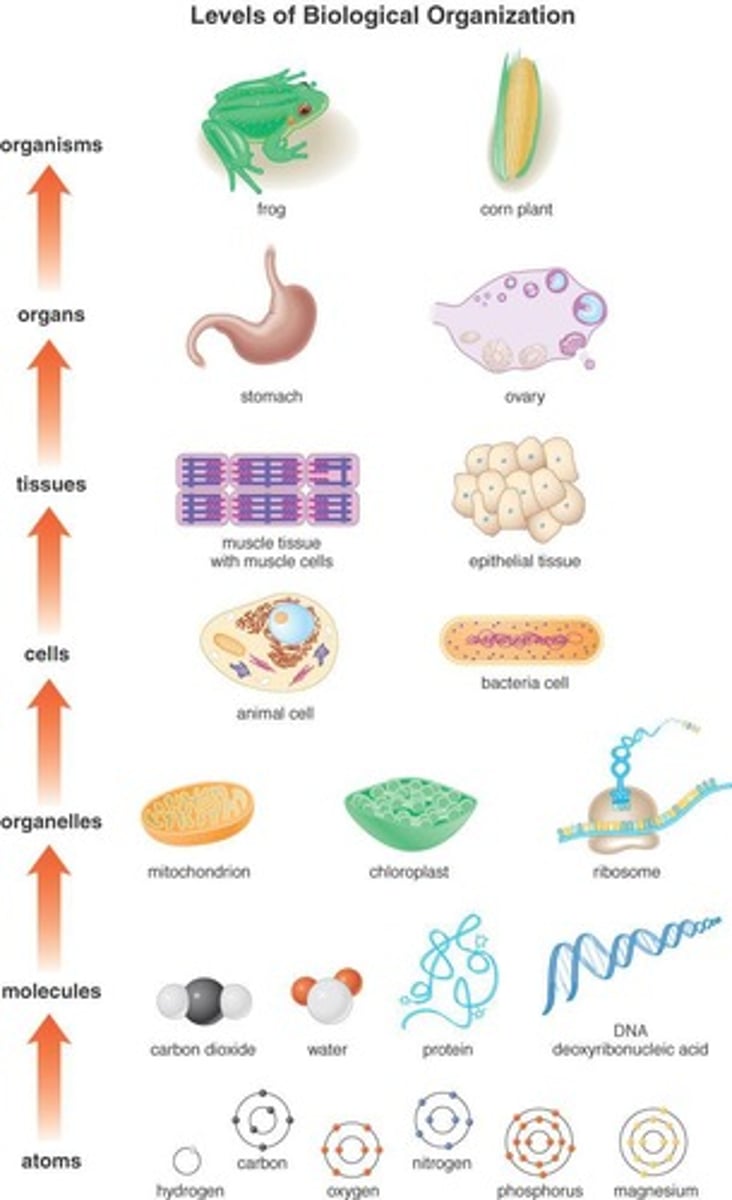
Levels of biological organization
The hierarchical structure of biological entities, ranging from molecules to organisms.
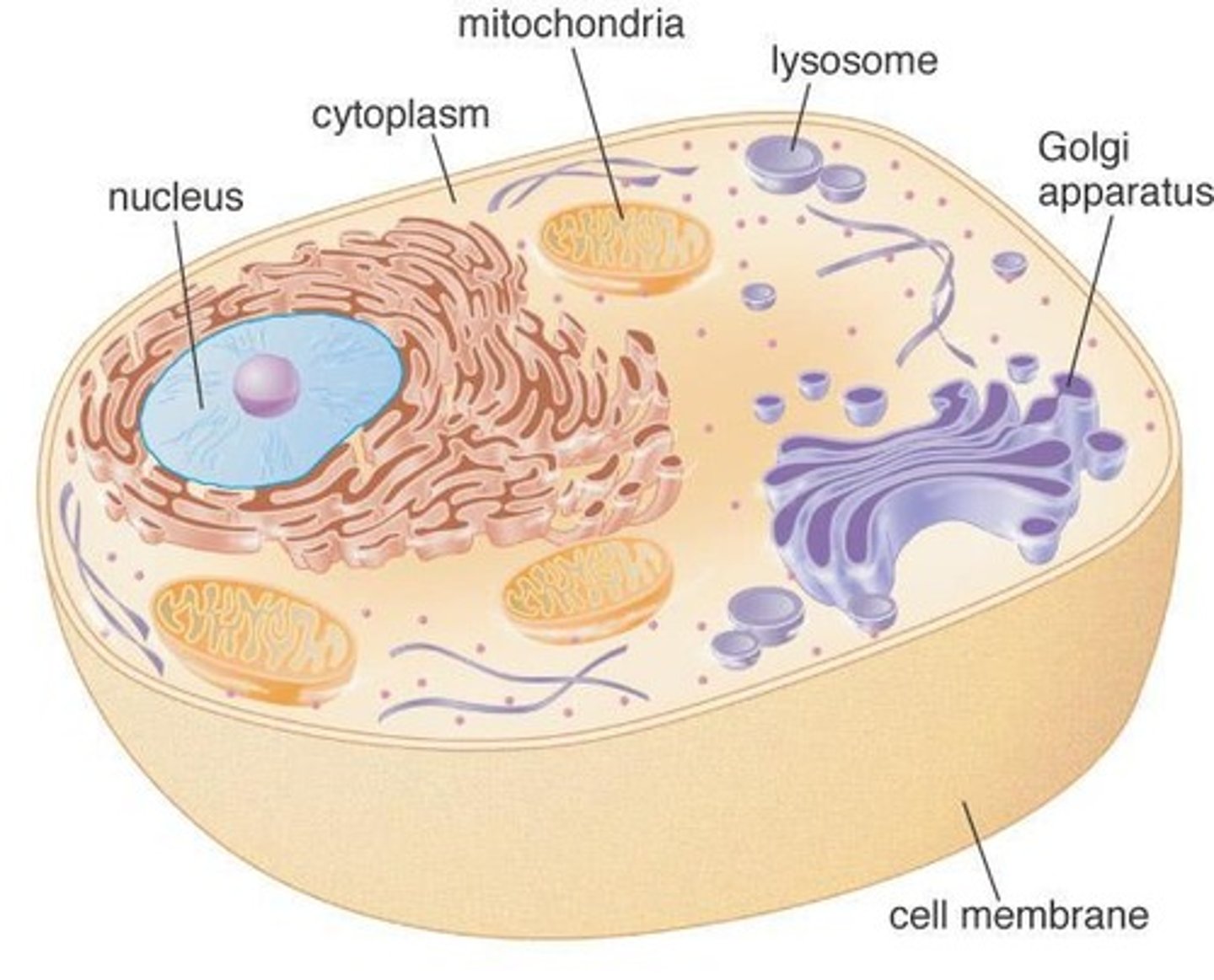
Cell structure
The arrangement and organization of cellular components, significant in biotechnology research and product development.
Types of organisms in biotechnology
Organisms researched and utilized in biotechnology, including plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, and protozoans.
Prokaryotic cells
Cells without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, typically unicellular organisms like bacteria.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in multicellular organisms.
Macromolecules
Large complex molecules essential for life, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Genetic engineering
The manipulation of an organism's DNA to create products or modify traits.
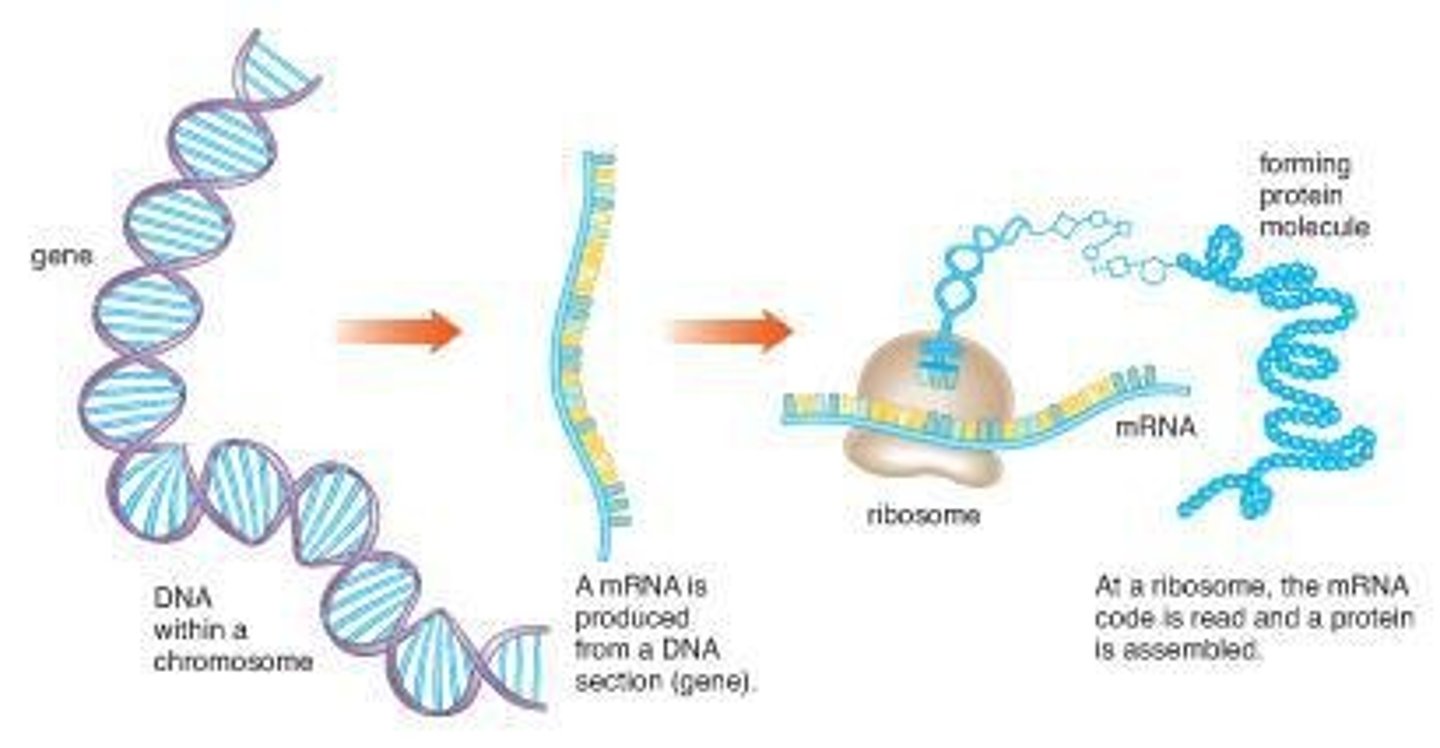
Central Dogma of Biology
The framework describing the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, crucial in genetic engineering.
Biotechnicians
Professionals who work with organisms and their components to manufacture biotechnology products.
Raw materials of biotechnology
Components such as molecules and cells used in the production of biotechnology products.
Functional units of multicellular organisms
The organization of cells into tissues and organs, which perform specific functions.
Characteristics of life
Features that define living things, including growth, reproduction, response to stimuli, breakdown of food molecules, and production of waste.
Unicellular organisms
Organisms consisting of a single cell.
Multicellular organisms
Organisms composed of multiple cells that work together.
Cells
The smallest units of life, containing organelles and capable of performing life processes.
Tissues
Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organs
Structures composed of different types of tissues that work together to perform complex functions.
HER2 antibody
A molecule used in the treatment of certain types of breast cancer.
Organism
a living thing
Cell
the smallest unit of life that makes up all living organisms
Escherichia coli
a bacterium that is commonly used by biotechnology companies for the development of products
Multicellular
composed of more than one cell
Cytology
cell biology
Anatomy
the structure and organization of living things
Physiology
the processes and functions of living things
Respiration
the breaking down of food molecules with the result of generating energy for the cell
Unicellular
composed of one cell
Tissue
a group of cells that function together (eg, muscle tissue or nervous tissue)
Organ
tissues that act together to form a specific function in an organism (eg, stomach that breaks down food)
Proteins
one of the four classes of macromolecules; folded, functional polypeptides that conduct various functions within and around a cell (eg, adding structural support, catalyzing reactions, transporting molecules)
Eukaryotic/eukaryote
a cell that contains membrane-bound organelles
Protist
an organism belonging to the Kingdom Protista, which includes protozoans, slime molds, and certain algae
Organelles
specialized microscopic factories, each with specific jobs in a cell
Mitochondria
membrane-bound organelles that are responsible for generating cellular energy
Sugar
a simple carbohydrate molecule composed of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen
Starch
a polysaccharide that is composed of many glucose molecules
Nucleic acid
a class of macromolecules that directs the synthesis of all other cellular molecules; often referred to as 'information-carrying molecules'
Lipids
one of the four classes of macromolecules; includes fats, waxes, steroids, and oils
Pancreas
an organ that secretes digestive fluids as well as insulin
Hormone
a molecule that acts to regulate cellular functions
Chlorophyll
the green-pigmented molecules found in plants; used for photosynthesis (production of chemical energy from light energy)
Photosynthesis
a process by which plants or algae use light energy to make chemical energy
Chloroplast
the specialized organelle in plants responsible for photosynthesis (production of chemical energy from light energy)
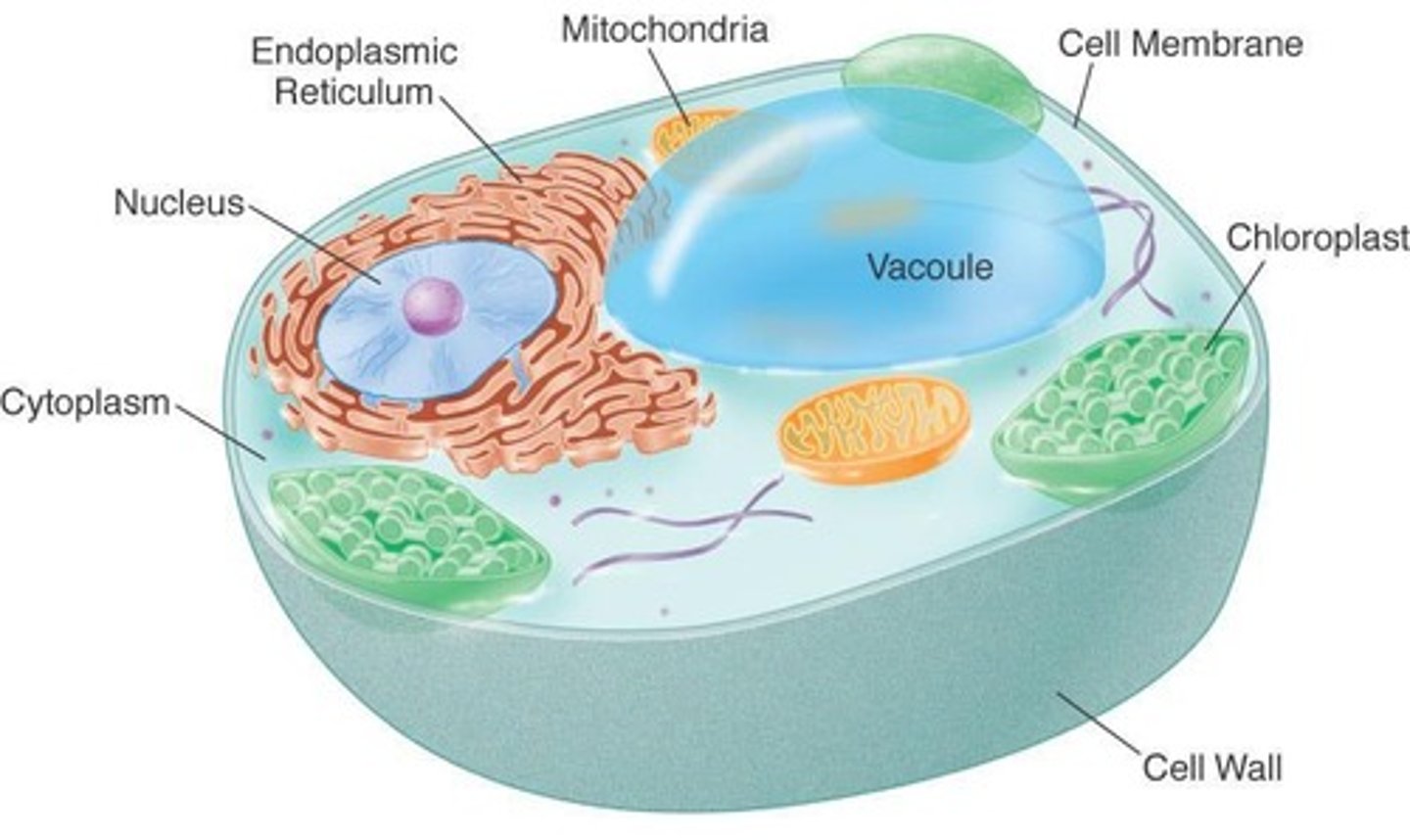
Cytoplasm
a gel-like liquid of thousands of molecules suspended in water, outside the nucleus
Lysosome
a membrane-bound organelle that is responsible for the breakdown of cellular waste
Ribosome
the organelle in a cell where proteins are made
Cell wall
a specialized organelle surrounding the cells of plants, bacteria, and some fungi; gives support around the outer boundary of the cell
Cellulose
a structural polysaccharide that is found in plant cell walls
Plasma membrane
a specialized organelle of the cell that regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell
Glucose
a 6-carbon sugar that is produced during photosynthesis reactions; usual form of carbohydrate used by animals, including humans
Adenosine triphosphate
a nucleotide that serves as an energy storage molecule
Nucleus
a membrane-bound organelle that encloses the cell's DNA
Chromosomes
the long strands of DNA intertwined with protein molecules
Enzyme
a protein that functions to speed up chemical reactions
Pigments
the molecules that are colored due to the reflection of specific wavelengths
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
a class of RNA molecules responsible for transferring genetic information from the chromosomes to ribosomes where proteins are made; often abbreviated mRNA
Amino acids
the subunits of proteins; each contains a central carbon atom attached to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a distinctive "R" group
Polypeptides
a strand of amino acids connected to each other through peptide bonds
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)
an animal cell line commonly used in biotechnology studies
Vero cells
African green monkey kidney epithelial cells
HeLa cells
human epithelial cells
Prokaryotic/prokaryote
a cell that lacks membrane-bound organelles
Carbohydrates
Molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically in a ratio of 1:2:1.
Monosaccharides
Monomer units that cells use to build polysaccharides; the most well-known is glucose.
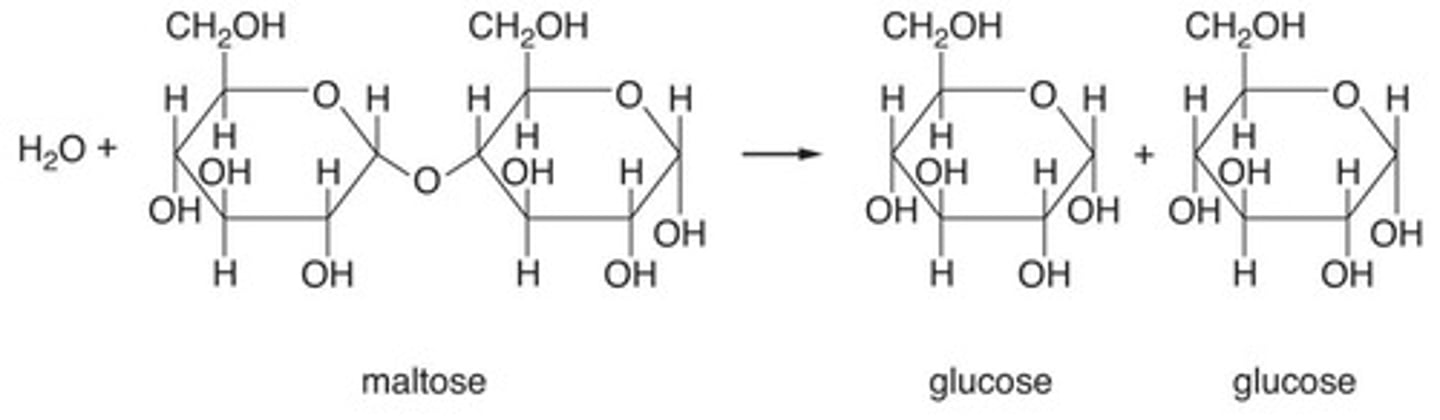
Disaccharides
Formed by enzymes creating a bond between two monosaccharides; an example is sucrose, which is composed of fructose and glucose.
Polysaccharides
Molecules built from carbohydrate monomers, serving as excellent structural and energy-storing molecules.
Maltose
A disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules bound at carbon No.1 and carbon No.4.
Triglycerides
A group of lipids that are a type of fat.
Phospholipids
Lipids that make up cell membranes, forming a bilayer with hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic glycerol heads.
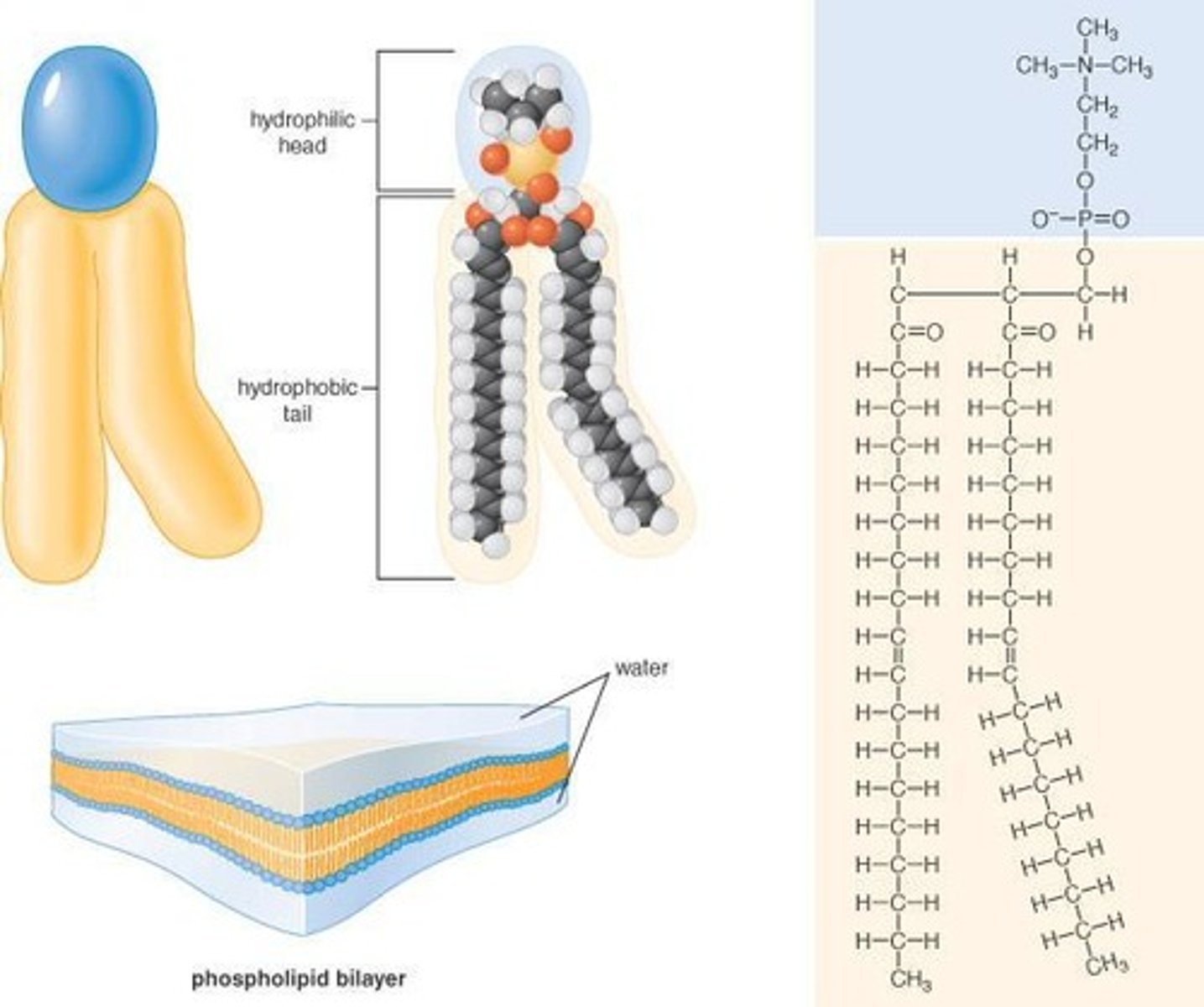
Steroids
A group of lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.
Polypeptide
A long chain of amino acids connected through peptide bonds.
Functional protein
A protein that consists of one or more folded polypeptides.
Nucleic acids
Macromolecules composed of nucleotide monomer units, including DNA and RNA.
Nucleotide
A molecule composed of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
Nitrogenous base
A component of nucleotides that can be single- or double-ringed.
5-carbon sugar
A component of nucleotides that forms part of the structure of DNA and RNA.
Phosphate group (PO4)
A component of nucleotides that is involved in the formation of nucleic acids.
Double helix
Structure formed by two strands of nucleotide monomer units.
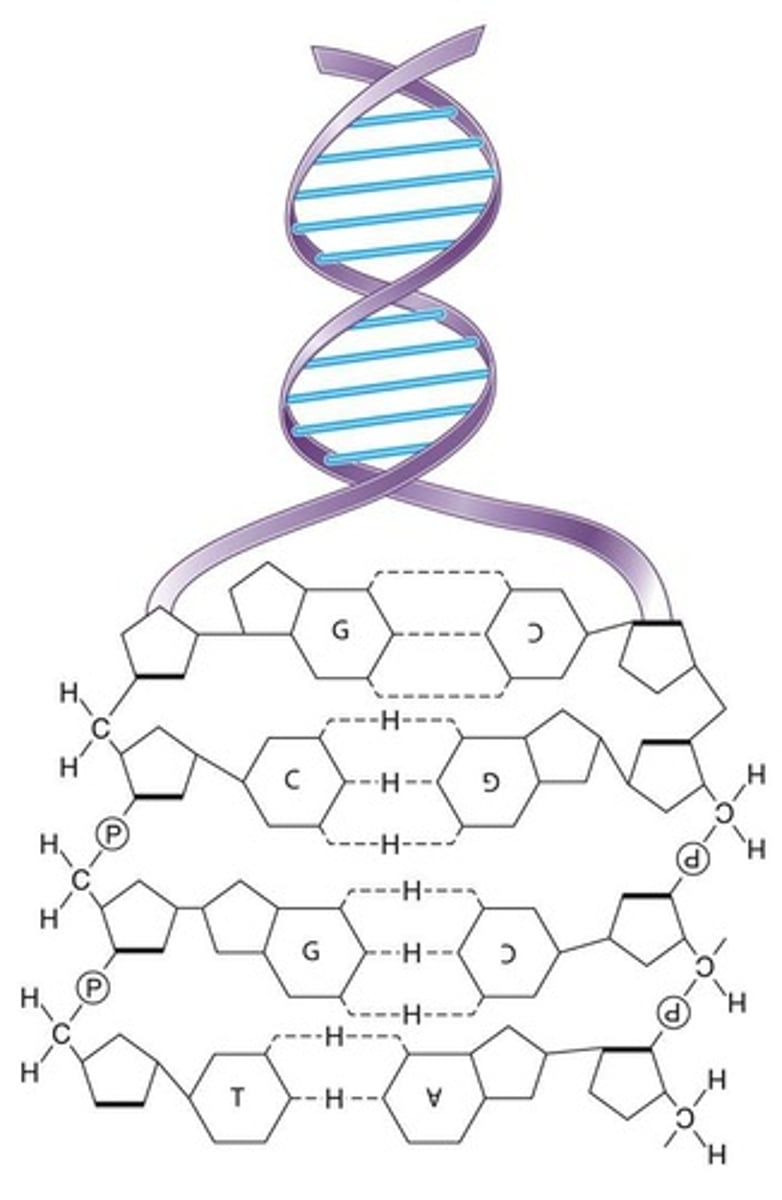
Anti-parallel strands
The orientation of the two strands in a DNA molecule.
Adenine
A nitrogenous base that bonds to thymine with 2 hydrogen bonds.
Thymine
A nitrogenous base that bonds to adenine with 2 hydrogen bonds.
Guanine
A nitrogenous base that binds to cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds.
Cytosine
A nitrogenous base that binds to guanine with 3 hydrogen bonds.
Macromolecule
A large molecule usually composed of smaller repeating units chained together.
Organic
Molecules that contain carbon and are only produced in living things.
Cytoskeleton
A protein network in the cytoplasm that gives the cell structural support.
Monomers
The repeating units that make up polymers.
Polymer
A large molecule made of many repeating subunits.
Monosaccharide
The monomer unit that cells use to build polysaccharides; also known as a 'single sugar' or 'simple sugar'.
Disaccharide
A polymer that consists of two sugar molecules.
Polysaccharide
A long polymer composed of many simple sugar molecules (usually glucose or a variation of glucose).
Fructose
A 6-carbon sugar found in high concentration in fruits; also called fruit sugar.
Sucrose
A disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose; also called table sugar.
Lactose
A disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose; also called milk sugar.
Amylose
A plant starch with unbranched glucose chains.
Amylopectin
A plant starch with branched glucose chains.
Glycogen
An animal starch with branched glucose chains.
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells break down glucose to create other energy molecules.
Deoxyribose
The 5-carbon sugar found in DNA molecules.
Hydrophobic
Repelled by water.