Animal Science Practical 2 (mine)
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Anatomy
The branch of science that corresponds with the structure of organisms (skeletal, digestive ,reproductive, etc.).
Cranial
Towards the head of the animal in relation to the entire body. This can also refer towards the front of the leg on an animal.
Caudal
Towards the tail of the animal in relation to the entire body.This can also refer towards the back of the leg on an animal.
Rostral
Within the head this refers to towards the nose.
Caudal
within the head refers towards the poll.
Medial
Refers towards the center or midline of the animal.
Lateral
Refers towards the outside or away from the midline or center of the animal.
Dorsal
Directed towards the spine of the animal's thoracic trunk.
Ventral
Directed towards the belly or the ground of the animal's thoracic trunk.
Proximal
Parts of the limb closest to trunk of animal (above the knee or hock joint).
Distal
Parts of the limb closest to the ground (below the knee or hock joint)
Palmar
The part of the foot that is contacting the ground.
Dorsal
In reference to the limbs, the opposite of palmar of the foot.
Integumentary System
Acts as a protective barrier to internal organs.
Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac.
Muscles can be divided into three categories:
Smooth Muscles
Involuntary movement; located in the body systems with autonomic function such as the digestive tract and determining size of the eye pupil due to light (dilation vs. constriction).
Skeletal Muscles
Voluntary movements; movements the animal can control such as movement of the limbs, trunk, and head. Skeletal muscles also make up the meat humans are accustomed to consuming such as beef, pork, and lamb.
Cardiac Muscles
Involuntary movement; these muscles are restricted to the heart.
Bones, Cartilage, and Teeth.
Skeletal system includes:
Brain, Spinal Cord, and Peripheral Nerves.
Nervous system consists of:
Trachea, Larynx, and Pharynx.
The airway contains:
Bronchi and Alveoli
Within the lungs, there are branches and little air sacs known as:
Ventilation
The movement of air in and out of the lungs.
Cardiovascular System
This system contains the heart and blood vessels to transport blood to the tissues in the body and to the lungs for the exchange of gas (carbon dioxide and oxygen).
Arteries
Carries oxygenated blood at high pressure to the entire body.
Veins
Carries de-oxygenated blood at lower pressures back to the heart.
Capillaries
Small, branching blood vessels connecting veins and arteries.The main function of capillaries is to exchange materials from blood and tissue (oxygen, carbon dioxide, cellular waste from metabolism).
Pulmonary circulation
Refers to the blood that circulates through the lungs.
Systemic circulation
Refers to the blood that circulates throughout the entirety of the body.
Two kidneys, two ureters, bladder, and urethra.
The urinary system consists of:
Immune System
Is responsible for fighting off any pathogenic microorganisms that can cause an animal to become ill.
Hormones
Are responsible for growth and development of the animal.
USDA Quality grades
a composite evaluation of factors that affect palatability of meat (tenderness, juiciness, and flavor). These factors include carcass maturity, firmness, texture, and color of lean, and the amount and distribution of marbling within the lean.
Dressing percentage
The ratio of dressed carcass weight to the weight of the live animal, expressed as a percentage
Yield Grade
is an estimate of the percent retail yield of boneless, closely trimmed retail cuts from the high-value parts of the carcass–the round, loin, rib, and chuck.
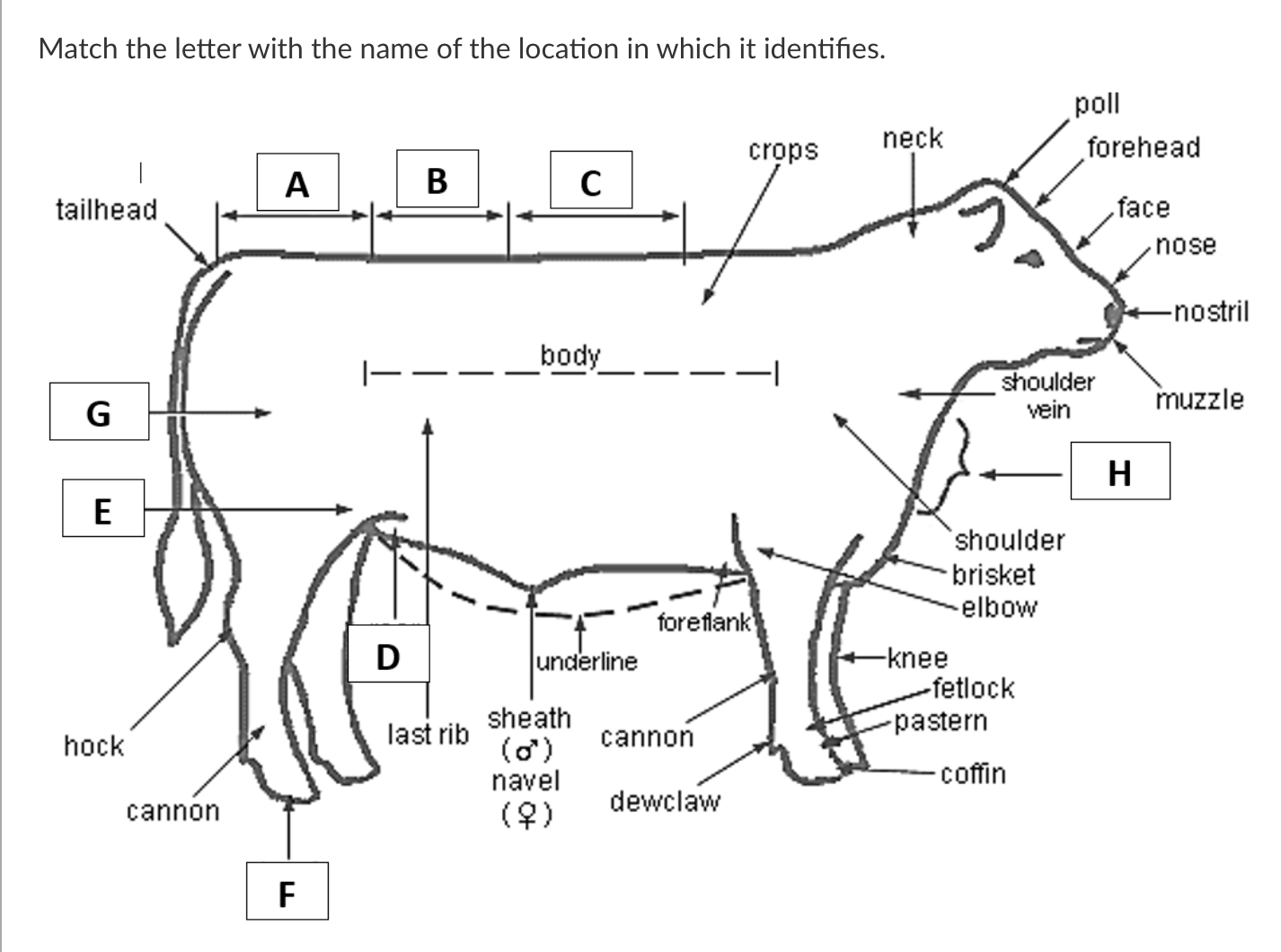
A
Rump
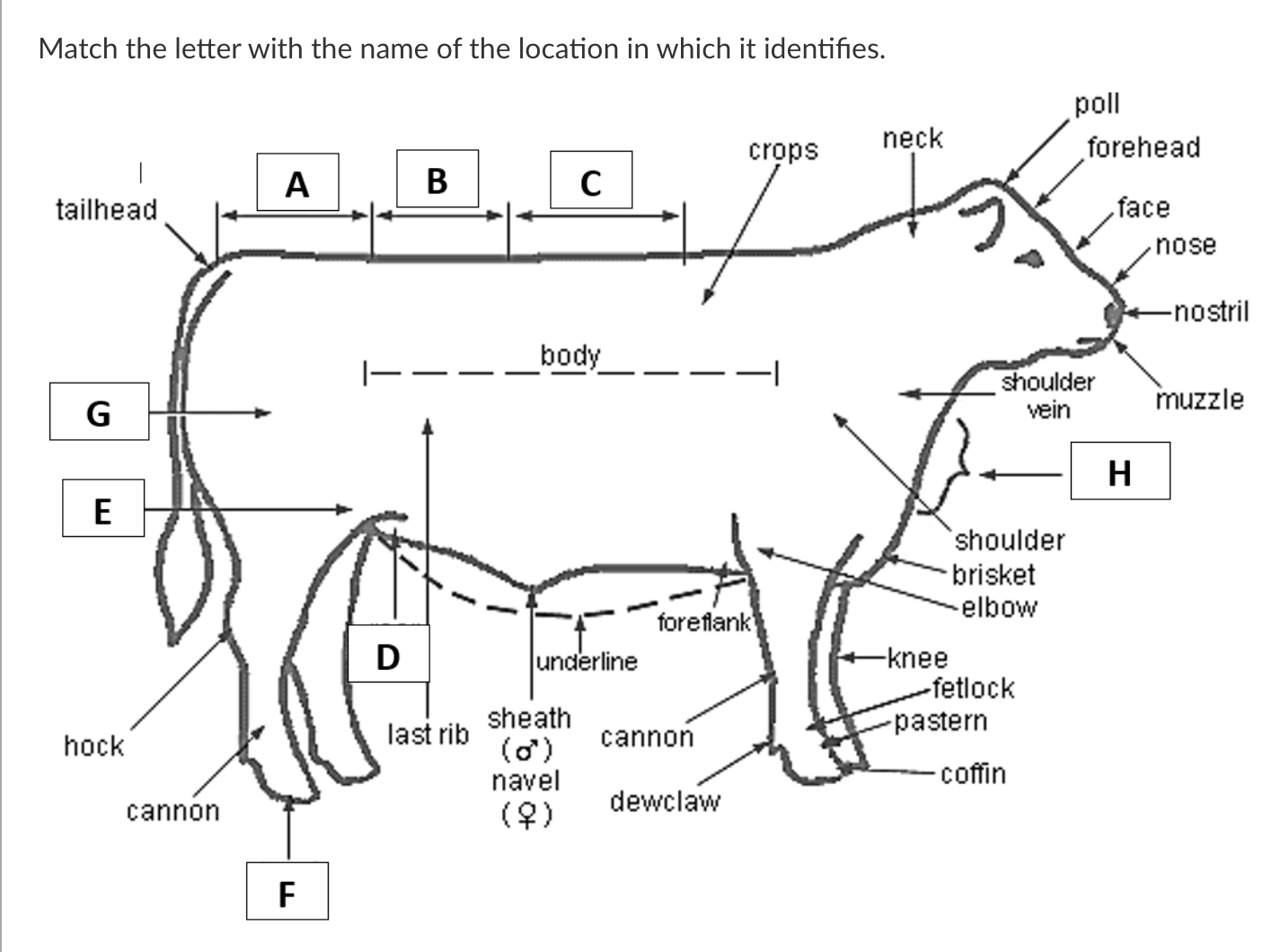
B
Loin
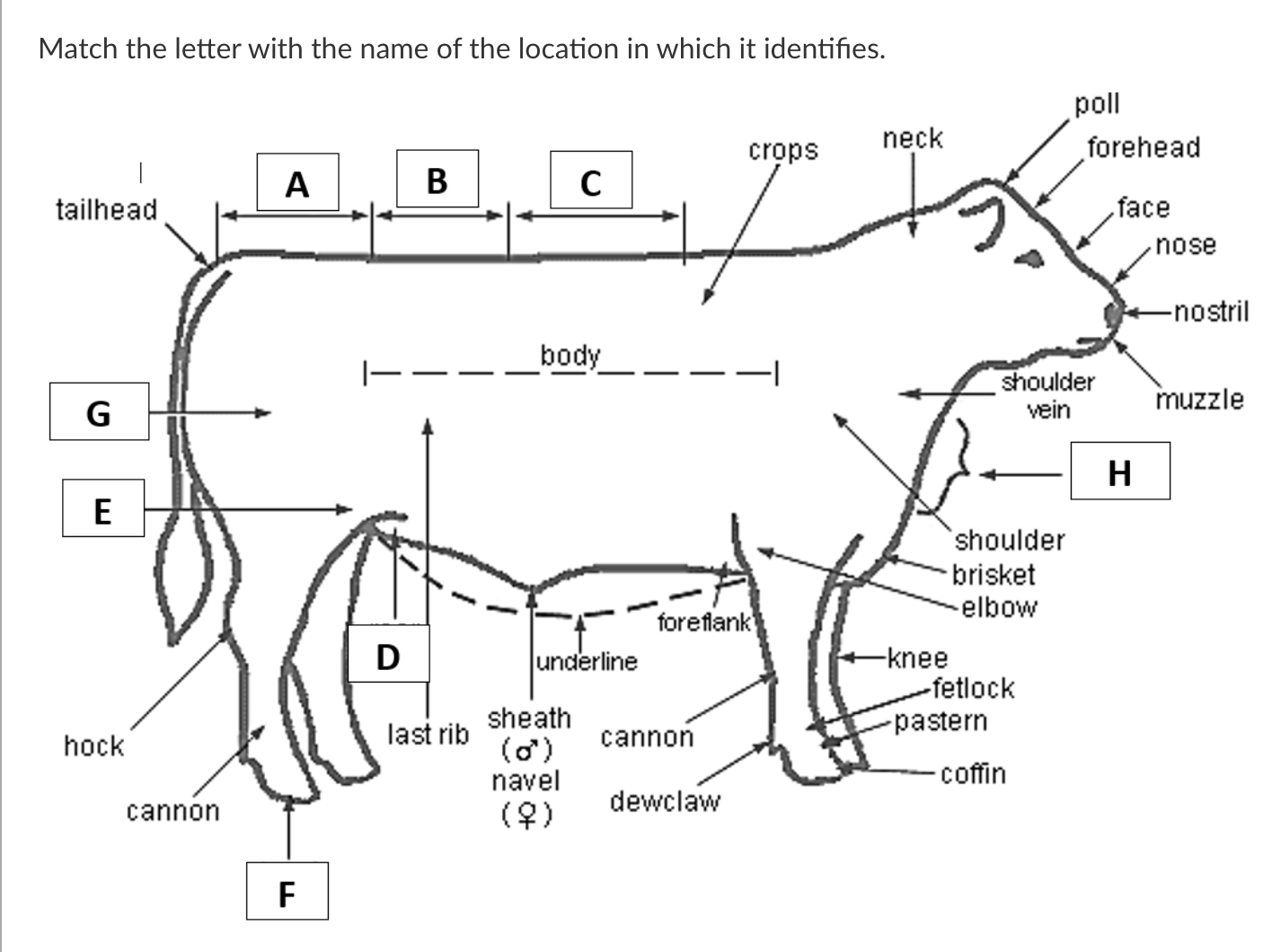
C
Back
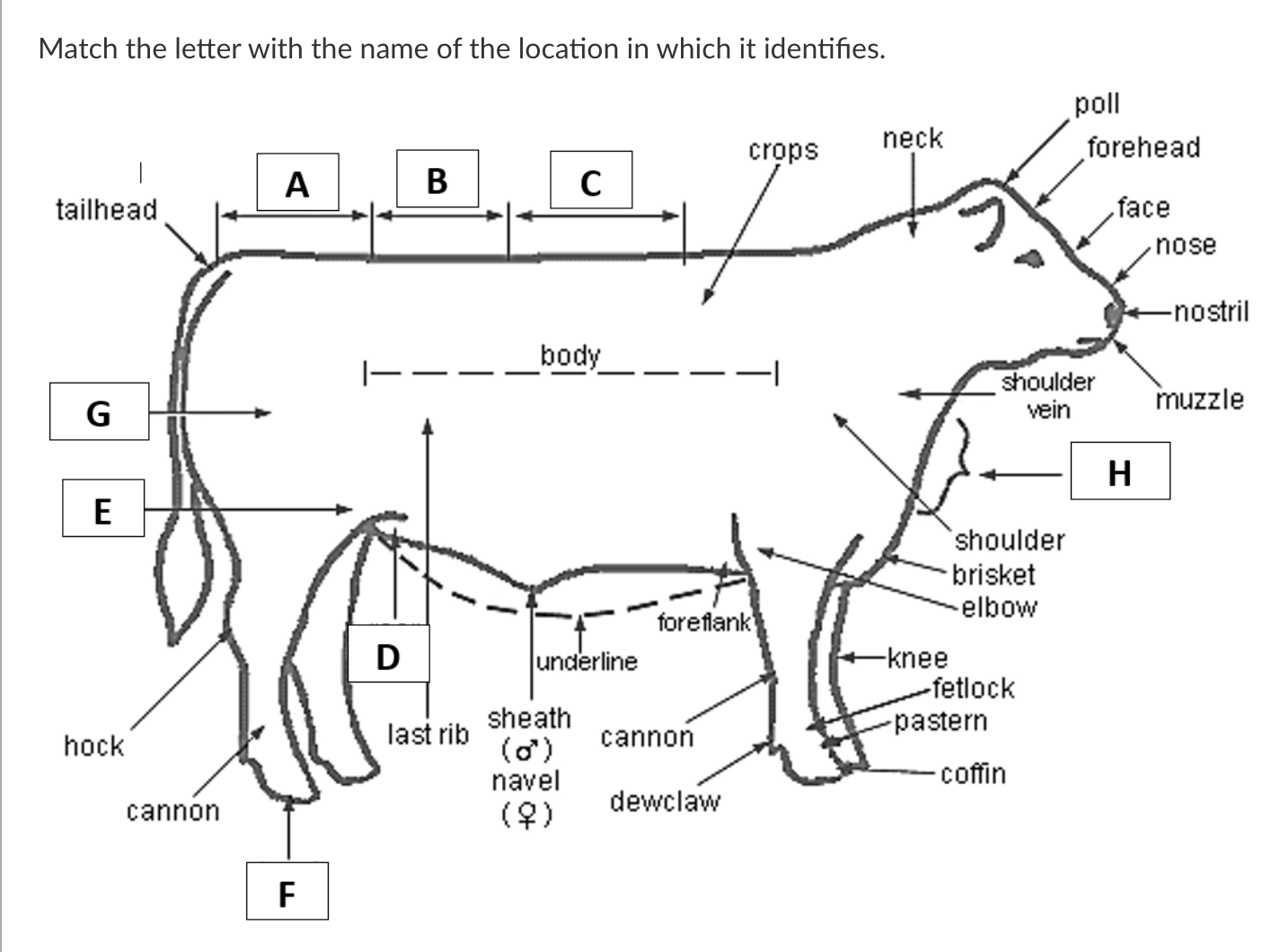
D
Rear Flank
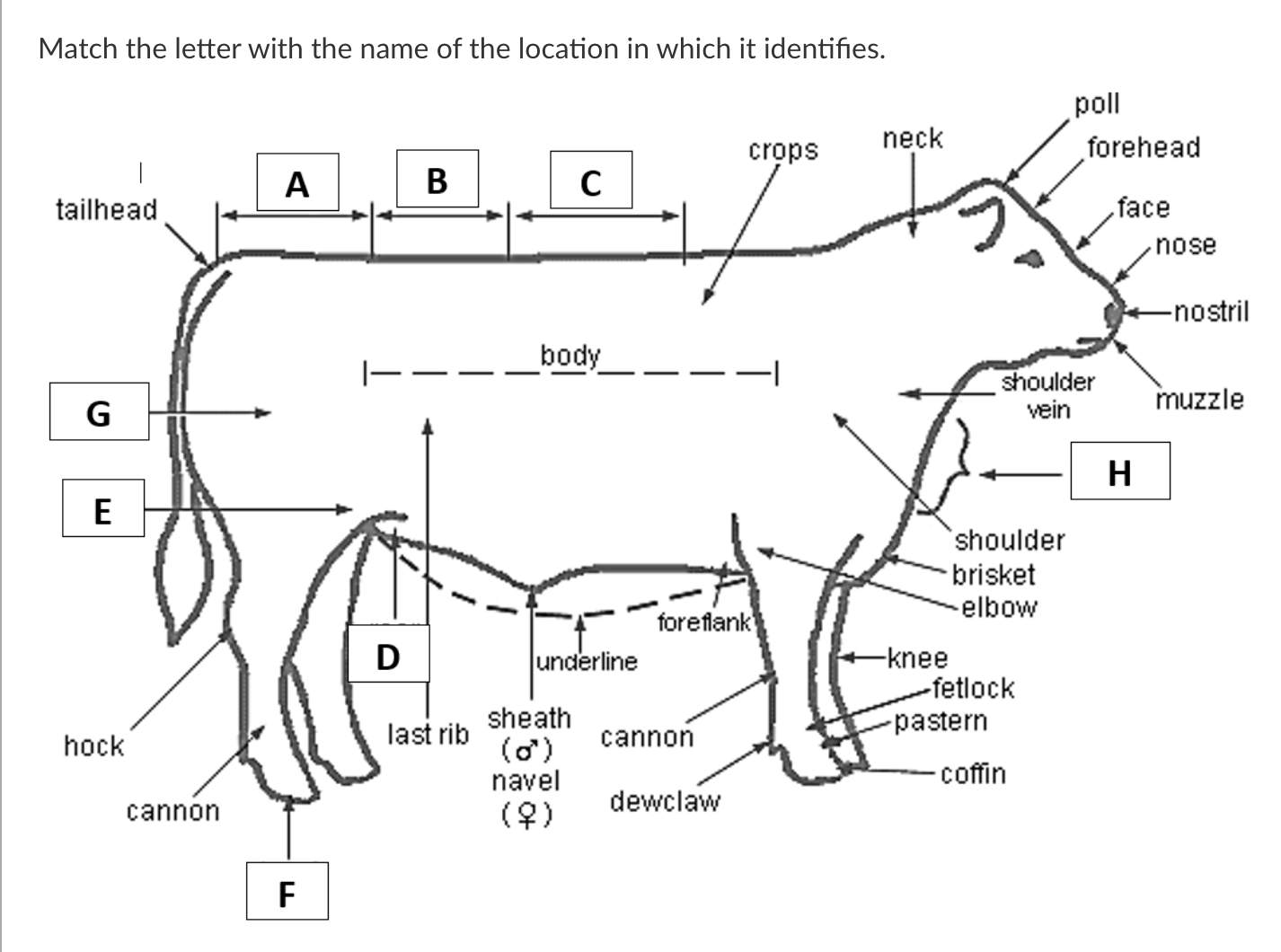
E
Stifle
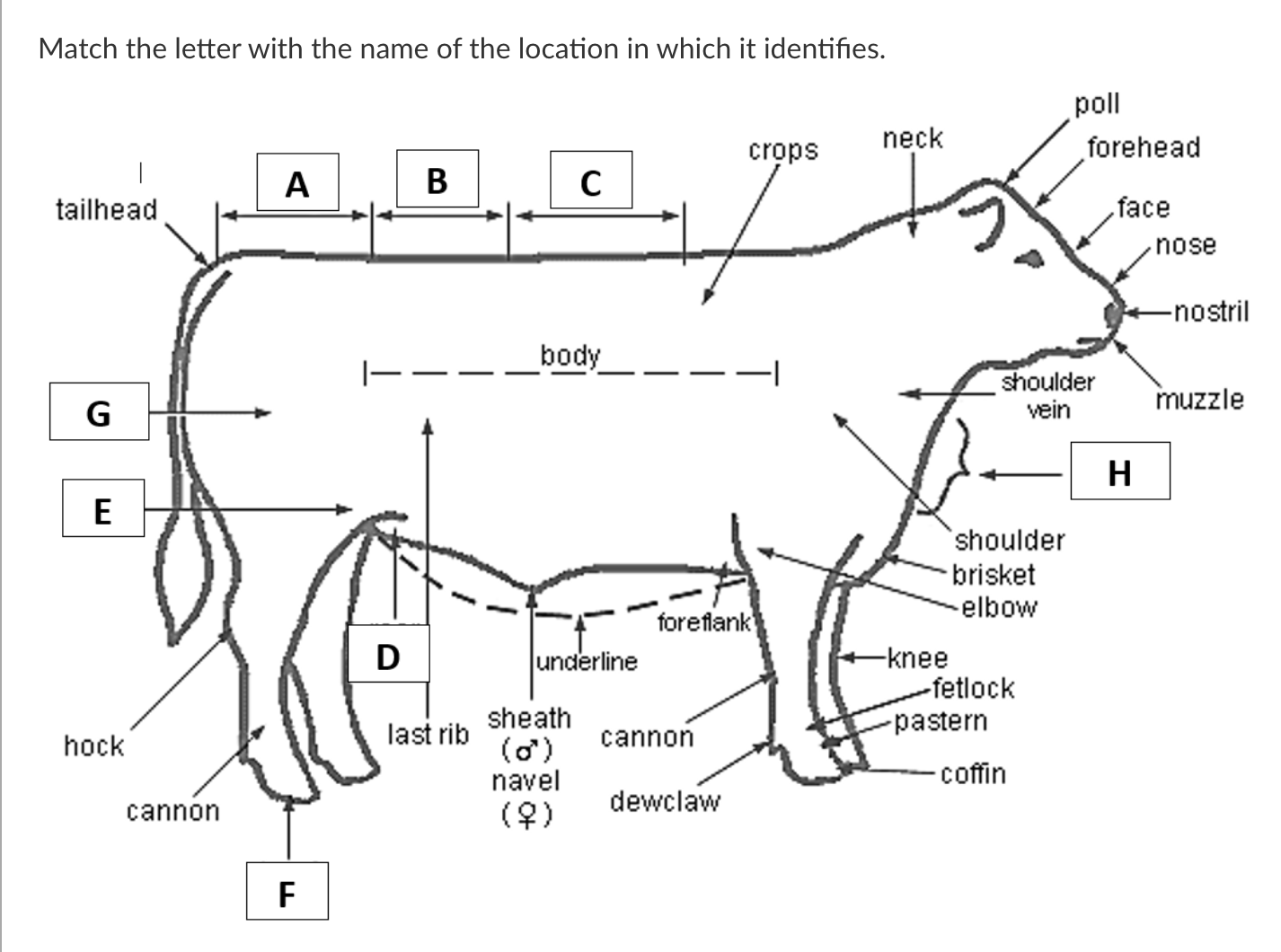
F
Hoof
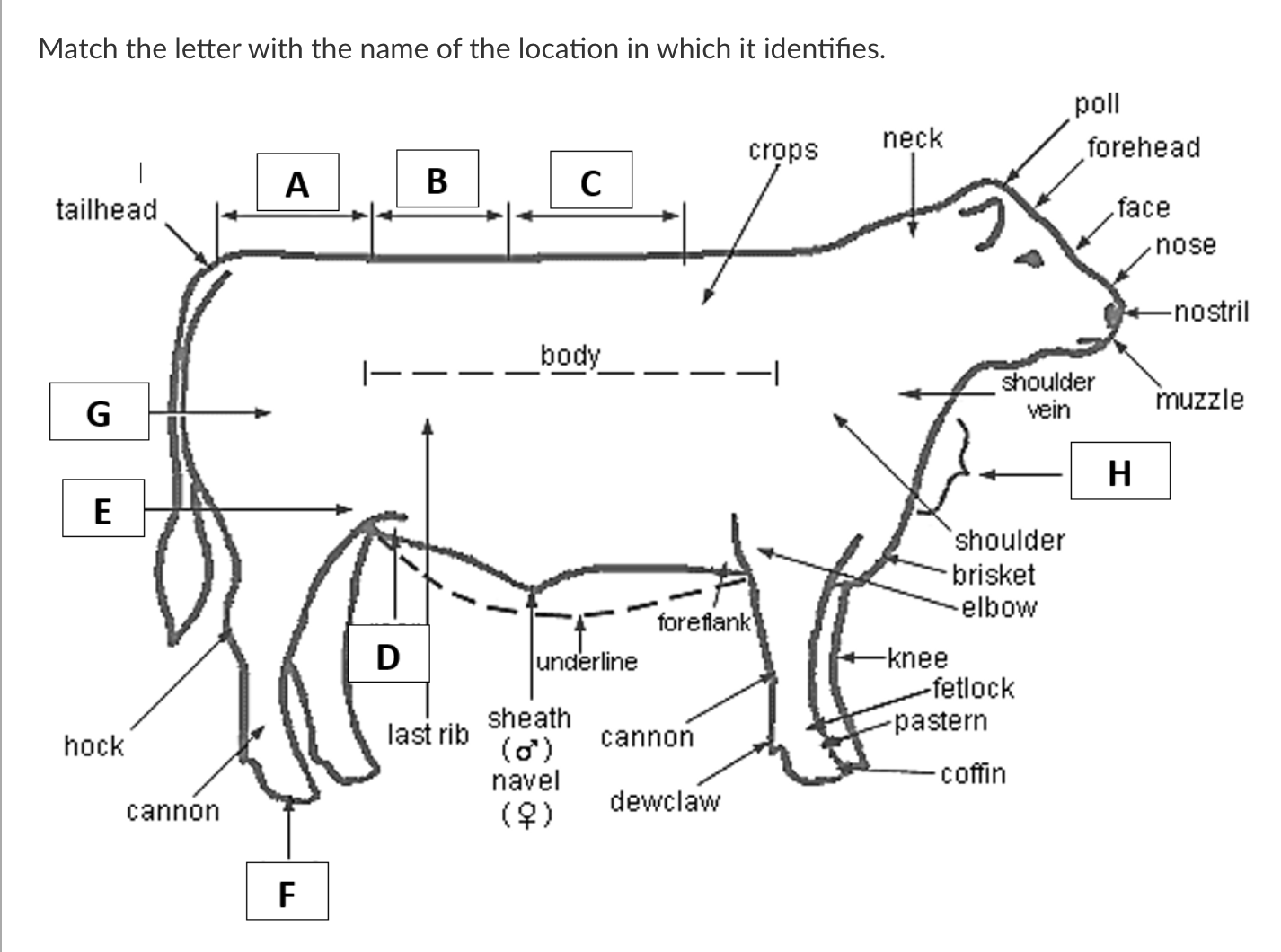
G
Quarter
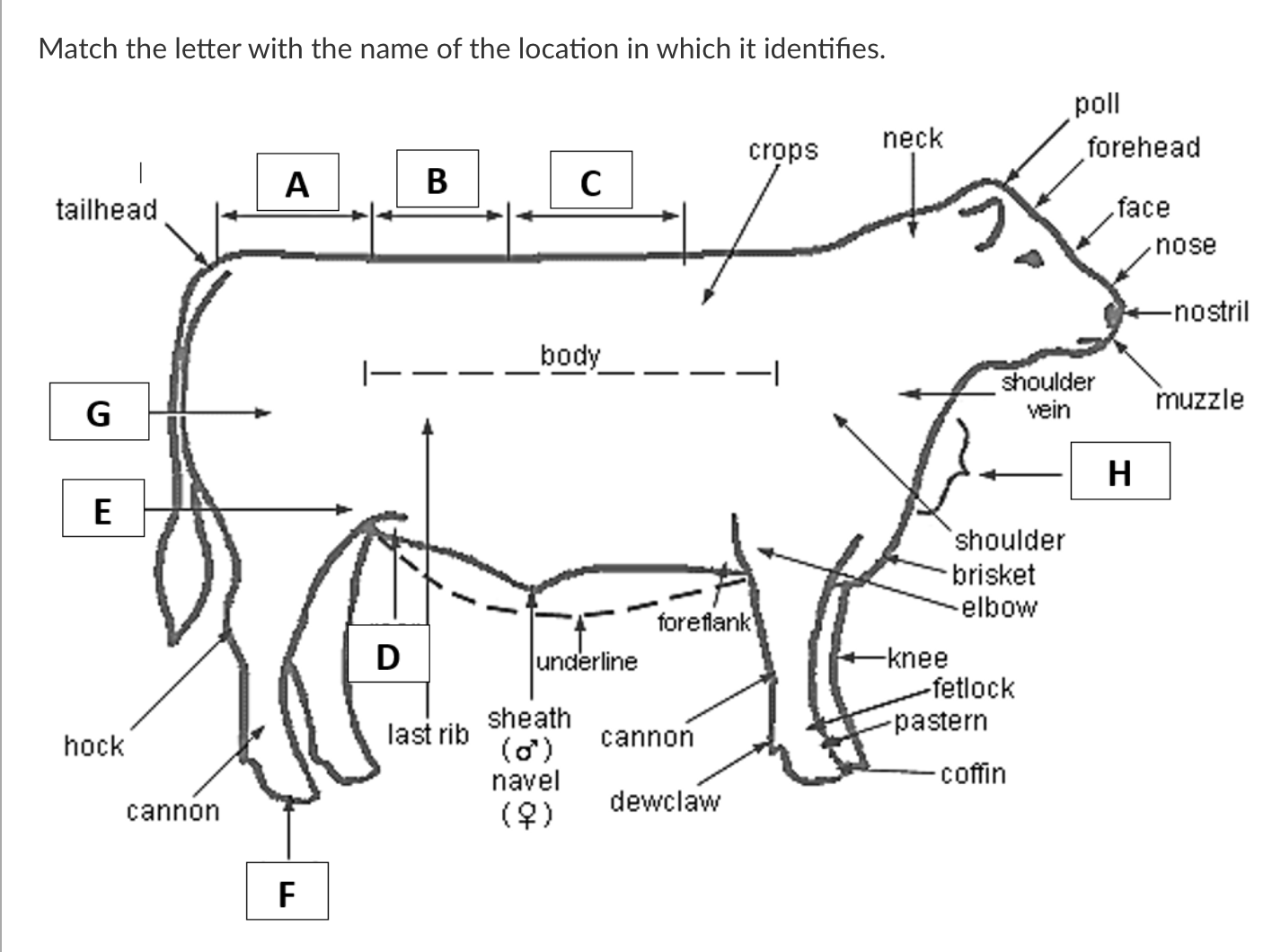
H
Dewlap
A cow that looks to be emaciated on physical evaluation having no palatable fat over her spine or ribs would receive a BCS of?
1
Femininity is a must in females and will correlate to udder quality.
true
Grasses and legumes are examples of concentrates.
false
Grains like milo, corn and barley are examples of concentrates
true
Where is the point of balance or the neutral zone located on the horse?
shoulder
Which of the following is one of the 6 regions evaluated for body condition scoring in horses ?
Feet and Legs
Along the neck
Frame
Muscling
along the neck
Which of the following is not one of the three uses for horses in the United States?
Recreation
Meat
Performance
Reproduction
meat
What type of parlor does the Southwest Regional Dairy Center have?
rotary
How are the manure alleys in the barn at the Southwest Regional Dairy cleaned?
recycled effluent
What color leg band denotes that cows at the Southwest Regional Dairy have received antibiotics?
red
What type of barns does the Southwest Regional Dairy Center have?
freestalls
Located at the cow’s breast, the lower chest area. This cut is low in fat content, it’s one of the cow’s most used muscles.
brisket
Located in the lower abdomen, the chest part of the cow. Due to the muscles, it’s a tough meat
shank
Located below the rib cut, in other words, the center belly of the cow.
short plate
located in the center back of the cow. Quite flavorful part of the making this one of the most expensive cuts.
rib
cut is located at the front chest and top of a cow including shoulder and neck parts.
chuck
Located in the lower back of the cow. This meat is very soft and tender, that’s why loin cuts are great for juicy steaks.
loin
Located in the rear part of the cow. Contains less fat content so making it a a tough cut, which also means that it’s a very cheap cut.
round
This primal meat cut is from the belly or underside part of the cow. Sub-primal cuts: Ground Beef, London Broil, and Flank Steak.
flank
avg. beef dressing %
64
avg. sheep / lamb dressing %
51
avg. pork %
74
Is the boston shoulder the upper or lower part of a pork shoulder?
upper (picnic lower)
what is the main ingredient in TMR
corn silage
what is the predominant breed at SW diary center
crossbreed
what type of bedding is used at SW center
sand
who does the SW dairy center sell their milk to ?
Dairy Farmers of America
what kind of germicide is used to clean a cows teats?
iodine
why do we use HOJO's? Holstein, jersey crosses
holstein- milk quantity
jersey- fat, buttery milk
how often are the cows fed dairy
2x
what is recycled effluent
water recycled from lagoon
what through what # BCS are dairy cattle scored
1-5
what is the avg. cow temp
99-102 degrees
what is a rumen cannula?
the device used to open the outside of cow to rumen for research
is our center thru a private producer?
yes
approx. how many cows does the center have
400 ish
how many times and when are they milked
3x
6am
2pm
10pm
what is the advantage of the rotary parlor system
less employees needed
how long does it take to completely milk vs. a full rotation on the parlor?
5-7 min
11 min rotations
at what temp. do cattle begin to heat stress
65 degrees F
what is the avg. amount of milk produced per cow per day
60-80 up to 96
what are part of the baseline evaluation for feeder cattle
size of frame , muscling, thriftiness
what is frame scoring
a tool used to evaluate the mature skeletal size of an animal
1-9
t or f: hip height on beef cattle are used to project finishing weights and is used to calculate frame score
true
t or f: structure is heritable and can be improved genetically
true
t or f: leg structure (hind specifically) shows the importance and longevity of a cow
true
define fleshing
the ability to naturally maintain body condition without supplements being fed thru various climates etc. (good vs. bad keepers)
what is the range for BCS
1-9
what are we looking for when evaluating the mammary system on a heifer
teat size and shape
udder depth
udder balance
udder quality
what are the top two things to be kept in mind when handling cattle
POB & flight zone
on avg. per capita, how much pork does the avg. american consume
50.6# per capita
t or f: pork is the most consumed worldwide at 36%
true
the amount of beef eaten in the US accounts for how much of the worlds % of beef eaten
21%
how much of meat sales does lamb account for
1%
on avg. how many head of beef do we slaughter a year
30.6 million
on avg. how many head of sheep/lamb do we slaughter a year
2.1 mil
on avg. how many head of hogs do we slaughter a year
121.3