chapter 3 boiii
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
word Equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP
2
New cards
Balance chemical equation for aerobic respiraation
C6H12C6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H20 + 38ATP
3
New cards
where does krebs cycle occur
mitochondria
4
New cards
How much ATP made in krebs cyle
2
5
New cards
how much ATP is made in
oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation
32
6
New cards
How much ATP is made in glycosis
2
7
New cards
stages of aeroobic respiration
glycolysis, the link reaction, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
8
New cards
structure of ATP
a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups
9
New cards
define metabolism
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms
10
New cards
what is anabolism
synthesis of complex molecules in living __organisms__ from __simpler__ ones together with the storage of energy; __constructive__ metabolism.
11
New cards
what is a substrate
the substance on which an __enzyme__ acts
12
New cards
what is catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules in living __organisms__ to form __simpler__ ones, together with the release of energy; __destructive__ metabolism.
13
New cards
example of catabolism
Catabolism occurs when you're digesting food. For example, it's the process that dissolves a piece of bread into simple nutrients your body can use, like glucose (blood sugar)
\
also the breakdown of proteins into amino acids, glycogen into glucose, and triglycerides into fatty acids.
\
also the breakdown of proteins into amino acids, glycogen into glucose, and triglycerides into fatty acids.
14
New cards
example of anabolism
Bone development and mineralization, as well as muscle mass gain, are examples of anabolism.
15
New cards
inorganic substance importance for cell + define
they are compounds that arent based on carbon chain and most dont contain carbon atams, most are small molecules, these include minerals and water beacause they dont have carbon, used as catalysts, pigments, coatings, surfactants, medicines, fuels
16
New cards
organic substance importance for cell + define
molecules that contain a carbon chain, also contain a number of hydrogen atams and can include oxygen, nitrogen and sulfer , like carbs, vitiamins, protiens and lipids
\
essential because they contain carbon in all living organisms
\
essential because they contain carbon in all living organisms
17
New cards
what is nutrience
A source of nourishment, such as food, that can be metabolized by an organism to give energy and build tissue.
18
New cards
decribe composition of carbohyrdates
C6H1206
19
New cards
what is monosaccharides carbs
Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units from which all carbohydrates are built
20
New cards
what is disaccharides carbs
A disaccharide is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined
21
New cards
what are polysaccharides
long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides.
22
New cards
composition of lipids
essential component of the cell membrane. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a phosphate group (hydrophilic)
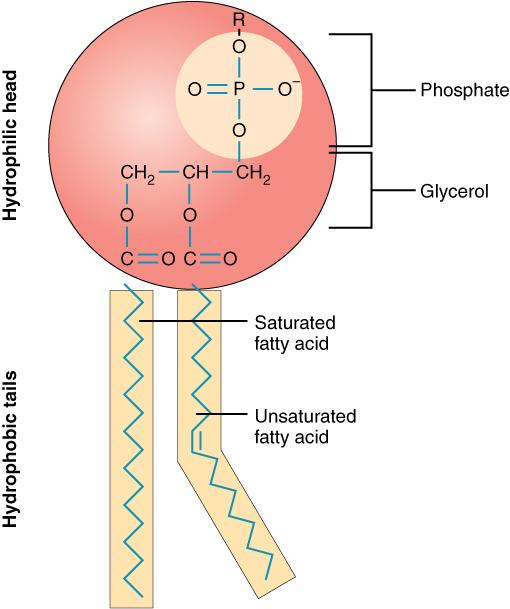
23
New cards
triglycerides formation
Triglycerides are composed of a glycerol molecule bound to three fatty acids
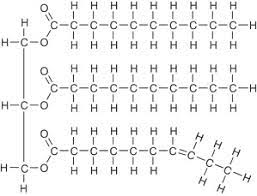
24
New cards
what is he composition of proteins, including the reactions leading to the formation of peptides, dipeptides and polypeptides, including peptide bond
polypeptide backbone with attached side chains. Each type of protein differs in its sequence and number of amino acids
\
peptides proteins: short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
\
diepeptide proteins: a molecule that consists of two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond.
\
polypeptide protein: A substance that contains many amino acids
\
what is a peptide bond?limks amino acids
\
peptides proteins: short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
\
diepeptide proteins: a molecule that consists of two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond.
\
polypeptide protein: A substance that contains many amino acids
\
what is a peptide bond?limks amino acids
25
New cards
difference between primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary protien structures
primary structure: the sequence of amino acids linked together to form a polypeptide chain
\
secondary: regular, local structure of the protein backbone, stabilised by intramolecular and sometimes intermolecular hydrogen bonding of amide groups. a helix b alpha
\
tertiary: the overall three-dimensional arrangement of its polypeptide chain in space.
\
quaternary: the association of several protein chains or subunits into a closely packed arrangement
\
secondary: regular, local structure of the protein backbone, stabilised by intramolecular and sometimes intermolecular hydrogen bonding of amide groups. a helix b alpha
\
tertiary: the overall three-dimensional arrangement of its polypeptide chain in space.
\
quaternary: the association of several protein chains or subunits into a closely packed arrangement
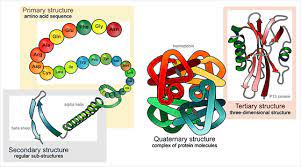
26
New cards
decribe structural and functional properties of enzymes
structures: Enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. three-dimensional structure
\
properties: increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. Natural catalysts
\
properties: increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. Natural catalysts
27
New cards
induced fit model vs lock in key
lock and key model states that the active site of an enzyme precisely fits a specific substrate. The induced fit model states that the active site of an enzyme will undergo a conformational change when binding a substrate, to improve the fit.
28
New cards
use of atp
ATP is consumed for energy in processes including ion transport, muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, substrate phosphorylation, and chemical synthesis
29
New cards
what is ADP
last phosphate in ATP (ADP + Pi = ATP)
30
New cards
steps involved in cellular respiration
glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
31
New cards
contrast aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration,
anarobic aerobic
\
\
32
New cards
describe aerobic respiration
A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars).,
\
1 glycose goes through glycolisis in the cytoplasm and gets converted to pyvurate ( a co enzyme) which produces 2 atp
\
if there is ozygen then the pyvurate will go onto aerobic respiration in the mitochondria to the link reaction
\
then from there coA and coA (pryvurate) will go through the krebs cycle letting CO2 easte and that produces 2 atp, then it will go through oxidative phosphorylation.
\
that produces 34 atp
\
1 glycose goes through glycolisis in the cytoplasm and gets converted to pyvurate ( a co enzyme) which produces 2 atp
\
if there is ozygen then the pyvurate will go onto aerobic respiration in the mitochondria to the link reaction
\
then from there coA and coA (pryvurate) will go through the krebs cycle letting CO2 easte and that produces 2 atp, then it will go through oxidative phosphorylation.
\
that produces 34 atp
33
New cards
when will aerobic respiration occur
light exercise as oxygen is able to be taken in
34
New cards
when will anarobic respiration occur
intense exercise where you cannot take much oxygen in (like sprinting)
35
New cards
things that effect the rate of reaction with enzymes
enzyme conc, substrate conc, temperature, pH, cofactors, coenzymes and inhibitors
36
New cards
how to calculate rate of reaction
how much product produced/ time it took
37
New cards
how does enzyme conc, substrate conc, temperature, pH, cofactors, coenzymes and inhibitors effect rate of reaction
enzyme concentration = higher enzyme conc, means more enzyme activity and enzymes using all the substrates, this happens up to a point then the enzyne levels pleateau cause not enough substrats /-
\
Substrate conc - more substrates = high enzyme activity because more substrates but then theres not enough so enzymes level pleateay /-
\
PH = if ph is too high or too low the enzyme will lose its shape (denatured) so they can no longer lock to form substrate complexes and ezyme activity drops /\\
\
\
\
Substrate conc - more substrates = high enzyme activity because more substrates but then theres not enough so enzymes level pleateay /-
\
PH = if ph is too high or too low the enzyme will lose its shape (denatured) so they can no longer lock to form substrate complexes and ezyme activity drops /\\
\
\
38
New cards
what is a cofactor
change the shape of activiation site so that enzyme can combine with substrate
39
New cards
what is a coenzyme
no protien organic moleculte like vitiams that change the shape of an activiation site