BCM.18 - FREE ENERGY
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Gibbs free energy formula
∆G=∆H-T∆S
What is Gibbs free energy
- A way of determining if a reaction will occur (‘be spontaneous’).
- G is the maximum energy available to do useful chemical work at constant pressure and temperature.
Change in G MUST be
-ve for reaction to occur
Exergonic
releases free energy
Endergonic
requires free energy
A reaction is driven by
Whichever of entropy or enthalpy has a -ve value
Standard free energy change (∆G0) is defined at
standard temperature and pressure, for 1 M concentrations.
25°C (298 K)
•1 atm (101 325 Pa)
•All the chemicals in the system are in their reference states: for soluble things, that means at a concentration of 1 molar.
Biologically modified version of ∆G0
∆G0'
–[H+] = 10−7 M (pH must be 7)
–[H2O] = 55.6 M ( water take up whatever volume is left after getting all the other components to 1 M )
Why do we use ∆G0'
Raw ∆G0' values ...
1 M conc for metabolites is unrealistic
Impossible to get 1M of water as its pure concentration is 55.6M
Are not used to directly predict anything
∆G depends on
the relative concentrations of reactants and products.
Free energy calculation for realistic conditions
ΔG = ΔG0' + RT ln[C][D]/[A][B]
[products]/[reactants] =
Mass action ratio (Γ)
G can be negative even if ∆G0 positive ....
if [reactants] sufficiently > [products]
Equilibrium constant (Keq) is the
value of the mass action ratio when ∆G=0
What does if mean if...
•Γ < Keq
•Γ > Keq
•Γ = Keq
1)“Too many reactants”
∆G negative - exergonic
Forwards reaction spontaneous
2) “Too many products”
∆G positive - endergonic
Forward reaction not spontaneous
Backwards reaction favoured
3)“Just right”
∆G zero - equilibrium
No net reaction
If ∆G=∆G0+RT ln([C]eq [D]eq)/([A]eq [B]eq )=0
Therefore ..
∆G0=-RT ln(Keq)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) has a high....
“phosphoryl transfer potential”
∆G for reaction is very negative
ATP hydrolysis (here to AMP) can be coupled to...
Nonspontaneous reactions to drive them
Ion gradients are also a .....
Energy is derived from their...
store of free energy
collapse eg H+ gradients forming ATP
Two things that drive ion movements into cells
Chemical potential ( conc gradient )
Electrical potential ( voltage gradient )
In relation to the nerst equation, reactions are exergonic if
1) More ions on outside of membrane than inside
2) If outside of membrane is more positive than inner
Nerst Equation
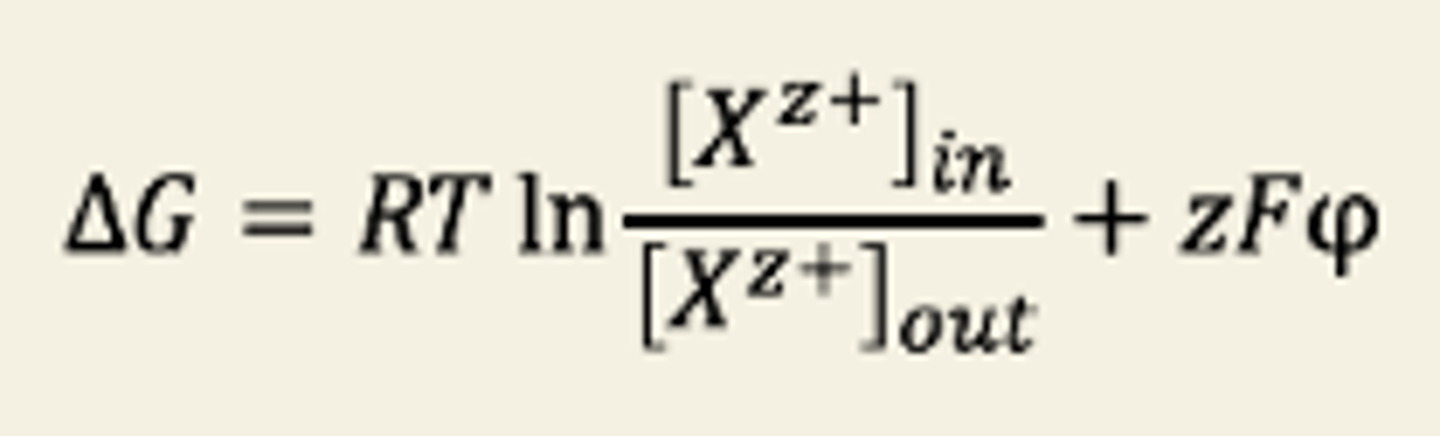
The Nernst equation can predict
φ from equilibrium ion distributions and vice versa.
Assumption of Nerst equation
- Membrane is permeable to one ion
- G = 0, assuming system is at equilibrium
- neutral concentration gradient of the permeant ion (i.e. until the ions start crossing the membrane, there is no voltage difference across it)
Other ways to write nerst
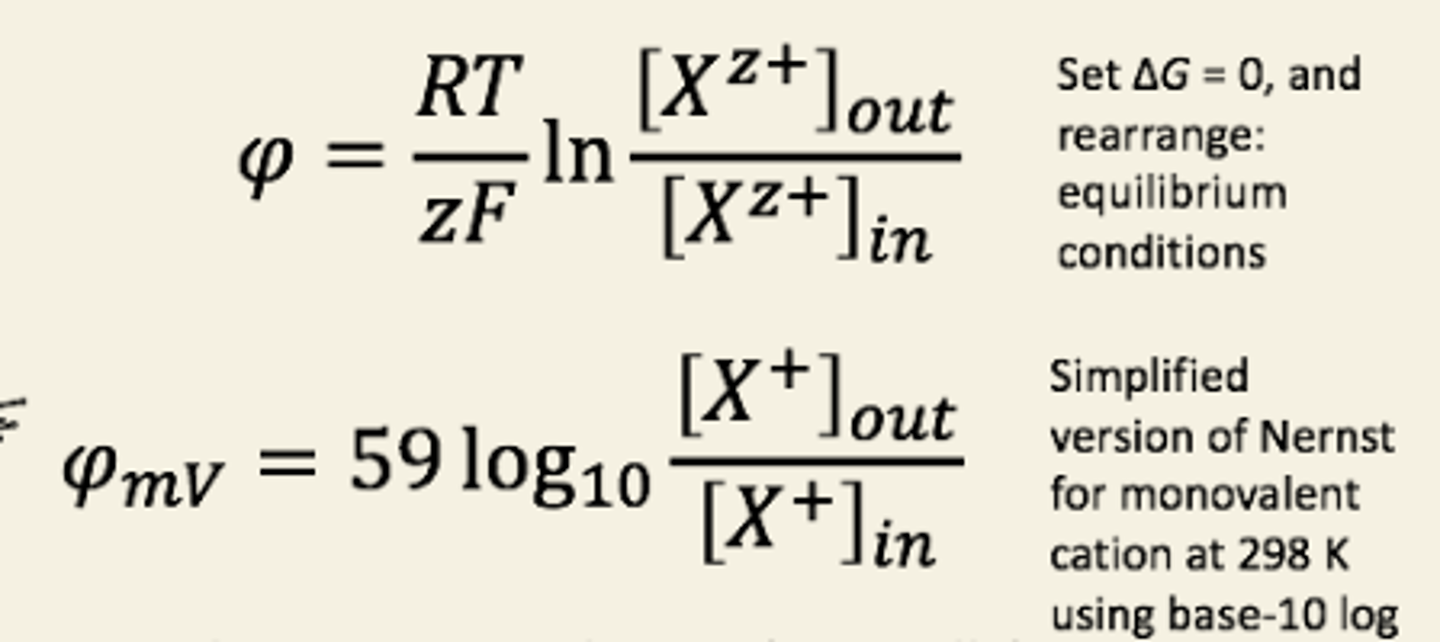
If 2 ions are equally permeable and of opposite charge,
the membrane potential will be 0.