Ch. 32: Nucleotides and their Polymers
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
nucleotides
building blocks of nucleic acids
functions of nucleotides
store and transfer genetic information (DNA and RNA), energy currency (ATP and GTP), signaling molecules (cAMP and G-proteins), coenzymes (NAD+ and FAD)
components of nucleotides
five-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base, at least one phosphate group
pyrimidines
nitrogenous bases with 1 ring with 4 carbons and 2 nitrogens (C, U and T)
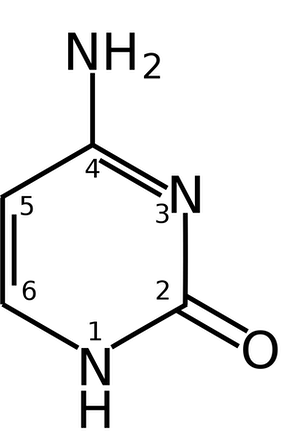
pyrimidine used in RNA and DNA, can spontaneously deaminate to uracil
cytosine
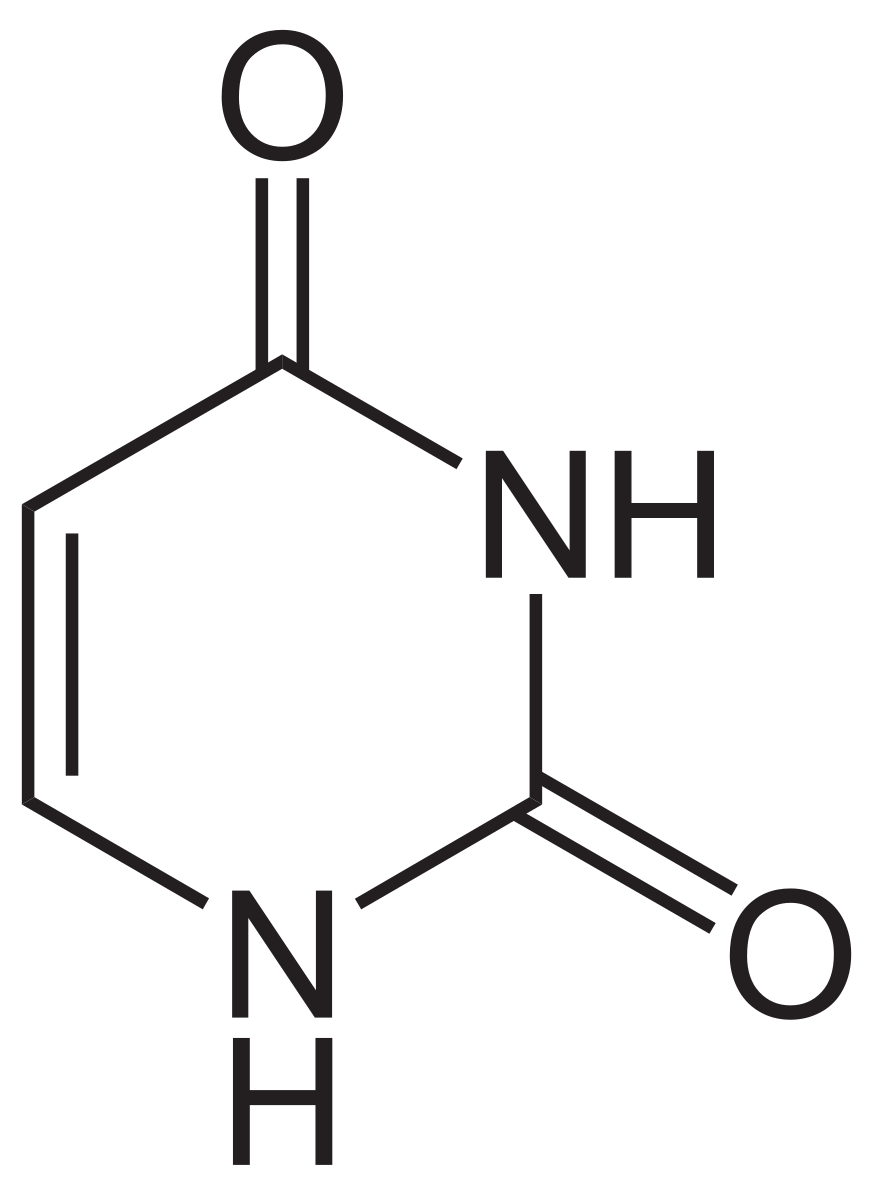
pyrimidine used in RNA, unstable
uracil

pyrimidine used in DNA, methylated for stability
thymine
purines
nitrogenous bases with imidazole fused to a pyrimidine ring (A and G)
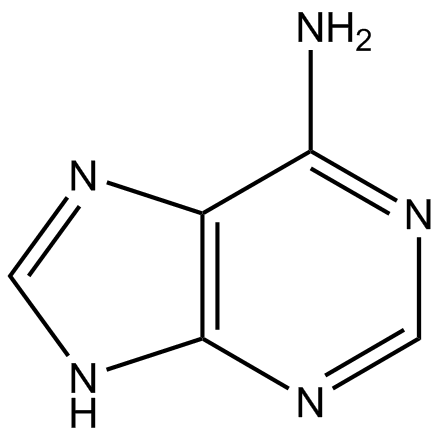
purine with amine group
adenine
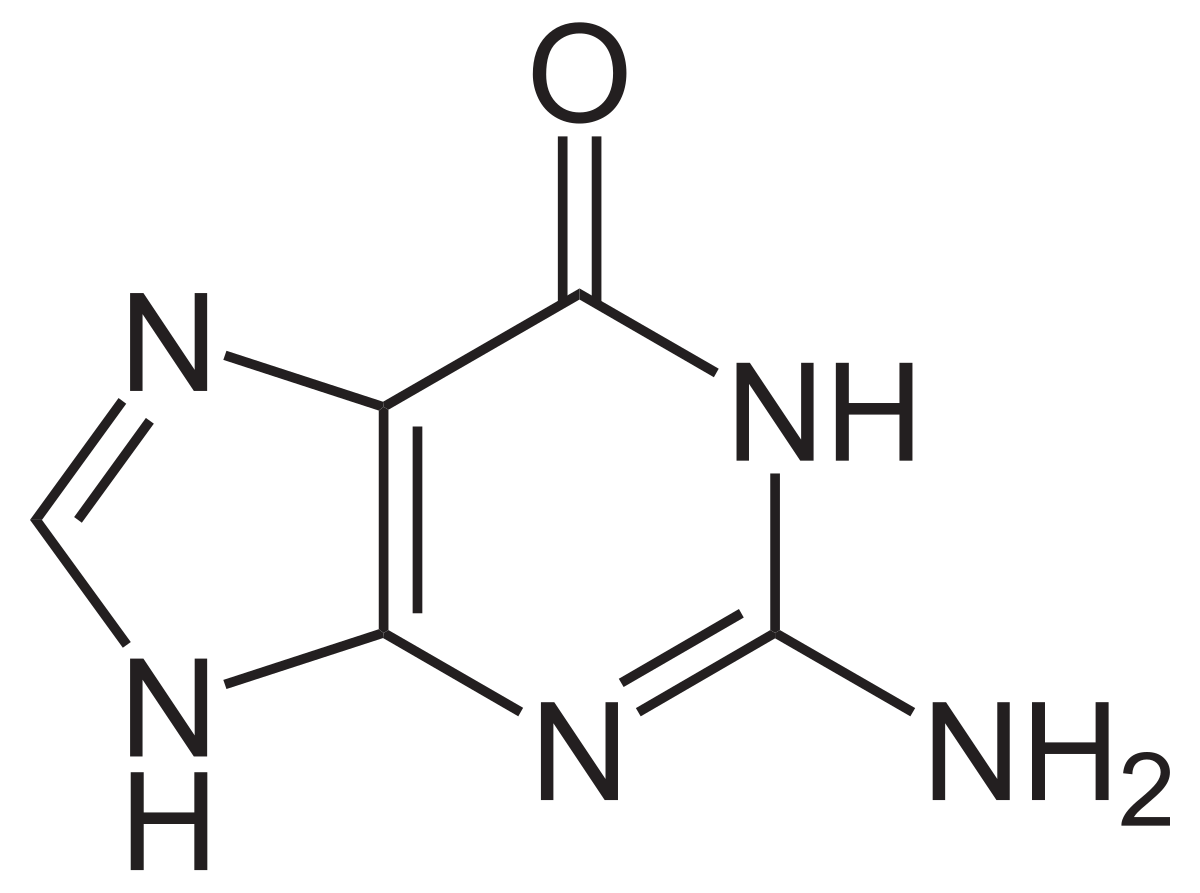
purine with amide
guanine
nucleotide synthesis
“de novo (from new)” multiple steps, highly regulated, uses LOTS of energy
nucleotide salvage
uses free bases, adds a sugar in 1 step
nucleotide degradation/catabolism
become smaller compounds
pyrimidine synthesis
made from glutamine (nitrogens), aspartate (nitrogens), 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate PRPP (sugar), tetrahydrofolate-Vitamin B9 (carbons), makes orotidine 5’ monophosphate (OMP)
regulation of pyrimidine synthesis
inhibited by CTP, activated by ATP
carbamoyl phosphate synthase II (CPS2)
catalyzes first committed step in pyrimidine synthesis, takes glutamine, 2 ATP and CO2 to form carbamoyl phosphate
ribonucleotide reductase
reduces UDP to dUDP, CDP to cCDP
purine synthesis
made of glutamine (nitrogens), aspartate (nitrogens), glycine (helps build rings), tetrahydrofolate-Vitamin B9 (carbons), and PRPP (sugar), makes Inosine-5’-Monophosphate (IMP)
1st step in purine synthesis
starts with PRPP (sugar), adds base to sugar
regulation purine synthesis
IMP, GMP, AMP (pathway products) inhibit synthesis
pyrimidine catabolism
cytosine deaminates to uracil, and uracil and thymine are degraded to produce acetyl coA and succinyl coA
pyrimidine salvage
cytosine/uracil degraded to produce UMP, thymine degraded to produce dTMP
purine catabolism
adenosine and guanosine degraded to produce uric acid, toxic products
purine salvage
accounts for 90% of daily purine synthesis (reduces uric acid), HGPRT catalyzes addition of PRPP
hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT)
catalyzes addition of PRPP sugar in purine salvage