MTSU Cell and Molecular Biology Exam 1 Study Guide
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Which of the following is an archaeon?
A) E.coli
B) Dictyostelium
C) Trypanosoma
D) Haloferax
D) Haloferax
How many genes are thought to be in the human genome?
A) 3,000
B) 30,000
C) 300,000
D) 3,000,000
B) 30,000
Which of the following model organisms contains a precise number of cells in the adult form (~1000)?
A) C.elegans
B) Arabidopsis
C) Zebrafish
D) Drosophila
A) C.elegans
Which of the following is not one of the main elements found in cells?
A) Sodium (Na)
B) Nitrogen (N)
C) Lithium (Li)
D) Iodine (I)
C) Lithium (Li)
Noncovalent interactions underlie which of the following?
A) DNA base pairing
B) Protein folding
C) Protein-protein interactions
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
What is the group carried by the activated carrier S-adenosylmethionine?
A) Methyl group
B) Carboxyl group
C) Electrons and hydrogen
D) Phosphate
A) Methyl group
What is the relationship between the mass of fuel molecules utilized by the cell and the mass of molecules created by anabolism?
A) These masses should be equal
B) The mass of fuel molecules will be greater
C) The mass of synthesized molecules will be greater
A) These masses should be equal
'F' is the single letter code for which amino acid?
A) Tryptophan
B) Proline
C) Phenylalanine
D) Glutamine
C) Phenylalanine
How many amino acids are coded for in the genetic code?
A) 17
B) 18
C) 19
D) 20
D) 20
True or False: Disordered regions of a protein will typically contain hydrophobic, uncharged amino acids.
A) True
B) False
B) False
Which of the following PTMs target proteins for proteasomal degradation?
A) Monoubiquitination
B) Multiubiquitination
C) K48 polyubiquitination
D) K63 polyubiquitination
C) K48 polyubiquitination
Which of the following amino acids can be phosphorylated (select 2)?
A) Serine
B) Tyrosine
C) Glycine
D) Alanine
A) Serine and B) Tyrosine
If human DNA contains 20% C on a molar basis, what portion is T?
A) 40%
B) 30%
C) 20%
D) 10%
B) 30%
Each human chromosome contains...
A) 1 centromere, 1 telomere, 1 origin of replication
B) 1 centromere, 2 telomere, 1 origin of replication
C) 2 centromere, 2 telomere, 1 origin of replication
D) 1 centromere, 2 telomere, many origins of replication
D) 1 centromere, 2 telomere, many origins of replication
What portion of each histone protein projects outward from nucleosomes? A) N-terminal tail
B) A central domain
C) C-terminal tail
D) No portion of histones project out from the nucleosome
A) N-terminal tail
Which of the following removes acetyl groups from histone tails?
A) HDMs
B) HMTs
C) HATs
D) HDACs
D) HDACs
Which of the following is not a component of histone octamers?
A) H1
B) H2A
C) H2B
D) H3
E) H4
A) H1
True or false: DNA polymerases synthesize DNA in the 3'-to-5' direction on the lagging strand?
A) True
B) False
B) False
What is DNA primase?
A) A DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
B) A RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
C) A DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
D) A RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
C) A DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Which enzyme is responsible for removing RNA primers on the lagging strand?
A) DNA ligase
B) RNAse H
C) RNAse A
D) RPA
B) RNAse H
Which of the following enzymes does not have to hydrolyze ATP in order to perform its function?
A) Topoisomerase I
B) DNA helicase
C) DNA ligase
D) Clamp loader
A) Topoisomerase I
When two bidirectional replication forks from adjacent origins meet, a leading strand always runs into a lagging strand?
A) True
B) False
A) True
Which of the following DNA lesions is an example of hydrolysis?
A) Depurination
B) 7-Methylguanine
C) ring-saturated pyrimidines
D) 8-oxo G
A) Depurination
True or false: Spontaneous depurination and the removal of a deaminated C by uracil DNA glycosylase leave identical substrates, which are recognized by AP endonucleases?
A) True
B) False
A) True
True or false: The DNA repair enzymes that correct damage introduced by deamination and depurination must preferentially recognize such defects on newly synthesized DNA strands
A) True
B) False
B) False
Noncovalent interactions underlie which of the following?
A) DNA base pairing
B) Protein folding
C) Protein-protein interactions
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
To which domain does Haloferax belong?
Archaea
To which domain does Trypanosoma belong?
Eukaryotes
To which domain does Dictyostelium belong?
Eukaryotes
To which domain does E.coli belong?
Bacteria
To which domain does Methanothermobacter belong?
Archaea
What is the major use of E.coli as a model organism?
serves as a simple model prokaryote
What is the major use of Yeast as a model organism?
serves as a minimal model eukaryote
What is the major use of Arabidopsis thaliana as a model organism?
it is the most commonly used plant model
What is the major use of Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism?
is a commonly used genetic model to study development and other processes
What is the major use of Danio rerioas a model organism?
commonly used as a vertebrate model of development
How large is the human genome (in nucleotide pairs)?
3,200 x 10^6 BP or
How many genes are in the human genome?
~30,000
What tends to be larger, introns or exons?
Introns
What are the minimum number of genes required for a viable (prokaryotic) cell?
~300
Identify the following type of chemical bond from the description
Their strength does not decrease in water
Covalent bonds
Identify the following type of chemical bond from the description
involves the clustering of non-polar groups so that they minimally disrupt the hydrogen bonding of surrounding water molecules
Hydrophobic forces
Identify the following type of chemical bond from the description
Very strong in a vacuum but weak in water
Ionic bonds
Name the activated carrier and the groups they carry
Name: ATP
Group Pi (phosphate)
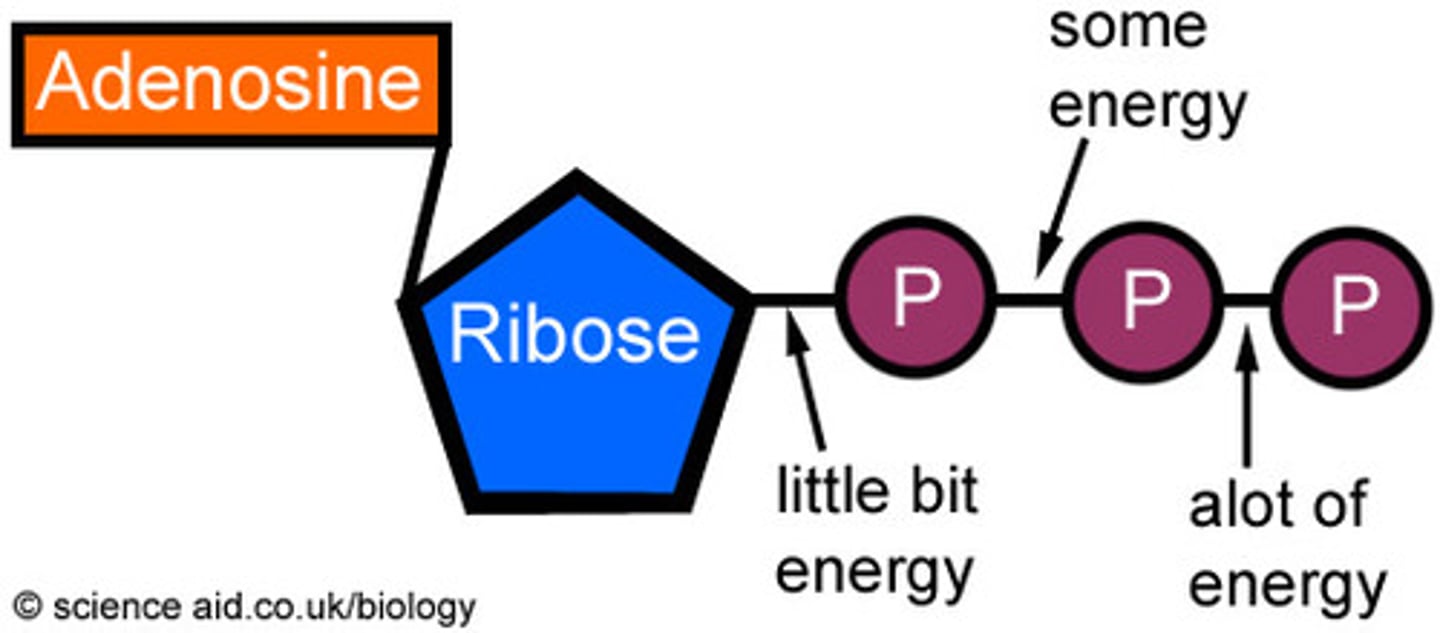
What groups does NADH carry
Electrons and hydrogens
What group is carried by Acetyl CoA
Acetyl group
What group is carried by S-Adenosylmethionine
Methyl group
Go back and put amino acid structures and questions on quizlet
we can be tested on any of the 20
Put stuff from slide 20 on here
(Post translational modifications via lys63 and lys48)
What is the function of histone H1?
Compacting chromatin
What is the function of histone H2Ax?
Marking the sites of DNA double strand breaks
Which region of histone proteins project out from the nucleosomes?
N-terminal tails
Modifications of histones that have biology meaning constitute a
histone code
What do we call the DNA clamp in mammalian cells?
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)
What are SSBs?
Single-stranded binding proteins
What is the function of DNA primase?
Production of RNA primers (DNA-dependent RNA synthesis)
Which component of the replication fork has six identical subunits, has ATPase activity and functions as a molecular motor?
DNA Helicase
What non-protein component does telomerase carry with it to help it do its job?
An RNA template
What types of cells would you expect to retain high telomerase activity in adults?
Stem cells (e.g. hematopoietic stem cells)
What do we call the looped DNA structure formed by telomeres?
t-loops
What mechanism repairs errors in newly synthesized DNA and requires MutS and MutL proteins?
Strand directed mismatch repair
What method is used by cells that have just replicated their DNA to flawlessly repair DNA double strand breaks?
Homologous recombination
What type of enzyme removes damaged bases and leaves the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone intact?
DNA glycosylases
Which of the following is frequently used as a model to study vertebrate development?
A) Caenorhabditis elegans
B) Drosophila melanogaster
C) Danio rerio
D) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
C) Danio rerio (zebrafish)
The living world can be divided into three domains, bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. To which of these does the slime mold Dictyostelium, belong
A) Bacteria
B) Archaea
C) Eukaryotes
C) Eukaryotes
Which of the following chemical bonds is equally strong in a vacuum and in water?
A) Covalent
B) Ionic
C) Hydrogen
A) Covalent
Which of the following could be described as an activated carrier?
A) Pyruvate
B) ATP
C) Glucose
D) Arachidonic acid
B) ATP
What group is carried on a high-energy linkage by the activated carrier, S-adenosylmethionine?
A) Phosphate
B) Glucose
C) Methyl group
D) Electrons and hydrogens
E) Acetyl group
C) Methyl group
Which combination of 4 elements make up 99% of the total number of atoms in the human body?
A) C, H, P, and O
B) C, H, P, and S
C) C, H, Fe, and O
D) C, H, N, and O
D)
Identify the amino acid in the picture to the right (Hint: it is one of the amino acids in proteins that is frequently phosphorylated)?
Identify the amino acid in the picture to the right (Hint: it is one of the amino acids in proteins that is frequently phosphorylated)?
B)
Which of the following amino acids is nonpolar?
A) Alanine
B) Aspartic acid
C) Glutamic acid
D) Serine
A) Alanine
The overall fold of an individual protein is called the...
A) A domain
B) Primary structure
C) Secondary structure
D) Tertiary structure
E) Quaternary structure
D) Tertiary structure
What type of histone binds nucleosomes at a 1:1 ratio and has a role in compacting chromatin?
A) H1
B) H2A
C) H2B
D) H3
E) H4
A) H1
What do we call enzymes that acetylate histones?
A) HATs
B) HDACs
C)HMTs
D) HDMs
A) HATs (histone acetyltransferases)
Which of the following enzymes seals 'nicks' in the DNA backbone during DNA replication?
A) DNA ligase
B) DNA clamp loader
C) DNA helicase
D) Topoisomerase II
A) DNA ligase
What is the name of the frog used to study eukaryotic development
Xenopus laevis
The activated carrier ATP carries what group in a high energy linkage
Phosphate
The activated carriers NADH, NADPH, and FAH2 carry what group in a high energy linkage
Electrons and Hydrogens
The activated carrier Acetyl CoA carries what group in a high energy linkage
Acetyl
The activated carrier Carboxylated biotin carries what group in a high energy linkage
Carboxyl group
The activated carrier S-Adenosylmethionine carries what group in a high energy linkage
Methyl group
The activated carrier Uridine diphosphate glucose carries what group in a high energy linkage
Glucose
Oxidation and reduction involves
electron transfer
Ways electron oxidation and reduction could occur include
The loss/gain of electrons
(Ionization)
A loss/gain of protons
(Dehydrogenation/hydrogenation)
The loss of gain of electron density