BIO 101 Chapter 1
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Evolution
is the process of change that has transformed life on Earth
it is the history of life on earth
Biology
the scientific study of life
what are some questions biologists ask
how a single cell develops into an organism
how the human mind works
how living things interact in communities
what are some properties of life
order
evolutionary adaptation
response to the environment
reproduction
growth and development
energy processing
regulation

organims living on earth are ______ of common ancestors
modified descendents
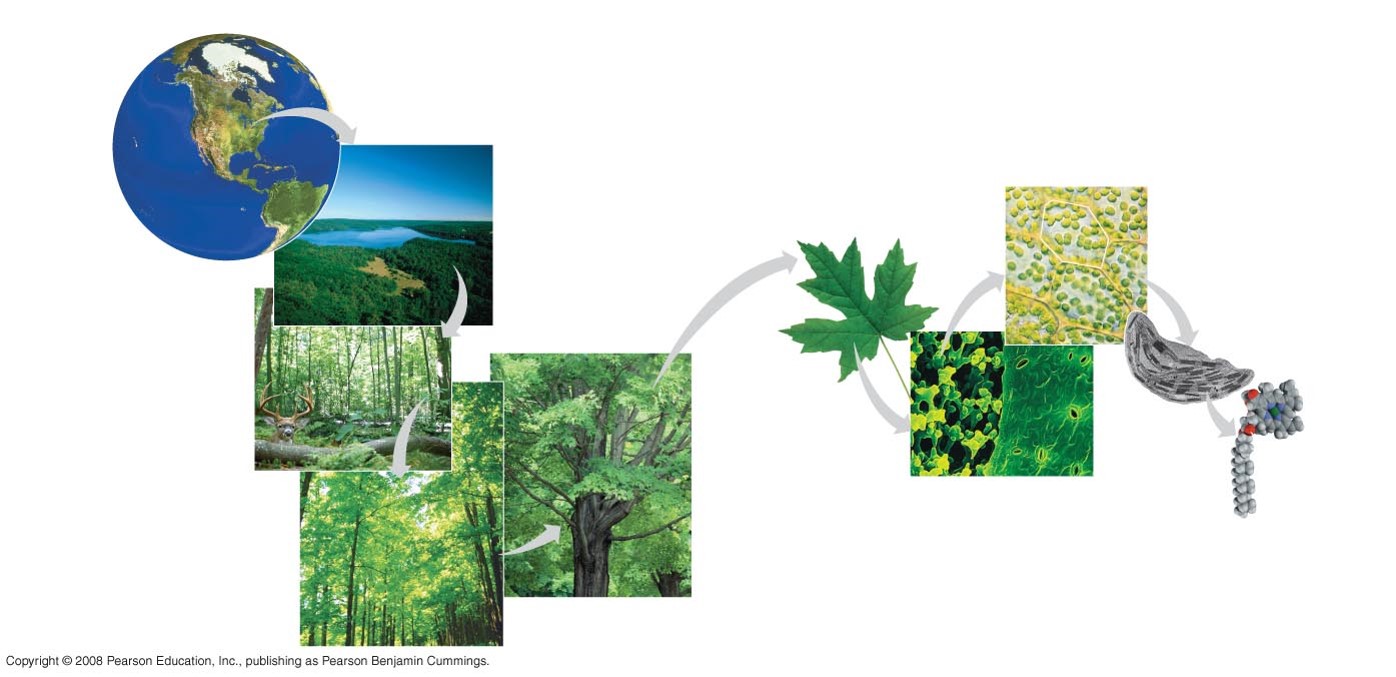

these are the levels of biological organization, describe each component
the smallest component is the atom, they stick to other atoms which make molecules
molecules —>organelles
organelles —> cells
a collection of cells make up tissues
the leaf represents an organ on a tree
the tree represents the organism
organisms fit together to form a population
a population consists of all the members of the same species in the same space
the community is made up of members of different species in the same space
all plants, animals, and nonliving features are a part of the ecosystem which comes together to form the biosphere
emergent properties
it is a result from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system
ex. (nonbiological) a functioning bicycle emerges only when all of the necessary parts connect in the correct way
reductionism
understanding biological systems by breaking them down into their simpler components
by examing the individual parts we can gain insight into how the whole system functions
ex. studying a single gene to understand its role in a larger biological process
an understanding of biology balances reductionism with the study of emergent properties
ex. new understanding comes from studying the interaction of DNA with other molecules
systems biology
focuses on understanding complex biological systems as integrated wholes rather than just their parts
aims to study interaction and relationships between different biological components (genes, proteins, cells, tissues) and how they lead to the function and behavior of the entire system
organisms interact with their _____, exchanging matter and energy
environment
the dynamics of an ecosystem include what two major processes
cycling of nutrients, in which materials acquired by plants eventually return to the soil
the flow of energy from sunlight to producers to consumers
why is the energy coming from sunlight not a cycle
becuase none of that heat or light is getting put back into the sun
work requires a source of ____
energy
what forms can energy be stored in
light
chemical
kinetic
thermal
energy flows though an ecosystem, usually entering as ____ and exiting as ___
light, heat
describe the relationship between structure and function
they are closley related,
everything in biology has a certain structure because of its function
ex. a leaf is thin and flat (structure) which maximizes the ability to capture light by chloroplasts (function)
ex. flowers are bright and colorful (structure) so it can attract pollinators and reproduce (function)
the ___ is the lowest leve of organization that can perform all activites required for life
cell
all cells are:
enclosed by a membrane
use DNA as their genetic information
what is the basis of all reproduction, growth, and repair of multicelular organisms
the ability of cells to divide
describe a eukaryotic cell
plant, animal, fungi, protus
has a membrane around the outside and a series of membrane enclosed organelles on the inside
contain nucleus (DNA is present here)
bigger than prokaryotic cell
describe a prokarytoic cell
bacteria and archae
does not contain membrane-enclosed organelles
has no nucleus
smaller than eukaryotic cells
DNA is present
the continuity of life is based on heritable information in the form of ___
DNA
what contains most of a cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA
chromosomes
what are genes
the units of inheritance that transmit information from parents to offspring
describe DNA struction and function
each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds of thousands of genes
DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents
DNA controls the development and maintenance of organisms
they tell the cell which proteins to make and how to make them
each DNA molecule is made up of two long chains arranged in a double helix
each link of chain is one of 4 kinds of chemical building blocks called nucleotides
what are the 4 bases used in DNA
A (adenine)
C (cytosine)
G (guanine)
T (thymine)
a type of protein critical to all cells is an organic catalyst called:
enzyme: they increase the rate of biochemical reations occuring in all living cells by lowering the activation energy
genes control proteins production ____
indirectly
DNA is transcribed into RNA then translated into a protein
what is a genome
the complete set of genetic material in an organism
the human genome and those of many other organism have been sequenced using ____
DNA sequencing machines
high-throughput technology
tests thousands of chemicals interacting a particular type of cell or organism
what is bioinformatics
how computers study our structural information and process a large volume of data
feedback mechanisms allow biological processes to _____
self-regulate
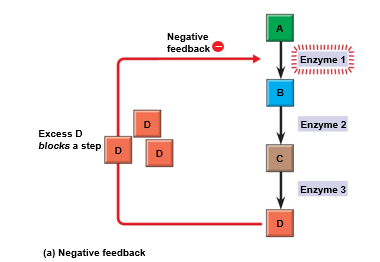
describe negative feedback
as more of a product accumulates, the process that creates it slows and less of that product is produced
ex. temperature regulation, blood glucose regulation
happens frequenlty
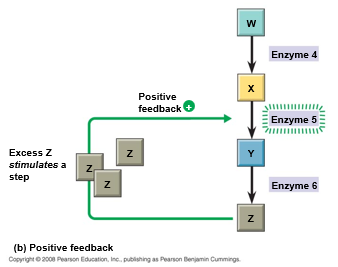
describe positive feedback
as more of a product accumulates, the process that creates it speeds up and more of the product is produced
ex. blood clotting, labor contractions during childbirth, lactation
does not happen as frequently
Theodosius Dobzhansky had stated, “nothing in biology makes sense except in _____
the light of evolution
what is taxonomy
the branch of biology that names and classifies species into groups of increasing breadth
what is the broadest unit of classification
domain
what are the three domains
all eukaryotic organisms
bacteria
archae
the domain eukarya includes three multicellular kingdoms”
plants
fungi
animals
other organisms were formerly grouped into a kingdom called Protista, though these are now often grouped into many separate kingdoms
example of unity found in the diversity of life
DNA is the universal genetic language common to all organisms
unity is evident in many features of cell structure
what two main points did Charles Darwin make
species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors
natural selection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification”
what were some of Darwin’s observations
individuals in a population have traits that vary
many of these traits are heritable
more offspring are produced than survive (natural selection)
competition in inevitable
species generally suit their environment
darwin inferred that
individuals best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
over time more individuals in a population will have the advantageous traits
the natural environment “selects” for beneficial traits
“unity in diversity” arises from _____
“descent with modification”
ex. the forelimb of the bat, human, horse and the whale flipper all share a common skeletal architecture (fossils can help us find evidence of anatomical unity from descent with modification)
true of false
Darwin proposed that natural selection could cause an ancestral species to give rise to two or more descendent species
true
science is derived from latin and means ____
to know
define inquiry
the search for information and explanation
what are the two types of scientific inquiry and define them
discovery science: describes natural structures and processes (what you observe)
hypothesis-based science: coming up with potential answers to well-framed questions
data falls into what two categories
qualitative: descriptive, characteristic like color
quantitative: recorded measuremnts, numbers
discovery science involves inductive reasoning which means
it draws conclusions from a series of observations
ex. the sun always rises in the east
observation can lead us to ask questions and propose hypothetical explainations called _____
hypotheses
how can a hypothesis be tested
by observation or experimentation
what is the “if…then” logic of hypothesis based science
deductive reasoning which uses general premesis to make specific predictions
ex. if organisms are made of cells (premise 1), and humans are organisms (premise 2), then humans are composed of cells (deductive prediction)
a hypothesis must be _____ and _____
testable, falsifiable
what happens if you fail to falsify a hypothesis
it does not prove the hypothesis
describe a controlled experiment
compares an experimental group with a control group
ideally, only the variable of interest differs between the control and experimental groups
a controlled experiment means that control groups are used to cancel the effects of unwanted variables
a controlled experiment does not mean that all unwanted variables are kept constant
in science, observations and experimental results must be _____
repeatable
in the context of science a theory is:
broader in scope than a hypothesis
general and can lead to new testable hypotheses
supported by a large body of evidence in comparison to a hypothesis