Reflection, Diffraction & Absorption
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What absorbs sound?
everything (clothes, people, objects, etc.)
What is T60?
the time it takes for a sound to decay by 60 dB
What causes a T60 value to be higher?
echoes
What is the ideal T60 value?
small value
What do obstacles cause?
large acoustic impedance
What is a ray?
a line perpendicular to the wave front
What do obstacles cause (in term of sound wave reflection)?
sound wave to be reflected back toward source with no change in speed
Does the inverse square law work for reflection of sound waves?
NO
What happens to energy in a medium?
energy is retained/stays in a medium
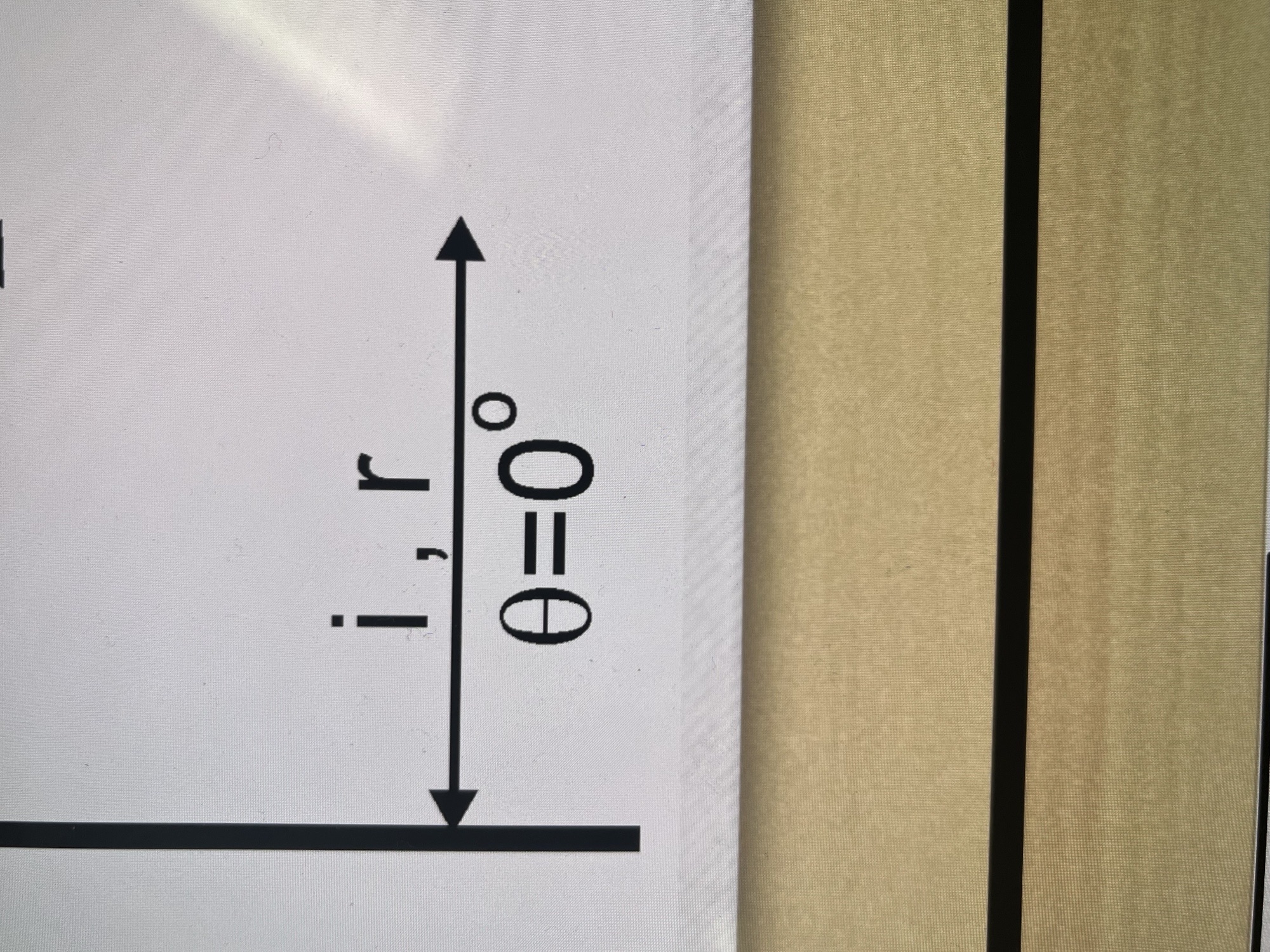
What does this represent?
a ray being reflected back on itself toward the source
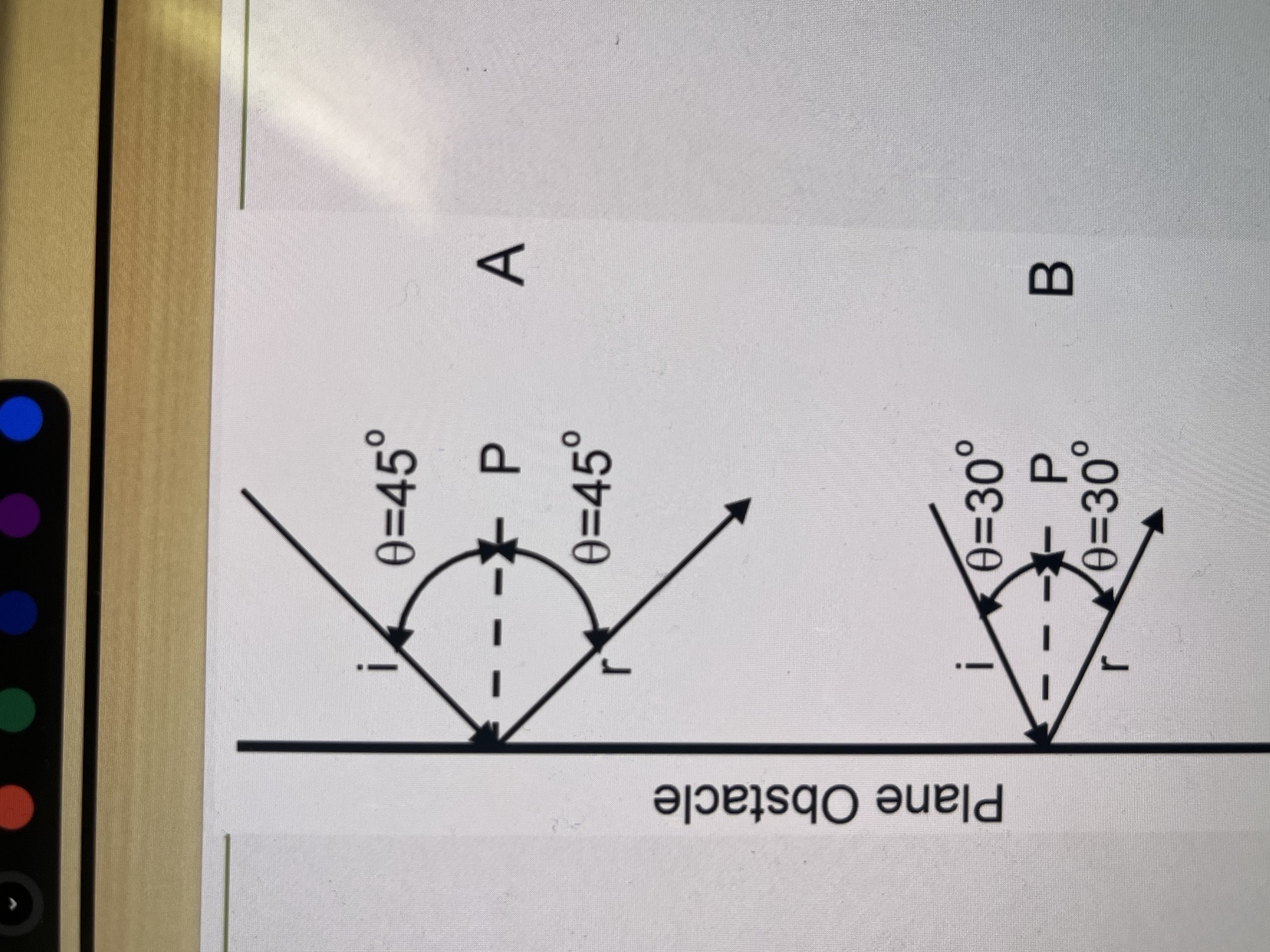
What does this represent?
rays reflecting back at an angle equal to the initial/incident ray
Is angle i and angle r always equal?
YES
What is convex?
-curved outward (towards the source)
-source on the right → draw right half of a circle
What is concave?
-curved inward (away from the source)
-source on the right → draw left half a circle
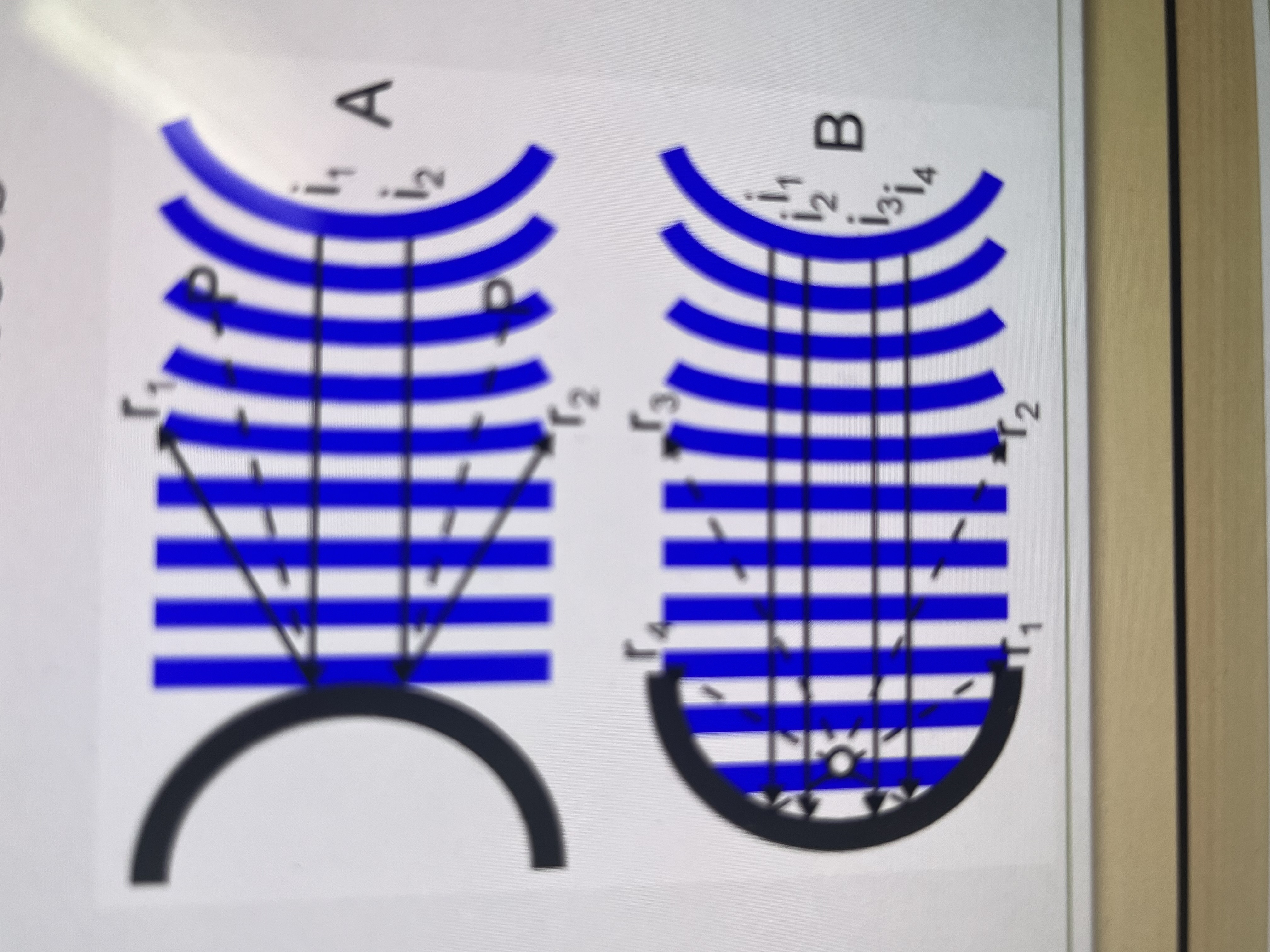
Which is convex and concave?
A: convex
B: concave
What happens to the incident rays after they hit a convex obstacle?
reflected rays diverge causing sound energy to scatter
What happens to the incident rays after they hit a concave obstacle?
reflected rays converge and sound energy is “collected”/concentrated
What point do reflected waves converge after reflecting off a concave surface?
focal point where energy density/intensity is maximal
What is the intensity of the reflected wave for a convex surface?
less than intensity of incident wave at equal distance
What is the intensity of the reflected wave for a concave surface?
greatest at the focal point
What is an example of when concave surfaces are used?
whispering galleries
Are angles of reflected rays to the perpendicular always equal to the angles of incident rays to the perpendicular?
YES
What are reflected waves also known as? (2)
1) echoes
2) reverberating waves
What are reverberant rooms?
rooms with hard surfaces to maximize reflections
What are anechoic rooms?
rooms with absorbing surfaces to minimize reflections
Is it ideal to have less/low reflections?
YES
What happens if you were to remove the roof of a room?
the reflections would decrease
What is another name for T60?
reverberation time
What is reverberation/T60?
-time required for sound energy to decay by 60 dB
-time required by sound intensity to be attenuated/reduced to one-millionth
What is diffraction?
wave bending around an obstacle and reforming
What happens to a wave when it undergoes diffraction?
-some energy is reflected back
-wave bends around the obstacle and reforms
-continues as a plane wave front
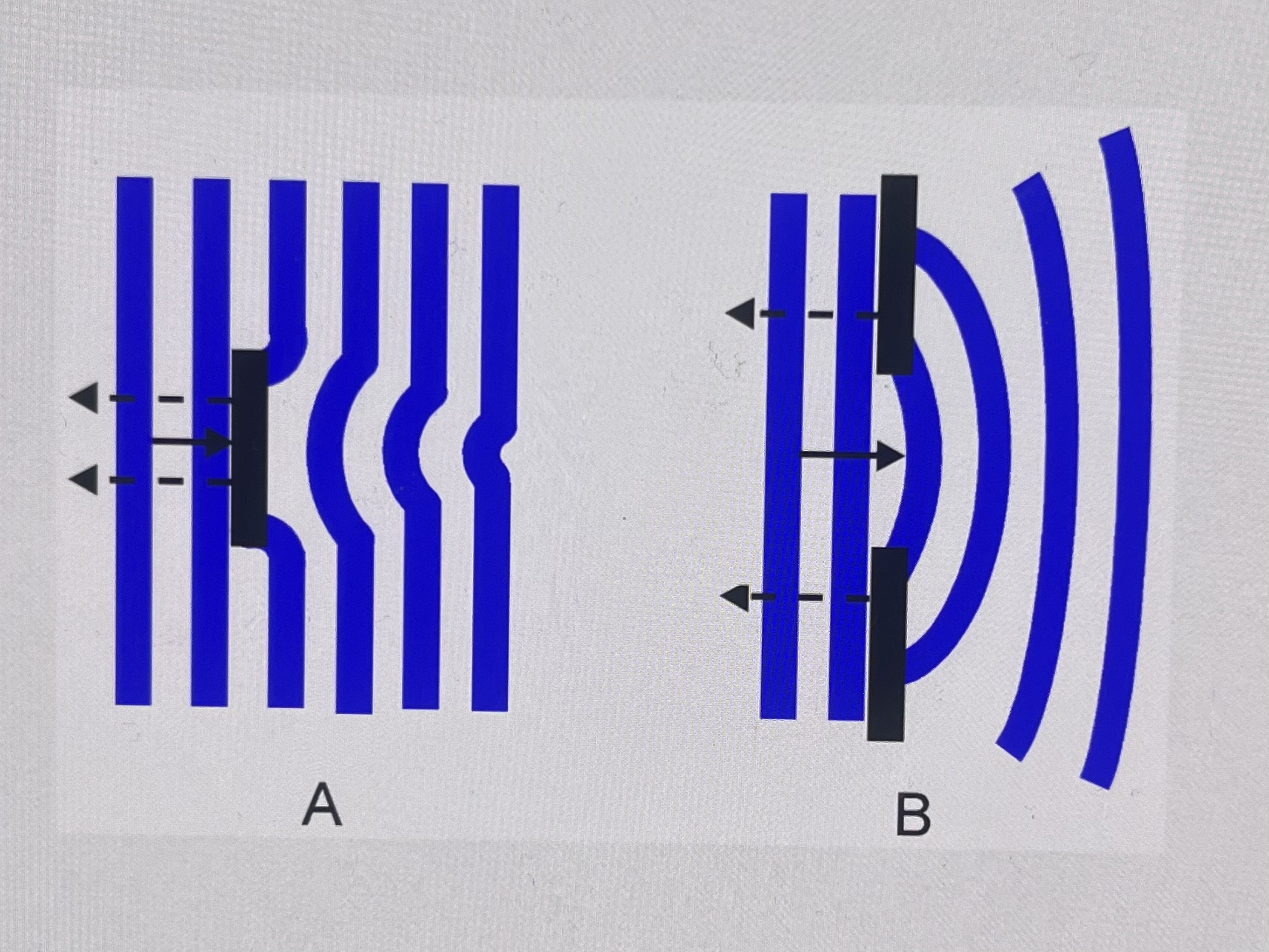
What does this show?
diffraction
What exists at any boundary where impendences differ?
opposition to sound transmission
What happens when impedance is infinite?
intensity of reflected wave (IR) will equal intensity of incident wave (Ii)
What is IR?
intensity of reflected wave
What is Ii?
intensity of incident wave
What happens when impedance is infinite? (absorption)
nothing is getting absorbed by the object
What happens when impedance is not infinite? (absorption)
some sound energy will be absorbed by new medium
What happens when impedance is not infinite?
intensity of incident wave is greater than the intensity of reflected wave
What is an example of absorption where impedance is not infinite?
throwing a cup of water at the wall
What symbol represents absorption coefficient?
a
What is absorption coefficient?
the proportion of energy in incident wave absorbed by material
What is the range of absorption coefficient?
0-1
What absorption coefficient is associated with a material being “good at absorbing”?
0.8 and above
What is the equation for absorption coefficient?
a= energy absorbed (Ia) divided by energy of incident wave (Ii) / total energy present
What is the absorption coefficient of a material that absorbs all energy?
a=1
What is the absorption coefficient of a material that absorbs nothing?
a=0
If SPL i= 80 dB and .1% is absorbed, what is SPL of sound wave retained in medium?
dB = 10 log 0.999
dB= -0.004
dB SPL= 80 + - 0.004
79.996 dB SPL
Does absorption coefficient vary with intensity of incident wave?
NO
Do materials with fixed absorption coefficients change with intensity?
NO
What type of absorption coefficient do anechoic rooms and sound isolated rooms have?
high absorption coefficient
What is the relationship between absorption and reflection?
inversely proportional
What is the relationship between absorption coefficient, reflection and reverberation time?
-absorption coefficient increase
-reflection and reverberation time decrease
What causes absorption coefficient of a material to change?
changes in frequency
What is the relationship between room volume and reverberation?
room volume increase, reverberation time/T60 value increases
What 2 things does total absorption in a room depend on?
1) absorption coefficients of materials in room
2) room volume
What is reverberation time/ T60?
time it takes for a sound to decay by 60 dB
What type of T60 is ideal?
low T60 value
What is the equation for T60?
T60= k (volume of room/area of opening)
What is an easy way to lower a T60 value in the hearing science classroom?
opening the 2 doors will lower T60 value
What happens as T60 value decreases?
sound energy escapes more quickly
What 2 things cause T60 to vary?
1) volume
2) frequency
What is the doppler effect?
-if source moves toward observer, pitch rises
-if source moves away from observer, pitch falls
What is an example of the doppler effect?
as a police car with sirens on comes closer the pitch will get higher