PAS 604 Transfusion Medicine
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
concentrated preparation of red blood cells that is obtained from whole blood by removing the plasma (as by centrifugation) and is used in transfusion
What are Packed Red Blood Cells (pRBC)?
hemorrhage and improve oxygen delivery to tissues
What are Packed Red Blood Cells (pRBC) used to tx?
- sickle cell crisis
- blood loss of > 30% of blood volume
- symptomatic anemia
What are indications for Packed Red Blood Cells (pRBC)?
- Hgb < 7 g/dL
- Hgb < 8 g/dL in patients with cardiovascular disease
When should a patient be transfused with pRBC?
1 g/dL
One unit PRBC should increase Hgb by ______
3%
One unit PRBC should increase HCT by ______
more
Whole blood has ______ complications than using pRBCs
setting of massive transfusion protocol (10 units of blood in a 70kg person within 24 hours)
When may whole blood be considered?
Hypocalcemia
What can result from whole blood binding with citrate, which is used in the storage of blood products?
< 10,000/µL
When is prophylactic transfusion done?
20,000-30,000/µL
What is therapeutic transfusion goal for bleeding?
at least 50,000/µL (in some cases 100,000/µL)
What is therapeutic transfusion goal for major surgery?
30,000/µL
One unit of apheresis platelets should increase the platelet count in adults by ~ _____________
Contains all of the coagulation factors
What is fresh frozen plasma (FFP)?
Thawed
_________ plasma has lower factors V and VIII and is not indicated in consumption coagulopathy (DIC)
- active bleeding and an INR > 1.6
- before an invasive procedure if a patient has been anti-coagulated
- emergent reversal of warfarin
- DIC
When is FFP indicated?
thawing fresh frozen plasma and collecting the precipitate
How is cryoprecipitate prepared?
factor VIII and fibrinogen
What is there high concentrations of in cryoprecipitate?
DIC
When is cryoprecipitate MC used?
5-10 mg/dL
Each unit of cryoprecipitate raises fibrinogen by:
100 mg/dL
Cryoprecipitate goal to maintain a fibrinogen level of at least:
mismatch or incompatibility of transfused product and recipient; involves naturally occurring antibodies and alloantibodies
What is an immune mediated transfusion reaction?
caused by the physical effects of blood components or the transmission of disease
What is a non-immune mediated transfusion reaction?
What is a mild allergic transfusion rxn?
more severe allergic reaction
What is an anaphylactic allergic transfusion rxn?
due to cytokines released from blood donor leukocytes
What is a febrile non-hemolytic transfusion rxn?
caused by bacteria or bacterial byproducts (e.g. endotoxin)
What is a septic transfusion rxn?
can result in hemolysis; immune mediated reactions due to recipient antibodies present to blood donor antigens; non-immune mediated when RBCs damaged before transfusion
What is an acute hemolytic transfusion rxn?
volume of product causes volume overload
What is Transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO)?
antibodies in donor product react with antigens in recipient; recipient immune system responds & releases mediators that cause pulmonary edema
What is Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)?
Rise in body temperature at least 1.8°F (1°C) above 98.6°F (37°C) within 24 hours after transfusion
What indicates Febrile Non-hemolytic Transfusion Reactions (FNHTR)?
platelets > pRBCs
When are Febrile Non-hemolytic Transfusion Reactions (FNHTR) MC?
Rigors, chills, discomfort
What are Febrile Non-hemolytic Transfusion Reactions (FNHTR) sx?
Leukoreduction
What decreases FNHTR rates?
patients who have been transfused repeatedly or those who have been pregnant
Who do Febrile Non-hemolytic Transfusion Reactions (FNHTR) happen in?
- release of antibody-mediated endogenous pyrogen
- release of cytokines
What is the mechanism of FNHTR?
broad spectrum abx
If suspicion for Transfusion-Associated Sepsis is high, start:
Destruction of donor RBCs within 24 hours
What are Acute Hemolytic Reactions?
aggressive hydration and diuresis
How are Acute Hemolytic Reactions managed?
fever, chills, rigors, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, hypotension, diffuse bleeding, hemoglobinuria, oliguria, anuria, pain at the site, chest/back/abdomen
What are the sx of Acute Hemolytic Reactions?
rapid transfusion of blood that overwhelms the circulatory system
What causes Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO)?
antibody
Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO) is not _______________ mediated
tachycardia, cough, dyspnea, hypertension; cardiomegaly and pulmonary edema are seen on CXR
What are signs and sx of Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO)?
measuring a BNP/NT-proBNP may assist; echocardiogram (know your patient’s EF)
How is Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO) dx?
diuresis and supplemental oxygen; ventilation support may be required
How is Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO) tx?
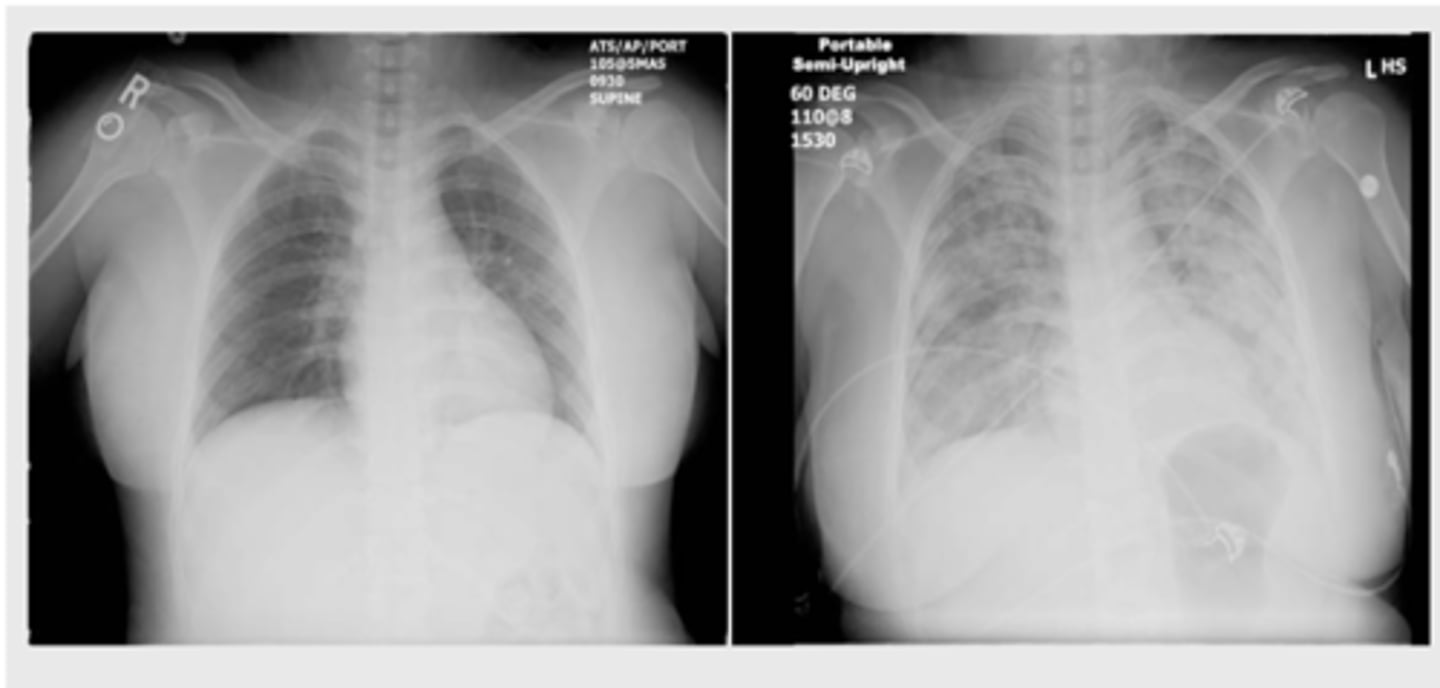
Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO)
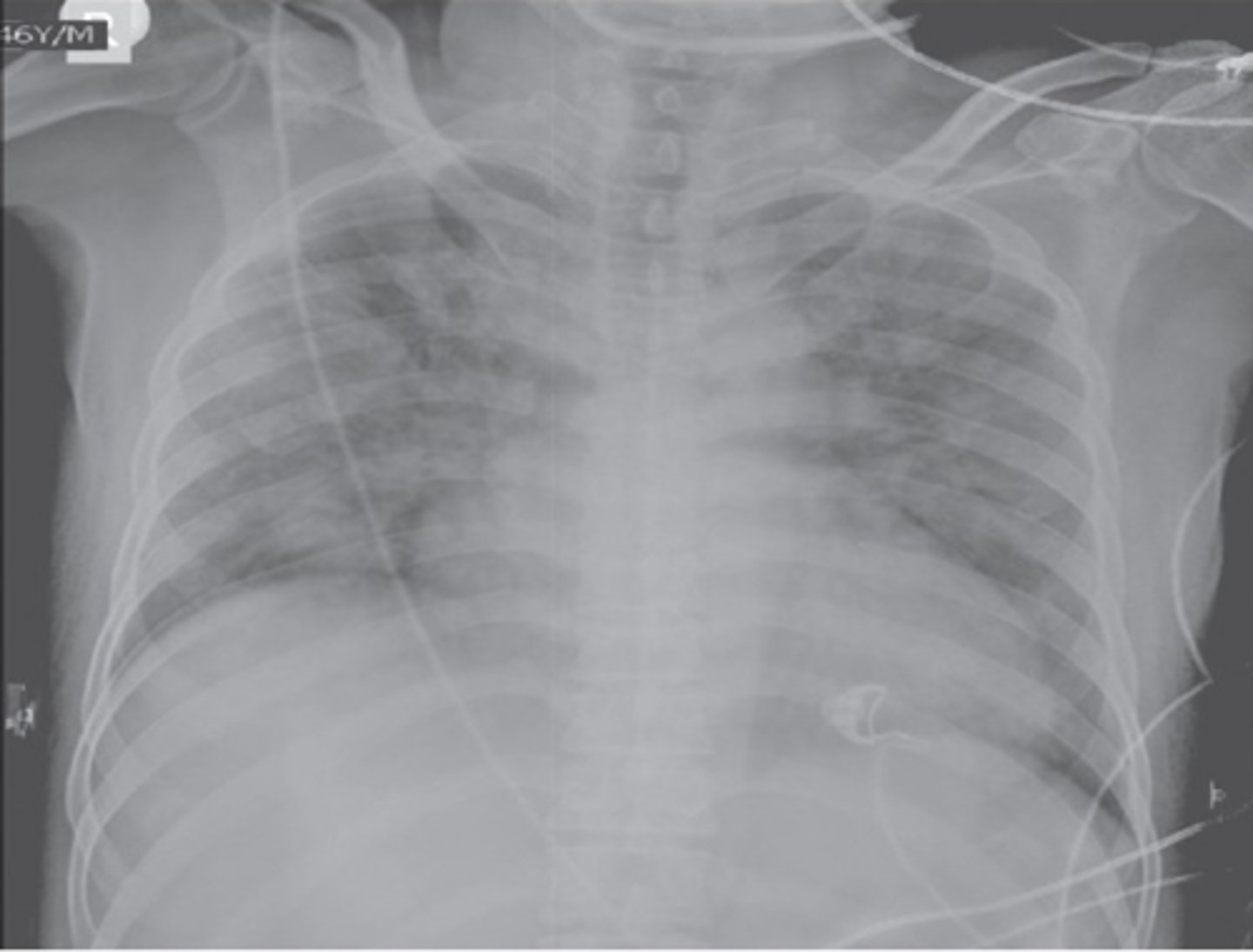
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema causing acute hypoxemia within 6 hours of the transfusion with clear temporal relationship to the transfusion
What is Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)?
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies or anti-HLA antibodies activate the recipient's immune system
What causes edema in Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)?
TRALI
Donor products that contain large amounts of plasma from multiparous women are associated with:
TRALI
- stop the transfusion
- save remaining bag
- maintain a patent IV line with normal saline
- confirm correct product was transfused
- contact transfusion service
What are immediate actions for acute rxns?
Donor lymphocytes recognize the patient as foreign and react against the recipient's body. The patient's immune system cannot clear the foreign lymphocytes
What is Transfusion-associated graft versus host disease?
anamnestic antibody response occurring after re-exposure to a foreign red cell antigen previously encountered by transfusion, transplantation, or pregnancy
What causes Delayed Hemolytic Reactions (DHTR)?
3-30 days after transfusion
When does Delayed Hemolytic Reactions (DHTR) occur?
falling Hct, slight fever, mild increase in serum indirect bilirubin, and spherocytosis on the smear
What are sx of Delayed Hemolytic Reactions (DHTR)?
by blood bank when a new positive direct antiglobulin test and new positive antibody screen are found
How is dx of Delayed Hemolytic Reactions (DHTR) often made?
1-6 weeks after transfusion
When does Graft versus Host Disease (GVHD) occur?
rash, fever, diarrhea, liver dysfunction, pancytopenia
What are signs and sx of Graft versus Host Disease (GVHD)?
irradiation of blood products
Gamma ____________ keeps donor lymphocytes from proliferating and can prevent transfusion-associated GVHD
Repeated failure of platelets to rise post transfusion
What is Platelet Refractory?
antibodies against HLA antigens
What causes immune Platelet Refractory?
splenomegaly, fever, sepsis, ABO mismatch, age of platelets
What causes nonimmune Platelet Refractory?
freshest, ABO-matched; HLA-matched
If immune cause, then _________, if HLA antibodies detected, then ___________
limited resource
Blood products are a:
diuresis
Blood products = volume; may need to balance transfusions with:
consent
Blood transfusion requires:
Acetaminophen and antihistamines
What are routinely given prior to transfusions to prevent FNHTRs or allergic reactions?