Flower structure and Pollination
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are angiosperms?
Plants which produce flowers.
What is the organ of sexual reproduction in plants?
The flower.
Many species of plants have flowers which are ‘hermaphrodite.’ What does this mean?
The flowers contain both male and female parts.
Draw a diagram showing the reproductive structure of a plant.
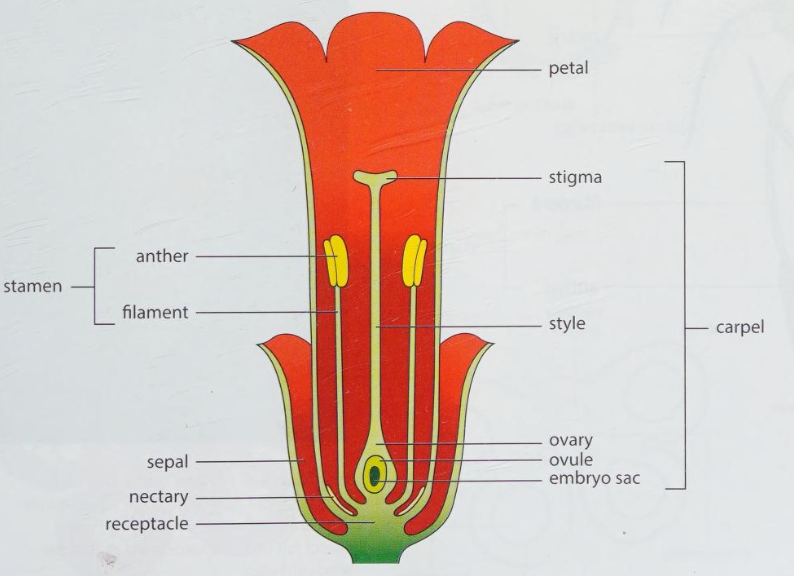
What is the male reproductive part of a flower called?
Stamen.
What does the stamen consist of?
Anther
Filament
What is the female reproductive part of a flower called?
Carpel.
What does the carpel consist of?
Stigma
Style
Ovary (contains the ovule)
What are the 2 methods of pollination?
Insect pollination
Wind pollination
Describe some key features of insect pollinated flowers.
Larger, brightly coloured petals (attracts insects)
Scent and nectar
Anthers within the flower
Stigma within the flower
Only a small quantity of pollen is produced
Pollen is often sticky / spiky to stick to insects
Describe some key features of wind pollinated flowers.
No petals / small, green petals
No scent produced
Anthers hanging outside the flower
Large, feathery stigma hang outside the flower
Large quantities of small, smooth pollen produced
Why do wind pollinated flowers produce large quantities of pollen?
To increase the chance of pollen landing on a stigma of the correct species.
Why do the anthers and stigma stick out of the flower in wind pollinated plants?
Pollen can be shed easily into the air and the stigmas can pick up pollen;
the anther is attached loosely so that even a slight breeze will shake pollen into the air.
the stigma is usually feathery to increase the surface area.
What is pollination?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the mature stigma of a plant of the same species.
Pollination brings the pollen grains, containing the male gametes, into contact with the female part of the flower, which can result in fertilisation.
What is self pollination?
Pollen from the anthers of a flower is transferred to the mature stigma of the same flower.
Self pollination results in inbreeding.
What is cross pollination?
Pollen is transferred from the anthers of one flower to the mature stigma of another flower on another plant.
Cross pollination results in outbreeding.
What are the advantages of self pollination?
Pollination is rapid with a high chance of success therefore increasing the chance of seed production and survival of the species.
The offspring have reduced genetic variation - the genes all come from the same plant and so if the plant is well-adapted to living in a particular environment / habitat, the genes are conserved in the offspring.
Good genomes are preserved – if there is little change in the environment, keeping the same adaptations increases the chance of species survival.
What are the disadvantages of self pollination?
There is a greater chance of two potentially harmful alleles being brought together at fertilisation.
Self fertilised species depend on independent assortment and crossing-over in meiosis and on mutation to bring about genetic variation in the genomes of their gametes.
Because of this, they display less genetic variation.
What are the advantages of cross pollination?
Cross pollination combines the gametes from two individuals, in addition to the events in meiosis and mutation, resulting in more genetic variation.
Reduced chance of harmful alleles combining.
What are the disadvantages of cross pollination?
Good combinations of alleles can be lost due to crossing over and random fertilisation.
How do flowering plant species ensure that cross pollination takes place?
Stamen and stigma matures at different times; if pollen falls on stigma which has not yet matured, fertilisation cannot take place.
Anther is below the stigma which means pollen cannot fall unto the stigma.
Genetic incompatibility- i.e. the pollen grains will not germinate on the stigma of the flower which produced it.
Separate male and female flowers on the same plant.
Seperate male and female plants.