Pig breed/production, Goat breeds/production, Sheep breeds/production
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms

Yorkshire
Most recorded breed in the us
Erect ears
Heavy muscling
High proportion of lean meat
a lot of backfat
Structural soundness and durability

Hampshire
“Belt”
4th most recorded breed in the US
High lean muscle production
High carcass quality
Minimal backfat
Large loin area
Good mothering abilities
Good longevity

Berkshire
3rd most recorded breed in the US
Fast and effective growth
Reproductive efficiency
Excellent meat flavor and value
Oldest swine registry in the US

Duroc
2nd most recorded breed in the us
Red pig with droopy ears
Excelled product quality
Good Carcass yield
Fast growth
Excellent lean grain efficiency

Landrace
Excellent mothering abilities
Heavy Milkers
Often crossed with other breeds
High length of body
High percent of carcass weight in loi/ham

Chester White
Originated In Chester county , PA
Droopy medium sized ears
Good mothering abilities
Durable
Structural soundness
Good muscle quality

Poland China (Other Breeds)
Originated in Ohio
Known for Large frame,length of body, Leaness and muscle
Droopy ears

Spotted (OB)
Originated in Ohio
Sub breed that split off from the Poland China
Characterized by large black and white spots
Known for High feed efficiency
rate of grain
Carcass quality

Meishan (OB)
Originated in China
one of the oldest domesticated pig breeds
known for Wrinkled face and skin
One of the most prolific breeds
Large litter size

Pietrain (OB)
Originated in Belgium
Characterization medium-sized, White with black spots, erect ears
Shorter than most breeds
Stockier in build
Broad along the back

Red Wattle
Originated in New Caledonia
South Pacific Island near Australia
Tasseled pig
pair of wattles
Breed is known for lean meat with excellent flavor
Swine Reproduction
Estrous Cycle length 18 - 24 days
Gestation length 114 days
Classifications Goats
Dairy,meat Fiber
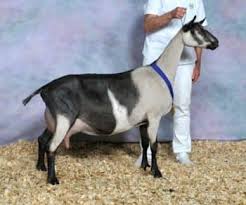
Alpine ( Dairy)
Originated in the Alps
Generally short haired
No distinct color established
Moderate size - 135 - 170
Heavy Milkers
Empasis on milk prodution and udder placement

Lamancha ( Dairy)
Developed in Oregon, USa
Excellent dairy temperment
Two Types of ears elf and gopher
High componet milk
High Fat

Nigerian Dwarf (Dairy)
West Africa Originated
Miniture Goat
Ideal weight 75 lbs
High prolificacy
up to five kids
Early onset of puberty
Smaller udder/ teats than other breeds

Nubian (dairy)
developed in England
Anglo - Nubian
Pendulous ears
Good udder quality
Large frame - 250 lbs
All purpose breed
moderate milk production with high average butter fat

Saanen (dairy)
originated in Switzerland
heavy milk production 3-4% milk fat
Color - white or light cream
performs best in cooler condition

Toggenburg (dairy)
Originated in Switzerland
Oldest known dairy goat breed
Medium sized - dos- 125 lbs
Excellent udder development
High milk production - averages 3.7% fat

Boer (meat)
Large meat breed - 200 lbs
Imported from South Africa into the US
Fats Growing breed within US
Excellent carcasses
150% kidding rate

Kiko (meat)
Originated in New Zealand
Crossbreeding feral does
Mixed with nubian, toggenburg and Saanen
Moderate frame - 100 lbs
imported to US in 1990s

Pygmy (meat)
West Africa Originated
Small frame
Now utilized more as a companion

Spanish (meat)
Developed in Spain
Primary meat goat before 1993
Grazed SW
feral, hardy,efficient,slow growth,poor milk
Smaller frame size in feral animals

Texmaster (meat)
developed in texas
crossing Tenesse Meat Goats with Boer goats
develop a meat to meet commmercial demands
Low Maintenace ,efficient fee utilization
rapid growth and thrifty

Angora (fiber)
Originated in Asia Mino
1571 - 1451 BCE
Produces Mohair
Small animals with considerable size variation
Susceptible to internal parasites

Cashmere (fiber)
Originated in the Himalayan region
Easy to raise
Sheared once a year - 2.5lbs fleece
Relatively new industry in US After 1980s

Pygora (fiber)
Developed in oregon
cross between Pygmy and Angora
Smaller size than Angora
Produce fine fibers for hand spinning
Distribution of Goats in the US
Distribution of goats in the US
Top meat - Texas ,CA, TN
Top Milk- CA,WIS,Texas
Fiber- Arizona, New Mexico, Texas
What is a Breed? What is a Breed?
A breed: a group of animals having similar characteristics
• These characteristics may include color, wool and/or wool characteristics,
breeding, and reproductive characteristics
• “Breeds” are something typically found in domesticated species where we can
control selection and mating for specific targets
Methods of Sheep Breed Classification
• Primary Function (Major Use):
• Ram (terminal)
• Ewe (maternal)
• Dual-purpose, Dairy, Heritage, etc.
• Wool Type:
• Fine, Medium, Coarse, Hair
• Face color:
• Black, White, Red, Gray, Brockled
• Origin of Breed:
• England (U.K.), U.S, Spain, South Africa
Adapted from B. Campbell
Wool Type
• Fine
• Coarse
• Meat
• Hair (not wool!)

Katahdin
• Mature body weight:
• Ram - 180-250 lb.
• Ewe - 120-160 lb.
• Developed in Maine.
• St. Croix X Suffolk X Wiltshire Horn.
• Easy care sheep, survivors
• Hair coat of any color or pattern.
• Largest hair breeds.
• Lean carcasses, lighter muscled
• Parasite resistance.

Merino
• Spain, for centuries, bred the sheep
with the finest wool and forbade the
trading of sheep with other countries
• Napoleon’s war with all of Europe
weakened Spain’s ability to control
export
• Col. Humphrey illegally brought back
100 Merinos in 1802
• Tremendous genetic pool improvement
• Consul Jarvis imported another 3,850
Ohio Wool Growers Association, 1876; Briggs, 1958;

Border Leicester
• Mature body weight (<200 lb ewes)
• Developed in England.
• Leicester X Cheviot crosses.
• U.S. - High rainfall, good pasture areas.
• Medium to large frame.
• Good milkers/mothers.
• Long-stapled, lustrous coarse wool for
hand spinning.
• Featured on the movie “Babe”

Cottswold
• Mature body weight (>200-300 lbs)
• “Gentle giants”
• Cotes (enclosures), wolds (hills)
• Historic breed (pre-1400s)
• Over ¾ million in U.S. ca 1914
• Under 400 in 1990s
• Removed from rare list
• Foundational breed for many others

Rambouillet
• Mature body weight (~200 lbs)
• Largest fine wool breed
• Developed from Spanish Merino
• In France and Germany.
• Backbone of Western U.S. sheep industry
• Adaptable to dry, arid conditions
• High quality fine wool fleece

Lincoln
• Mature body weight (250-300 lbs):
• Developed in England
• Leicester X “Lincolnshire” crosses
• Large, deep bodied, polled
• Course, lustrous, heavy fleece
• Dual-purpose sheep breed
11/18/24
7
Face Color
• Face color (and face wool) can tell you a lot about sheep breeds
• Black face – primarily terminal breeds, muscle, meat production
• White face – primarily wool or mothering breeds

Tunis
• Heat tolerant, out-of-season breeders
• Dual-purpose, moderate meat and wool
• Originally from North Africa imported to the
U.S. in 1799
• Devastation of the American Civil War nearly
eliminated the breed in 1865

Scottish Blackface
• Mature body weight:
• Ram - 150-175 lb.
• Ewe - 115-130 lb.
• Developed in the border area of Scotland
and England.
• One of the most important sheep breeds in
the United Kingdom.
• Used to improve pastures.
• Excellent mothers.
• Thrive well on brushy hillsides and
withstand harsh winter conditions.

Shropshire
• Mature Body Size (200-250 lbs)
• Developed in England.
• Introduced into U.S. In 1855
• Native sheep and Southdown, Leicester,
Cotswold crosses
• Flock favorite for many years.
• Good Mothers, but sed as terminal sire
• One of most popular breeds of sheep through
1950’s and 60’s, are once again gaining in
popularity (youth projects)

Hampshire
• Most influential carcass sheep East
of the Mississippi
• Adapt well to different geography
• Larger breed, roughly 250-300 lbs
• Fast growth, muscular, statured
• Imported in 1840s, gone by 1870
• Re-imported in the 1880s

Suffolk
• Developed in England, imported to U.S. in 1888
• Largest U.S. breed (up to 400 lbs), fastest growing, carcass quality
• Highest number of registration among all breeds in the U.S.
• Spider lamb and scrapie carriers

Dorper
• Mature body weight (~200 lbs):
• Developed in South Africa.
• Blackheaded Persian X Horned Dorset
• Mixture of hair and wool, does not
require shearing
• Non-selective grazers
• Rapid growth, quality carcasses
• Growing popularity

Corriedale
• Mature body weight (175-200 lbs)
• Developed in New Zealand – 1860s
• Breed officially established in 1924
• Merino x English Lincoln Longwool
• Heavy-yielding fleeces
• Moderately framed, decent carcasses
• Mothering ability, adapt well
• Black nose, black hooves.

Southdown
• High cutability carcass
• Only lost national carcass show 3
times between 1906 and 1956
• Moderately sized, roughly 200 lbs
• “Dual purpose”, medium wool
• Heritage breed
• Arrived with the colonists

Horned Dorset
• Originated in Southern England, was
original foundation for the Polled Dorset
breed.
• Introduced into U.S. in 1885.
• Horned characteristic is sex-influenced,
both rams and ewes have horns.
• Rams possess a heavy, masculine horn,
ewes possess a fine, feminine horn.
• Out-of-Season breeders.
• Excellent milkers.
• Known for mothering ability.

Polled Dorset
• Out-of-Season breeders
• Mature body weight (200-250 lbs)
• Developed in Southern England.
• Dorset Horn - to U.S. in 1885.
• Mutation at N.C.S.U in 1948 created Polled
strain.
• Excellent milkers.
• Excellent mothering ability.
• Excellent commercial ewe base.

Cheviot
• Mature body weight:
• Ram 160-200 lb.
• Ewe 120-160 lb.
• Developed in Hill Country between Scotland
and England.
• Small frame size.
• Highly adaptable.
• Excellent lamb vigor.
• Produce valuable small carcasses.

Texel
• Mature body weight (~200 lbs)
• Developed in Netherlands
• Introduced into U.S. in 1990
• Hardy, adaptable, medium sized
• High muscle-bone (lean-fat) ratios
• Extreme muscling
• Excellent carcass cutabilityC

Columbia
• Mature body weight (250+ lbs):
• First breed developed in the U.S. (1912)
• Dubois Research Station
• Lincoln x Rambouillet
• Large frame, heavy sheep
• Increased use as terminal sires to
increase the frame size in commercial
blends
• Heavy, medium fleece
• Pink nose, white hooves

Targhee
• Moderate wool cross (225 lbs)
• US Breed Developed in 1926
• Association in 1952, Mont. St. Univ.
• Named after the forest near Dubois
• Designed ¾ fine fleece, ¼ long wool

Montadale
• Mature body weight:
• Ram 200-275 lb.
• Ewe 160-180 lb.
• Developed in U.S.
• Cheviot X Columbia crosses.
• Found in many midwest farm flock states.
• White head and legs, white wool.
• Black nostrils and hooves.
• Produce excellent lean carcasses.
• Good maternal traits.

Polypay
• “Dream Breed” from US Exp.
Station
• 1960s, registration 1980s
• Combo of:
• Finn for prolificacy
• Rambouillet for wool fineness
• Dorset for long breeding season,
carcass
• Targhee for frame size
• Wool quality, mothering, growth

Club Lamb Industry
• Influenced by Suffolk,
Hampshire, Dorset, &
Southdown
• Lucrative industry
• Expensive: some rams can
sell for >$100,000
• Follow a trend
• Terminal production
How to Choose?
• Terminal Production:
• Emphasis: growth, feed efficiency, carcass, lamb livability.
• Reproduction:
• Emphasis: prolificacy, weaning weight, milk production, out-of-season lambing.
• Environment:
• Rangeland, wet grassland, Southern heat
• Fleece production:
• Fleece micron (smaller, the higher quality)
• Milk production (minor)