Chapter 14: Analysis of Circuits Containing Batteries and Resistors
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Circuits
Circuits
Batteries
Resistors
Circuits Containing Batteries and Resistors
Currents
Current Density
Drift Velocity
Resistance
Resistivity
Resistance from Resistivity
Resistors in Parallel
Resistors in Series
Complicated Resistor Arrays
Single Battery
Potential Drop Across Series Resistors
Current Through Parallel Resistors
Kirchhoff’s Law
Power Dissipated Across Resistors
Internal Resistance
12th
Last updated 2:42 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Current
Defined as the rate of charge flow per unit time through some surface with units of amps (A \= C/s).
2
New cards
Amps
SI unit of Current
3
New cards
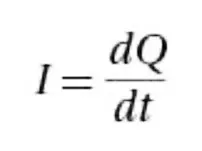
Definition of the magnitude of current
4
New cards
Current density (J)
is a vector field within a wire.
5
New cards
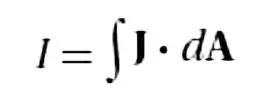
Relationship between current and current density
6
New cards
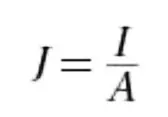
Relationship between current and current density for the case of a straight wire where the current density is uniform and parallel to the wire
7
New cards
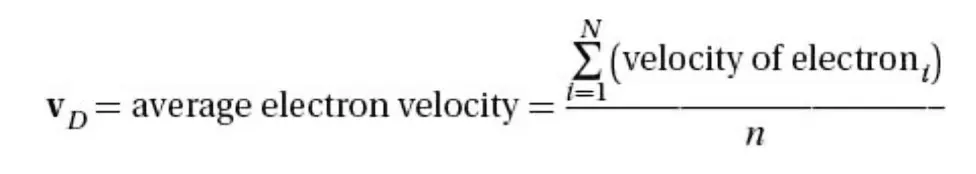
Definition of drift velocity
8
New cards
Charge carrier density (n)
is generally defined as the number of mobile electrons per volume.
9
New cards
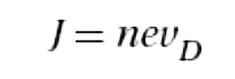
Relationship between current density and drift velocity
10
New cards
resistance of the resistor
The potential difference across a resistor is proportional to the current through the resistor, with a ratio defined as the \______.
11
New cards
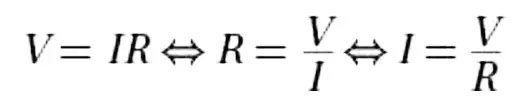
Ohm’s Law
12
New cards
Ohm’s law
is an experimental observation that V is independent of R and applies to many, but not all, materials.
13
New cards
ohms
SI units for resistance
14
New cards
voltmeter
used to measure a voltage
15
New cards
ammeter
used to measure a current
16
New cards
voltmeter
connected in parallel with circuit elements
17
New cards
ammeter
connected in series
18
New cards
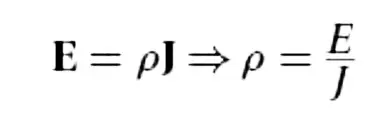
Definition of resistivity
19
New cards
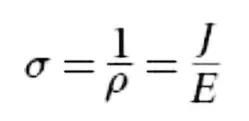
Definition of conductivity
20
New cards
conductivity
is defined as the reciprocal of resistivity
21
New cards
Resistivity
is the property of a certain material
22
New cards
resistance
is the property of a particular object that depends on both the resistivity and the geometry of the object
23
New cards
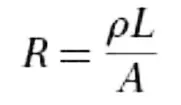
Resistance of a resistor with length L, cross-sectional area A, and resistivity ρ
24
New cards
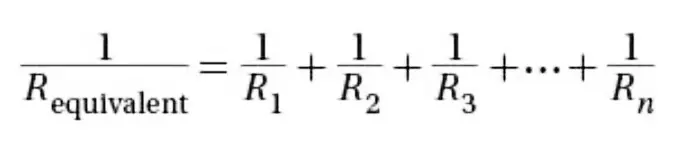
Resistors in parallel
25
New cards
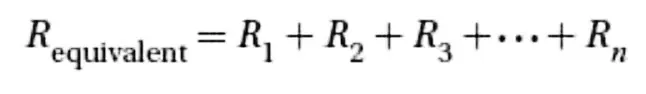
Resistor in Series
26
New cards
Node Rule
At any intersection of wires, the total current entering the intersection must equal the total current leaving the intersection.
27
New cards
Loop rule
The sum of the potential differences around any closed loop must be zero.
28
New cards
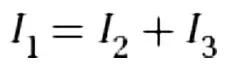
Node Equation
29
New cards
battery
is a chemical device that boosts the potential energy of electrons flowing through it.
30
New cards
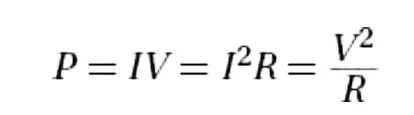
Rate of energy transfer to a resistor
31
New cards
real battery
A \_____ is a series arrangement comprising an ideal resistance-free battery and an internal resistor, even if all its components have resistance.
32
New cards
EMF
voltage of the resistance-free battery to the total electromotive force of the battery.
33
New cards
terminal voltage
refers to the voltage of the terminals of the real battery.
34
New cards
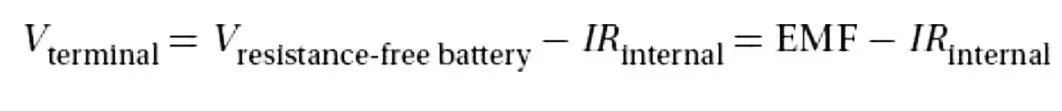
voltage across real batteries is actually a function of the current flowing through them