OCR A 3.2.1 Enthalpy changes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
enthalpy
-measure of heat energy in a chemical system (atoms, molecules or ions making up chemicals)
-energy stored within bonds
enthalpy change
-heat change in a reaction at constant pressure
-units: kJmol-1
-(enthalpy of products - enthalpy of reactants)

average bond enthalpy
when 1 mole of bonds of gaseous covalent bonds is broken
standard condition
-100kPa
-298K/25oC
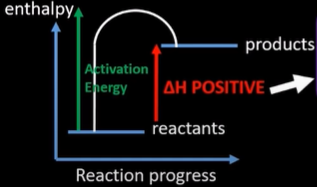
exothermic reactions
-reaction that release energy to surrounding
-reactant higher in energy than product
-negative enthalpy change
endo reaction profile
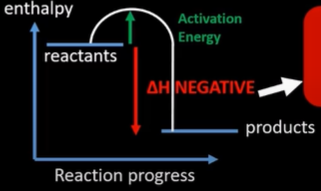
endothermic reactions
-reaction that absorb energy from surrounding
-products higher in energy than reactant
-positive enthalpy change
endo reaction profile
standard enthalpy change of reaction
-enthalpy change of reaction according to molar quantities in the equation under standard conditions

standard enthalpy change of neautralisation
-the enthalpy change when an acid and alkali react to form 1 mole of water, under standard conditions

standard enthalpy change of formation
-the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its element in their standard states, under standard conditions

standard enthalpy change of combustion
-the enthalpy change when 1 mole of substance is completely burned in Oxygen to make CO2 and H2O under standard conditions

what happens when bonds are broken
-to break bond energy needs to be absorbed
-bonds broken in reactants
-enthalpy change is positive; endo
endo and bonds
-when more energy is needed to break bonds than energy given out when bonds are formed
what happens when bonds are made between
-energy is released
-bonds made when products is being produced
-enthalpy change is negative
exo and bonds
-when more energy is released when bonds are formed than what was needed to break initial bonds
mean bond enthalpy (backstory)
-bonds of same type don’t have all have same amount of energy
-eg: CH4 dif energy needed to break 1st bond than 2nd bond
-so measure the enthalpy of break all bonds and find average
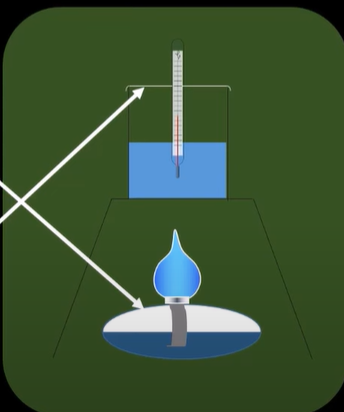
calorimetry combustion
-used to work out enthalpy change of combustion
-fuel is burned to raise temp of water by specific amount
-weigh fuel mass before and after
-energy from fuel often lost to surroundings instead of heating water
-lid placed on top to prevent heat loss
-wind shields to prevent draught moving flame
-calc using q=mcAt
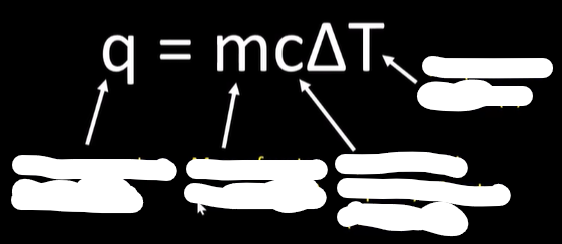
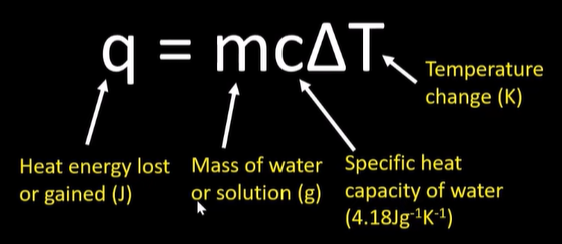


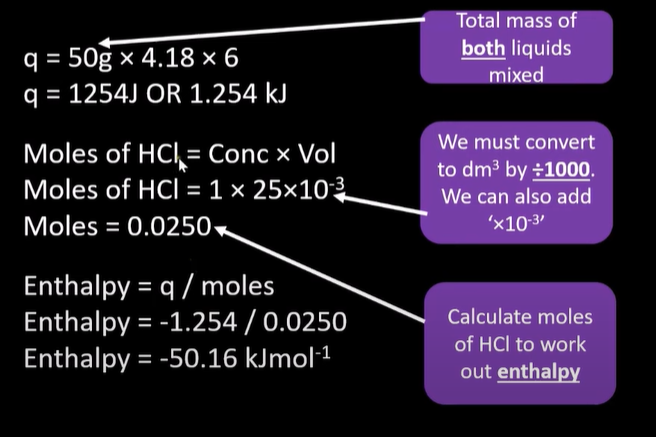
calorimetry solution
-add acid and measure temp
-add solid/alkali measure temp change
use q=mcAt

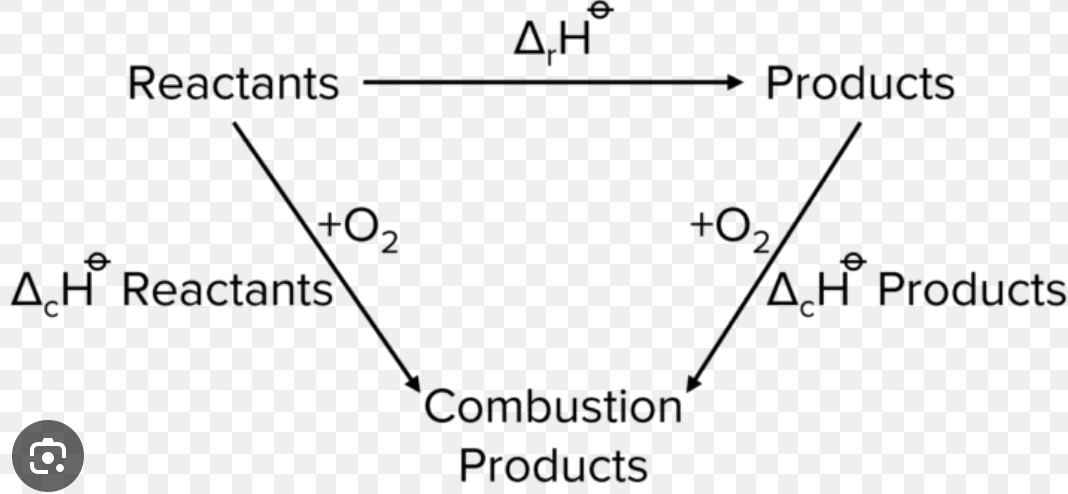
hess’s law
total enthalpy change of a reaction is dependant of the route taken
hess cycle formation
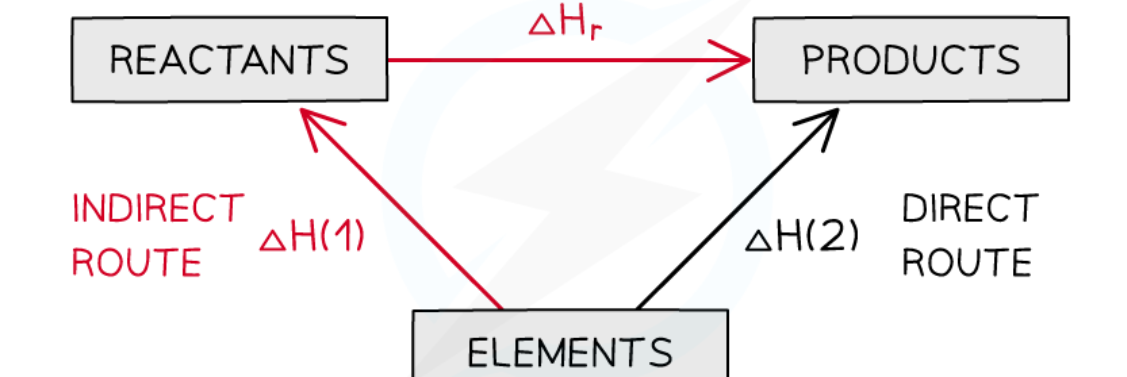
hess cycle combustion