Photosynthesis/cellular respiration/fermentation - Hon bio
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
chemical equation of photosynthesis

word equation of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → sugar (glucose) +oxygen
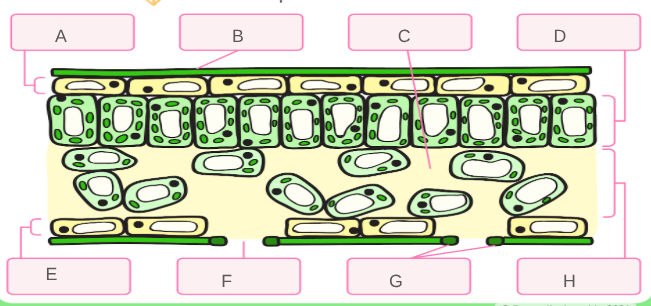
Label each part of the leaf tissue
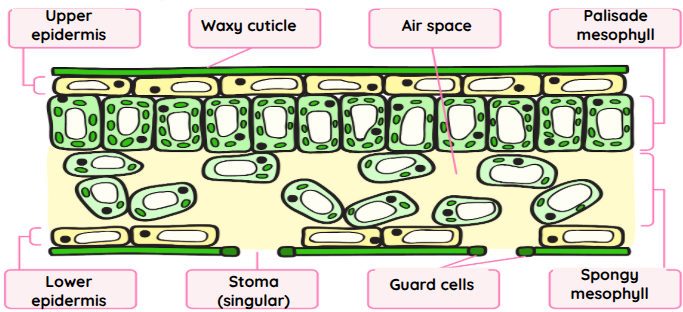
Upper and Lower Epidermis
These cover and protect the surface of the plant. They secrete the waxy cuticle. This layer is thin to allow light to penetrate it.
waxy cuticle
This is waterproof layer that helps to minimize the water loss from the plant.
Palisade Mesophyll
The cells of this tissue are tightly packed. They contain many chloroplasts containing chlorophyll to absorb light for photosynthesis.
Spongy Mesophyll
This tissue has many air spaces, which allows gas exchange to take place easily. It allows carbon dioxide to diffuse in and oxygen to diffuse out.
Guard Cells
These control the opening and closing of the stomata (small pores in the leaf). This controls water loss and gas exchange.
What does the xylem transport?
water and mineral ions
What does the phloem transport?
dissolved food (glucose)
In which direction does the xylem transport molecules?
up
In which direction does the pholem transport molecules?
up and down
Does the xylem require energy to transport molecules?
no; physical process
Does the phloem require energy to transport molecules?
yes

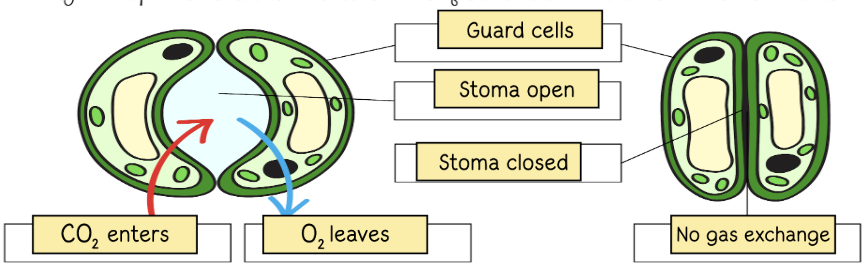
What is the purpose of the stomata in photosynthesis?
They control gas exchange (intake of C02 and outtake of 02) and regulate water vapor to prevent the plant from drying out.
Why are stomata able to close?
to prevent water loss (downside: also stops photosynthesis)

What are the reactants of photosynthesis? (select all that apply)
a. Carbon dioxide
b. Hydrogen
c. Oxygen
d. Water
e. Glucose
a. Carbon dioxide
d. Water
Besides these reactants, what else is needed for photosynthesis to occur?
light
What are the products of photosynthesis (the chemicals that are produced)? Select all that apply
a. Carbon dioxide
b. Hydrogen
c. Oxygen
d. Water
e. Glucose
c. Oxygen
e. Glucose
Which type of organisms can carry out photosynthesis?
Autotrophs
What is the name of the green pigment that absorbs light in plants?
chlorophyll
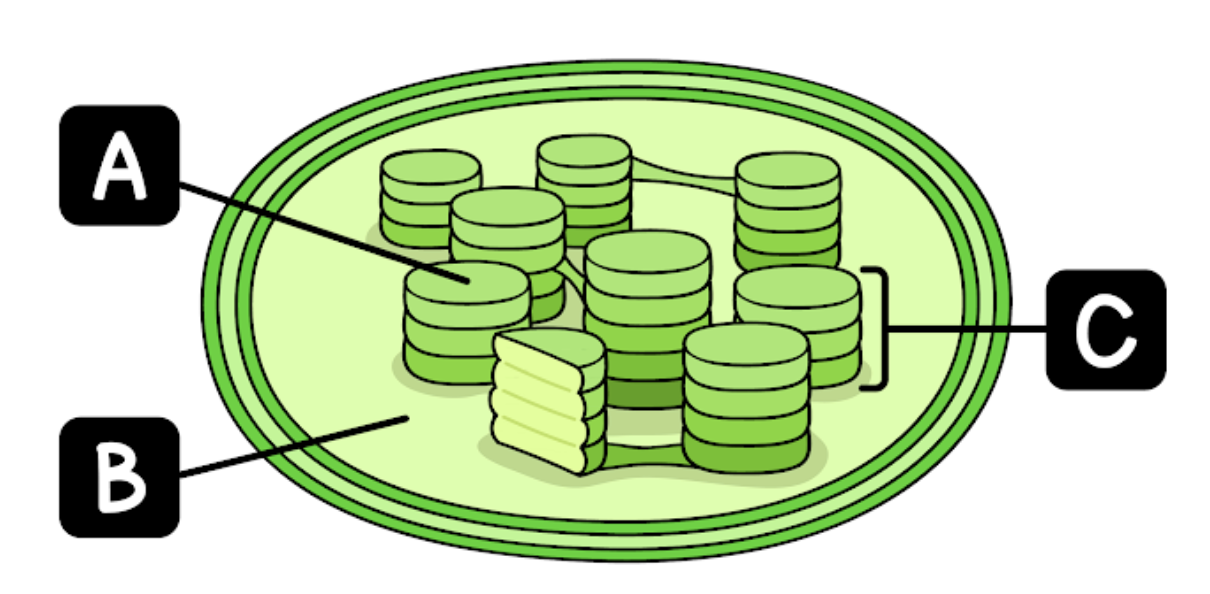
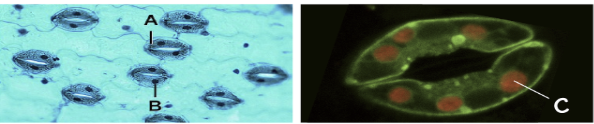
What is the name of the organelle shown in the diagram above?
Chloroplast
"The cells on either side of the stoma are called _______________ cells." What is the missing word in this sentence?
Guard
Which tissue in the leaf carries out the majority of photosynthesis?
Palisade mesophyll
Which factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis? Select all that apply.
a. Temperature
b. Availability of mineral ions
c. Light intensity
d. Carbon dioxide concentration
e. Oxygen concentration
f. Wind intensity
a.Temperature
c. Light intensity
d. Carbon dioxide concentration
Why do we see the leaf as green?
When light hits a green leaf, the chlorophyll pigment in the leaf absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light. Green wavelengths of light are reflected, which is why we see plant leaves as green.
What is light intensity?
how much light the plant receives
Photosynthesis is a ______ reaction
chemical
Can temperature control the reaction of photosynthesis?
Yes, high temperatures can denature proteins, while low temperatures can slow down enzyme activity. There is an optimal temperature at which enzymes function most efficiently.

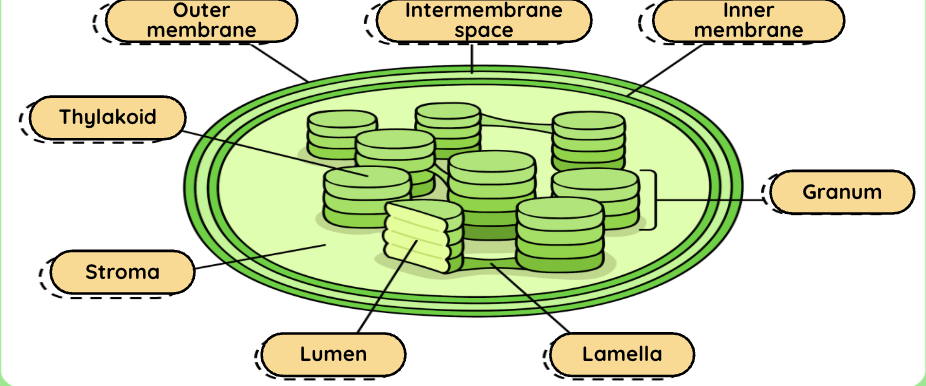
Where does the light-independent reaction take place?
stroma
Where does the light- dependent reaction take place?
thylakoids
light-dependent reactions ( label the thylakoid membrane)
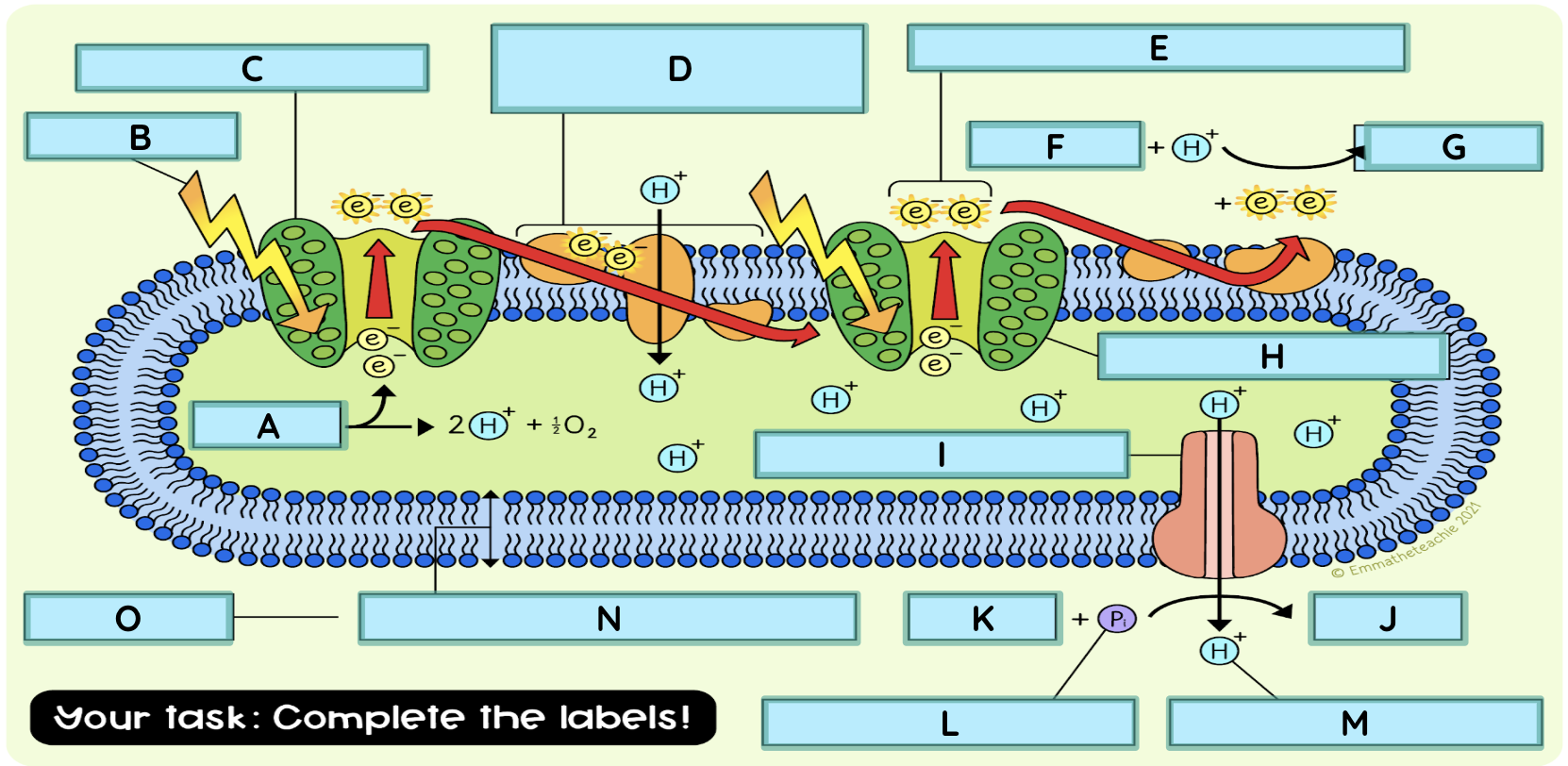
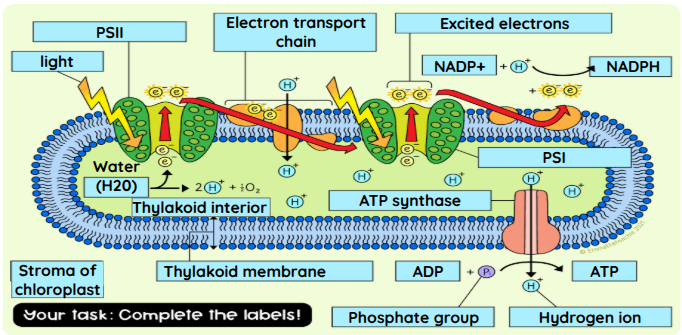
What is the source of energy for the light-dependent reaction in a thylakoid?
light energy from the sun
Where are chlorophyll molecules located?
inside chloroplasts (specifically in the thylakoid membrane and PSII and PSI.)
What happens when high energy electrons pass through the electron transport chain?
They lose energy, which is used to pump hydrogen ions and generate ATP and NADPH.
Which molecules combine to form ATP?
ADP and Pi (phosphate group)
Name the process where molecules combine to form ATP
phosphorylation
What is an electron acceptor?
a molecule or atom that receives electrons from another substance during a chemical reaction
What are the products of the dependent reaction that will go on to be used in the light independent reaction?
NADPH and ATP
How is ATP formed from ADP?
Through the addition of a phosphate group
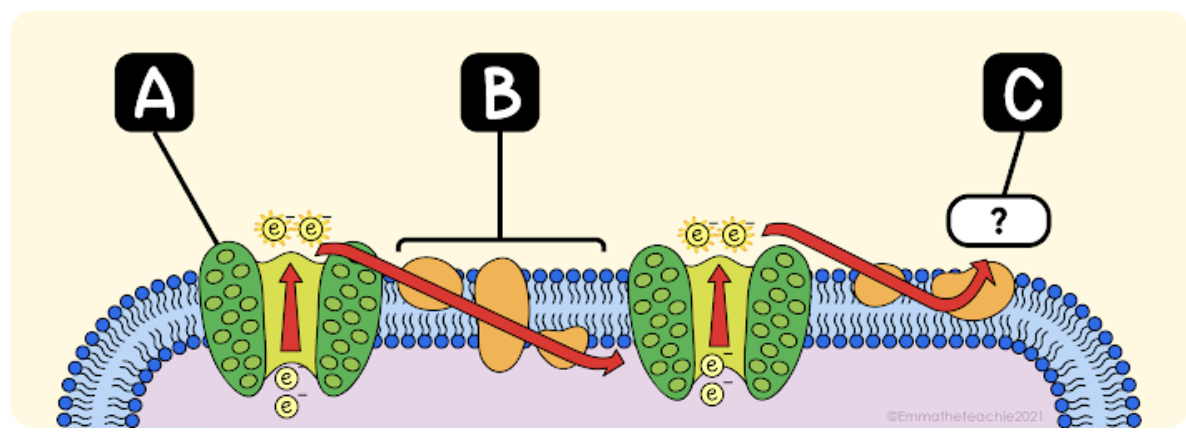
The electrons that are passed on from Part A to Part B must be replaced. What is the source of electrons for this?
water
What is the name of the process that turns ADP into ATP?
phosphorylation
In the light-independent reaction, a molecule called 3-PGA is reduced by NADPH. What does it mean if a molecule is reduced?
It gains electrons
How is ATP formed from ADP?
Through the addition of a phosphate group
What is the purpose of the light-dependent reaction?
To produce ATP and NADPH for the light-independent reaction
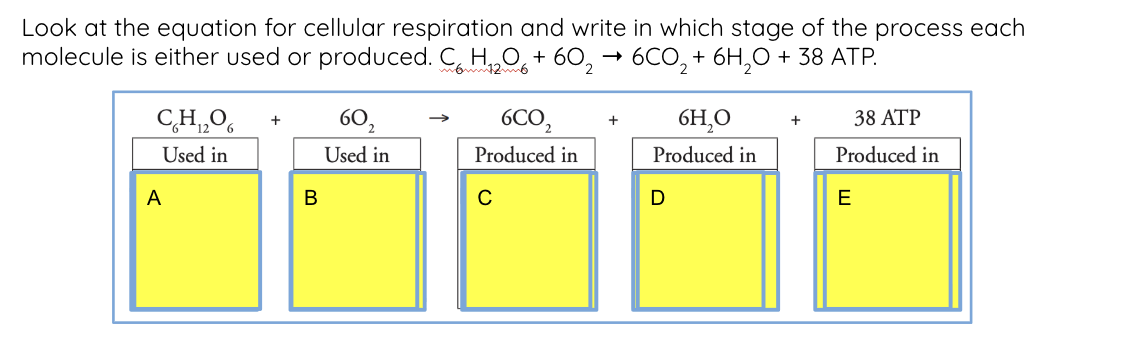
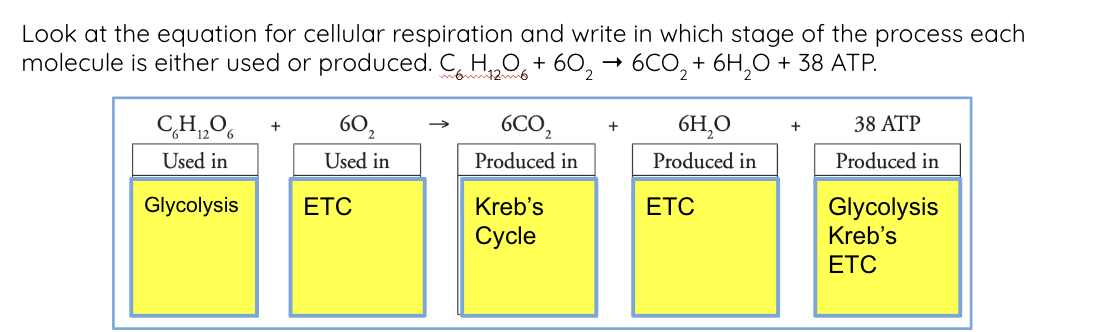
cellular respiration formula

cellular respiration in words
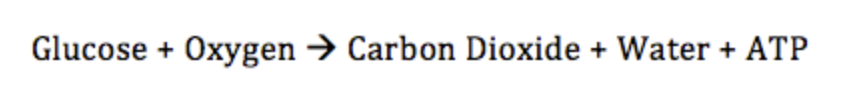
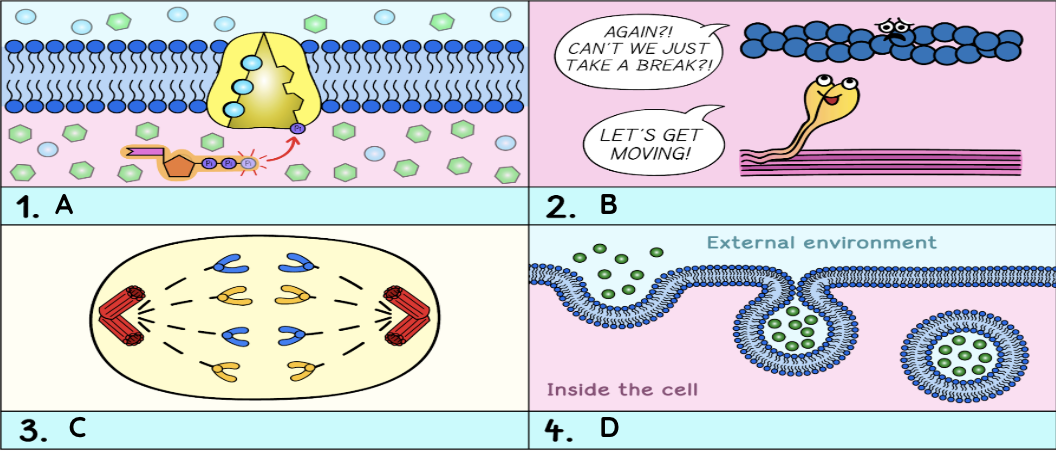
cellular respiration is…
a process that occurs in cells to convert chemical energy from glucose molecules into ATP
Where does cellular respiration take place in our bodies?
every cell in our body like muscle cells, nerve cells, skin cells, etc.
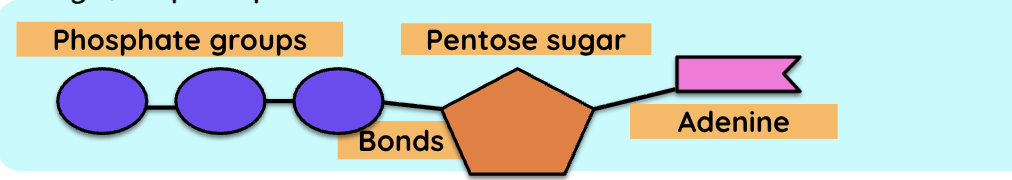
What does ATP stand for?
adenosine triphosphate
What does an ATP structure look like? Draw a model
What is glycolysis?
Glucose is converted into two pyruvate molecules. This releases energy to generate ATP from ADP and generate NADH from NAD+
Where does glycolysis take place?
cytosol - the liquid that surrounds organelles.
does glycolysis require oxygen?
does not require oxygen and is therefore referred to as anaerobic
What does it mean that NADH is a coenzyme that can accept electrons?
This means that it is able to “pick up” and transport electrons.
When does the intermediate/link reaction take place?
This takes place between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
What occurs in the intermediate/ link reaction?
Pyruvate is pumped into the mitochondrial matrix using active transport. It gets oxidized to form Acetyl coenzyme A - also called Acetyl-CoA. Two more NADH coenzymes and carbon dioxide are released.
What is the Krebs Cycle also known as?
The citric acid cycle
Where does the Krebs cycle take place?
mitochondrial matrix
What occurs in the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl CoA is used in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions (also called redox reactions).
What is produced from the Krebs Cycle?
The resulting products are carbon dioxide (a product of aerobic respiration), ATP, and the transfer of electrons to coenzymes NADH and FADH2.
Is oxygen required for the Krebs cycle?
Yes, it is aerobic and requires oxygen
Where is the electron transport chain located?
in the inner mitochondrial membrane
What occurs in the electron transport chain?
Electrons extracted in glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle are transported by coenzymes NADH and FADH2 to the electron transport chain. It is a series of proteins through which the electrons are transported.
Does the electron transport chain require oxygen?
Yes, it is aerobic and requires oxygen
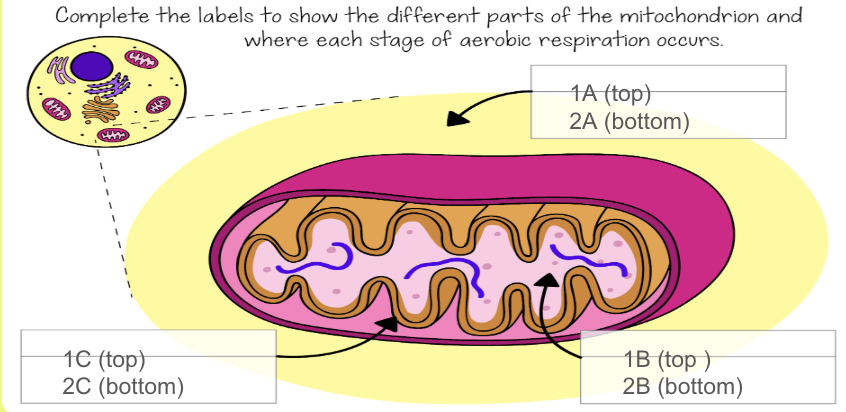
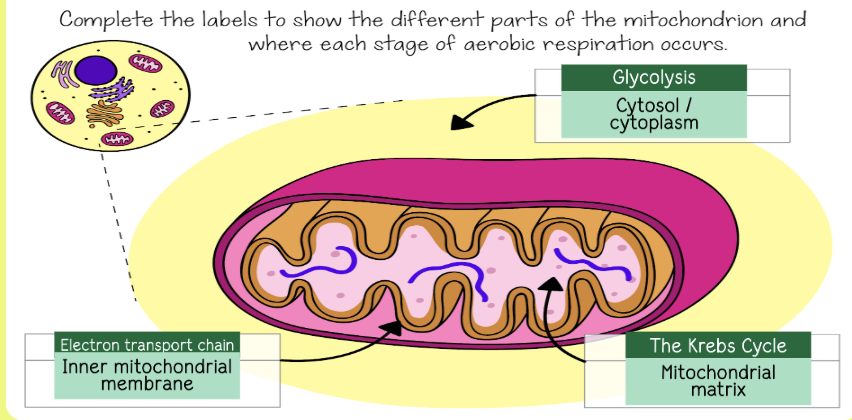
what is the singular version of mitochondria?
mitochondrion
What happens to pyruvic acid during the Krebs cycle?
first converted to Acetyl-CoA, releasing a carbon dioxide molecule and producing NADH
What are the two hydrogen-carrying molecules formed during the Krebs cycle?
NADH and FADH2
Summary of glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in a series of reactions in which glucose is converted into 2 pyruvate molecules. This releases energy to generate ATP from ADP. It also converts NAD+ into NADH. NADH is a coenzyme that can accept electrons. It will transport these to the electron transport chain.
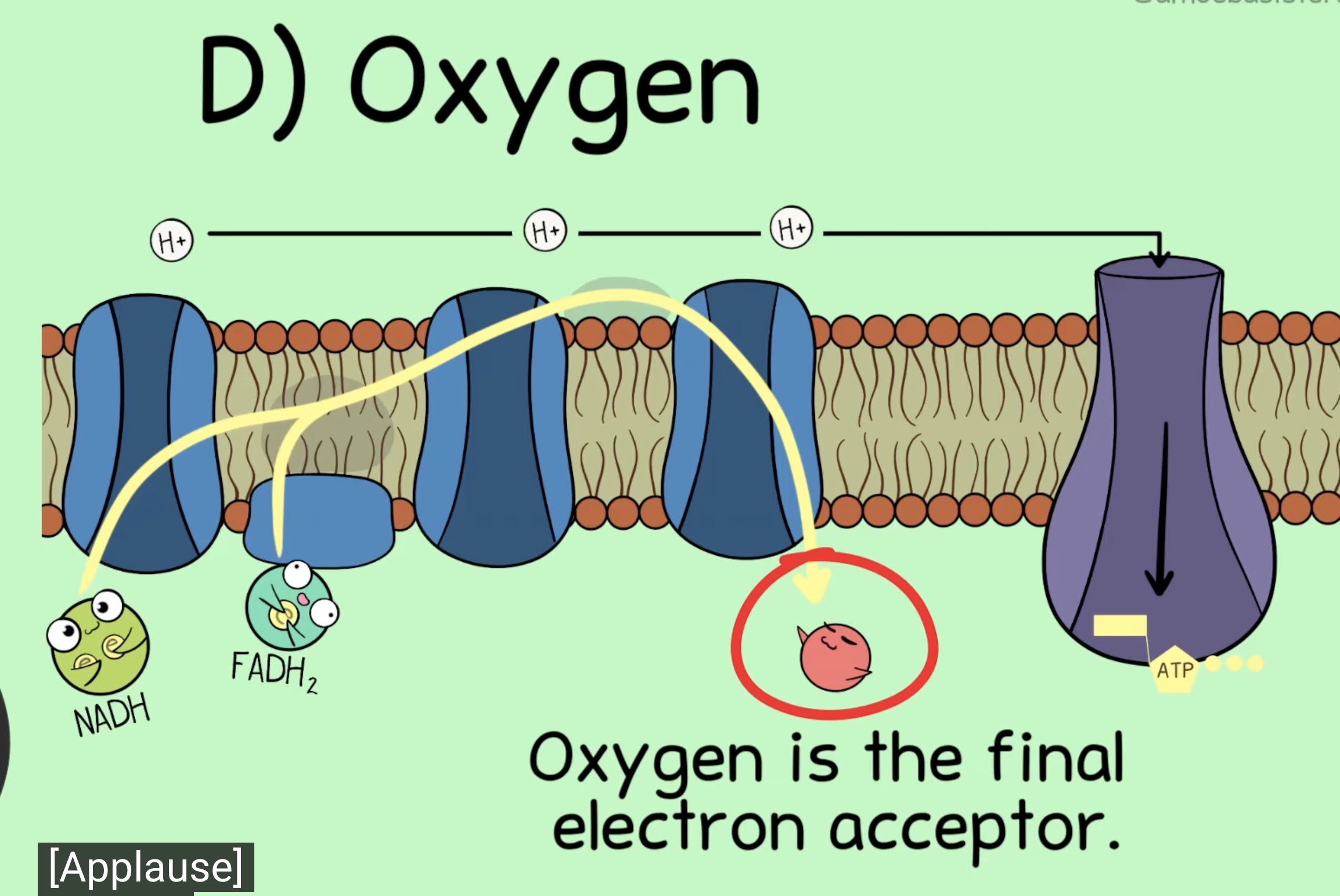
In aerobic cellular respiration, what is the final electron acceptor?
oxygen
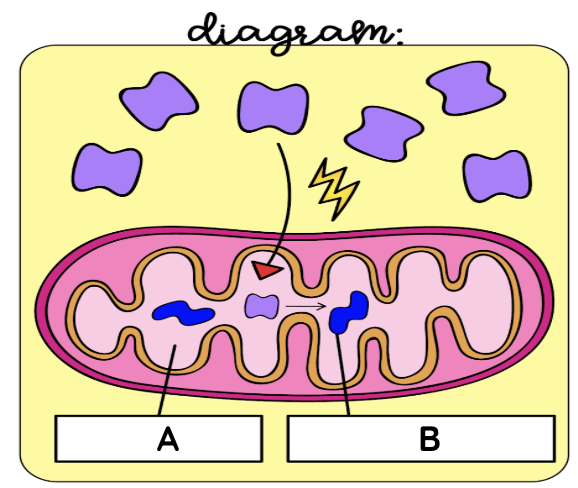
intermediate/link reaction
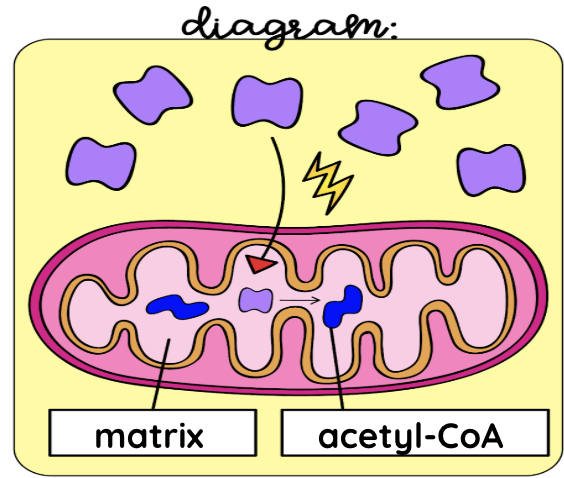
Intermediate/link reaction summary
Between glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, pyruvate must be transported from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix. It is pumped in using active transport. It is oxidized to form Acetyl-CoA, also known as Acetyl-CoA. This will be used in the Krebs Cycle. NADH and carbon dioxide are also produced.
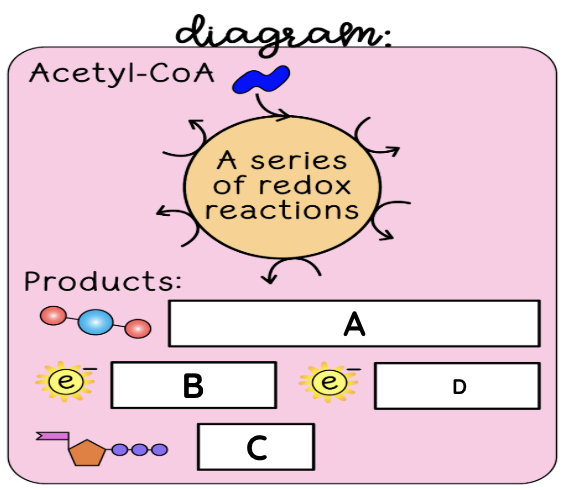
Krebs cycle
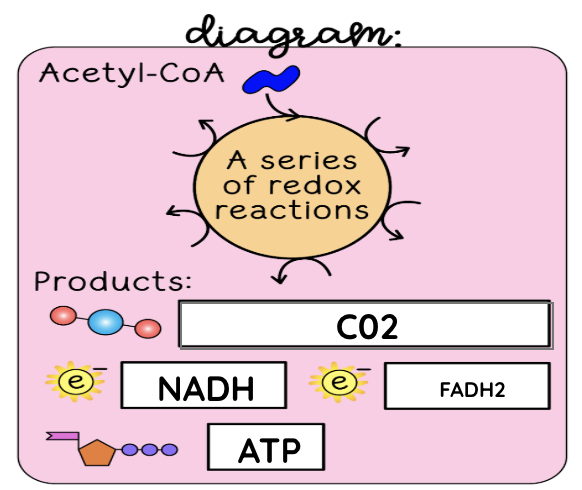
Krebs cycle summary
Acetyl-CoA is used in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions, also known as redox reactions. This needs oxygen to work. The Krebs Cycle releases the gas carbon dioxide. ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Electrons are transferred to the coenzymes NADH and FADH2.
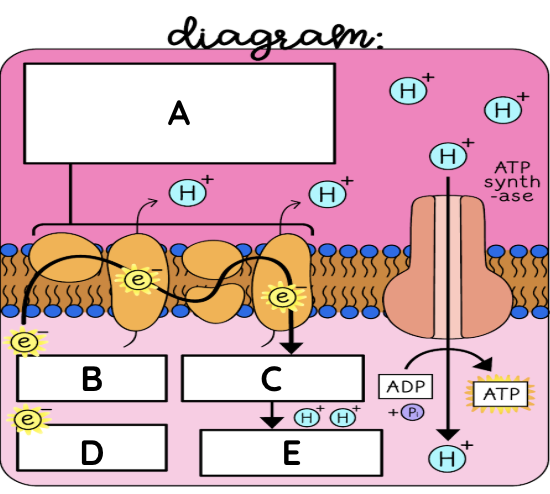
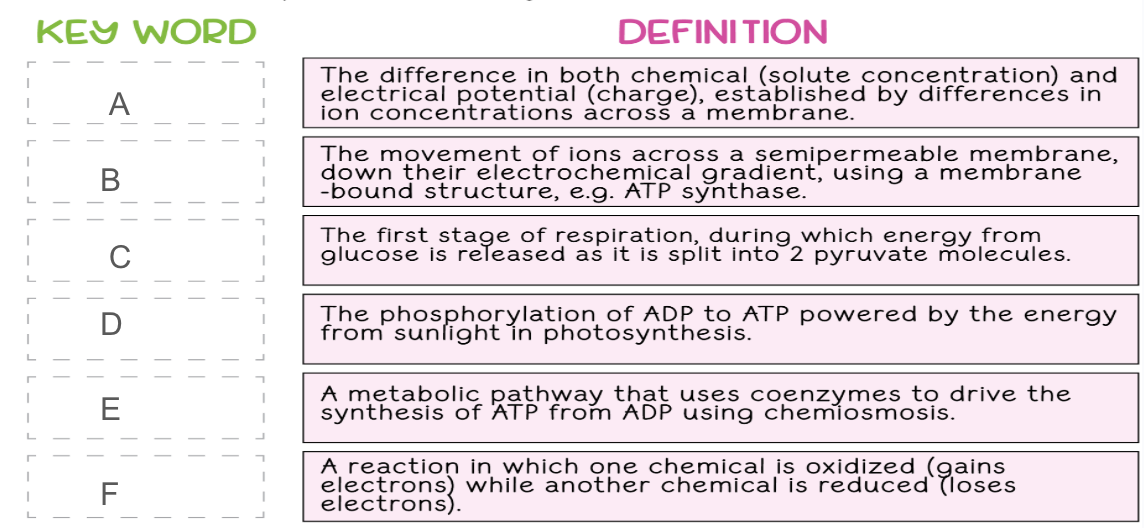
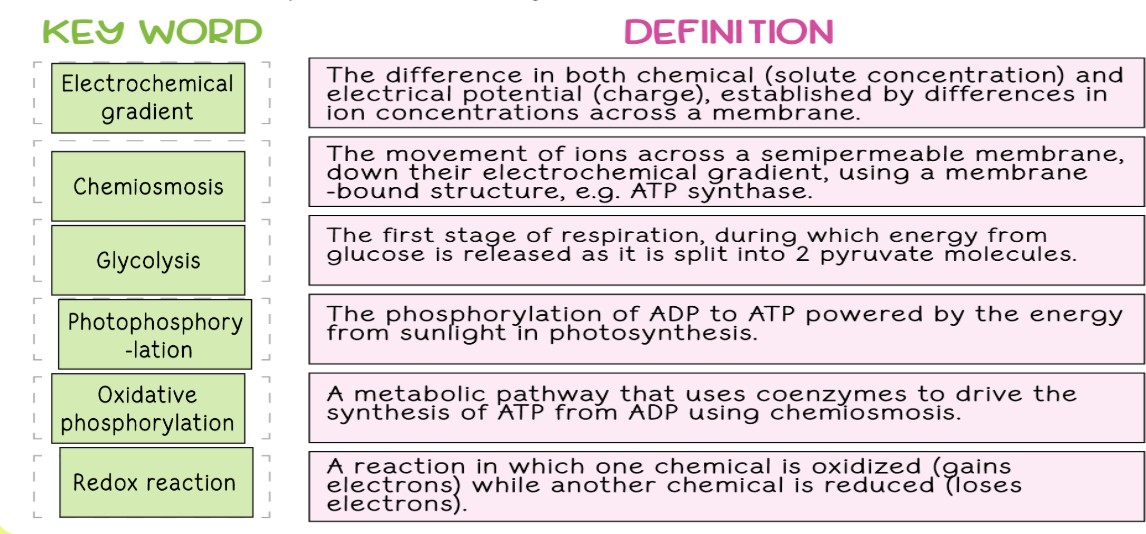
Electron transport chain
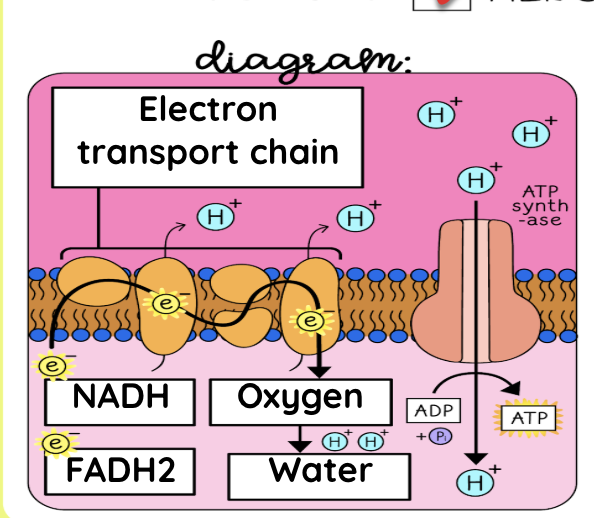
Electron Transport Chain summary for cellular respiration
NADH and FADH2 transport electrons to the ETC. As they pass along it, an electrochemical gradient of protons (H+ ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane is established. The flow of electrons back through ATP synthase by chemiosmosis drives the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor and forms water.
What substances do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane during the ETC stage?
H+
What high energy molecules are formed by the electron transport chain?
ATP
What atom accepts the hydrogen ion at the end of the electron transport chain?
What molecule is formed as a product of that acceptance?
oxygen, water
Compare the ATP available to cells when oxygen is present versus when it is absent. How might this help explain why brain and heart functions are so quickly affected when a person cannot breathe?
Since there would be so little ATP produced without oxygen, the cells of the brain and heart would die and the function would stop
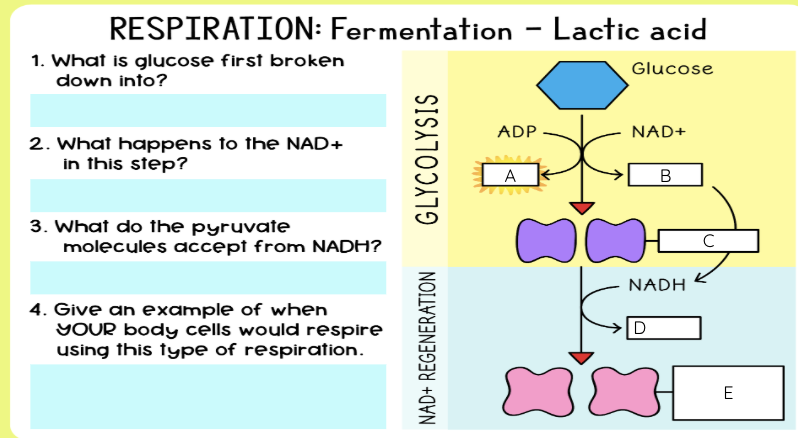
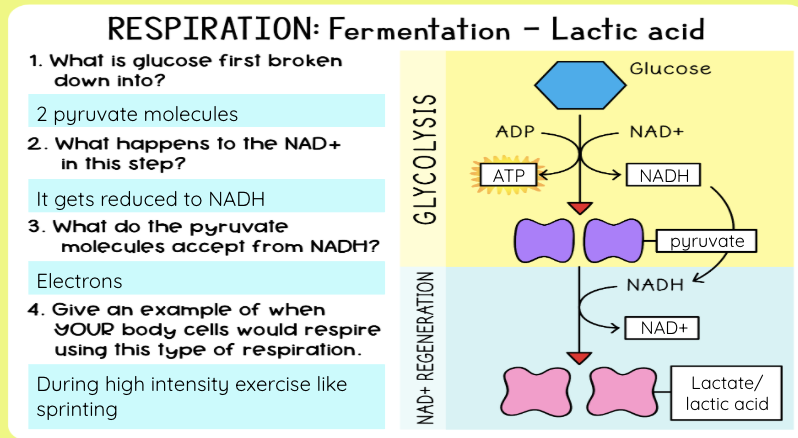
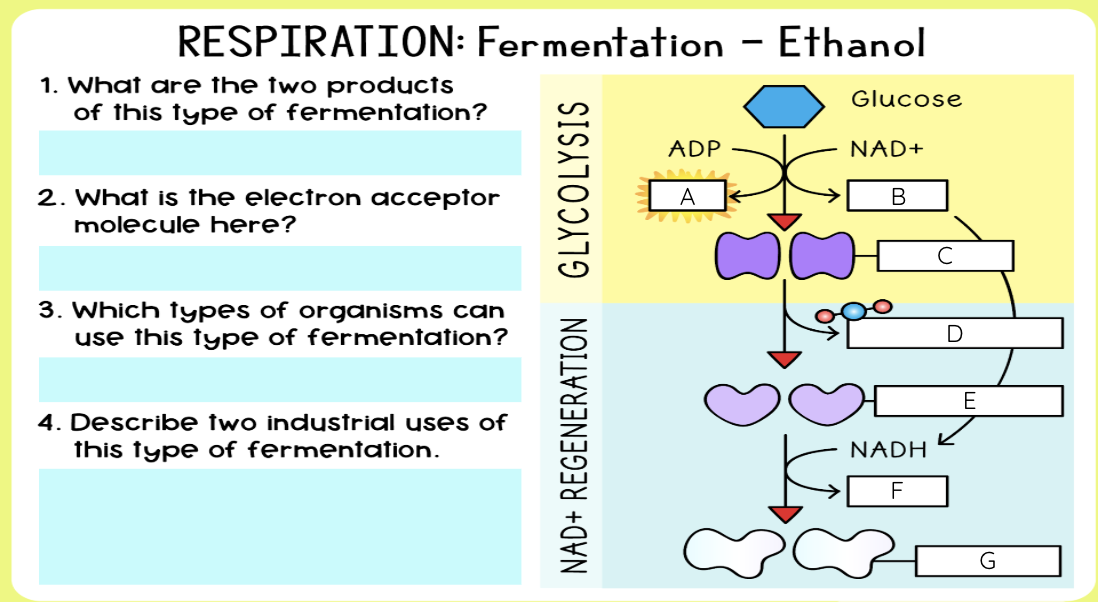
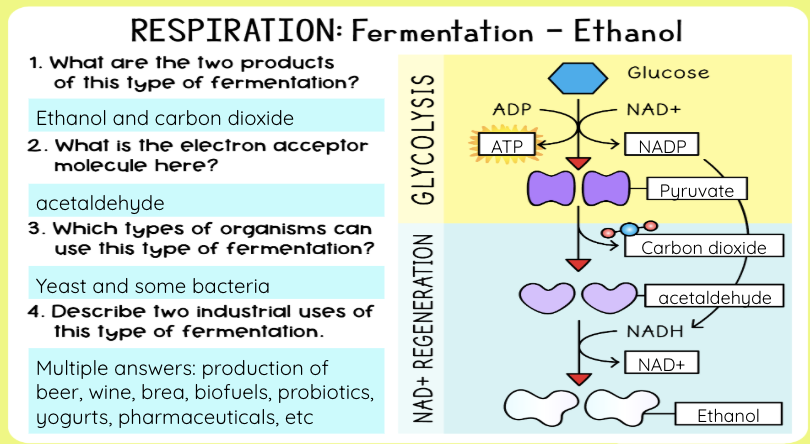
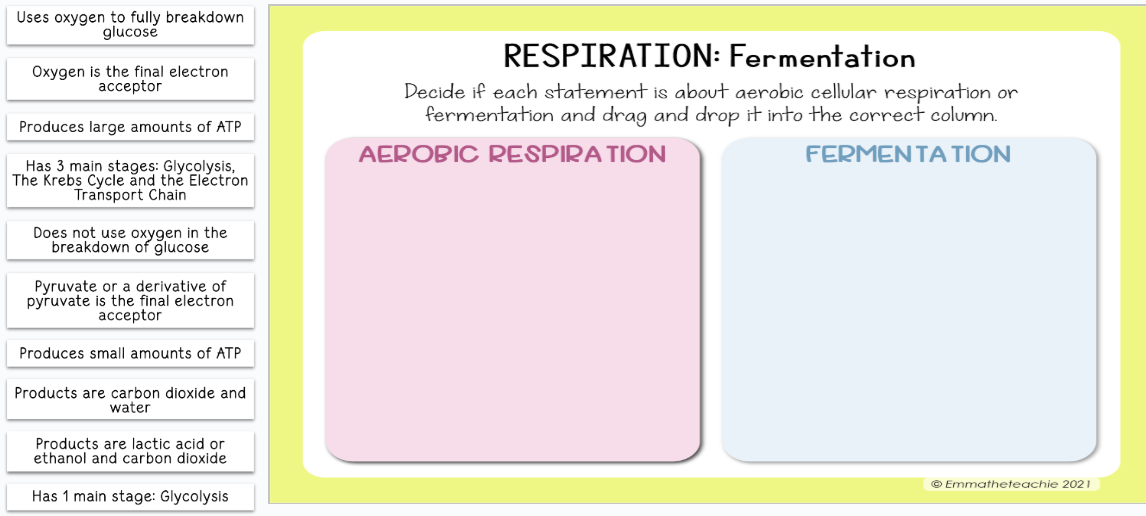
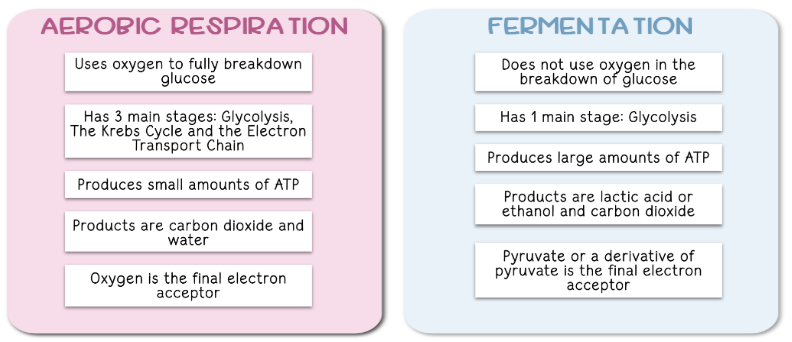
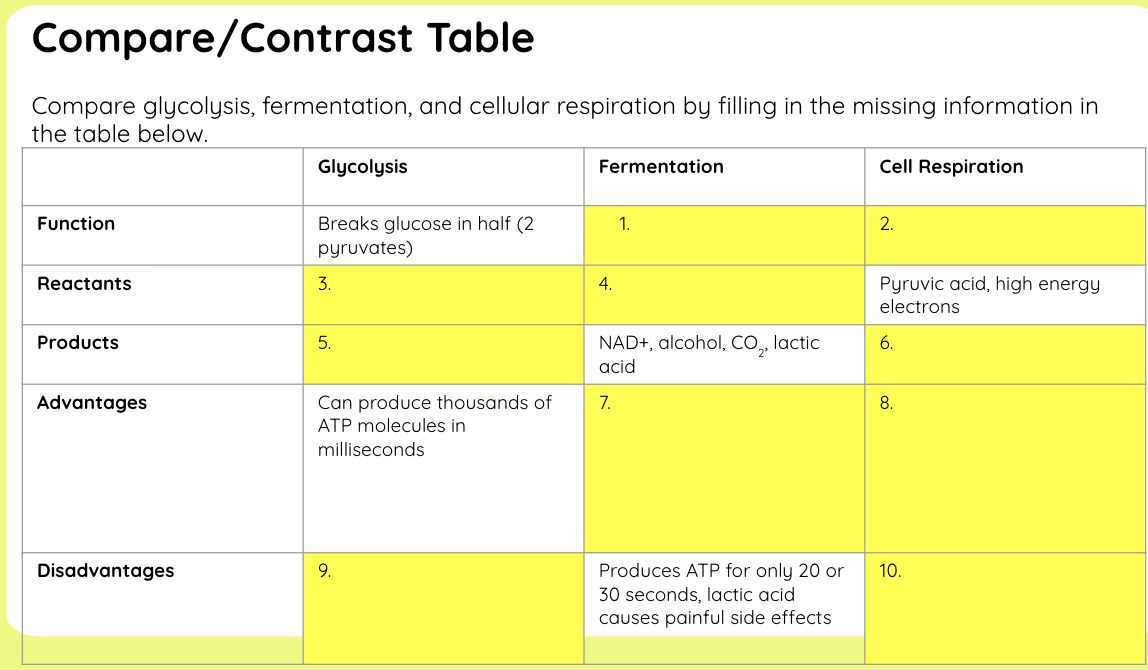
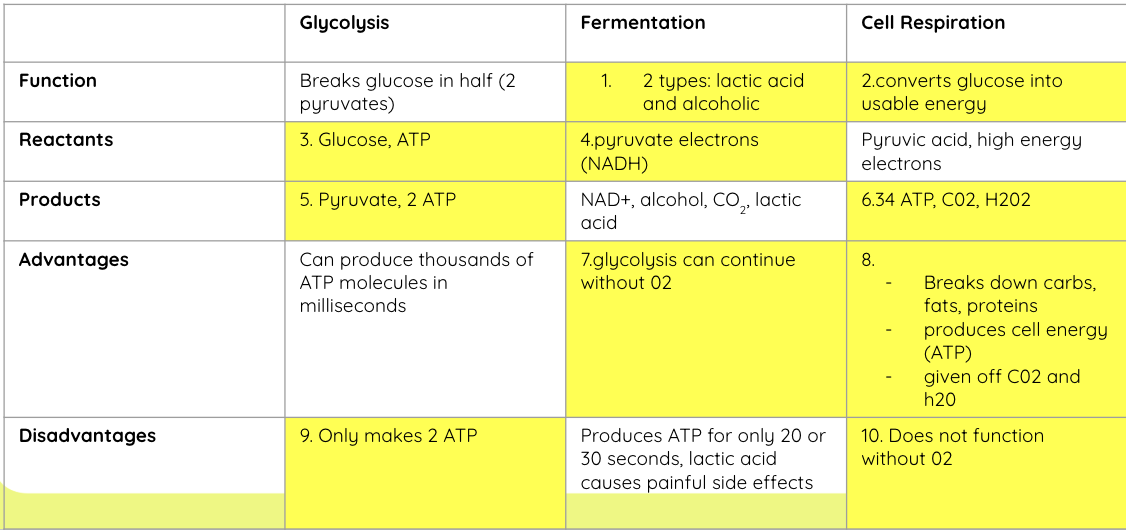
What is alcoholic fermentation?
Happens in yeast & plants
Pyruvate → ethanol + CO₂
NADH → NAD⁺
What is lactic acid fermentation?
Happens in muscle cells and bacteria
Pyruvate → lactic acid
NADH → NAD⁺
No CO₂ released