Ichthyology Final
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fish Final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Fin Fold theory
Multiple paired fins, the fins split from the same place
trends in the evolution of Actinopterygians
Reduction in bony elements
Position and use of dorsal fins
Placement and function of paired fish
Caudal Fin
Gas Gladder modifications
Branchiostegal rays
Jaws/feeding modifications
What did jaws evolve from
modified gill arches
Hyostylic jaw
Articulates with nasal area, maximum mobility.independence from jaw
Amphistylic jaw
primitive sharks/early fish: upper jaw to skull plus connection to gill arch
Autostylic jaw
Upper jaw connects with skull: better chewing
Orbitostylic Jaw
Sharks & rays, upper jaw articulates with eye socket: limit upper jaw movement
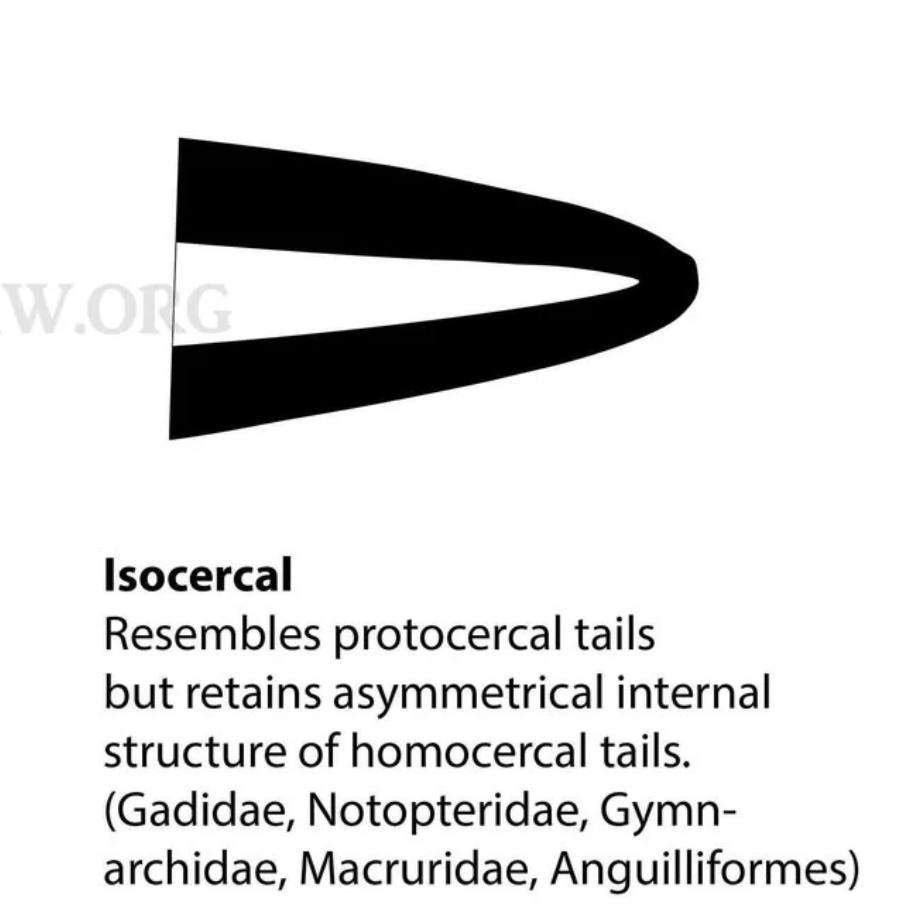
What is an isocercal tail
Similar to protocercal but retains asymmetrical internal structure (while like)
Illicium
Modified dorsal fin spine (fishing rod on anglerfishs head)
Esca
Bioluminescent lure at tip (fleshy bulb with glowing bacteria)
How and why do some fish produce bioluminescence?
Through chemical reactions or organs like photophores
used for camouflage, luring prey, starling predators, mating
9 feeding guilds
Detrivores, herbivores, Piscivores (Carnivore), Invertivores (Carnivore), Insectivores, Planktivores, Zooplanktivores, Molluscivores, Omnivores
Detritivores
Eats dead organic plant material
Herbivores
eats plant material
Piscivore (carnivore)
eats meat of other fish
Invertivores
eats invertebrates
Insectivores
Planktivores
eats plankton
Zooplanktonivores
Eats zooplankton and small plankton
Molluscivores
eats mollusks (clams)
Omnivore
eats plants and other fish
Gut structure difference of herbivore and carnivore
Carnivores have larger stomachs, smaller intestine
Herbivores have smaller stomach, larger intestines
stomach
initial acid digestion
pylorus valve
Regulate food movement into intestine
Pyloric Caeca
additional digestive enzymes, neutralizing acid
Pancreatic tissue
digestive enzymes regulate blood sugar
liver
amino acid breakdown, energy storage
gall bladder
bile absorption
Intestine
nutrient absorption
5 components of fish diet
Proteins → growth
Lipids → energy
Carbs → energy
Vitamins
minerals
How is diet evaluated
count + fatty acid analysis + stable isotope analysis
How does temperature influence fish respiration
Higher temp = decreased oxygen-holding capacities
adaptions to increase O2
Thin epithelium (skin)
More tightly packed lamella (longer)
adjust ventilation
methods to get O2
Swimming movement can irrigate gills (sharks/fishes)
Flowing water
Diffusion through skin (larval/scaleless fish)
bimodal breathing
Breath both air & water: can cope with hypoxia
Obligate breathing
must breathe at surface (modified gills, skin diffusion of O2): allows for movement cross land and continued respiration
RBC’s/ Erythrocytes
Respiration (O2 → CO2 transfer)
higher temp + higher activity = more RBCs
WBC’s/LEukocytes
Clotting/Antibody/engulf foreign cells, many different kinds
4 telost chambers
Sinus venosus
Atrium
Ventricle
Bulbs arteriosus
Sinus venosus
collects blood from body
Atrium
1st location to acerbate blood flow
Ventricle
main pump (blood movement)
Bulbus arteriosus
Doesn’t increase pressure (dampens/lengthens ventricle effects)
Total Spawners
release all eggs at once
Functional spawners
produce eggs continuously and spawn frequently
batch spawners
Single reproductive season, spawn eggs in short period
semelparity spawners
spawn once and then die
Iteroparity spawners
repeates reproduction
Benthic Spawners
spawn in coarse, vegetation, and fine substrates
Brood Hiders
spawn by building a coarse substrate, crevices
Nest builders
use rock/grave/plant material crevices (bubbles)
Bearers
Carry eggs/fry with them internally or externally
Temperature size rule
size/age at maturity varies by temperature
cold water = slower growth, larger size/age at maturity = fewer, larger offspring
Promiscuous
Mass spawning events (Clupeiformes, smelt)
Polyandry
several males to each female (lamprey, salmon)
Polygyny
several females to each male (Gobiidae)
Monogamy
uncommon, single pair mating (Guppy’s
how does lower pH influence affinity
Lower hemoglobin O2 affinity
Opportunistic Characteristics
Early maturity
fast growth
lots of offspring
small eggs/small clutches
highly variable environments
Periodic Characteristics
Maturing a bit later
high fecundity
lots of eggs/small eggs
seasonal changes
Equilibrium Characteristics
Slower
larger eggs/larvae
small clutches
parental care
What is indeterminate growth?
growth is not limited by genetically predetermined size, and continues throughout an organisms life
Heterocercal v. Homocercal tail
Ancestral (vertebral column) - Derived (symmetrical)
Red v. White Muscles
white = less blood supply for quick bursts
red = band along side fish for long sustained
ways fish regulate buoyancy
hydrostatic lift
generation of life by shape/angled fish
Reduction of heavy tissues (body/bones)
incorporation of gas/swim-bladder method
Physostomus bladder
fish must go to the surface to swallow/gulp-air
Physoclistous bladder
fish DOES not need to go to the surface to collect air
derived (bass/sunfish/perch/walleye)
Physostomous v. Physoclistous
Open; regulated by pneumatic duct (ancestral)
closed; filled from gas gland, gas released by oval patch of capallaries (derived)
Pneumatic duct
brings air from esophagus to swim bladder
Partial pressure of oxygen must be higher in _____ than in _____
Blood vessels; swim bladder
2 types of thermoregulation
Behavioral: movement into areas with desired water temp
Physiological: counter current heat exchange (muscles generate heat)
heater cells
modified muscles → more volume mitochondria & sacroplasmic reticulum → Ca pumped into SR resulting in ADP → ADP uptake by mitochondria → heat
Osmoconformes
no regulation (hagfish)
Hypoosmotic
internal salt concentration is 1/3 external (bass)
Hyperosmotic
gills always wanting to absorb NaCL, water enters osmotically → reabsoportion of NaCl (yellow perch) ?
How sharks regulate sharks
Increase salt concentration of body tissue-secrete TAMO into blood, Urea & TAMO raise blood and minimize water loss
3 types of scales and their ancestry
Ctenoid → derived
Ganoid → Ancestral
Placoid → derived
Ctenoid
(derived) large mouth bass, crappie, spiny rayed fish
Ganoid
(Ancestral) Trout, minnows, salmon
Placoid
(derived) sharks and rays
Outer v. Inner Dermis
Outer: thin, mucous cells to protect fish
Inner: thicker, connective tissue (blood vessels/nerves)
Stenohaline v. Euryhaline
S= organisms that tolerate only a narrow range of salinity
E= organisms that can adapt and survive wide range of salinity
Hemoglobin does what to O2 and CO2 (muscles)
Carries oxygen to the muscles and the CO2 to muscles
Purpose of epibranchial organ
helps with taste