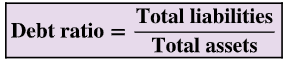Ch.2- Basis of Financial Statements
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Source Documents
Source of information for accounting entries that can be either paper or electronic form; also called business papers.
Account
Record within an accounting system in which increases and decreases are entered and stored in a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
General Ledger
Record containing all accounts (with amounts) for a business; also called ledger.
Ledger
Record containing all accounts (with amounts) for a business; also called general ledger.
Creditors
Individuals or organizations entitled to recieve payments.
Debtors
Individuals or organizations that owe money.
Unearned Revenue
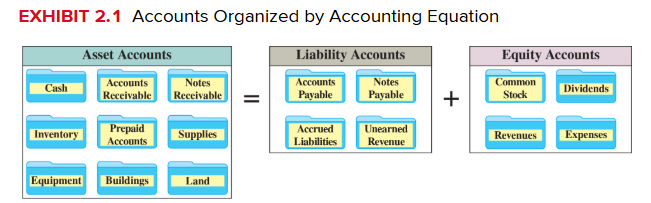
Liability created when customers pay in advance for products or services; earned when the products or services are later delivered.
Accounts Payable
Promises to pay later. From purchases on credit or on account of merchandise for resale, supplies, equipment, and services.
Accounts Payable - Suppliers name
Notes Payable
Written promissory not to pay a future amount. Different from AP because they come from a formal contract called a promissory note and usually require interest.
Accrued Liabilities
Are amounts owed that are not yet paid; wages payable, taxes payable, and interest payable.
Equity Accounts
Owner’s claim on a company’s assets is called equity, stockholders’ equity or shareholder’s equity. Equity is the owner’s residual interest in the assets of a business after subtracting liabilities. Equity is impacted by four types of accounts.

Owners Investment
When an owner invests, it increases both assets and equity. The increase to equity is recorded in the account titled Common Stock. Owner investments are not revenues of the business.
Owners Distributions
When corporations distribute assets to its owners, it decreases both company assets and total equity. The decrease to equity is recorded in an account titled Dividends.
Revenue Accounts
Sales of products and services to customers are recorded in revue accounts, which increase equity. Ex: sales, commissions revenue, professional fees revenue, rent revenue, and interest revenue.
Revenues always increase equity.
Expense Accounts
Costs of providing products and services are recorded in expense accounts, which decrease equity. Ex: advertising expense, salaries expense, rent expense, utilities expense, and insurance expense.
Expenses always decrease equity.
Chart of Accounts
List of accounts used by a company; includes an identification number for each account.
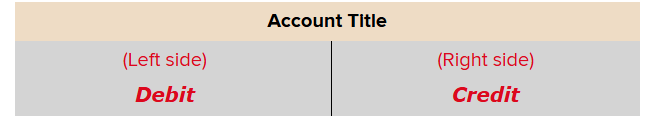
T-account
Tool used to show the effects of transactions and events on individual accounts; shaped in the form of a T.
Debit
Recorded on the left side; an entry that increases an asset or expense account, or decreases a liability, revenue, or equity account; abbreviated Dr.
Credit
Recorded on the right side; an entry that decreases an asset or expense account, or increases a liability, revenue, or equity account; abbreviated Cr.
Account Balance
Difference between total debits and total credits (including the beginning balance) for an account.
Double-entry Accounting
Accounting system in which each transaction affects at least two accounts and has at least on debit and one credit.
At least two accounts are involved, with at least on debit and one credit.
Total amount debited must equal total amount credited.
Journal
Record in which transactions are entered before they are posted to ledger accounts; also called book or original entry.
Journalizing
Process of recording transactions in a journal.
Posting
Process of transferring journal entry information to the ledger; computerized systems automate this process.
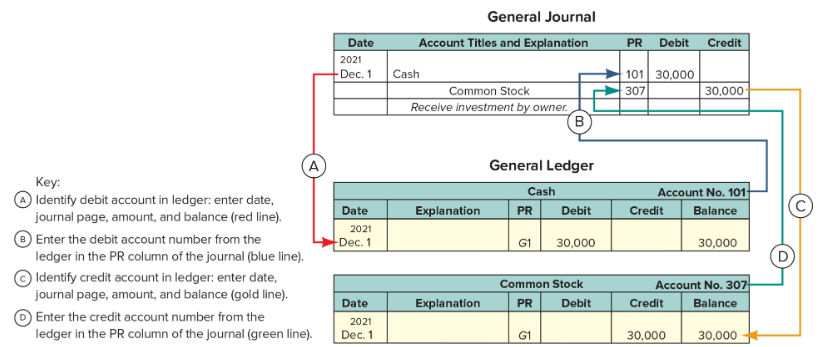
General Journal
All-purpose journal for recording the debits and credits of transactions and events.
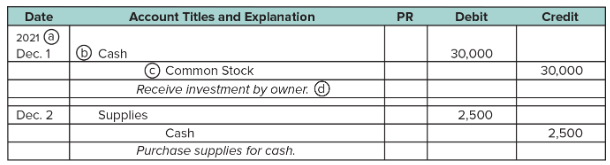
Posting Reference (PR) Column
A column in journals in which individual ledger account numbers are entered when entries are posted to those ledger accounts.
Balance Column Account
Account with debit and credit columns for recording entries and another column for showing the balance of the account after each entry.
Trial Balance
List of ledger accounts and their balances (either debit or credit) at a point in time; total debit balances equal total credit balances.
Debt Ratio
Ratio of total liabilities to total assets; used to reflect risk associated with a company’s debts.