Biology
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the content of Paper 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
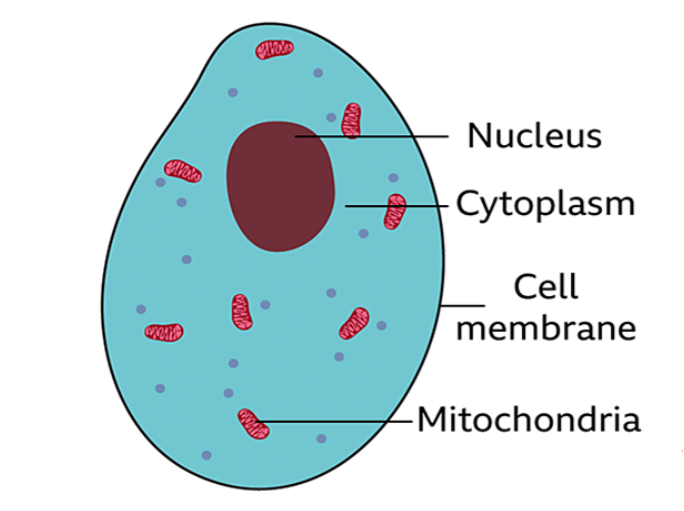
animal cell
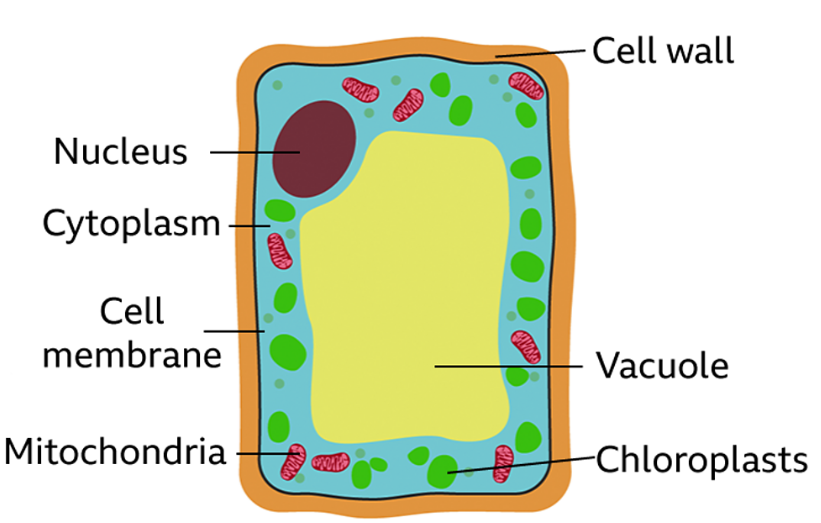
plant cell
Define nucleus
contains the genetic material (DNA) of the organism controls the cell’s activities
define cytoplasm
a jelly-like substance found in animal and plant cells that contains dissolved nutrients, salts, and organelles.
Define cell membrane
a flexible outer layer that surrounds the cell in which chemical reactions happen. This is mainly water
Define mitochondria
tiny parts of cells floating in the cytoplasm where energy is released rom glucose from food.
Define cell wall
a tough outer layer of the cell, which contains cellulose to provide strength and support to the plant
Define vacuole
A space inside the cytoplasm that contains a watery liquid call cell sap. It keeps the cell firm.
Define chloroplasts
structure found in the cells of green parts of plants only (leaves and stem) which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll in which photosynthesis occurs
Define ribosome
part of a cell where proteins are made
Define plasmid
Only found in bacterial cells. A small loop of DNA
Define genetic material
Long strands of genes not tightly pack in a nucleus
Define Eukaryotic
A complex cell with a nucleus
Define prokaryotic
A smaller cell without a nucleus
Define osmosis
The net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution. It’s a passive process
Define Diffusion
The net movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. it’s a passive process
the function of the mouth
mechanical breakdown/chew food
the function of the slivery glands
produce salvia with amylase enzymes to breakdown starch
the function of the oesophagus
(Gullet): push chewed food to stomach. food moved by muscle action
function of the liver
Makes bile Bile: a) provides neutralises stomach acid and b) emulsifies lipids (increases there surface area ) this helps lipids digestion by enzymes
the function of the gall bladder
stores bile
the function of the pancreas
production of digestive enzymes
the function of the small intestine
absorption of small soluble particles
the function of the appendix
useless organ which harbours bacteria (good and bad )
the function of the stomach
Partial digestion of food/ mechanically churns food with HCL and protease enzymes
The function of the large intestine
re-absorption of water
The function of the rectum
Muscular section of the large intestines
The function of the anus
where faeces leaves the body
Why do the intestines have villi?
As it increases the surface area of the intestines
What 3 adaptations do the villi have which help speed up the diffusion of nutrients into the blood?
- Micro villi
- Good blood supply
- Thin walls
Define tissue
A group of cells with a similar structure and function
Define organ
A group of tissues preforming specific functions
Define an organ system
A group of organs which work together to form organisms
The apparatus list for the Food tests RP
Food:potato, carrot, crisps, biscuits, cheese
Spotting tile
Pipette
10cm3 measuring cylinder or plastic syringe
Beaker
Boiling tubes
tests tubes
kettle or water bath
Iodine solution
Benedict’s reagent
Biuret reagent
Ethanol
Eye protection
What are some safety notes for the Food tests RP ?
Where eye protection
If chemicals on skin rinse under cold water
In case of burns rinse under cold water for 20 minutes
In the food test RP what do we use to test for starch?
We would use Iodine
In the food test RP what would we use to test for glucose ?
We would use Benedict’s solution
In the food tests RP what would we use to test for protein ?
We would use Biuret solution
In the food tests RP what would we use to test for Lipid ?
We would use Ethanol
What are the steps to test for starch ?
Put a small piece of the food to test on a spotting tile .
Add two drops of the solution you would use onto the food
If the solution goes blue-black it contains it
What are the steps to test for glucose ?
Mix a small sample of the food with the solution about 3cm3 in a boiling tube
Leave it for 2 minutes
If the solution goes a brick red it contains it
What are the steps to test for protein ?
Mix a small sample of the food with the solution about 3cm3 of the solution
leave it for two minutes
If the mixture goes play purple it contains it
What are the steps to test for Lipid ?
Mix a small sample of the food with about 1cm3 of the solution in a dry test tube
Pour the ethanol into a test tube of cold water
If the water goes milky white the food contains it
Define Coronry heart disease
When fatty material builds up and stops the flow of blood to the heart muscle
Define coronary arteries
The arteries that supply the heart muscle
What is a stent
A mesh tube used to keep the coronary arteries open
What are statins
Drugs used to reduce blood cholesterol preventing CHD
What is a faulty valve
When the blood flows in the opposite direction through the heart. Will need replacing with a biological or mechanical valve
what is a artificial heart
Short term mechanical heart used while waiting for a transplant
define pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood to the body
The function of the Aorta
Carries oxygenated blood to the body
the function of the pulmonary vein
Brings oxygenated blood from the lungs
The function of the left atrium
Pushes blood to the left ventricle
The function of the heart valves
prevents back flow of blood
In the lungs, which gas diffuses from the avieoli into the blood
Oxygen
The function of the left ventricle
pumps blood to body
The function of the right ventricle
Pumps blood to lungs
The function of the vena cava
brings deoxygenated blood from the body
What is Transpiration
The loss of water vapour through the leaves of the plant
What is translocation
The movement of sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant through the phloem
What does toxicity mean
if it is toxic
What does efficacy mean
How well it works
what does dosage mean
How much of the drug you need to take so it works
define placebo
a pill whiteout the drug in it taken to check drug effectiveness
define double blind trials
When the doctor does not know if they are giving the medicine or a placebo. Prevents bias
Define blind trails
When the doctor knows who has the placebo and who has the medicine but the patients do not. Easier to set up but could lead to bias
define vaccine
Small amount of dead or inactive pathogen to simulate white blood cells to produce antibodies
Define active transport
Movement of molecules against their concentration gradient
What type of process is active transport? and what does that process need.
Its an active process so it requires energy for the cell
Fill in the gaps:___ concentration to a ____ concentration
low, high
What is the function of carbohydrates ?
Gives us energy. Too much can mean that the energy is stored as fat.
Give two examples of carbohydrates
pasta, bread
what is the function of Protein?
Needed for growth. They help us make new cells and repair damaged ones.
Give two examples of protein
chicken, fish
What is the function of fat ?
These store energy. They also insulate our bodies and protect our organs. Too much can cause us serious health problems
Give two examples of fat
oils, cakes
What is the function of vitamins and minerals ?
Needed in small amounts to allow our bodies to function (work) properly and for chemical processes to take place
Give two examples of vitamins and minerals
fruit, veg
Enzyme active site
A specific region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
Enzyme substrate specificity
Enzymes are highly specific and only bind to specific substrates
optimal temperature for enzymes
Between 20oc to 40oc
Enzyme
A biological molecule that catalyzes chemical reactions, is highly specific to it’s substrate,and maintains optimal reaction rates and efficiency.
What type of energy is derived from carbohydrates?
Glucose
What do the white blood cells do?
- Small fragments of cells
- Help blood clots
- Network of fibres that trap more platelets
- Forms scabs
Name 5 things found in plasma
RBC, WBC, platelets, glucose and CO2
What is the job of the haemoglobin?
Bind with oxygen to make oxyhaemoglobin
State 2 adaptations of the red blood cells
1. No nucleus so there is more space for haemoglobin
2. Bioconcave to increase surface area
Which plant does aspirin originate from?
willow
How can scientists be sure that claims about new drugs are valid?
have the claims peer reviewed
Where in the heart is the pacemaker found?
the right atrium
Describe two ways that the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
any two from: • (artery) has a thicker muscle (tissue) • (artery) has a thicker elastic (tissue) • (artery) has a narrower lumen • (artery) does not contain valves
How do Salmonella bacteria in food cause the symptoms of vomiting and diarrhoea?
(bacteria) release / produce toxins
During vigorous exercise, anaerobic respiration occurs in a person’s body. Explain two effects of anaerobic respiration on the person’s body.
any two from: • (effect) muscle fatigue or oxygen debt occurs (1) (reason) caused by (build-up of) lactic acid (1) • (effect) (continued) heavy / deep / fast breathing (1) (reason) to provide the oxygen needed to break down (built-up) lactic acid (1) • (effect) (continued) increased heart rate (1) (reason) to provide the oxygen needed to break down (built-up) lactic acid (1) • (effect) fewer / weaker muscle contractions (1) (reason) (because) less energy is released / available
What type of cell is created when a mouse lymphocyte and a tumour cell combine?
hybridoma