IB Biology HL - Cell Membranes
1/332
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
333 Terms
Lipid Bilayer
Membrane barrier separating cell from surroundings.
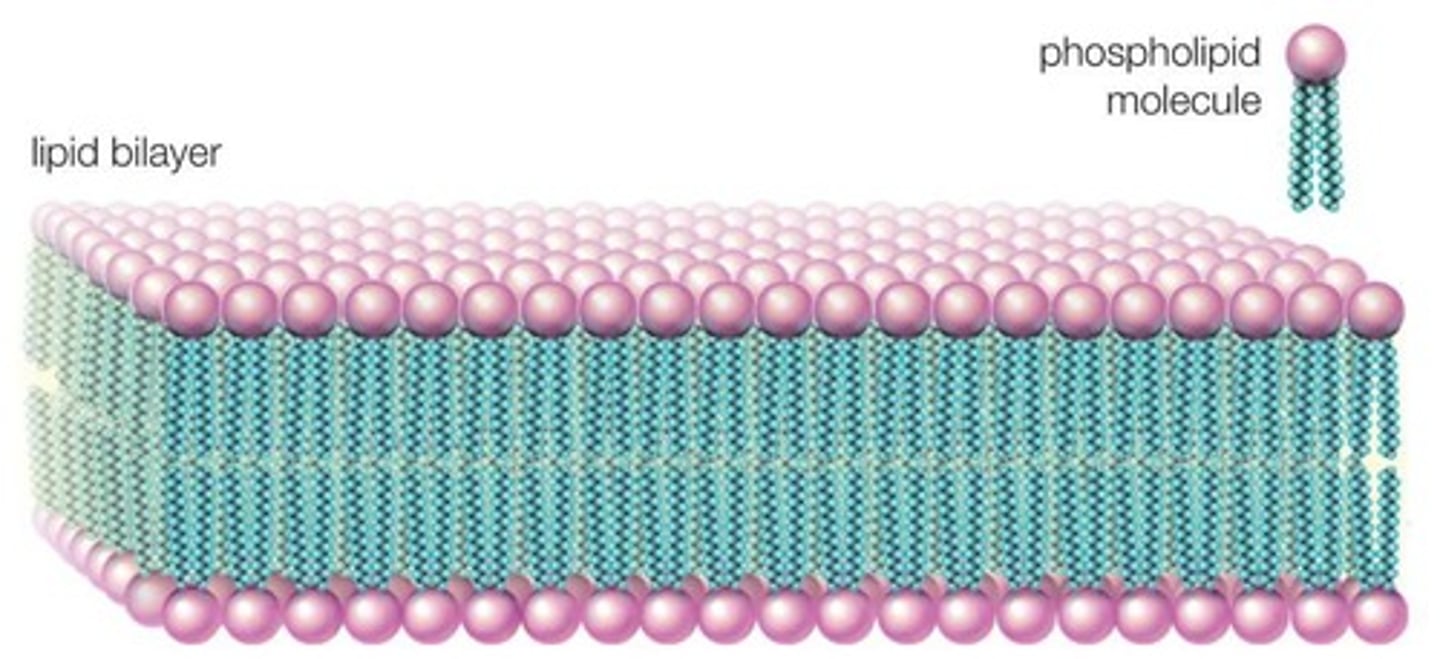
Phospholipid
Amphipathic lipid forming bilayer structure.
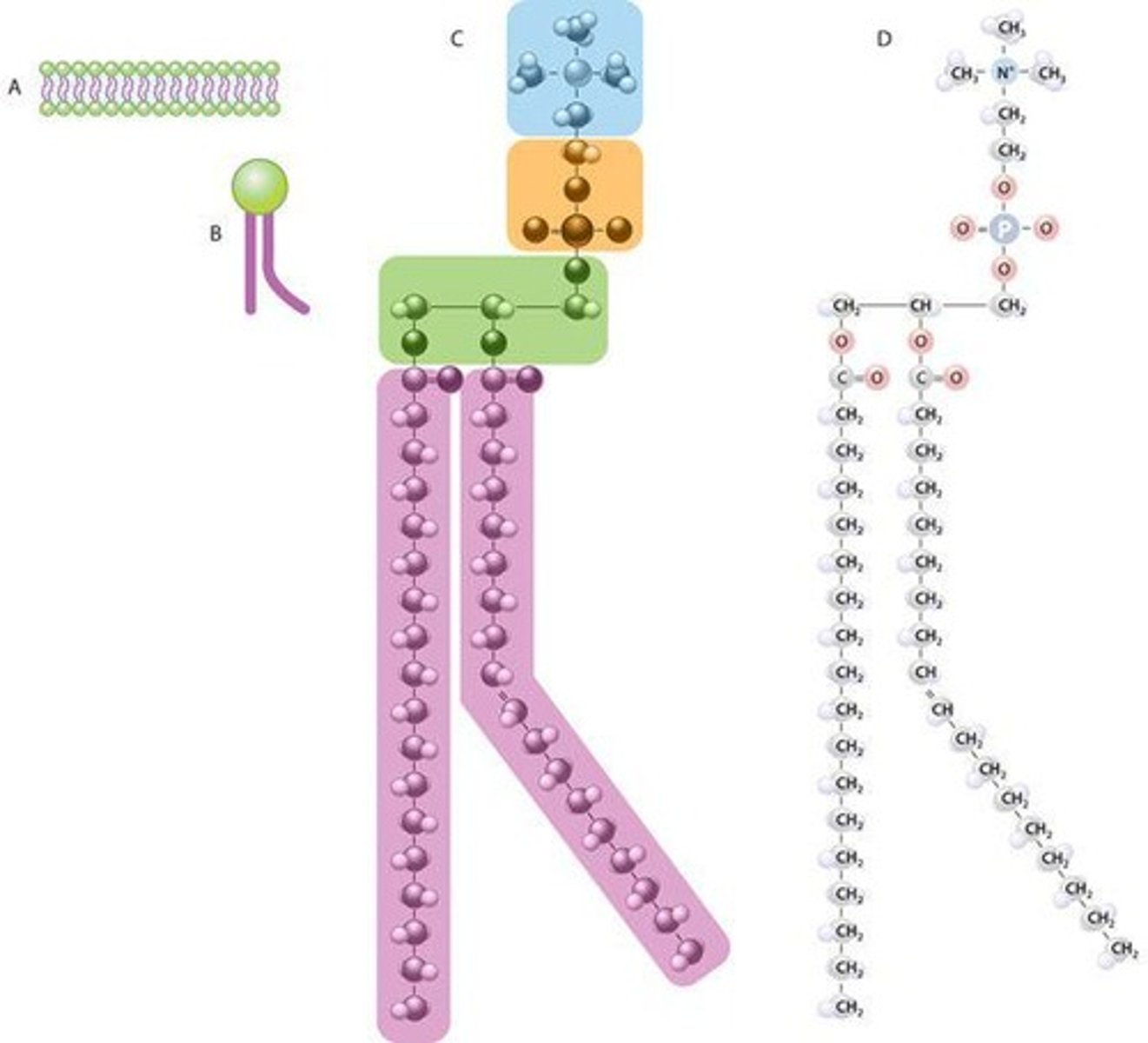
Amphipathic Nature
Molecule having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
Hydrophobic
Repellent to water; non-polar region of bilayer.
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water; polar region of bilayer.
Micelle
Spherical arrangement of phospholipids in water.
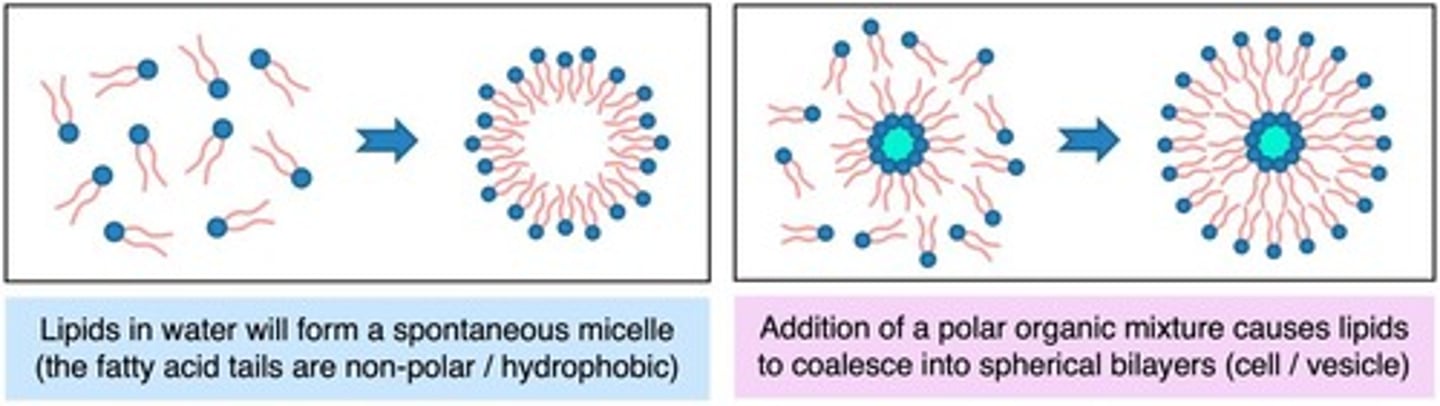
Protocell
Primitive cell-like structure formed by lipid bilayers.
Plasma Membrane
Cell membrane surrounding cytoplasm; selectively permeable.
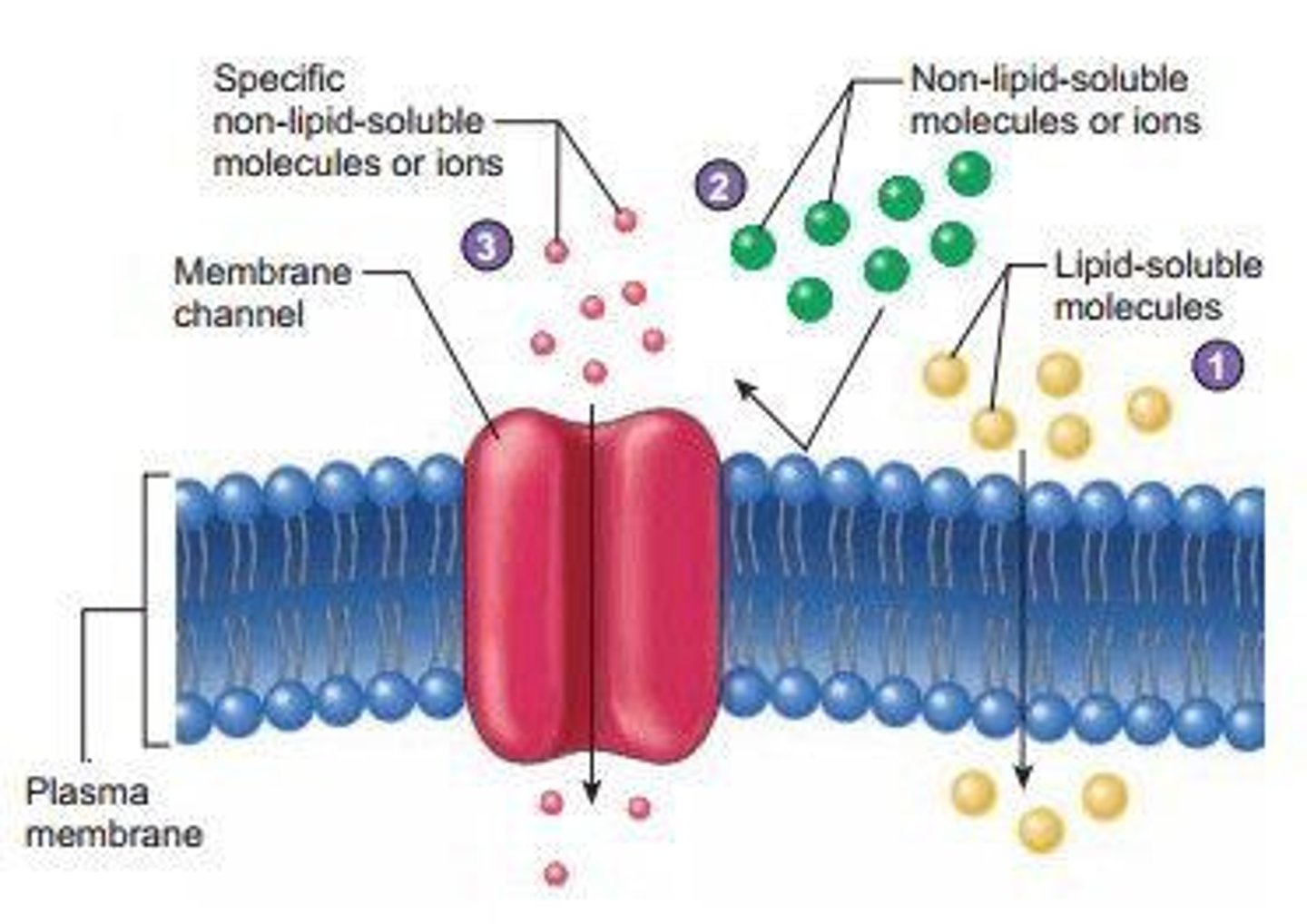
Selective Permeability
Regulation of molecule passage across the membrane.
Transport Proteins
Proteins facilitating movement of substances across membranes.
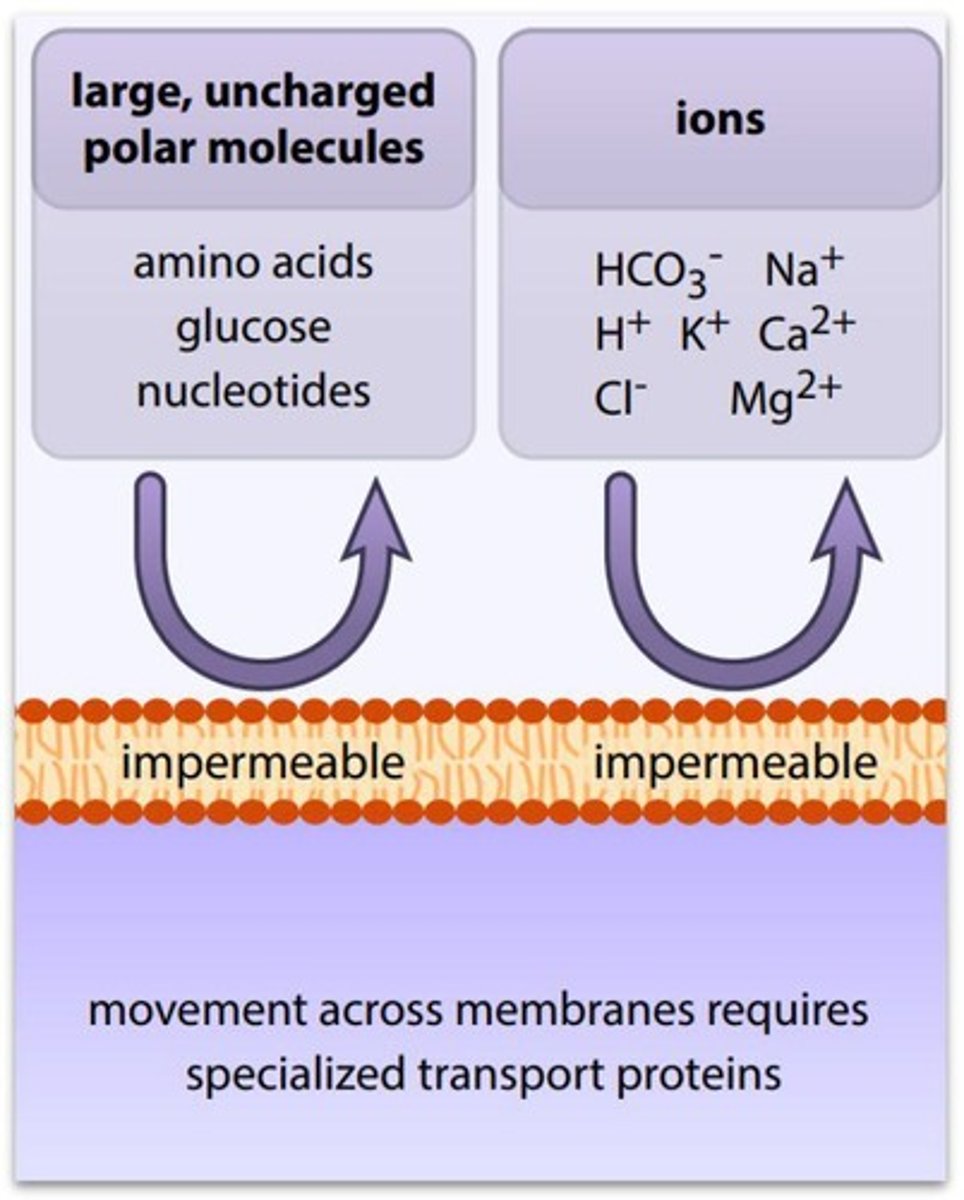
Compartmentalization
Separation of cellular processes into distinct areas.
Nutrient Accumulation
Cells concentrate nutrients beyond extracellular levels.
Electrical Potential
Charge difference across a membrane, crucial for neurons.
Integral Proteins
Membrane proteins spanning the lipid bilayer.
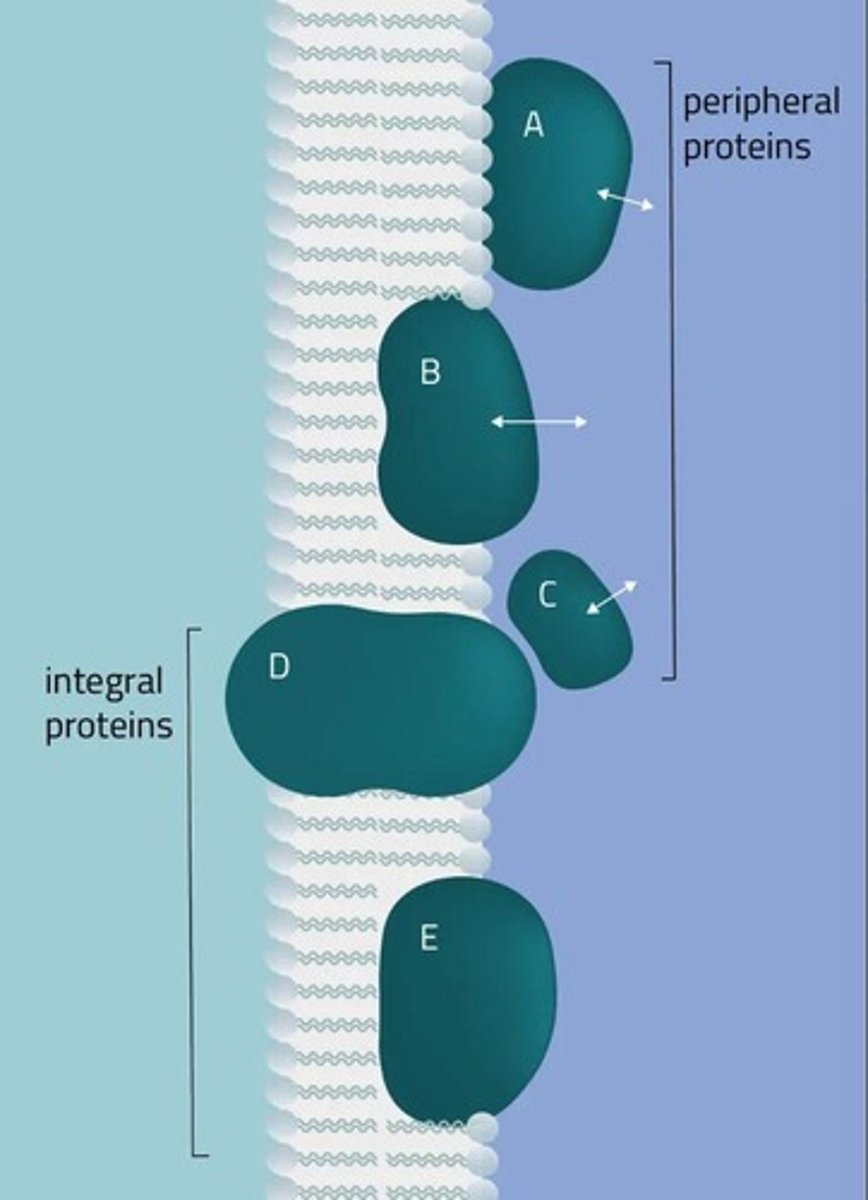
Peripheral Proteins
Membrane proteins associated with membrane surfaces.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Forces stabilizing integral proteins within the bilayer.
Enzymes in Membranes
Membrane-associated proteins speeding up metabolic reactions.
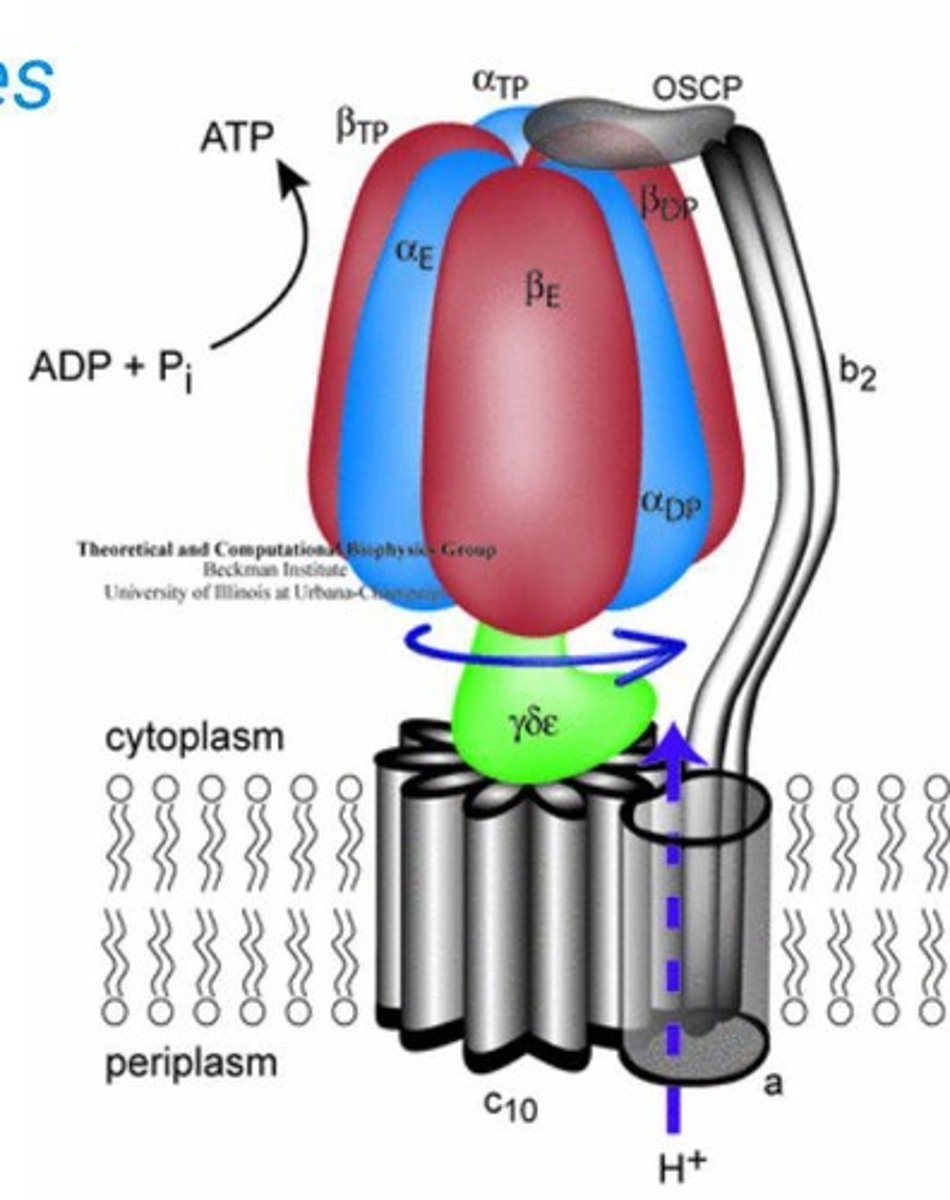
ATP Synthase
Integral protein generating ATP from ADP and phosphate.
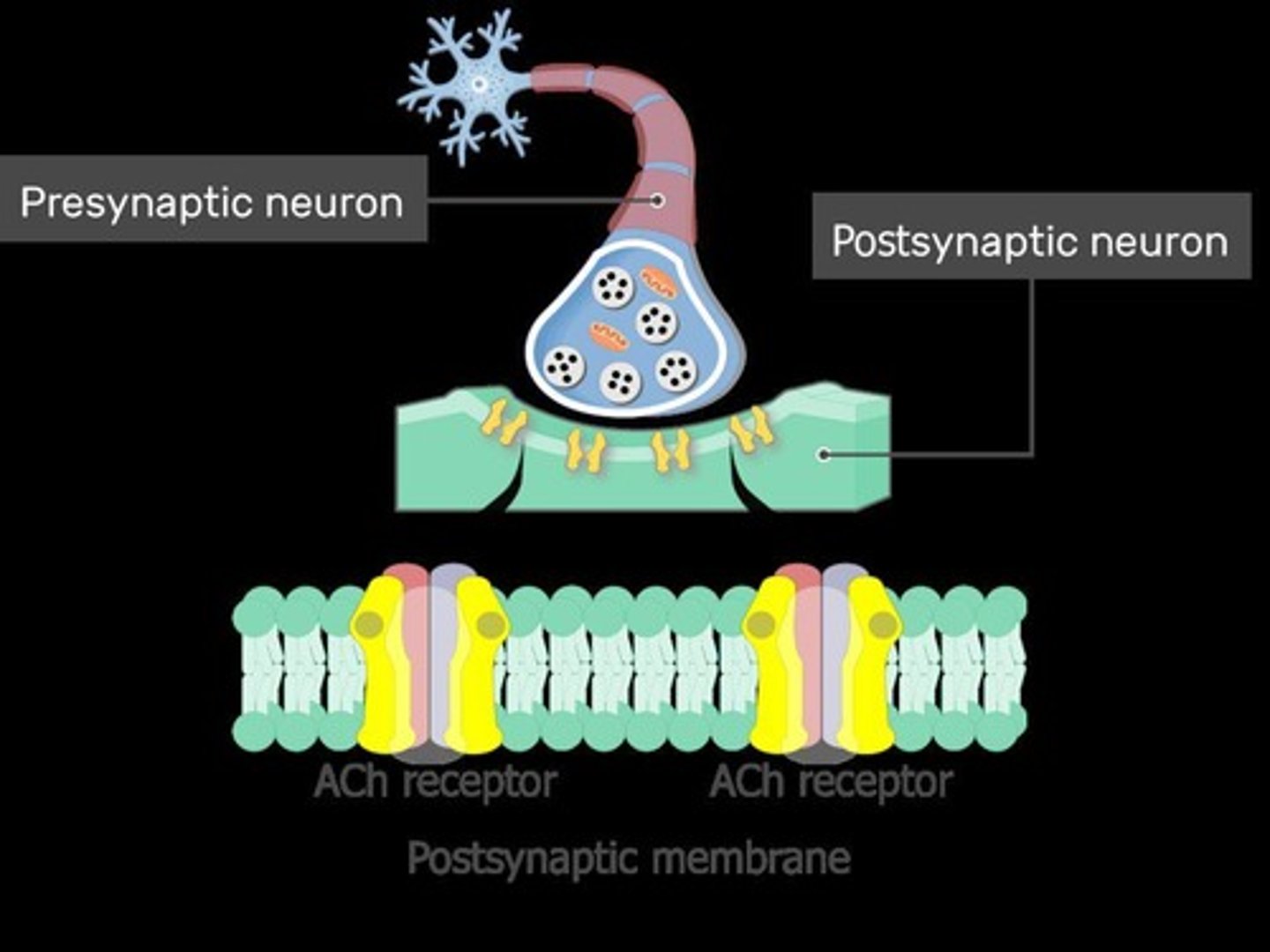
Chemical Receptor Proteins
Membrane proteins receiving external chemical signals.
Acetylcholine Receptor
Protein responding to neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Cytosol
Liquid component of the cytoplasm within cells.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures synthesizing proteins for membranes.
Vesicle
Transport structure delivering proteins to cell membranes.
Chemoreceptors
Sensory neurons detecting chemical stimuli.
Channels
Facilitated diffusion pathways for molecules.
Pumps
Active transport mechanisms requiring energy.
Recognition Proteins
Identify and interact with other cells.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate chains attached.
Adhesion Proteins
Facilitate cell adhesion to form tissues.
Cell Adhesion
Cells sticking to each other and ECM.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Meshwork providing support and communication.
Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
Proteins forming junctions between cells.
Tight Junctions
Prevent leakage between closely packed cells.
Gap Junctions
Channels allowing efficient intercellular communication.
Adherens Junctions
Anchor cytoskeleton to plasma membrane.
Desmosomes
Strong junctions resisting mechanical stress.
Metastatic Cancer
Loss of adhesion allowing tumor spread.
Integrins
Anchorage proteins connecting cells to ECM.
Passive Transport
Movement without energy input across membranes.
Active Transport
Energy-requiring movement against concentration gradients.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration.
Simple Diffusion
Passive transport of small, hydrophobic molecules.
Osmosis
Passive transport of water across membranes.
Equilibrium
Equal concentrations; no concentration gradient.
Gas Exchange
Oxygen and carbon dioxide movement via diffusion.
Aquaporin
Channel protein enhancing water permeability.
Facilitated Diffusion
Transport of large/polar molecules via channel proteins.
Channel Proteins
Proteins allowing specific molecule passage across membranes.
Gated Channels
Channel proteins that open/close in response to signals.
Voltage-Gated Channels
Open/close based on membrane electrical potential changes.
Ligand-Gated Channels
Open/close in response to chemical messenger binding.
Protein Pumps
Transport proteins requiring ATP for molecule movement.
Selectivity in Membrane Permeability
Membrane allows selective passage of substances.
Proton Pumps
Transport proteins crucial for photosynthesis and respiration.
Sodium-Potassium Pumps
Maintain action potentials in neurons by ion exchange.
Auxin Efflux Pumps
Establish concentration gradients for plant growth.
Gastric Proton Pump
Secretes hydrogen ions, increasing stomach acidity.
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Medications blocking proton pumps to reduce stomach acid.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in substance concentration across a membrane.
Hydrophobic Molecules
Substances that do not interact well with water.
Hydrophilic Molecules
Substances that interact well with water.
Cell Specialization
Differentiation of cells for specific functions.
Membrane Permeability
Ability of substances to cross the cell membrane.
Nonpolar molecules
Easily diffuse through membranes, e.g., O2, CO2.
Polar molecules
Diffuse slowly through membranes, e.g., H2O.
Saturation point
Maximum rate of facilitated diffusion due to protein limits.
ATP
Energy source for active transport processes.
Glycolipids
Lipids with carbohydrate chains for cell adhesion.
Cell-to-cell recognition
Allows immune cells to identify self vs. foreign cells.
ABO blood types
Determined by specific glycoproteins on red blood cells.
Glycocalyx
Layer formed by glycoproteins and glycolipids on membranes.
Fluid mosaic model
Dynamic membrane structure with diverse components.
Membrane asymmetry
Different compositions on extracellular and intracellular membrane faces.
Cell membrane fluidity
Ability to maintain flexible membrane structure.
Temperature effect on fluidity
Higher temperature increases membrane fluidity.
Unsaturated fatty acids
Lower melting points, enhance membrane fluidity.
Saturated fatty acids
Higher melting points, strengthen membranes at high temperatures.
Fatty acid tail length
Longer tails decrease fluidity due to increased interactions.
Vesicle formation
Membrane fusion during endocytosis and exocytosis.
Cell division
Ensures even distribution of membrane molecules.
Protein interactions
Crucial for cell signaling and communication.
Oligosaccharides
Short carbohydrate chains linked to proteins or lipids.
Membrane components
Include lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Saturated chains
Fatty acid chains that pack tightly, reducing fluidity.
Unsaturated chains
Fatty acid chains with kinks, increasing membrane fluidity.
Cholesterol
Amphipathic molecule affecting membrane fluidity and permeability.
Endocytosis
Transport of molecules into the cell via vesicles.
Exocytosis
Transport of molecules out of the cell via vesicles.
Phagocytosis
Endocytosis where cells engulf and digest materials.
Pseudopods
Temporary projections used by amoeba for feeding.
Gated ion channels
Channel proteins that open/close in response to stimuli.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Ligand-gated channels requiring acetylcholine to open.
Depolarization
Process of membrane potential becoming more positive.
Repolarization
Restoration of resting membrane potential after depolarization.
Sodium-potassium pump
Transporter moving Na+ out and K+ into neurons.
Threshold potential
Membrane potential required to trigger action potential.
Action potential
Rapid change in membrane potential during neuron signaling.
Na+ influx
Rapid entry of sodium ions during depolarization.
K+ efflux
Outflow of potassium ions during repolarization.
Resting potential
Stable membrane potential before action potential occurs.