Chapter 3: Organic Molecules
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen
Why does carbon bond with four other elements?
It is to gain four more electrons since Carbon only has four electrons in its outer shell. Carbon normally shares electrons with Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen.
Hydrocarbons
Chains composed of carbon and hydrogen
Functional Groups (R-groups)
molecules that are attached to hydrocarbons that gives them their properties.
Monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Dehydration Synthesis
WATER is REMOVED from the chemical reaction, which then allows monomers to bond
Hydrolysis
WATER is ADDED to break bonds.
Polymers => Monomers
Carbohydrates
energy source and also used for organism's structure.
monosaccharides
single molecule (simple sugar)
ex. glucose
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides bonded together
ex. Maltose (glucose + glucose)
Polysaccharides
large molecules formed by multiple monosaccharides. Energy storage molecules
Starch = glucose storage for plants
Glycogen = glucose storage for animals
Structural: cellulose for plant walls and chitin for lobsters
Lipids
long chains of carbon and hydrogen
used for: cell membrane, waterproof skin, hair, feathers. Also used for long-term energy storage
ex: steroids, fats, phospholipids
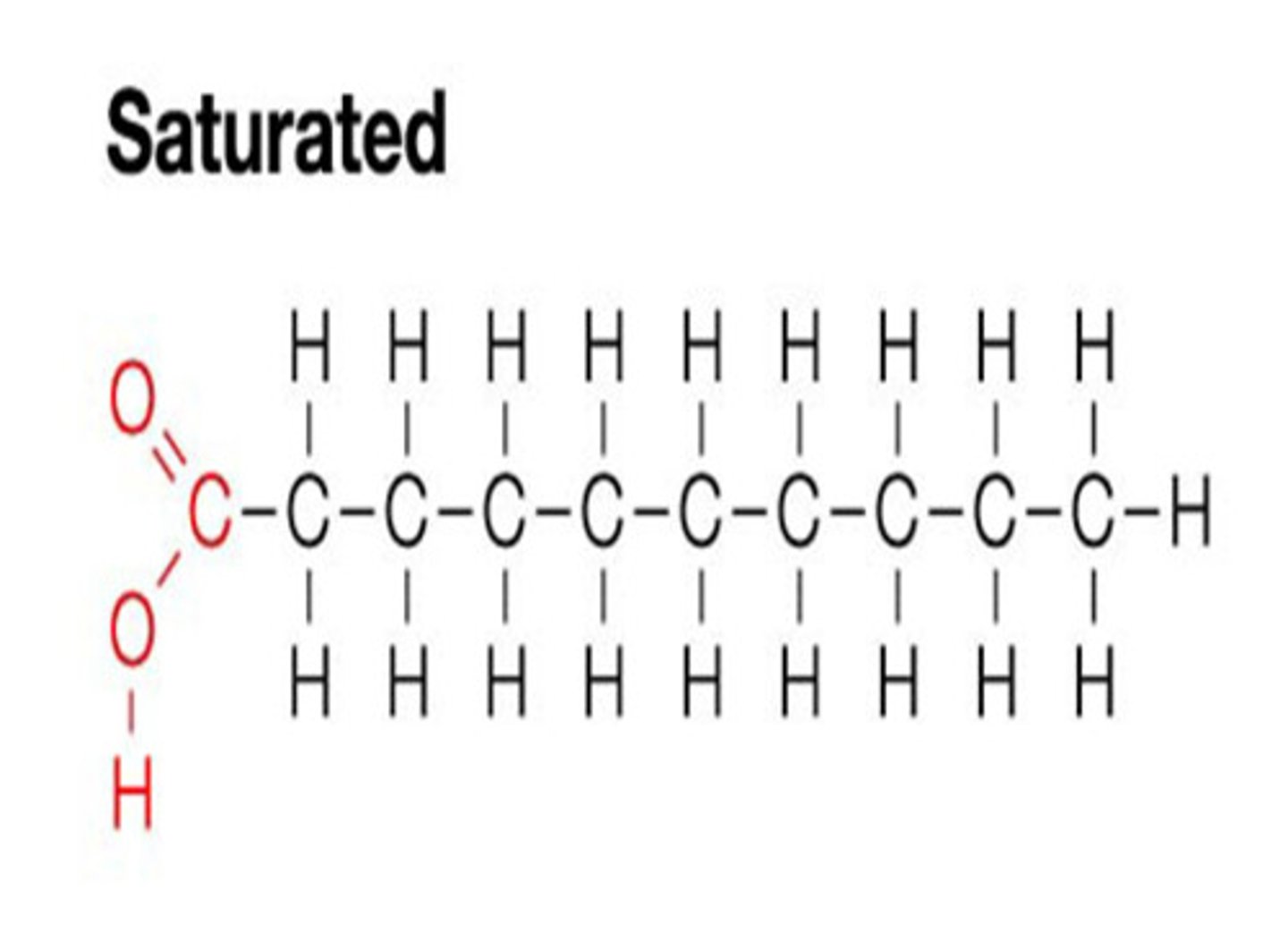
Saturated Fats
SOLID at room temperature. It does not have double bonds.
ex: Butter
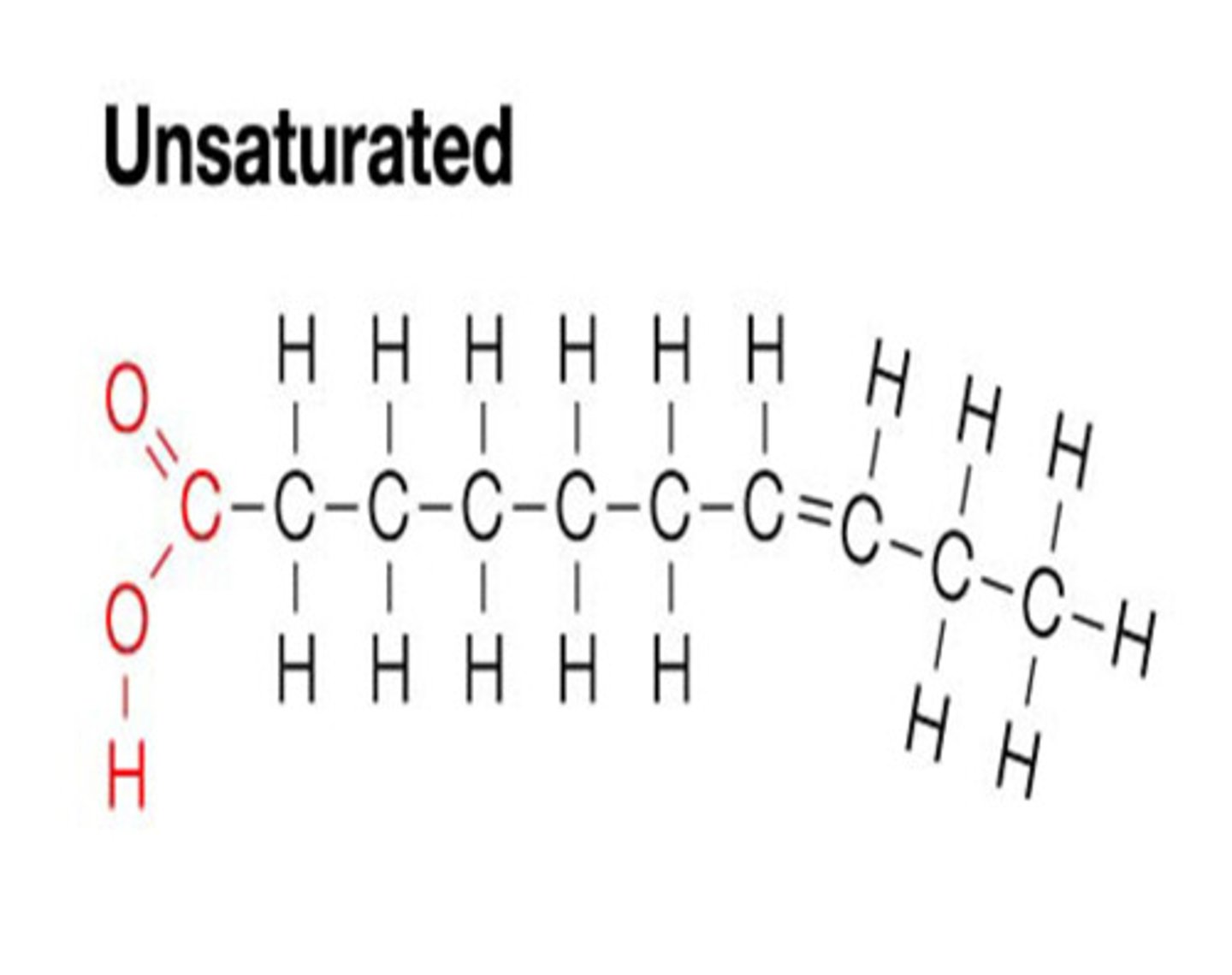
Unsaturated Fats
LIQUID at room temperature. Has double bonds.
ex: oil
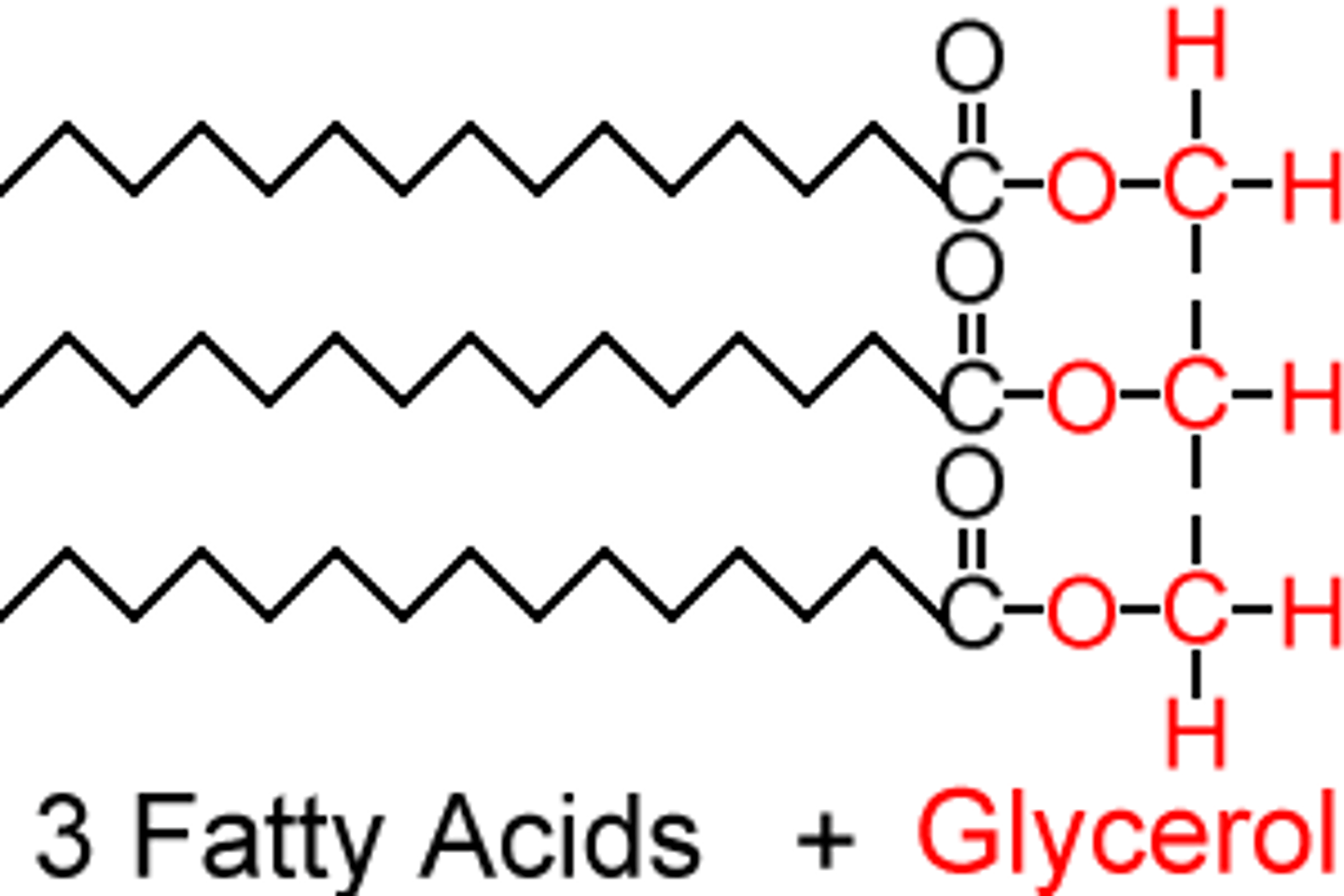
Triglycerides
composed of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
storage for extra calories
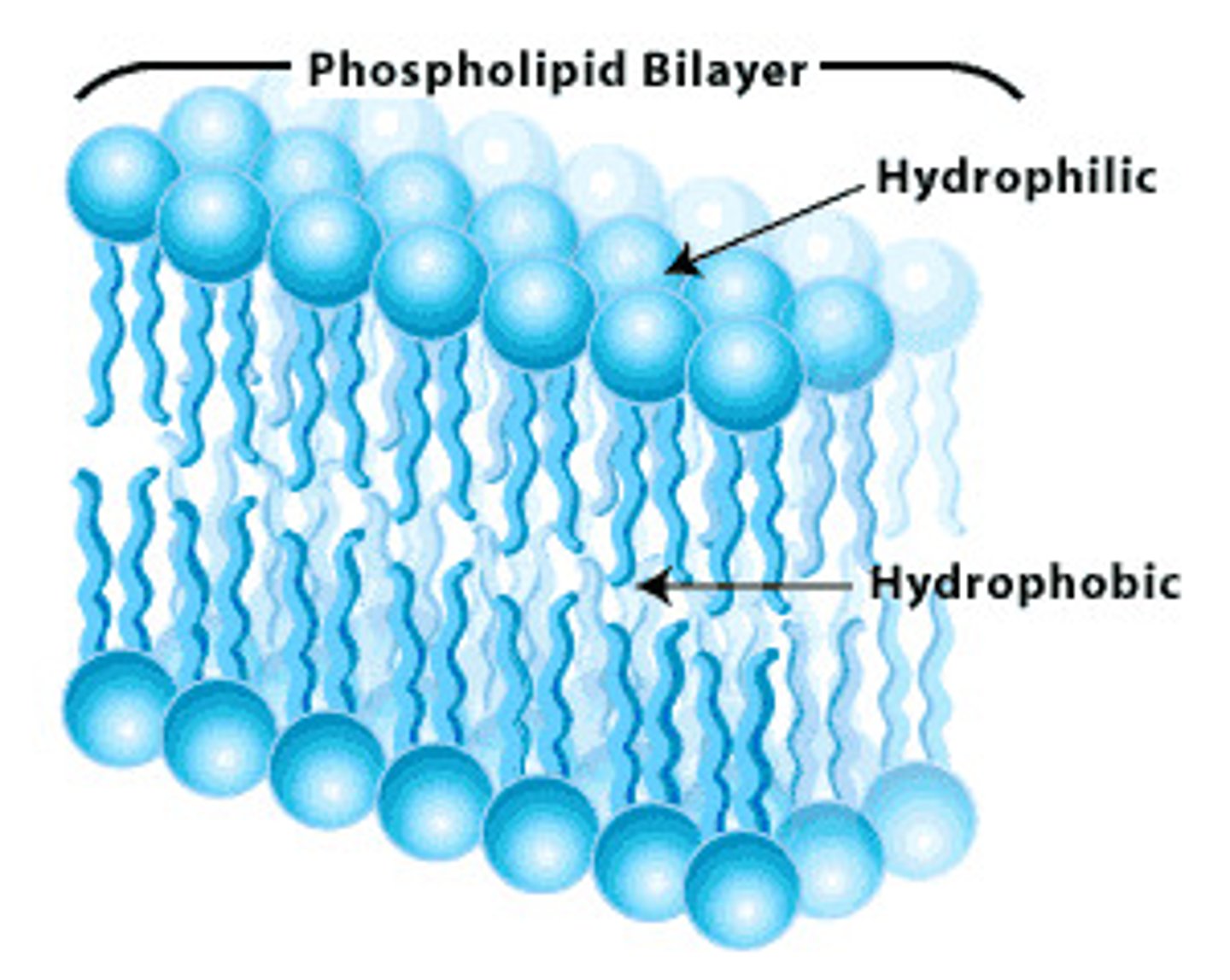
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Present in the cell membrane: Polar head and non-polar tail
Steroids
lipids with four fused ring carbon skeletons
Cholesterol
Steroid common in cell membranes, also in many hormones.
Proteins
Consists of one or more polypeptide (chain of amino acids)
Used in cell defense, storage, communication movement, and structural support.
Amino acids
organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
r group determines its properties
It is a monomer
Polypeptides
long chains of amino acids
it is a polymer
Four levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix (coils) or beta pleated sheet (folds) in polypeptide chain. (via H-bonds)
tertiary structure
interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
quaternary structure
Results from two or more polypeptide subunits.
nucleic acids
Polymers of nucleotide monomers.
DNA and RNA
composed of phosphate, 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogen base
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acids
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Double Helix
stores genetic information
(Bases: Guanine, Adenine, Thymine and Cytosine)
RNA
ribonucleic acid
Sugar: Ribose
Single-stranded
helps to make protein
(Bases: Guanine, Adenine, Uracil and Cytosine)
Central Dogma
DNA gets Transcribed (Transcription) to RNA. Then, RNA gets Translated (Translation) to Protein