American Imperialism: US History
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
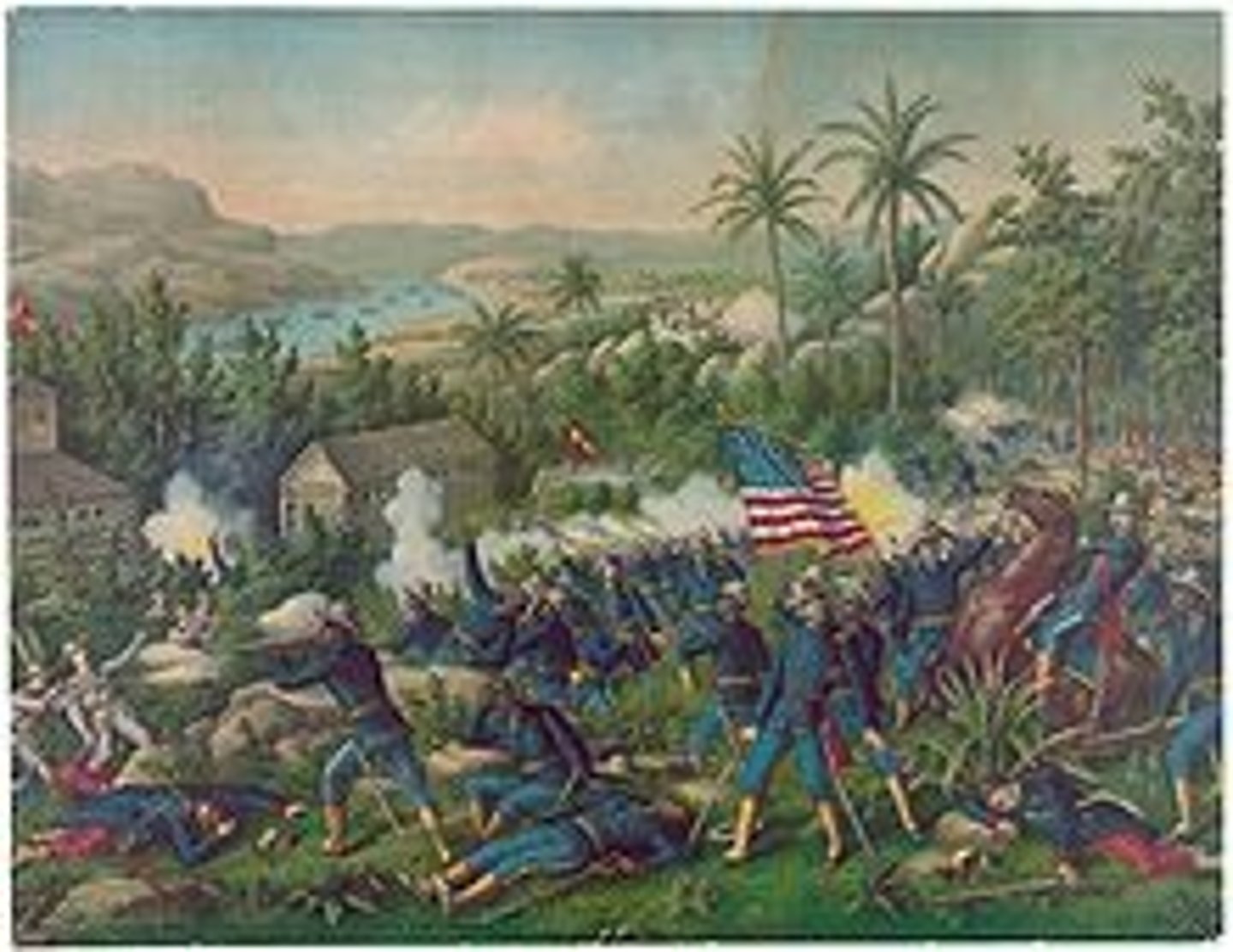
Spanish-American War
A war between Spain and the United States fought in 1898. The war began as an intervention by the United States on behalf of Cuba.

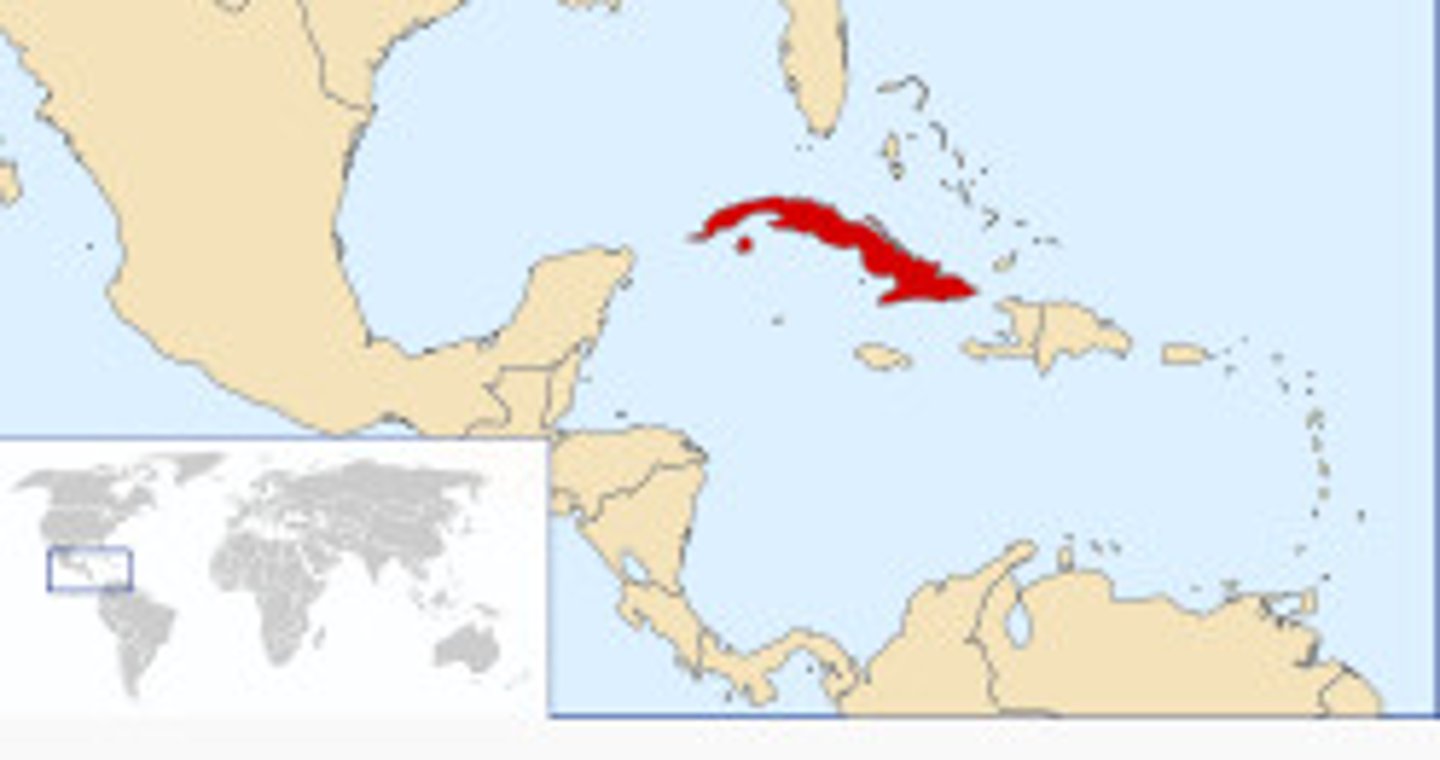
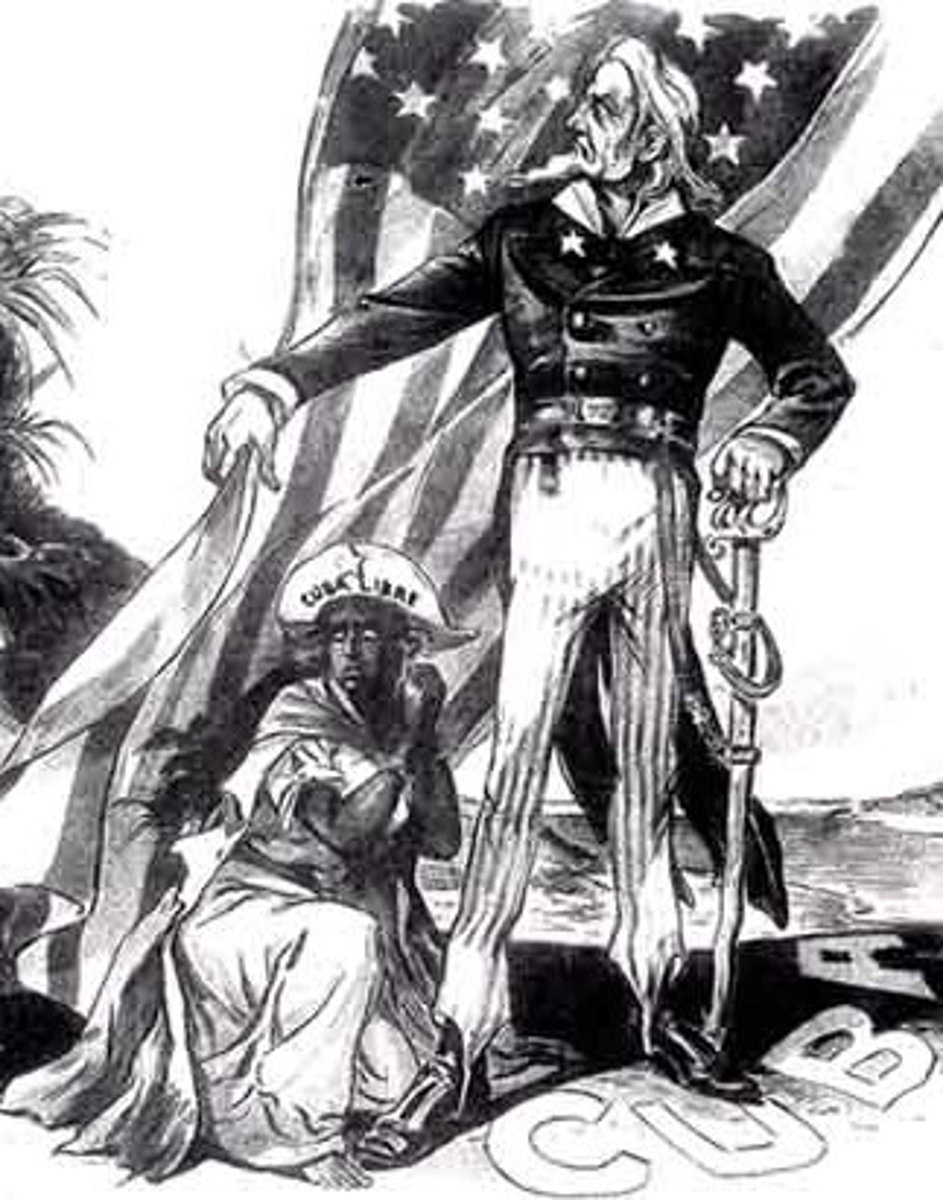
Cuba
An Island south of the US that was brutally crushed by Spanish troops. US was concerned, having LOTS of investment in there. Inhabitants are forced into prison/concentration camps, published in US newspapers and pitied.
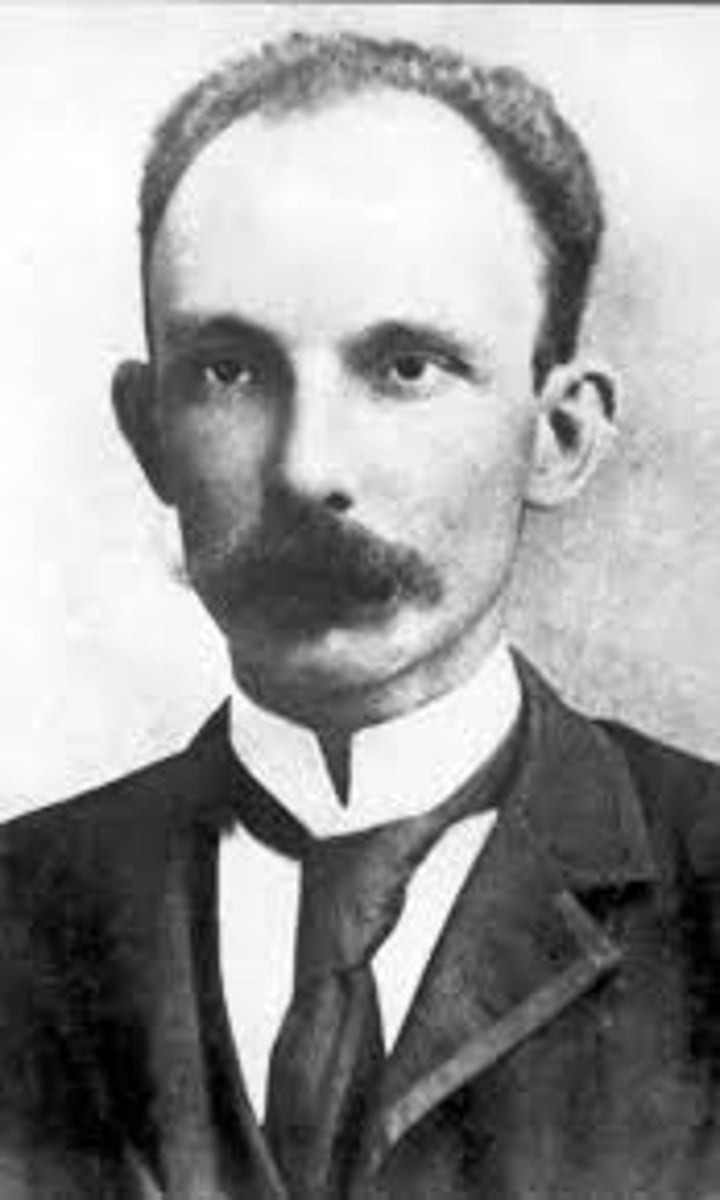
Jose Martí
Led the fight for Cuba's independence from Spain from 1895 through the Spanish-American War. Spoke against American occupation in Cuba.

Yellow Journalism
Journalism that exploits, distorts, or exaggerates the news to create sensations and attract readers

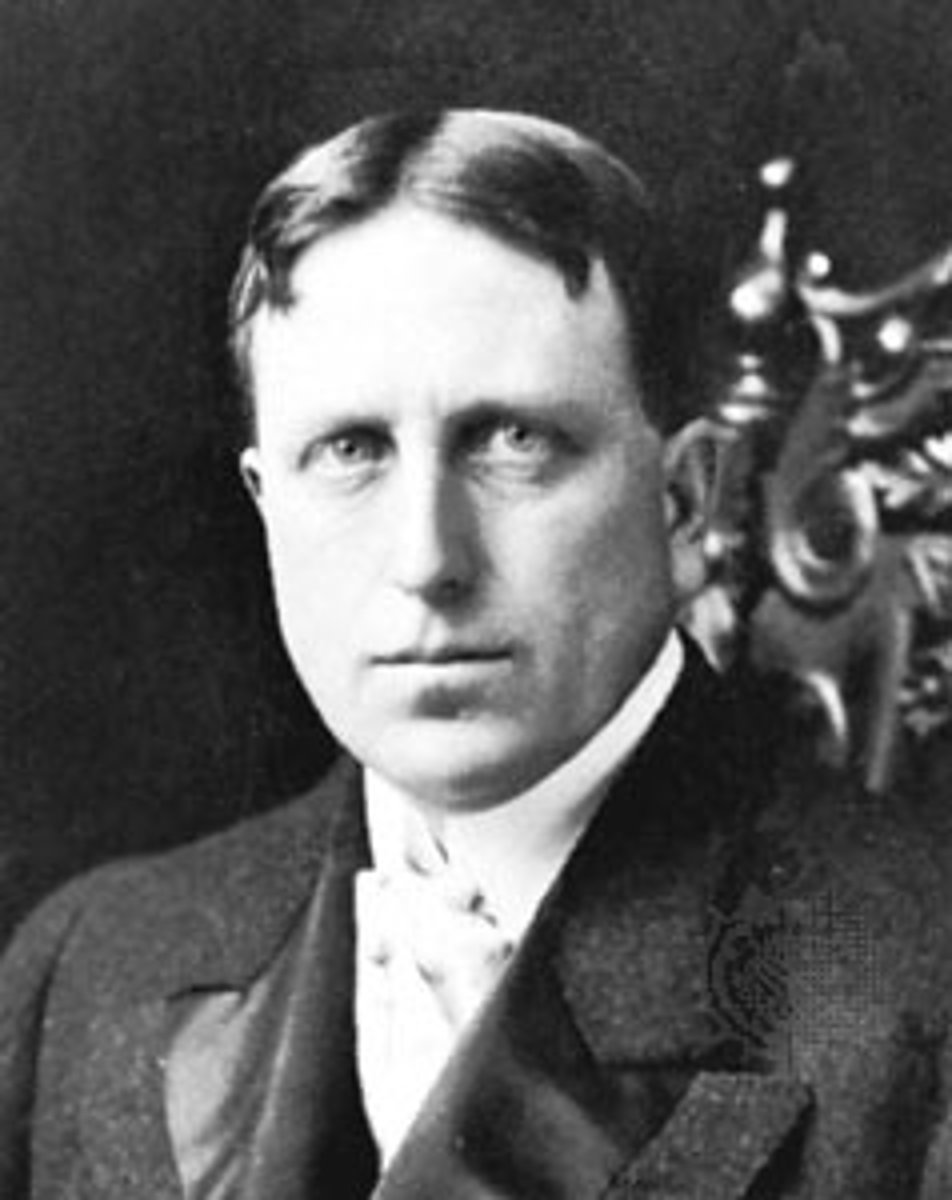
William Randolph Hearst
Newspaper editor in New York City who grew competitive and employed yellow journalism in order to entice readers to buy their papers; both men stopped at nothing in order to get a good story, and so were able to deliver shocking stories and exciting anecdotes.

Humanitarian
Concerned with or seeking to promote human welfare.

De Lome letter
This letter, written by the Spanish Ambassador to the United States, Enrique Dupuy de Lôme, was re-printed in the New York Journal; it was highly critical of President McKinley and viewed by many as an official Spanish insult against the US.

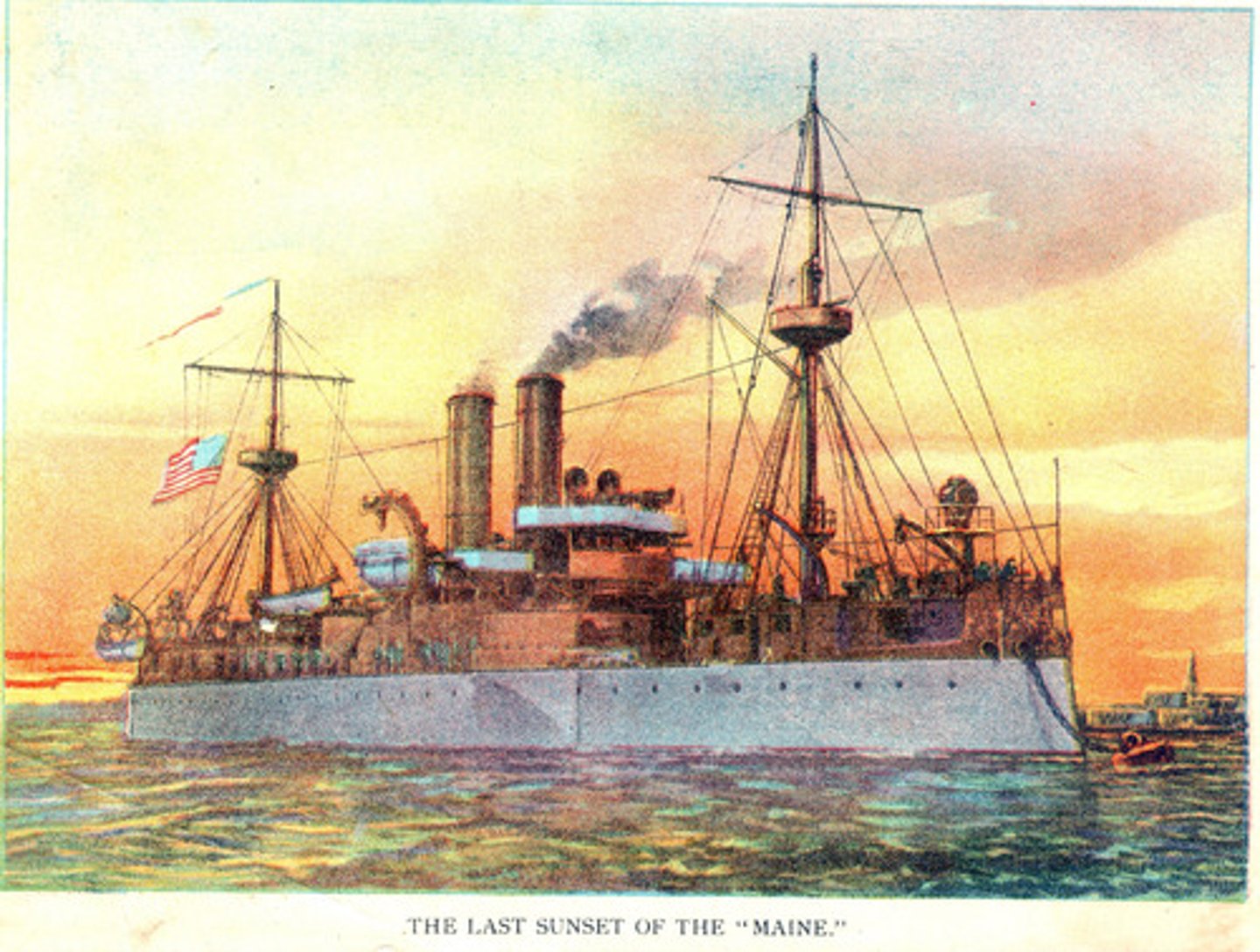
U.S.S Maine
The battleship sent to Havana to protect Americans and their property; an explosion sank it; killing 260 men. Newspapers said the ship was blown up by Spain and it became a call for war.
Rough Riders
The First United States Volunteer Calvary, a mixture of Ivy League athletes and western frontiersmen who volunteered to fight in the Spanish-American War. Recruited by Theodore Roosevelt, they won many battles in Florida and enlisted in the invasion army of Cuba.
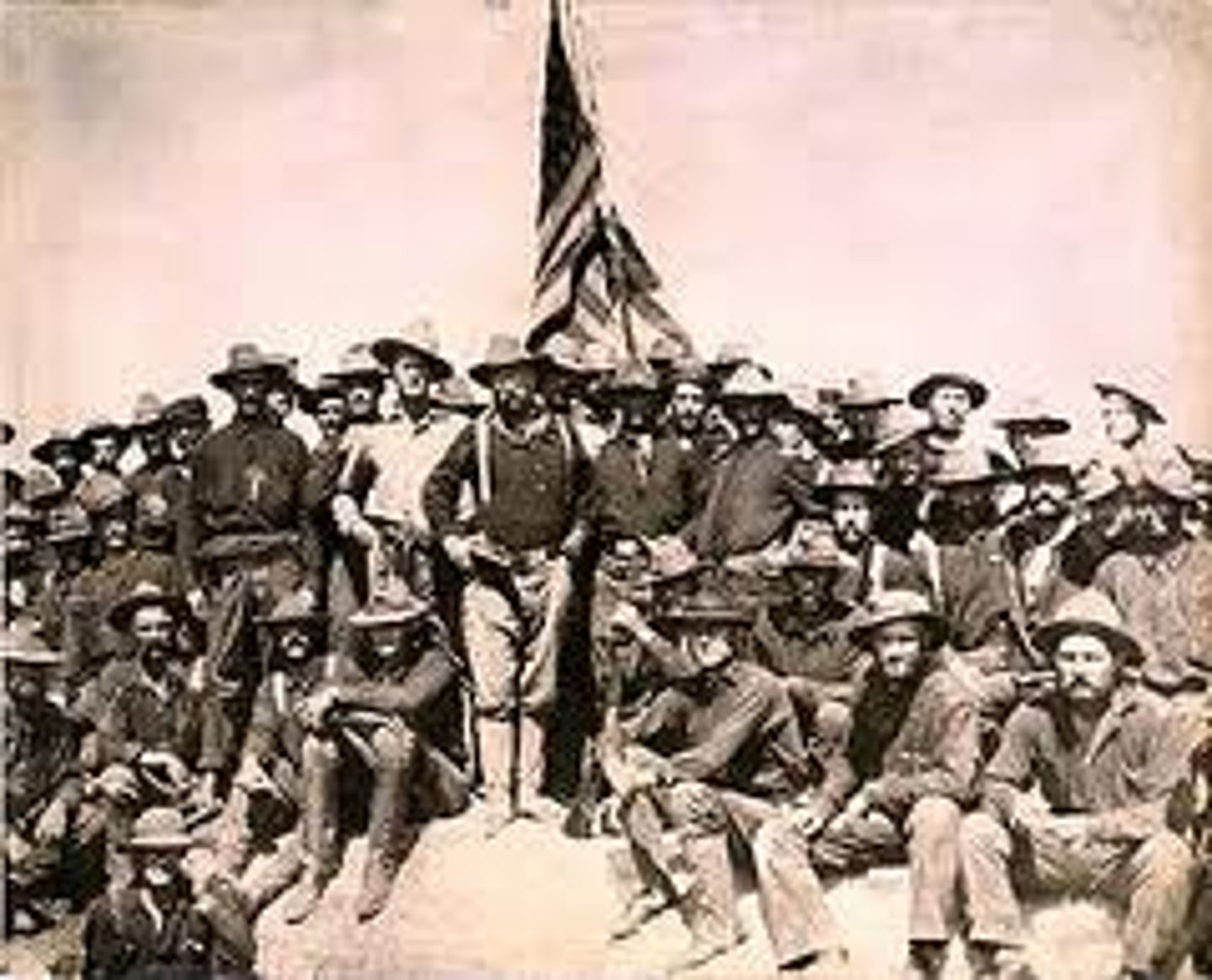

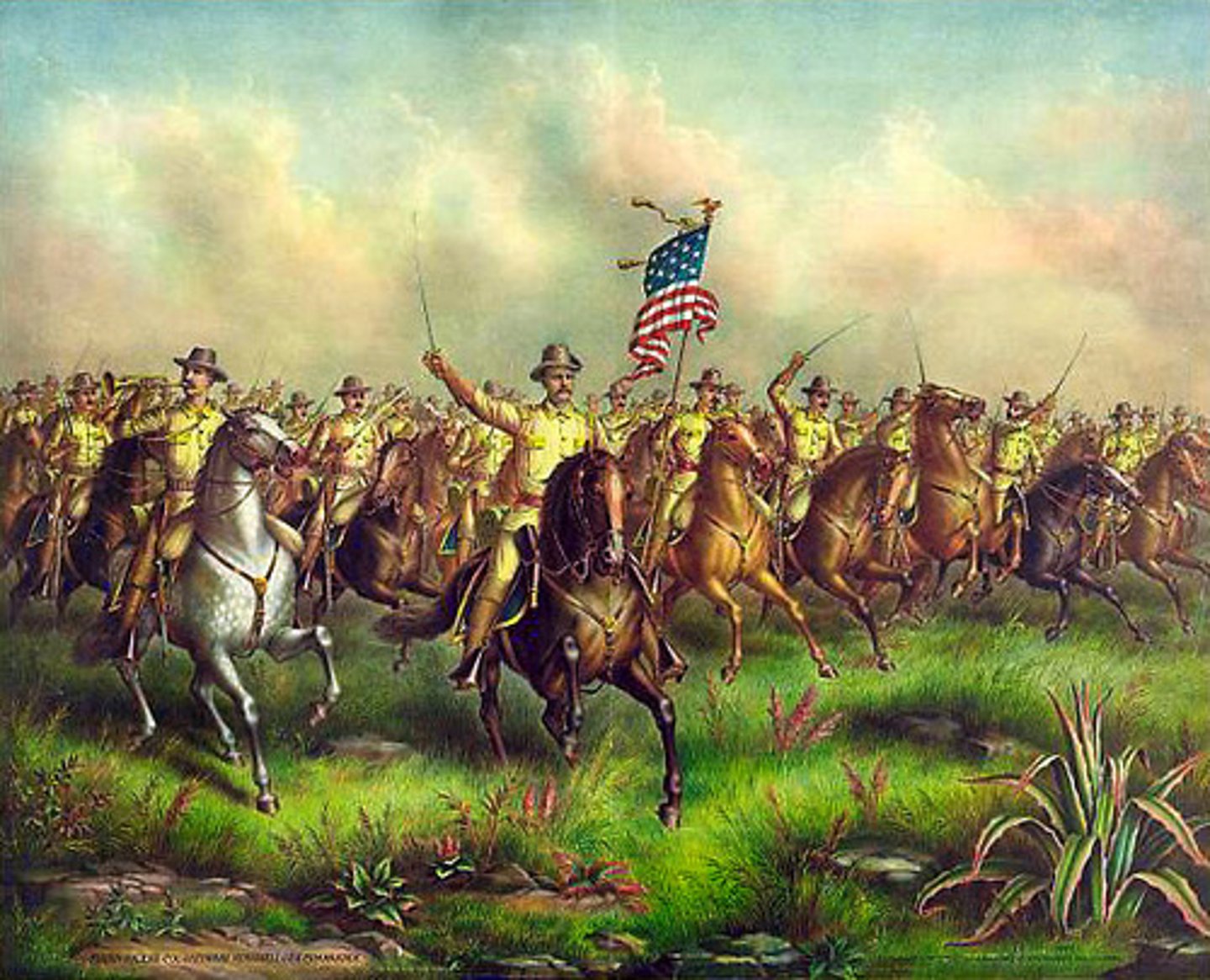
San Juan Hill
One of the most important battles of the Spanish-American War. Roosevelt and Rough Riders defeated Spain. Placed America at an advantage. Two days later, American ships destroyed the Spanish fleet in Cuba. In August, the US and Spain agreed to a treaty ending the war.

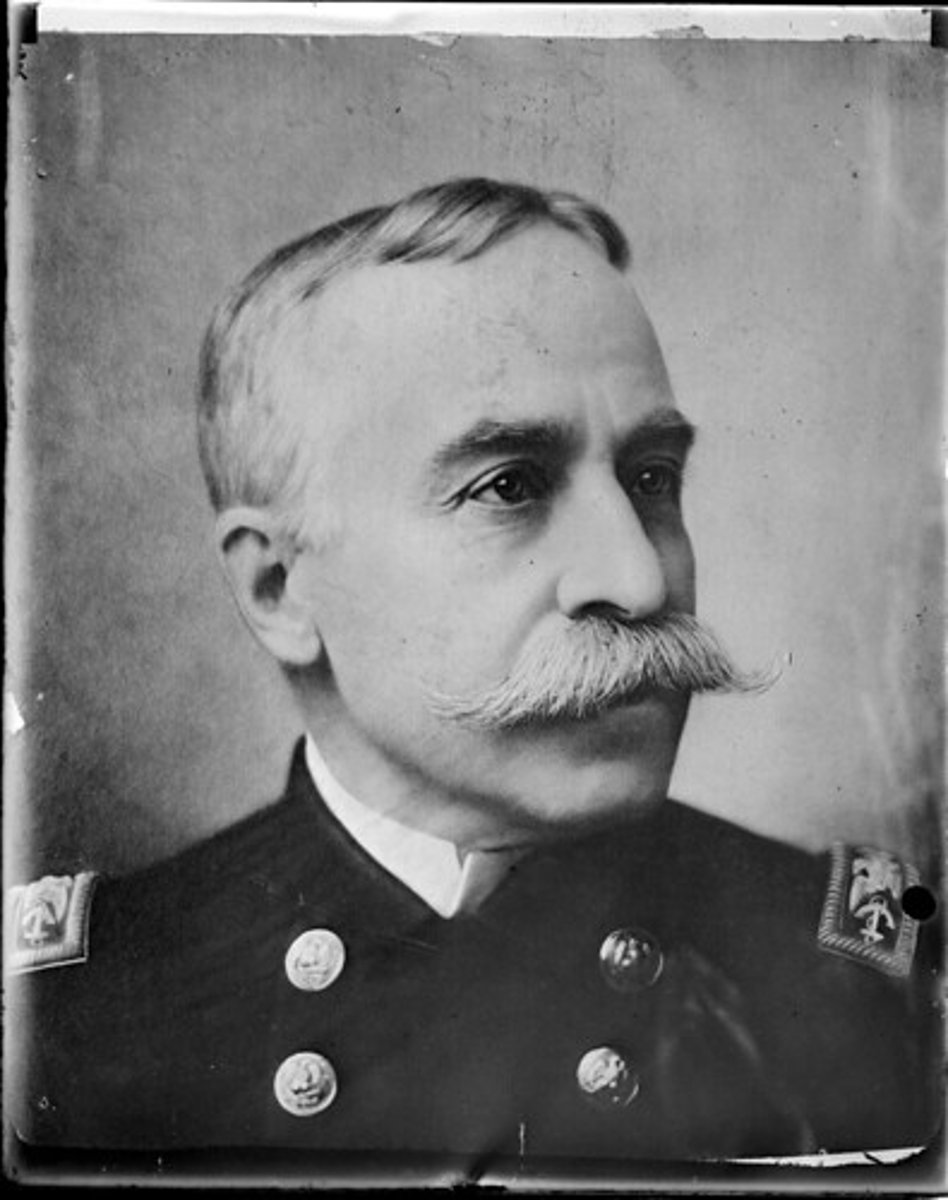
Commodore Dewey
Followed Roosevelt's order to attack Spanish forces in the Philippines when war was declared; completely destroyed the Spanish fleet stationed at Manila Bay. His victory shed light on the adjusted purpose of war with Spain, from just freeing Cuba to stripping Spain of all of its colonies.

Manila Bay
This Battle took place on 1 May 1898, during the Spanish-American War. The American Asiatic Squadron under Commodore George Dewey engaged and destroyed the Spanish Pacific Squadron under Admiral Patricio Montojo that marked an end to wooden ships to the more powerful American Steel Navy.

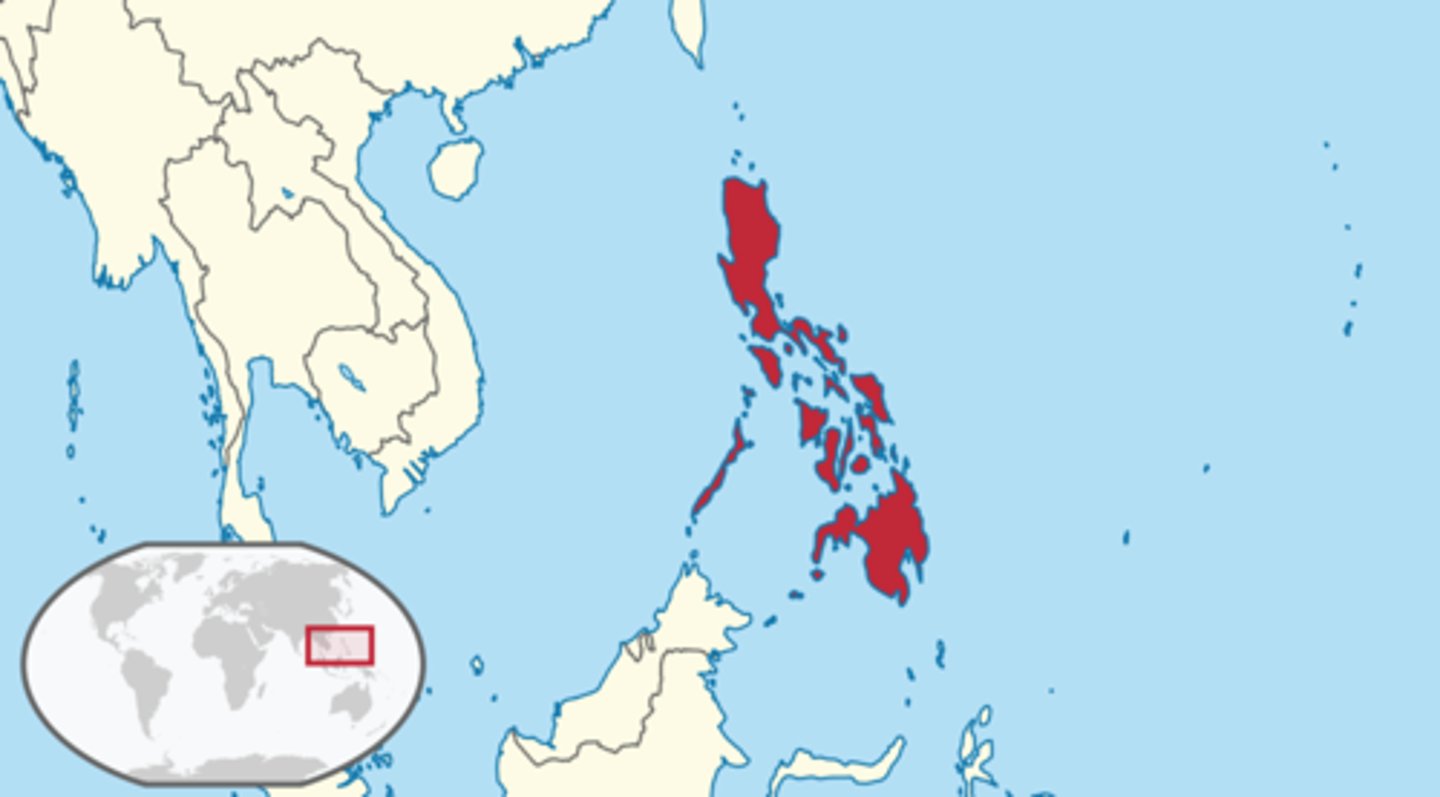
Philippines
Sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. An armed conflict between a group of Filipino revolutionaries and the United States which arose from the struggle of the First Philippine Republic to gain independence following annexation by the United States.
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

Alfred Thayer Mahan
Wrote The Influence of Sea Power upon History, which argued that control of the sea was the key to world dominance; it stimulated the naval race among the great powers. Which describe "the most important American strategist of the nineteenth century."

"White Man's Burden"
A phrase used to justify European imperialism in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries; it is the title of a poem by Rudyard Kipling.

Anti-Imperialist League
Objected to the annexation of the Philippines and the building of an American empire. Idealism, self-interest, racism, constitutionalism, and other reasons motivated them, but they failed to make their case; the Philippines were annexed in 1900

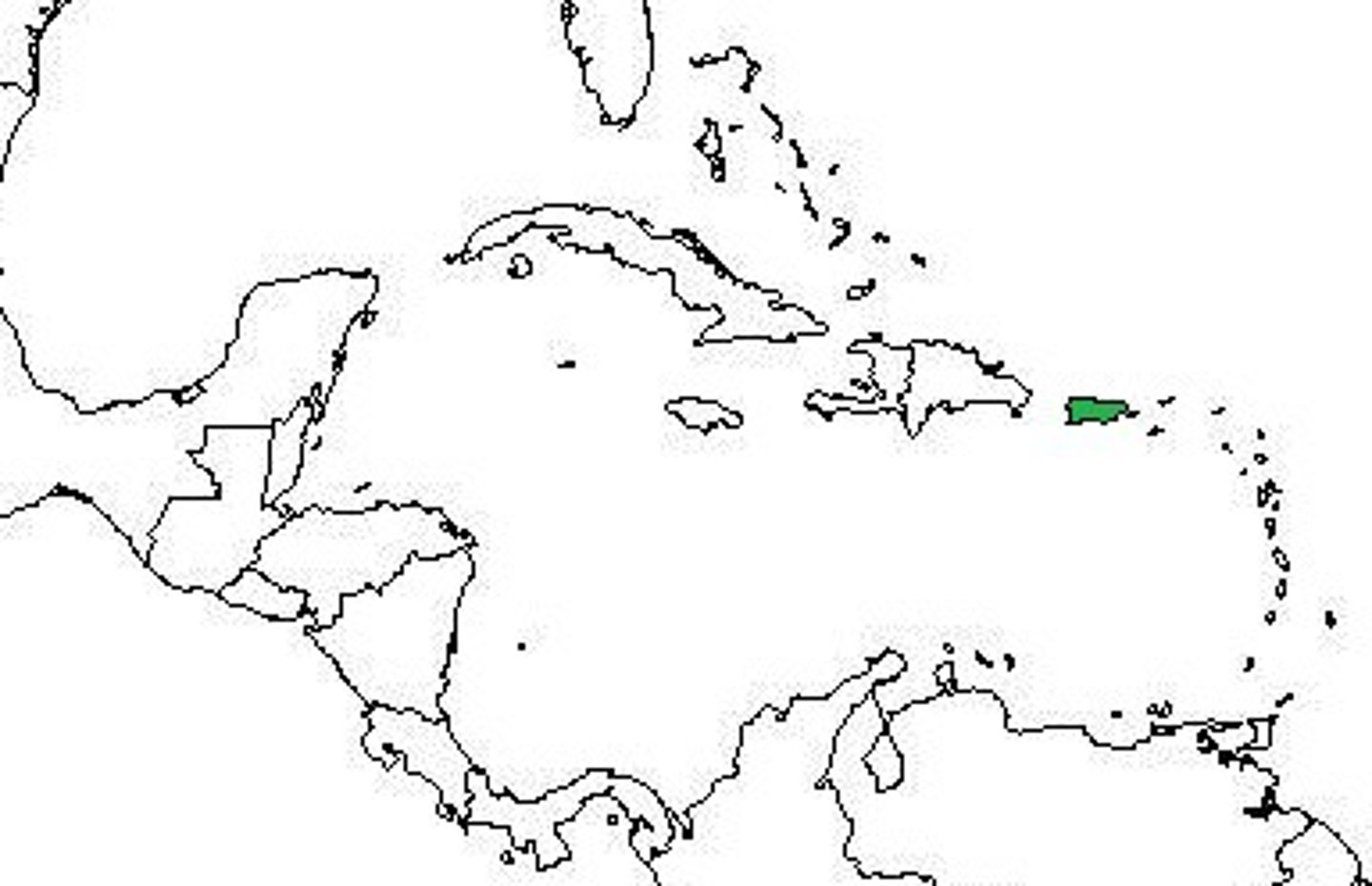
Puerto Rico
Caribbean island given to the US by Spain as a payment for the cost of the Spanish American War.
Teller Amendment
Act of Congress in 1898 that stated that when the United States had rid Cuba of Spanish rule, Cuba would be granted its freedom. It prevented Cuba from turning hostile towards the U.S

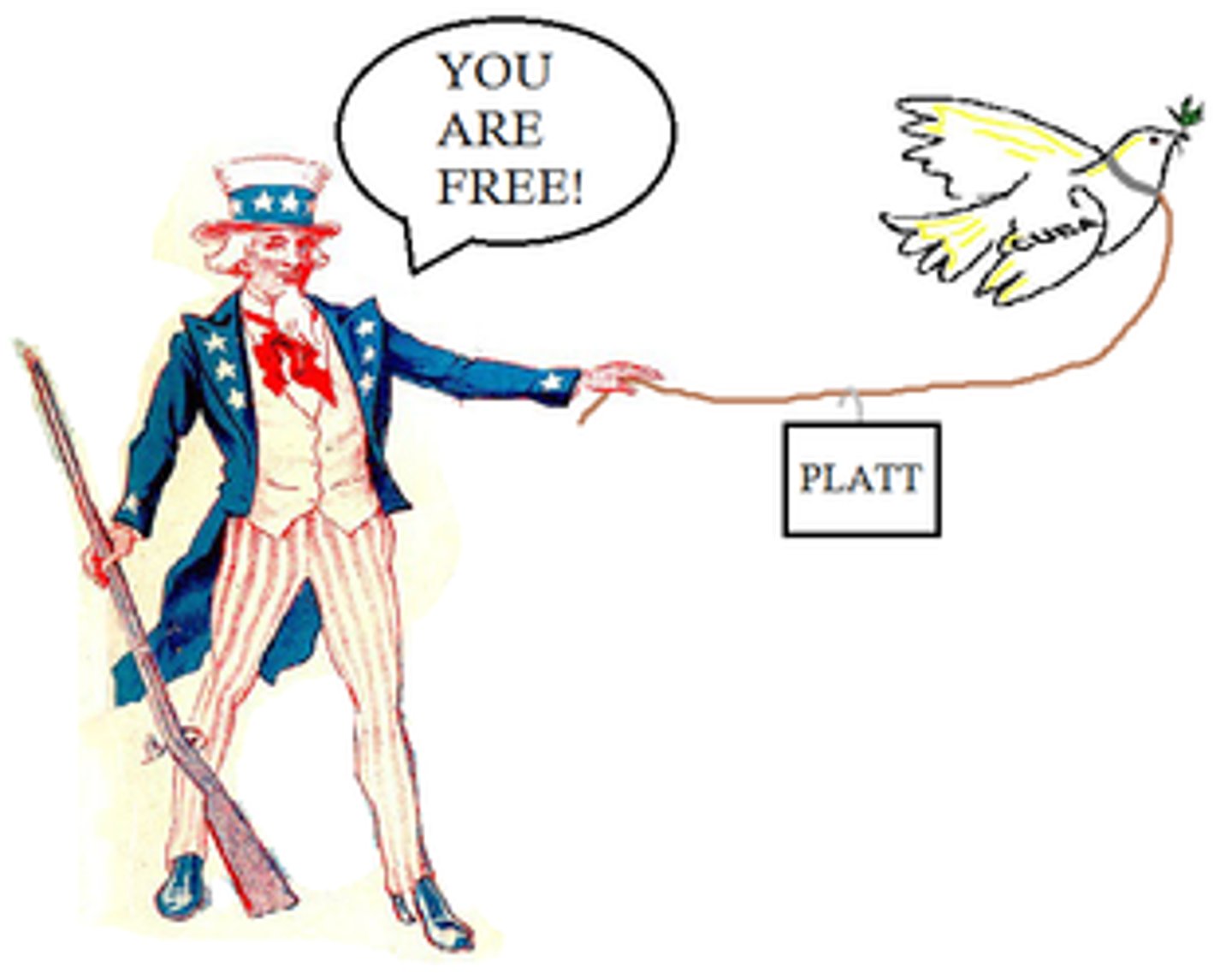
Platt Amendment
This amendment to the new Cuban constitution authorized U.S. intervention in Cuba to protect its interests. Cuba pledged not to make treaties with other countries that might compromise its independence, and it granted naval bases to the United States, most notable being Guantanamo Bay.
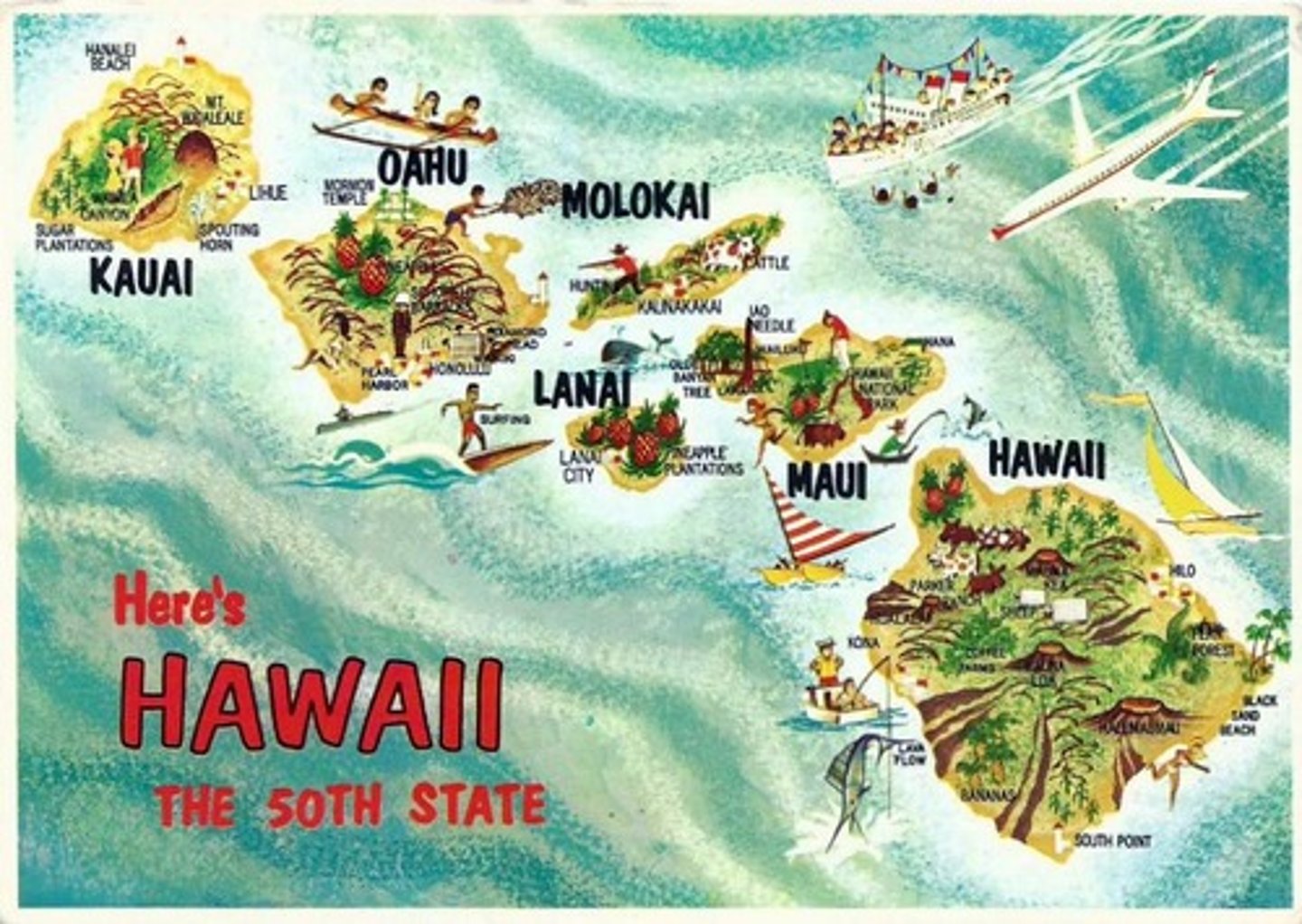
Hawaii
Is an isolated volcanic archipelago in the Central Pacific. U.S. wanted this island for business and so it's sugar could be sold in the U.S. duty free, Queen Liliuokalani opposed so Sanford B. Dole overthrew her in 1893, William McKinley convinced Congress to annex it in 1898
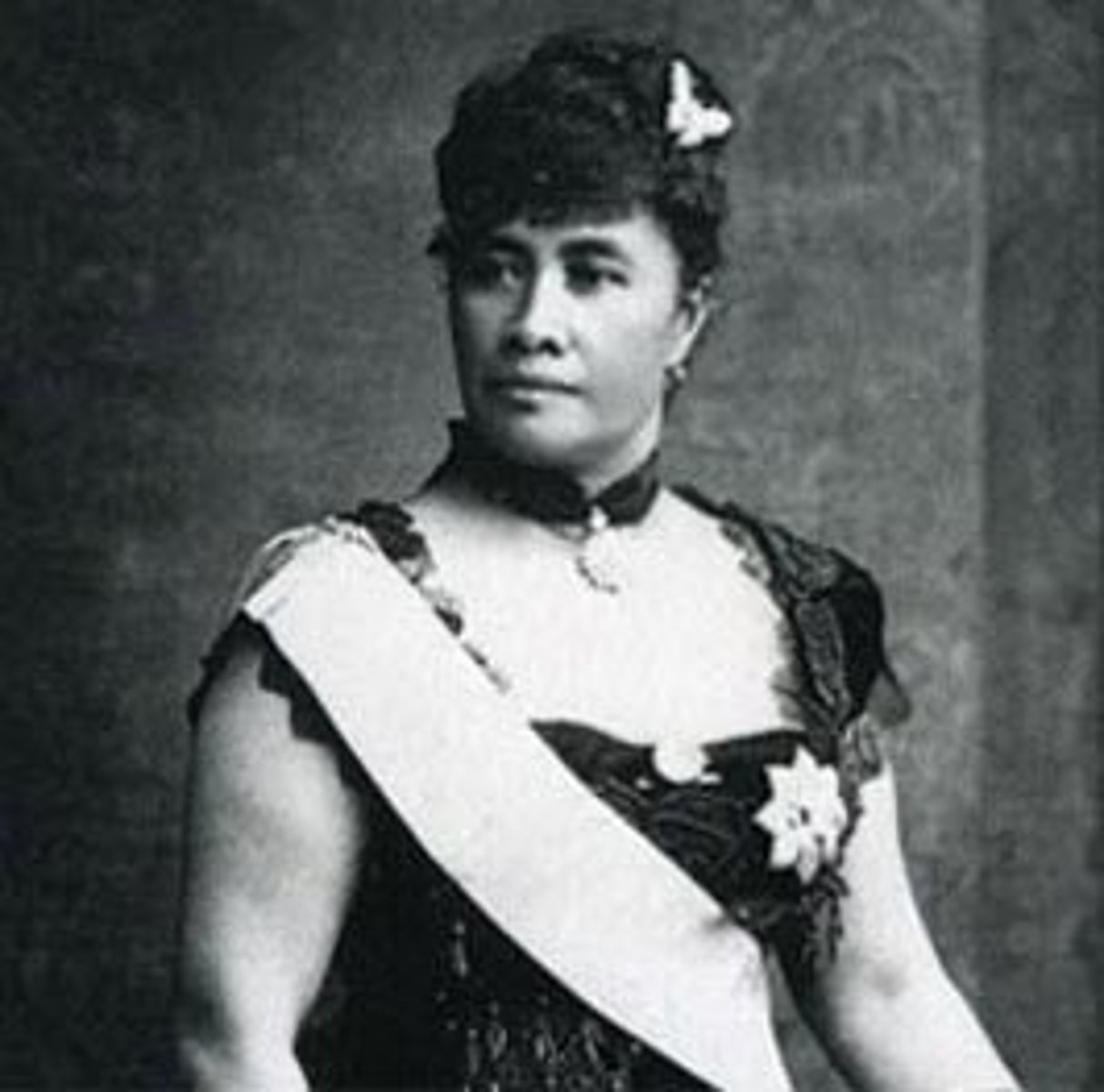
Queen Liliuokalani
Last reigning monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaii. She took the throne in 1891 following the death of her brother, King Kalakaua. She was a strong voice for native Hawaiians, whose power had been limited by the increasing influence of U.S. settlers in Hawaii.

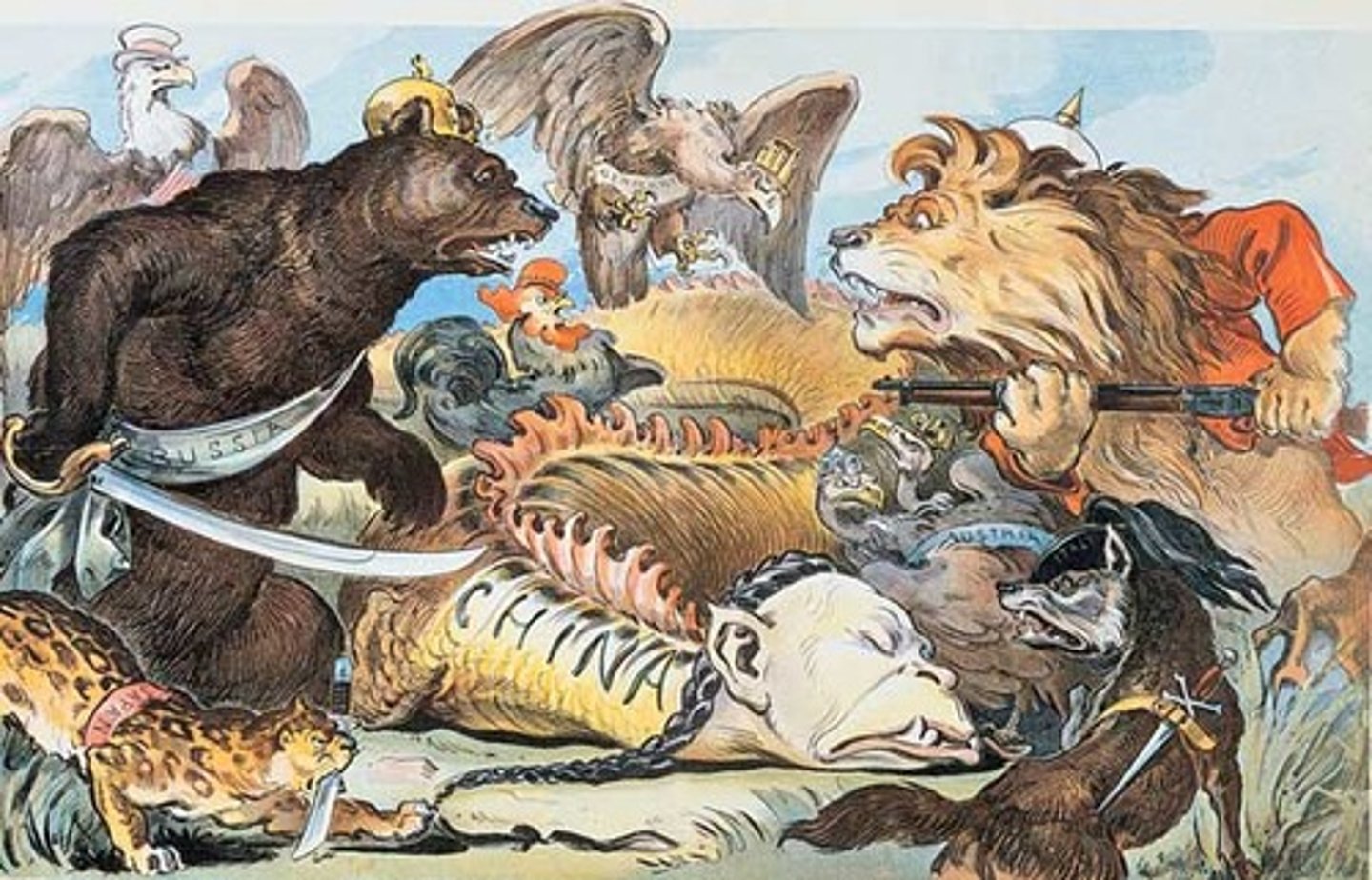
Spheres of Influence
A country or area in which another country has power to affect developments although it has no formal authority.

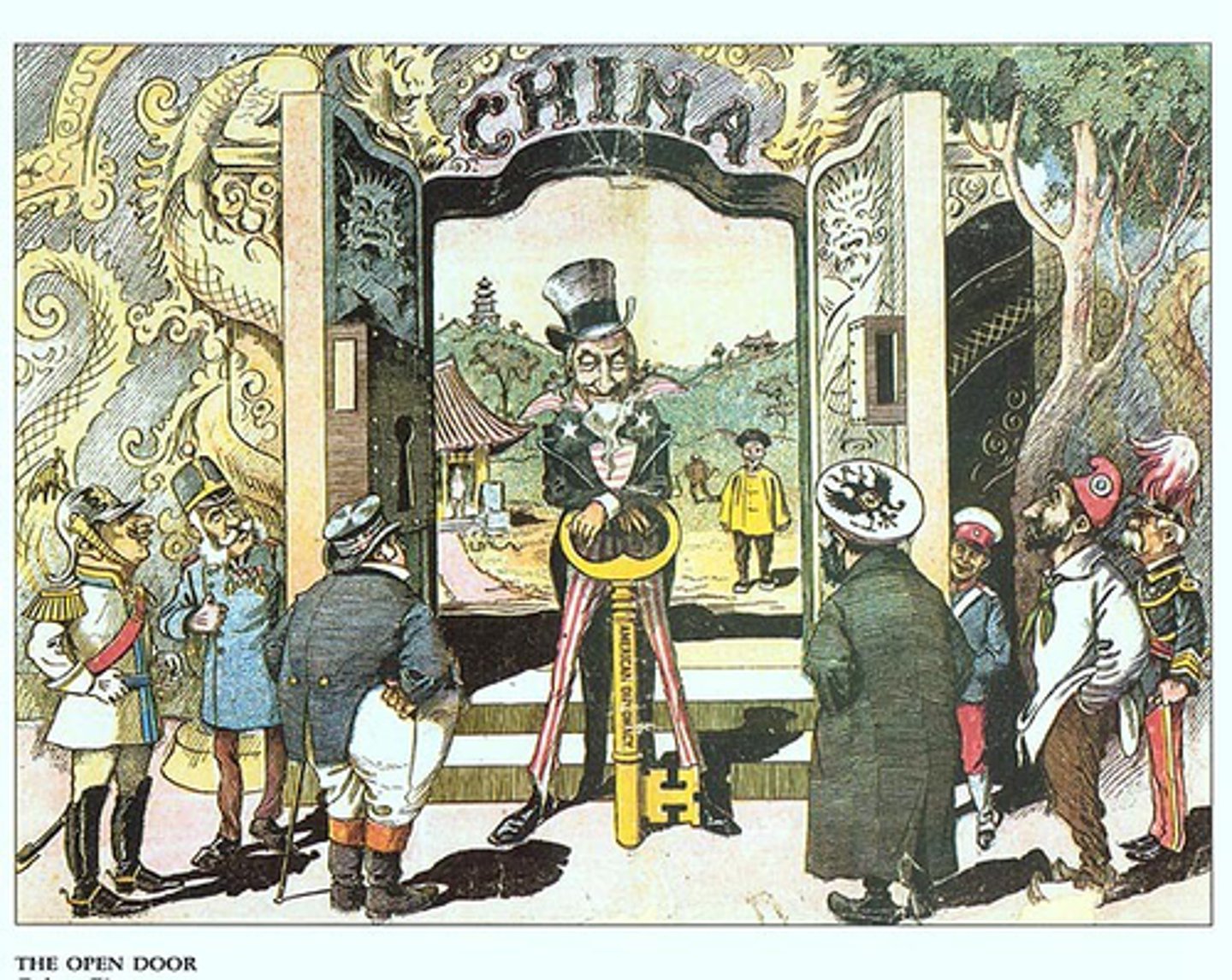
"Open Door" Policy
Is a term in foreign affairs initially used to refer to the United States policy established in the late 19th century and the early 20th century, begging the nations of the world to respect Chinese rights and influence in the spirit of fair competition.

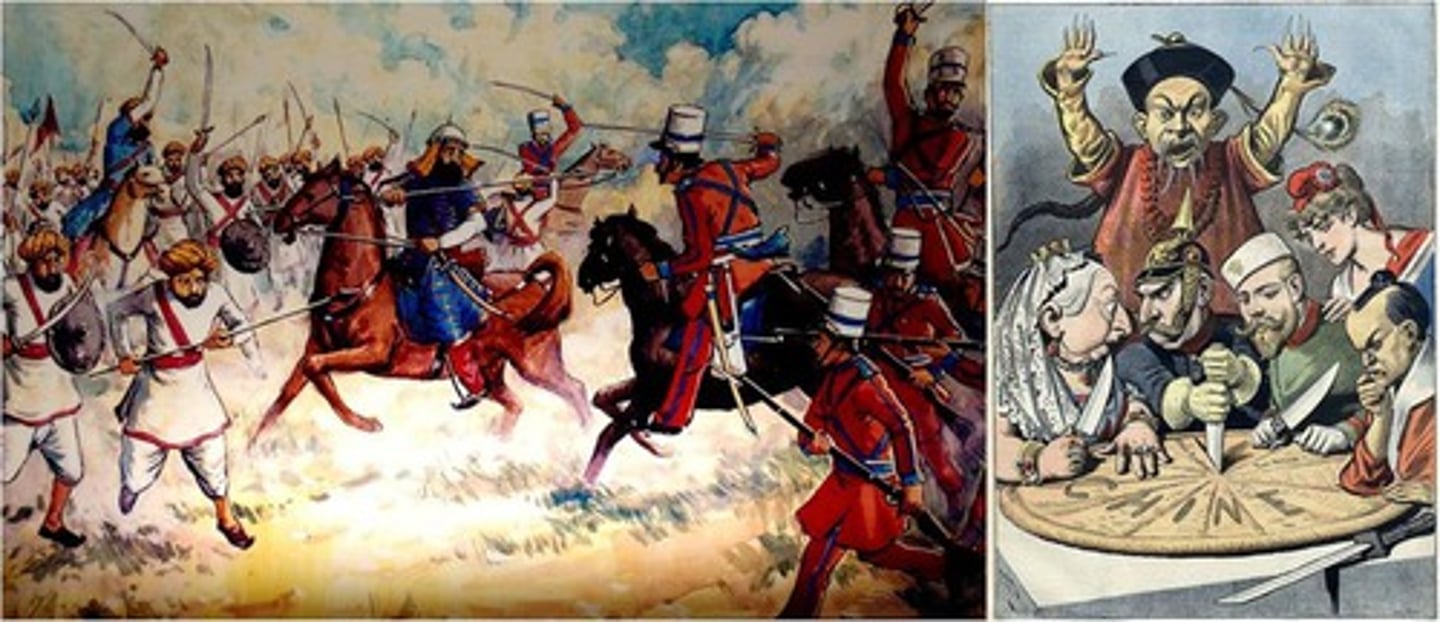
Boxer rebellion
a Chinese secret organization called the Society of the Righteous and Harmonious Fists led an uprising in northern China against the spread of Western and Japanese influence there.

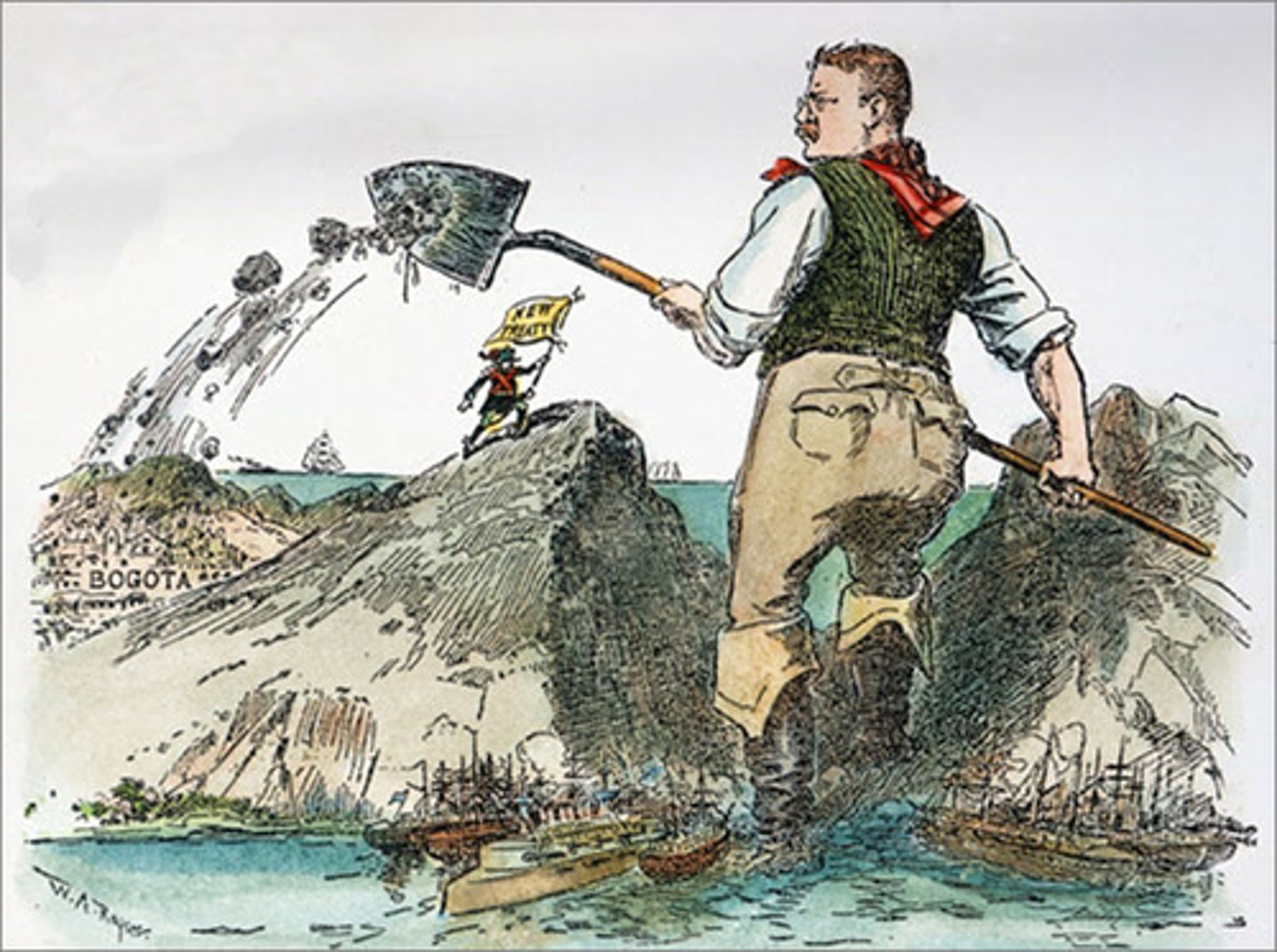
Panama Canal
a quicker passage to the Pacific from the Atlantic and vice versa. It cost $400,000,000 to build. Columbians would not let Americans build the canal, but then with the assistance of the United States a Panamanian Revolution occurred. The new ruling people allowed the United States to build the canal.

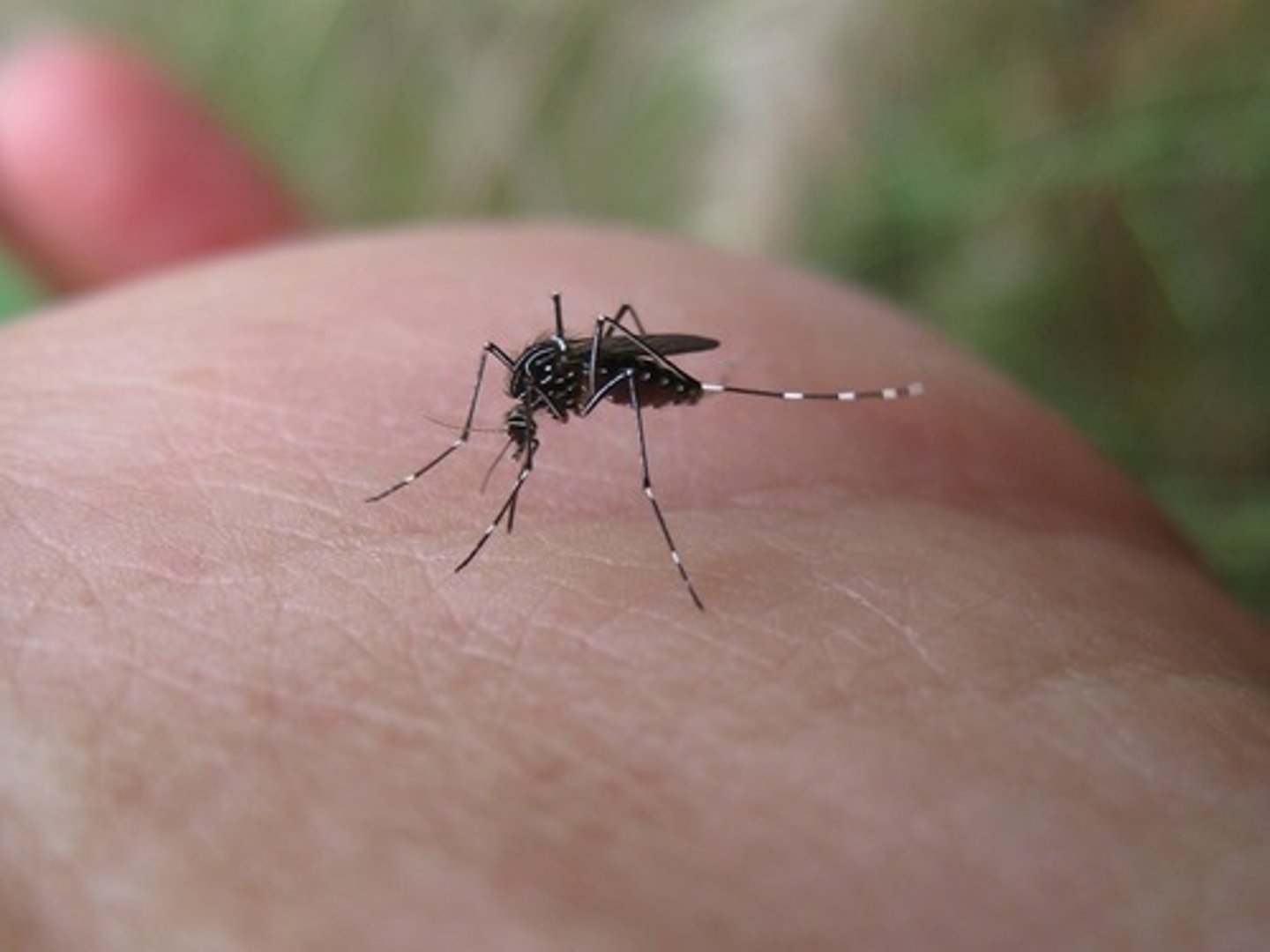
Yellow Fever
A tropical viral disease affecting the liver and kidneys, causing fever and jaundice and often fatal. It is transmitted by mosquitoes. Caused problem in the construction of the Panama Canal.

Monroe Doctrine
A principle of US policy, originated by President James Monroe in 1823, that any intervention by external powers in the politics of the Americas is a potentially hostile act against the US.
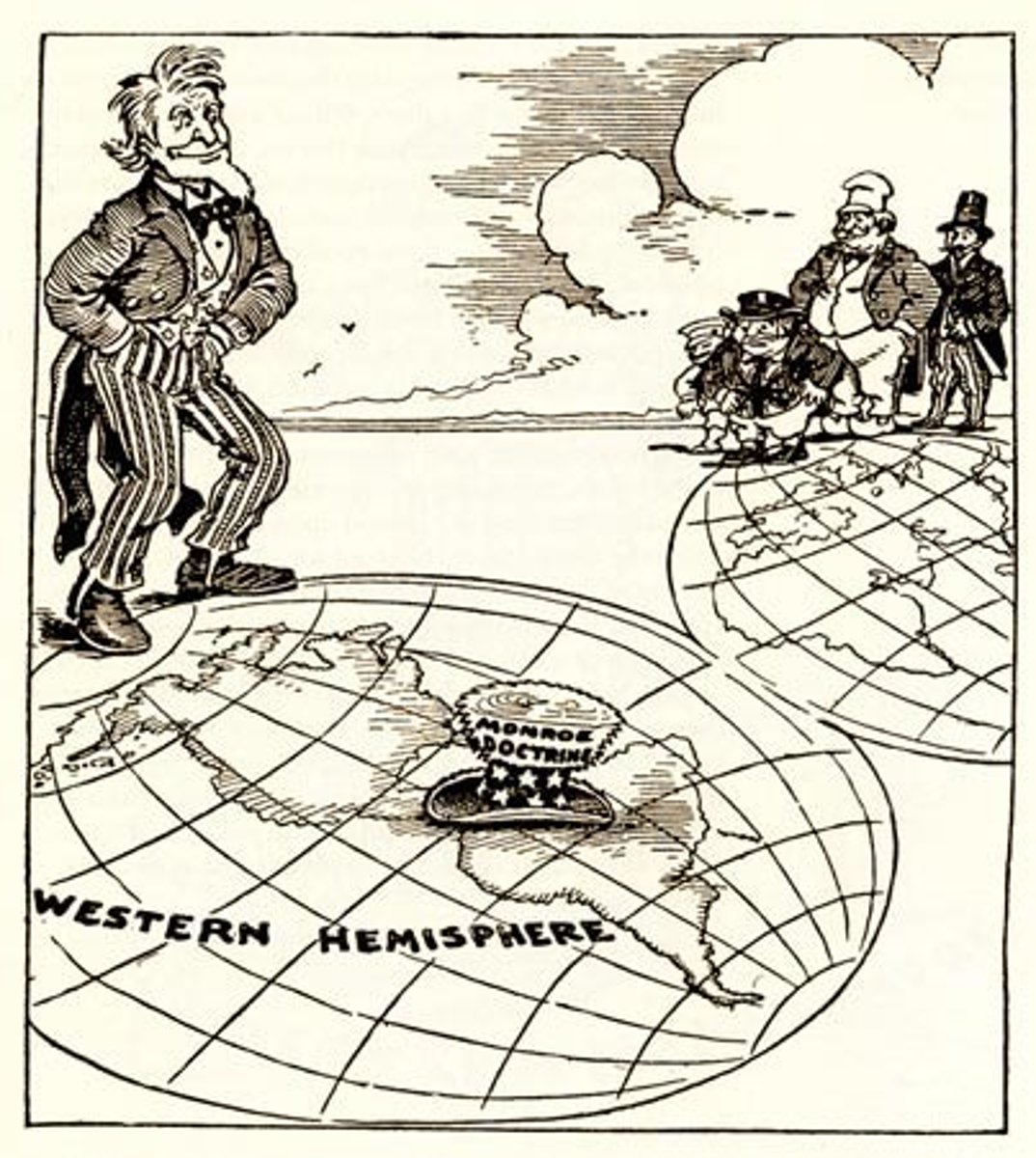
Roosevelt Corollary
Roosevelt's 1904 extension of the Monroe Doctrine, stating that the United States has the right to protect its economic interests in South And Central America by using military force

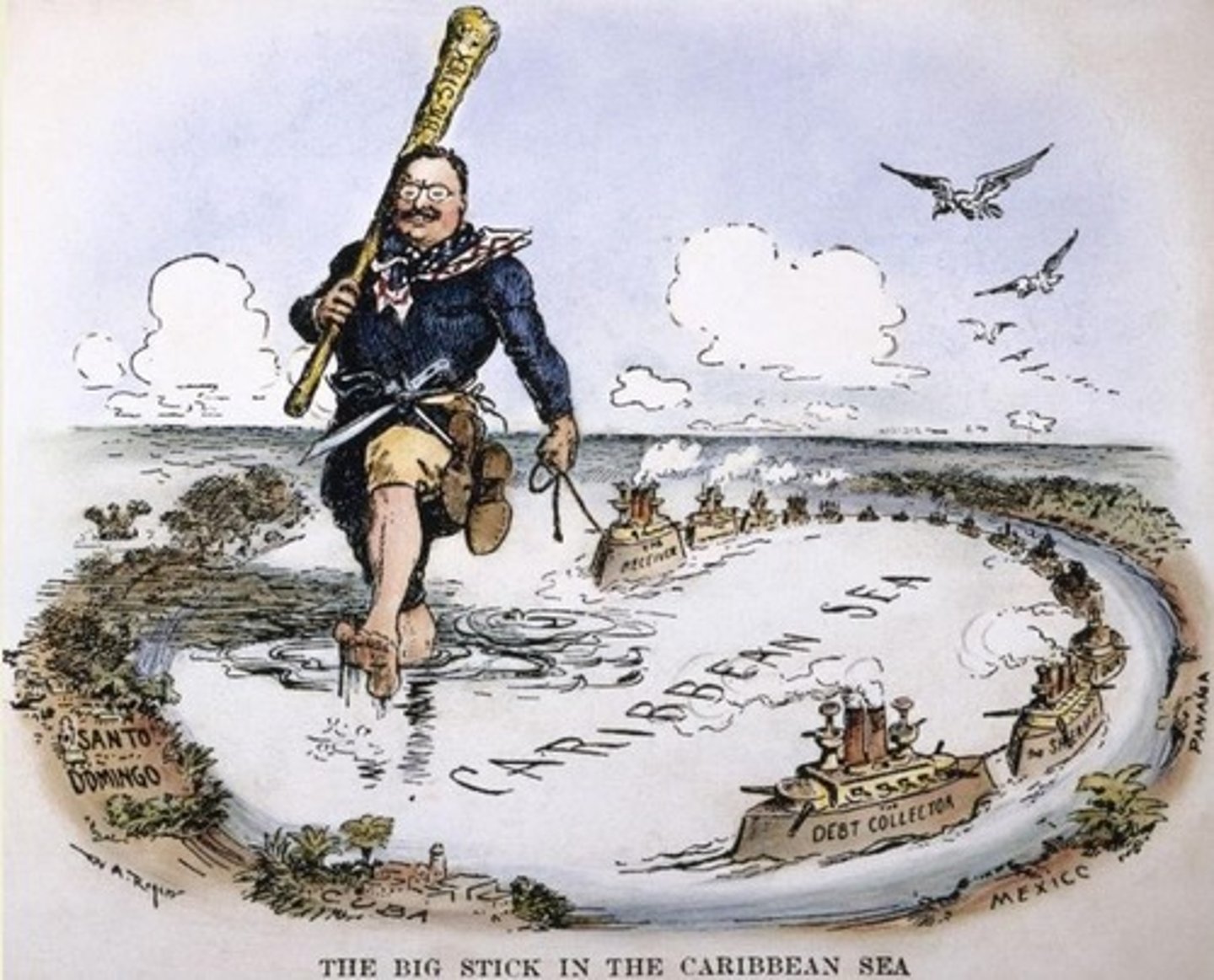
"Big Stick" policy
Refers to U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt's foreign policy: "speak softly, and carry a big stick.

"Dollar Diplomacy"
Term used to describe the efforts of the US to further its foreign policy through use of economic power by guaranteeing loans to foreign countries. Used by President Taft.

"Watchful Waiting"
Refers to Wilson waiting to see which faction of Mexico would eventually take over; a phrase used by him in a State of the Union Address.
