531 Unit 1 Lec 5-7
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
Eutomer
Active enantiomer
2
New cards
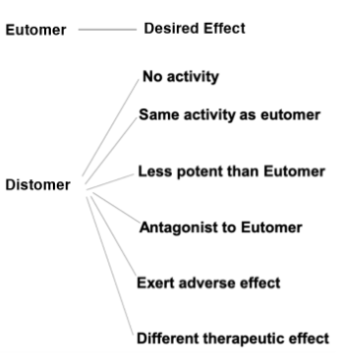
Distomer
Less potent enantiomer
3
New cards
Formula for Total number of stereoismoers of a chiral molecule
2 ^N
\
N= chiral centers
\
N= chiral centers
4
New cards
Methods to prepare enantiomerically pure forms of drug molecules
1)Use enentiomericallt pure starting materials
\
2)If the molecule has a carboxylic acid or basic amine, separate enantiomers at the END by making diastereomic salts
\
3)Use an enzyme to selectively modify one of the enantiomers of the racemate to facilitate separation OR prepare from an achiral starting material
\
4)Use a synthetic chiral catalyst to prepare one enantiomer at a key step in the synthesis from an achiral starting material
\
5)Separate enantiomers by chiral chromatography
\
2)If the molecule has a carboxylic acid or basic amine, separate enantiomers at the END by making diastereomic salts
\
3)Use an enzyme to selectively modify one of the enantiomers of the racemate to facilitate separation OR prepare from an achiral starting material
\
4)Use a synthetic chiral catalyst to prepare one enantiomer at a key step in the synthesis from an achiral starting material
\
5)Separate enantiomers by chiral chromatography
5
New cards
Explain diastereomic salts
When you hace 2 enantiomers of an acid or base, adda single enantiomer of a base or acid to create a salt THEN separate those salts by their solubilities thus separating the enantiomers
6
New cards
Explain how to use an enzyme to
prepare enantiomerically pure forms of drug molecules
prepare enantiomerically pure forms of drug molecules
Attacks from only one end so it doesnt make both enantiomers
\
Esterases, redureductases, crases, and other enzymes can distinguish between enantiomers and create single enantiomers
\
Allows separation of racemic mixture by modify only one enantiomer, create single enantiomer from achiral starting material
\
Esterases, redureductases, crases, and other enzymes can distinguish between enantiomers and create single enantiomers
\
Allows separation of racemic mixture by modify only one enantiomer, create single enantiomer from achiral starting material
7
New cards
Explain synthetic chiral catalysts
These catalysts act like enzymes in that they bind the starting molecule and modify it to produce mostly one enantiomer of a chiral product
\
→We made them
→D vs L , L (left), D (right)
→D vs L are specific for creating a certain enantiomer
\
→We made them
→D vs L , L (left), D (right)
→D vs L are specific for creating a certain enantiomer
8
New cards
Explain chiral chromatogrpahy
You have gunk, run it through a staw with hooks and the hook is specific for something, rinse out the gunk, rinse again to get it off the hook
* In this case, the hook is specific for an enantiomer
\n
Too expensive
* In this case, the hook is specific for an enantiomer
\n
Too expensive
9
New cards
What is synthetic biology
The use of recombinant DNA technology to create genetically modified organisms for the synthesis of novel products
\-For drug discovery usually for more efficient synthesis of bioactive molecules
\-For drug discovery usually for more efficient synthesis of bioactive molecules
10
New cards
What are chiral switch drugs
Development of a single enantiomer version of a racemic drug that has already been approved
\
No huge difference
\
Ex: Omeprazole→ Esomeprazole
\
No huge difference
\
Ex: Omeprazole→ Esomeprazole
11
New cards
What is torsional strain
lectrons repelling as the H atoms passing each other
\-Steric repulision if two spheres bigger than H
\-Steric repulision if two spheres bigger than H
12
New cards
What is Baeyer’s Ring Strain
• Rings with small internal angles are highly strained: 3,4 membered rings
• For cyclohexane, the chair is the most stable
• For cyclohexane, the chair is the most stable
13
New cards
What is an exception to the rules of the most stable conformational isomers?
• Sometimes the most stable conformation is based on an intramolecular interaction that can override steric considerations
\
Ex: Acetylcoline, a highly flexible molecule, is surprisingly found in both solution and crystals in the gauch conformation
\
Ex: Acetylcoline, a highly flexible molecule, is surprisingly found in both solution and crystals in the gauch conformation
14
New cards
What is the bioactive conformation
The target/protein bound conformation.
15
New cards
How do rings improve binding affinity and specificity
* Increase affinity by reducing entropy loss upon binding
* Increase specificity because rigid molecule cannot access alternative bioactive conformations via bond rotations
* Increase specificity because rigid molecule cannot access alternative bioactive conformations via bond rotations
16
New cards
Crosslinkers
Atoms that link two areas of a molecule to constrict its conformation. This pre-pays the entropic cost before the binding step
\-This is part of rational design
\-This is part of rational design
17
New cards
What is drug residence time
\-New evidence suggests that the main way to increase drug efficacy is to focus on maintaining the drug residence time (tau) (that is it bound to its target)
18
New cards
Induced fit
binding model in which a protein conformaitonal change is initiated by ligand binding because the ligand is inducing the change
19
New cards
Conformational selection
model which a rare protein conformation binds the ligand directly
20
New cards
Lead optimization
Process of improving drug for use in humans and involves optimizing
ADME
ADME
21
New cards
ADME
→ Absorption: Modes of administration; if orally administered, transporting through epithelial lipid bilayers of GI tractto circulations
→Distribution: penetrations of tissues, passeing through cell membranes, crossing BBB
→Metabolism: Metabolic breakdown
→Excretion: consistent pattern of excretion
→Distribution: penetrations of tissues, passeing through cell membranes, crossing BBB
→Metabolism: Metabolic breakdown
→Excretion: consistent pattern of excretion
22
New cards
Lipinski’s rule of 5
1) Not more than 5 hydrogen bond donors
2)Total N + O atoms which are Hbond acceptors must be less than or equal to 10
3)Should have Less than 10 rotatable bonds
4)Should have Low molecular weight
2)Total N + O atoms which are Hbond acceptors must be less than or equal to 10
3)Should have Less than 10 rotatable bonds
4)Should have Low molecular weight
23
New cards
What bonds are not rotatable
amide bonds, ring bonds, double and triple bonds are not rotatble
24
New cards
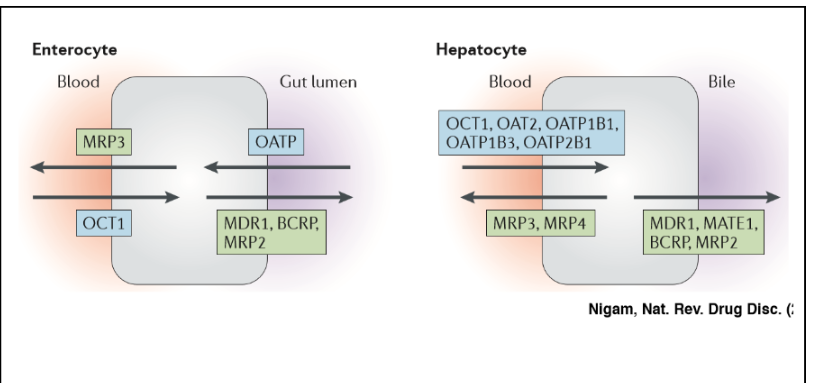
Solute carrier proteins (SLCs) \n
import molecules into cells
→Organic Cation Transporter (OCT)
→Organic Anion Transport Protein (OATP)
→Organic Cation Transporter (OCT)
→Organic Anion Transport Protein (OATP)
25
New cards
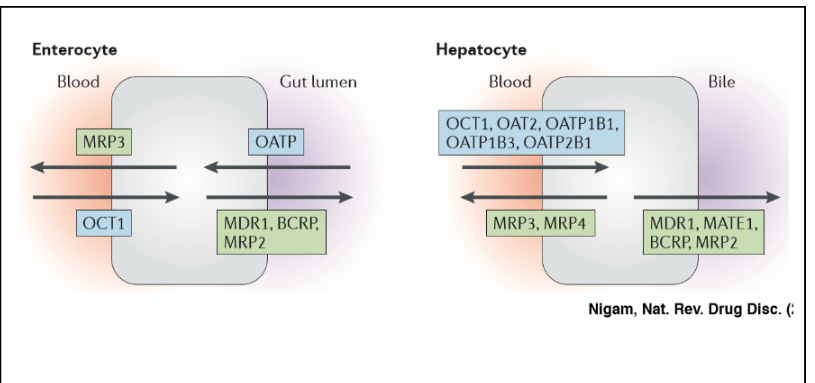
ATP-Binding cassette proteins (ABCs)
export molecules out
26
New cards
Drug that are both extensively metabolized and are substrates for ABC/MDR/MRP efflux pumps have _____bioavailability
poor
27
New cards
BCS Group I
general good oral activiity
→High solubility
→High permeability
→High solubility
→High permeability
28
New cards
BCS Group II
Solubility is rate limiting step for absorption
→Low solubility
→High permeability
→Low solubility
→High permeability
29
New cards
BCS Group III
permeability is rate limiting
→High solubility
→Low permeability
→High solubility
→Low permeability
30
New cards
BCS Group IV
Usually low oral biavailablility . Often substrates for Pglycoprotein
→Low solubility
→Low permeability
→Low solubility
→Low permeability
31
New cards
Pka considerations for bioavailability
•CNS bioavailability requires neutral species for passive diffusion in addition to low MW
•You want pka fraction as close ot neutral as possible
•Acids absorbed in stomach, bases absorbed in small intestine
•You want pka fraction as close ot neutral as possible
•Acids absorbed in stomach, bases absorbed in small intestine