ANSC 2202 - Distal GI Tract
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Liver (and its functions)
Largest gland in the body
Accessory organ
Functions:
Clears out drugs and toxins
Formation of bile (for breakdown of fats)
How does the liver vary in size across species?
Carnivore: 3-5% of body weight
Omnivores: 2-3%
Herbivores: 1-1.5%
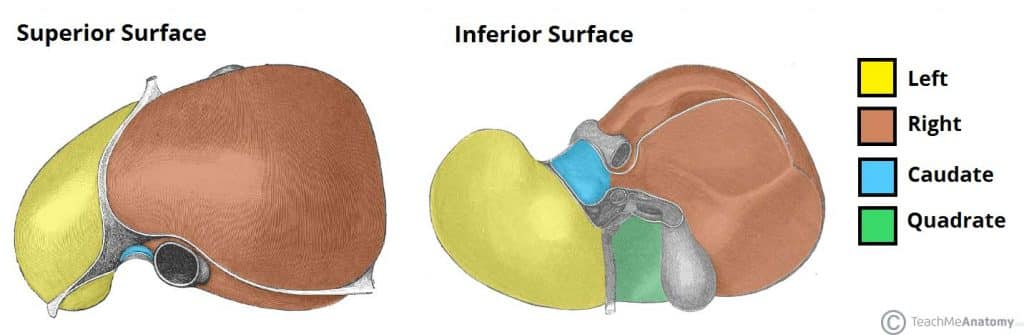
4 Lobes of the Liver
Left
Right
Quadrate
Caudate
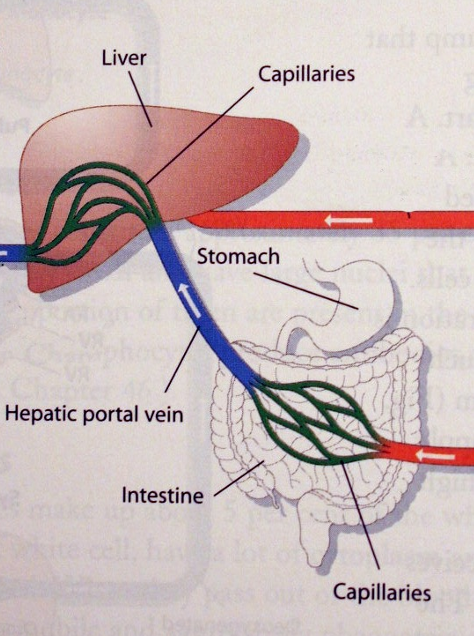
What do capillaries in the liver and intestines do?
Absorb nutrients from digestion
Liver: the Porta
Where blood vessels and nerves enter the liver
Portal vein
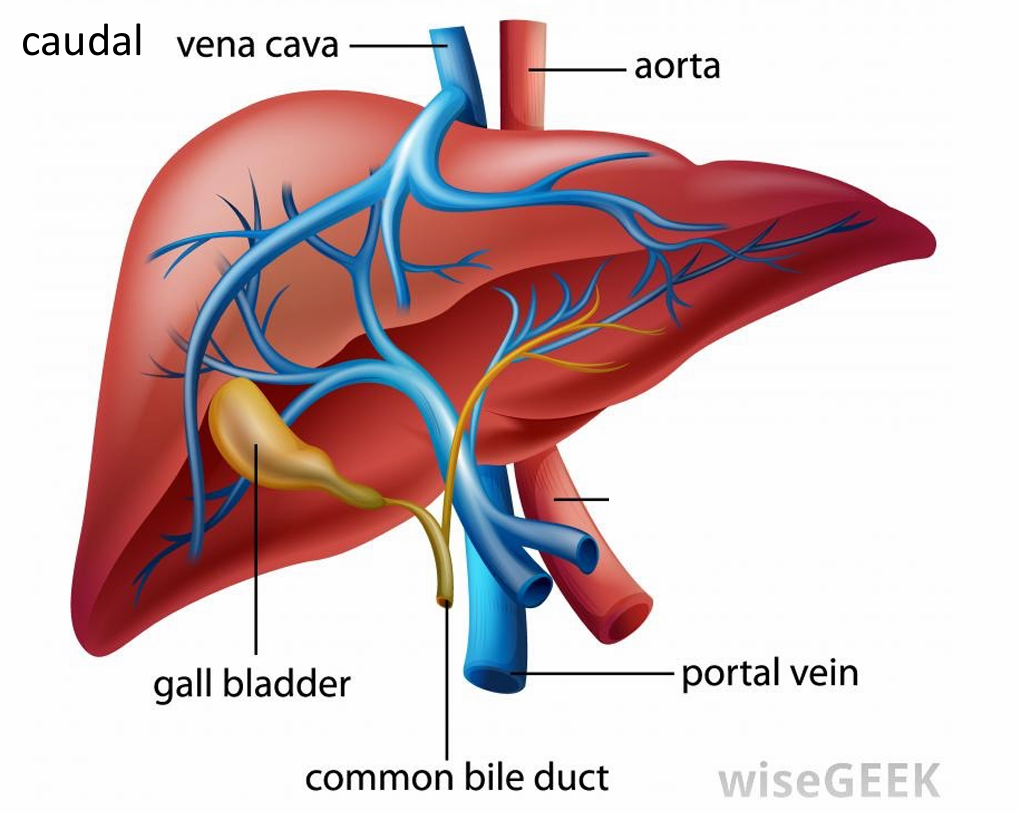
Gallbladder
Stores bile
Common bile duct: liver to duodenum
HORSES & RABBITS DO NOT HAVE A GALLBLADER
Small Intestine parts
3 Parts:
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
How does the small intestine vary in size across species?
Horses: 80+ feet
Dogs: 3-4x body length
Sheep & Goats: 25x body length
Dueodenum
Relatively short
Receives ingesta (food) from the pylorus
Anchored to the body
Adjacent to the pancreas
Sigmoid loop
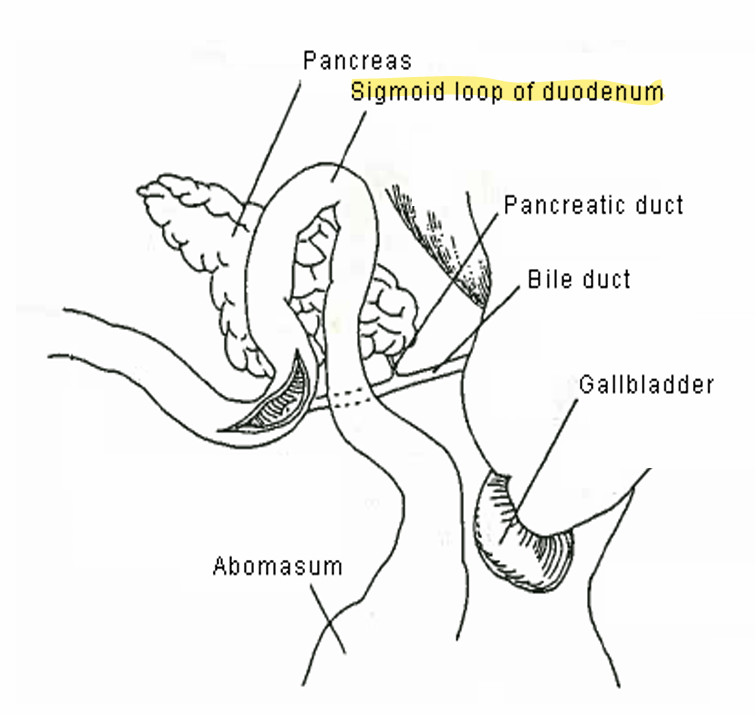
Pancreas
Exocrine:
Secretes through duct
Produces enzymes that aid in digestion
specifically of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
The insides/lining of our organs are considered external surfaces, so endocrine secretes onto them.
Endocrine:
Secretes into blood
Secretes hormones
insulin, glucagon, and gastrin
Jejunum
Longest part of the small intestine
Great range of motion
Jejunal Arcades
Blood vessels attached to the jejunum
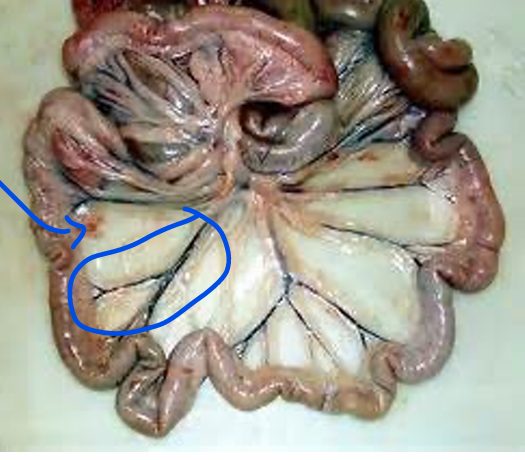
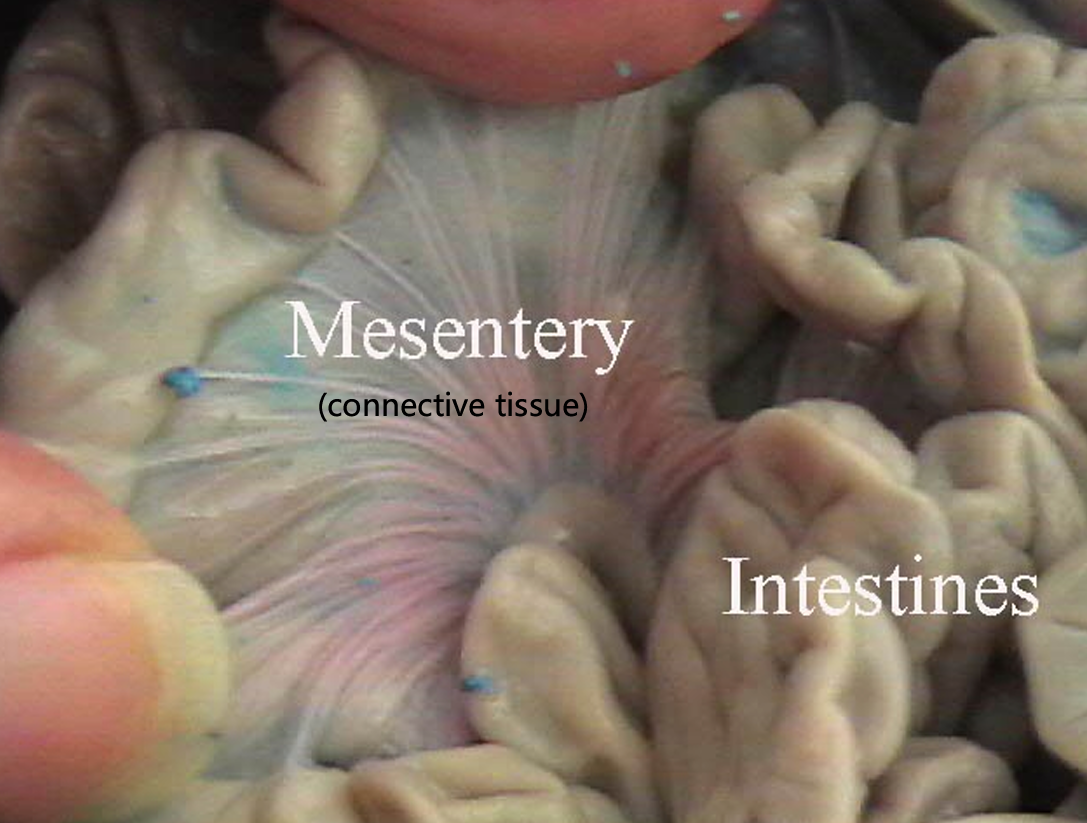
Mesentery
Attaches jejunum to the body wall
Connective tissue
Carries blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to the digestive organs
Ileum
Short
Empties into the cecum
Ileocecal fold
Connection between ileum and cecum
Large Intestine
Absorbs water
What does the large intestine do in horses?
Fermentation
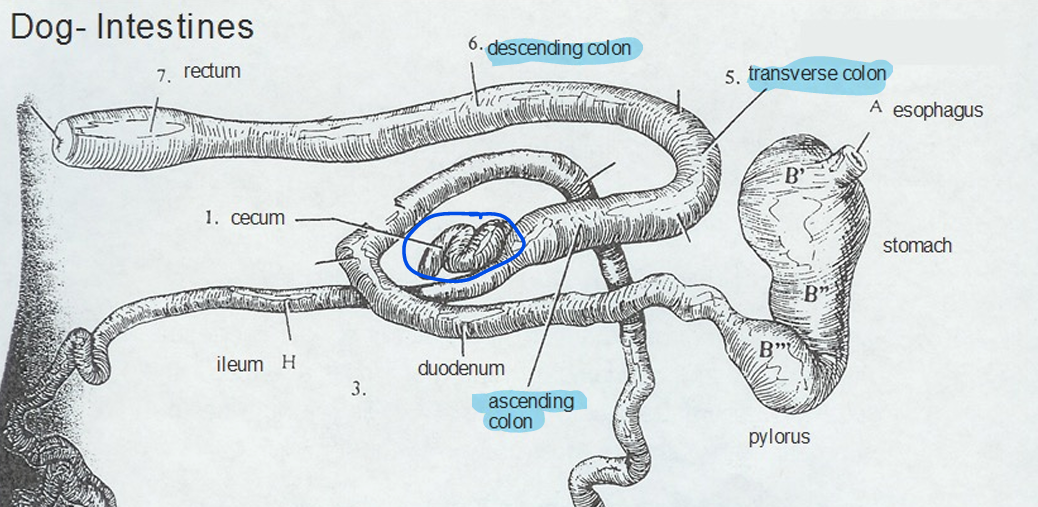
Parts of the Large Intestine
Cecum
Colon
Rectum
How does the large intestine vary in size across species?
Carnivores: relatively small
Herbivores: large and complex
All animals, to some capacity, can break down fiber in the large intestine
Ruminants are ____ fermenters
Foregut (Rumen)
Horses are ____ fermenters
Hindgut (cecum and colon)
Cecum
Latin: blind
Pouch that does not connect to anything at the end
At the junction of the ileum and the colon
Functions:
Water absorption
Fermentation
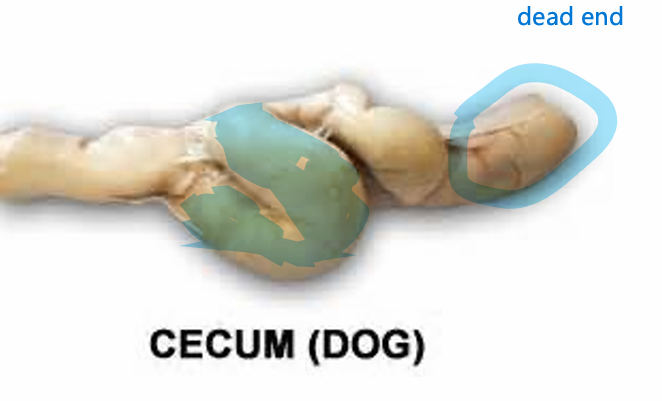
Cecum species variation
Dogs: S-shaped
Ruminants and pigs: relatively small
Horses: comma shaped, 3 ft long
Colon (3 parts)
Ascending (beginning part)
Spiral colon (ruminants and pigs)
Horses = large colon
Transverse (between ascending and descending)
Hard to identify in our species
Descending (ending part)
Longest part
Horses = small colon
Note that the ascending, transverse, and descending names are typically used for humans and arent very meaningful for the direction in animals.
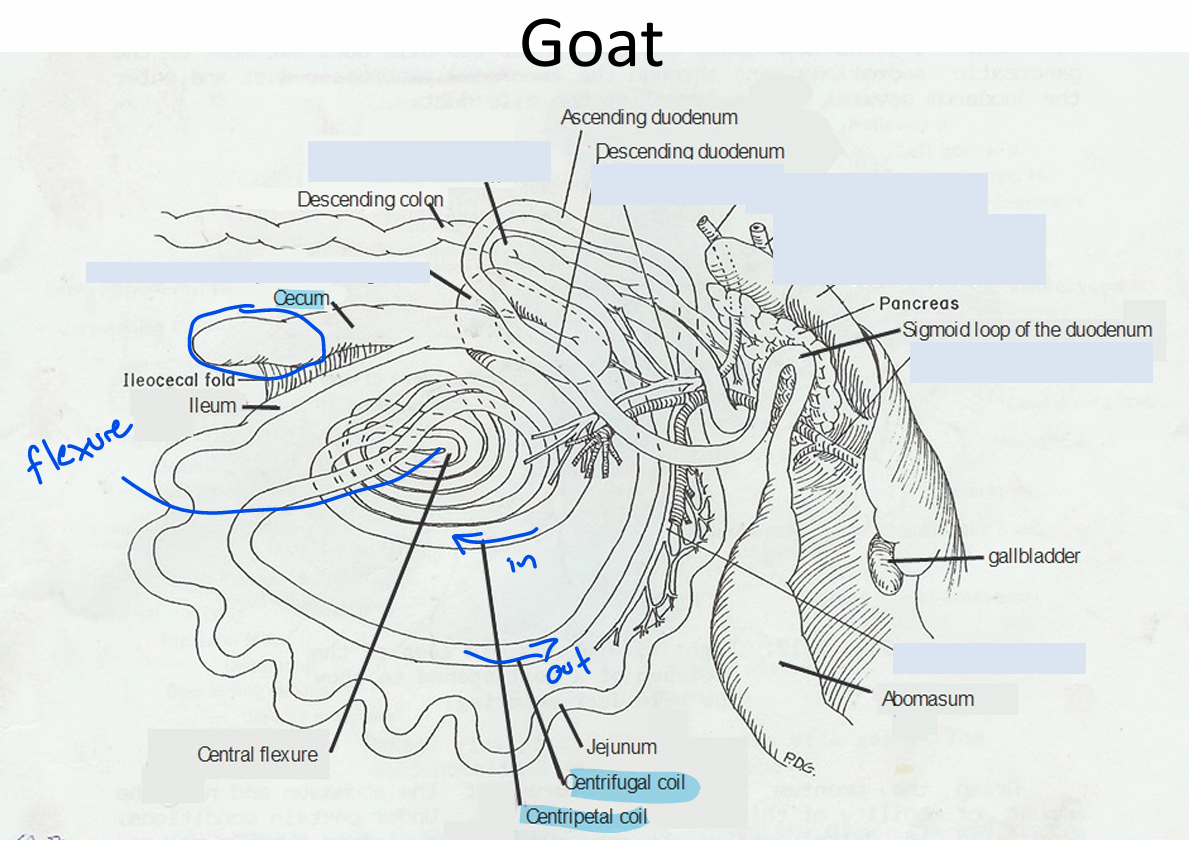
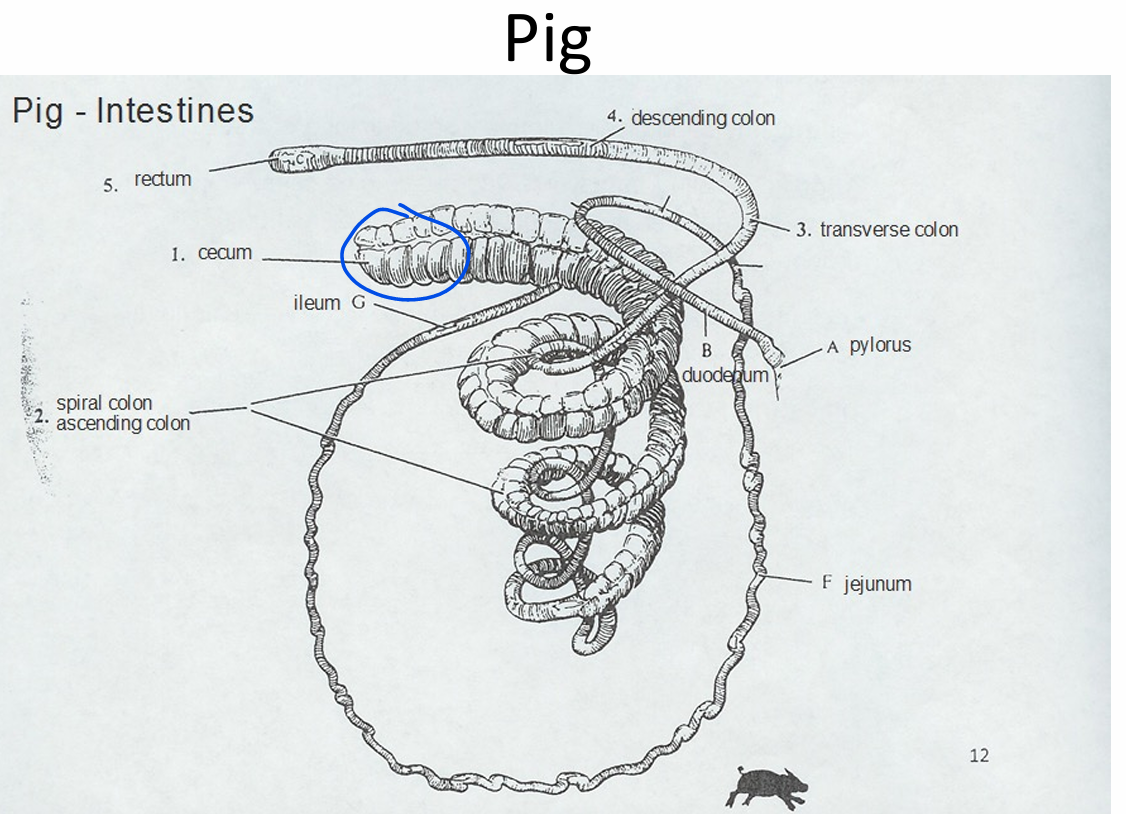
Spiral Colon
Ruminants and Pigs
3 Parts:
Centripetal coils: inwards
Central flexure: where coil folds upon itself
Centrifugal coils: outwards
(Centrifugal spins things in a circle and throws them to the outside!)
Pig: Spiral Colon
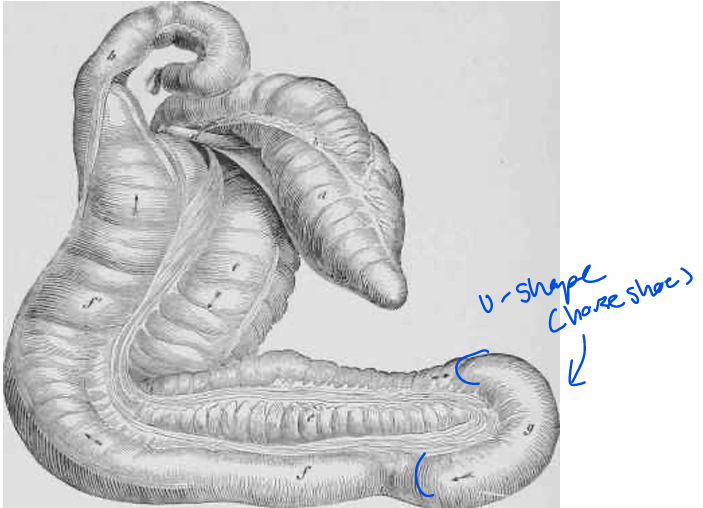
Equine Colon: Large Colon
Ascending is called the “large colon”
10-12 ft long, double horseshoe (two u-shapes)
Can hold over 20 gallons
Functions in fermentation
1010 (10^10) bacteria per mililiter
Only attached to the body wall in one place
This leads to a lot of issues
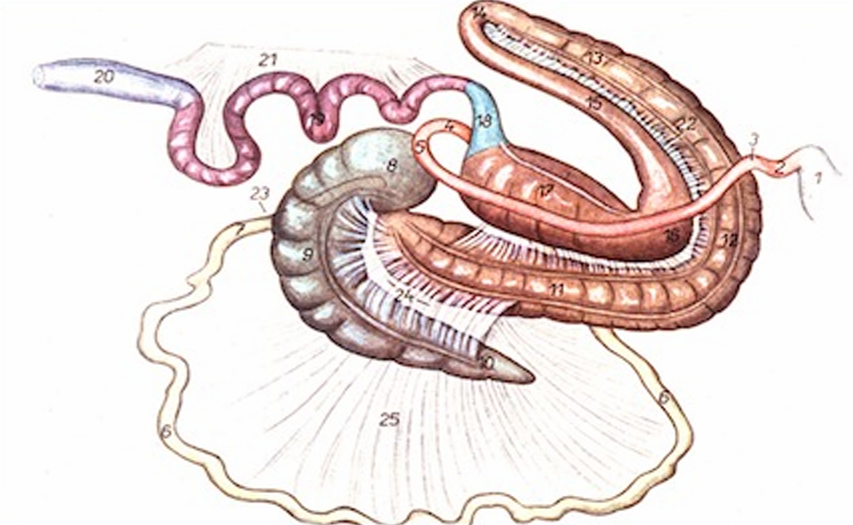
Equine Colon: Small Colon
Descending colon is called the “small colon”
About 11.5 ft long
Where fecal balls are formed
Rectum
From descending colon to anus
Within pelvic cavity
Dorsal to reproductive organs
Shortest part of entire GI
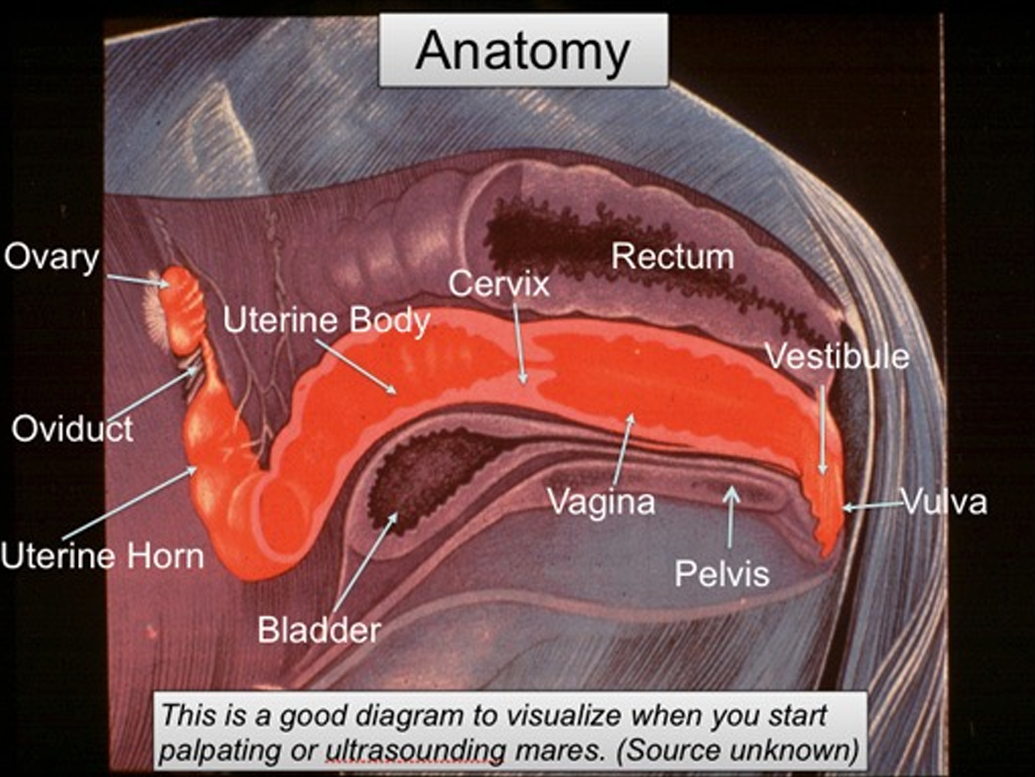
Anus
Caudal most opening of the gastrointestinal tract
Anal sacs/glands
In dogs and cats
Secretes an “evil-smelling” fluid
Probably territorial marker
Can become impacted or inflamed
Typically in dogs—causes them to scoot around
Colic
In horses, abdominal pain
Has many, many causes in both small and large intestine
Torsion
Entrapment
Tumors
Inflammation
Gas distention
Treatment involves rehydration (difficult), pain medication, or surgery
Terms
