19: Whole Body Radiation Effects
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Whole body radiation effects are typically seen in what situations?
atomic bomb or nuclear accident survivors
two types of whole body radiation effects?
somatic
genetic
term. Somatic (effects)
def. effects that occur during a person’s lifetime
term. Genetic (effects)
def. effects on future generations
give example of genetic effects
If someone’s gonads get irradiated, and then they have a spontaneous abortion, or a baby with genetic defects
Whole body radiation effects, can be _____ effects or_____ effects
stochastic
non-stochastic
term. stochastic effects
def. effects that have no threshold dose
FYI: they are binary. Either you get them or you don’t
Typical Stochastic effects
carcinogenesis
genetic mutations
term. Non-stochastic effects
def. somatic effects that increase in severity with an increase in dose
(↑ dose = ↑ severity)
Examples of non-stochastic effects
Most effects:
erythema
epilation
dry mouth
etc
def. the average time between exposure and death
term. mean survival time
E,g, There are 2 people exposed to nuclear radiation. The first person dies within 10 days of being exposed. And the second person dies within 20 days of being exposed. What is the mean survival time?
(20+10)/ 2 = 15
True or False: Whole Body Effects of radiation can be either acute or chronic
True
term. acute
def. short time period; within a few weeks of the exposure or less
term. LD 50/30
def. the lethal dose to 50% of the population within 30 days
LD 50/30 aka
LD 50
Dose for LD 50/30 (for whole body)
400cGy
FYI: avg. 300-500 for whole body
minimum observed whole body dose for death
100cGy
maximum observed whole body dose ever survived
850cGy
3 Acute Radiation Syndromes (whole body) aka
Manifest Syndrome
What are the 3 acute radiation syndromes (aka manifest syndromes)
Hematologic
GI
CNS
affecting 3 of the 10 body systems
term. Syndrome
def. A series of symptoms
In addition to the Manifest Syndromes, what are 2 other stages related to these syndromes that typically occur with each person that has received a large whole body dose exposure
Prodromal Syndrome
Latent Period
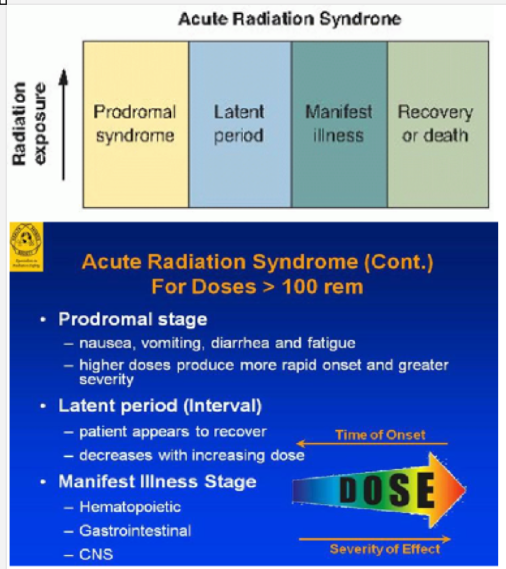
term. Prodromal Syndrome
def. the immediate radiation sickness following a large whole body exposure.
Prodromal Syndrome happens in doses in excess of _____cGy
50
Prodromal Syndrome examples
hair loss
NV
Diarrhea
Skin Reddening
Low Blood Counts (fatigue)
term. Latent Period
def. the period FOLLOWING the prodromal syndrome during which there is NO sign of sickness
The length of the prodromal & latent periods exhibit a (direct/ inverse) relationship with dose
inverse
↓ Dose = ↑ length Prodromal/Latent Periods
What are the dose ranges for the 3 Manifest Sydromes
Hematologic Syndrome……..……100-1000cGy
GI Syndrome……………………….1000-5000cGy
CNS Syndrome……………………..>5000cGy
Which of the Manifest Syndromes, is the one that is potentially curable and why?
Hematologic, cuz the avg. whole body lethal dose is 400cGy and the highest survived dose was 850cGy, and hematologic dose range is 100-1000cGY
Description of Hematologic Syndrome
the Prodromal & Latent periods can each last for weeks
Description of GI Syndrome
Shorter Prodromal & Latent periods; usually just a few days long each
Description of CNS Syndrome
short prodromal & latent period IF AT THERE EVEN IS ONE
Cause of death for the following Syndromes
Hematologic: massive infection (WBC)
GI: fluid and electrolyte loss (NV & Diarrhea)
CNS: Patients die within a FEW HOURS due to intercranial pressure ( confusion, convulsion, NV, vision loss