3.3.11 Amines
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the -NH2 group known as?
The amino group
What is an aryl group?
Benzene ring (C6H5)
What are the rules for naming amines?
Find the longest carbon chain attached to the N. Other groups must have N-alkyl to show they are attached to the N, not the other carbon chain.
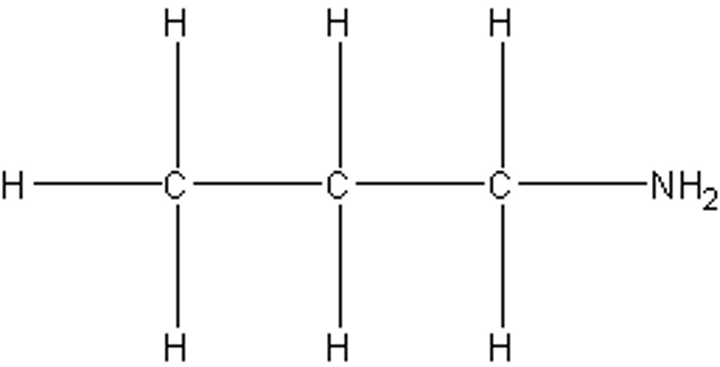
Draw propylamine.
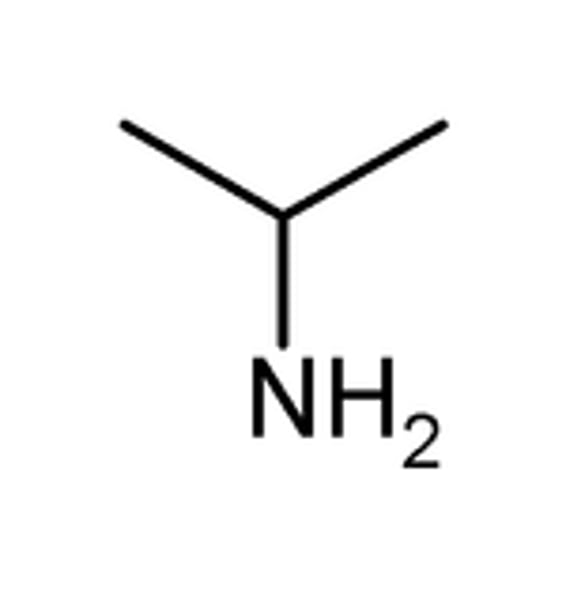
Draw 2-aminopropane.
The amino form of NH2 is written instead of amine, because the position of the NH2 on the carbon chain must be shown.
Draw dimethylamine.
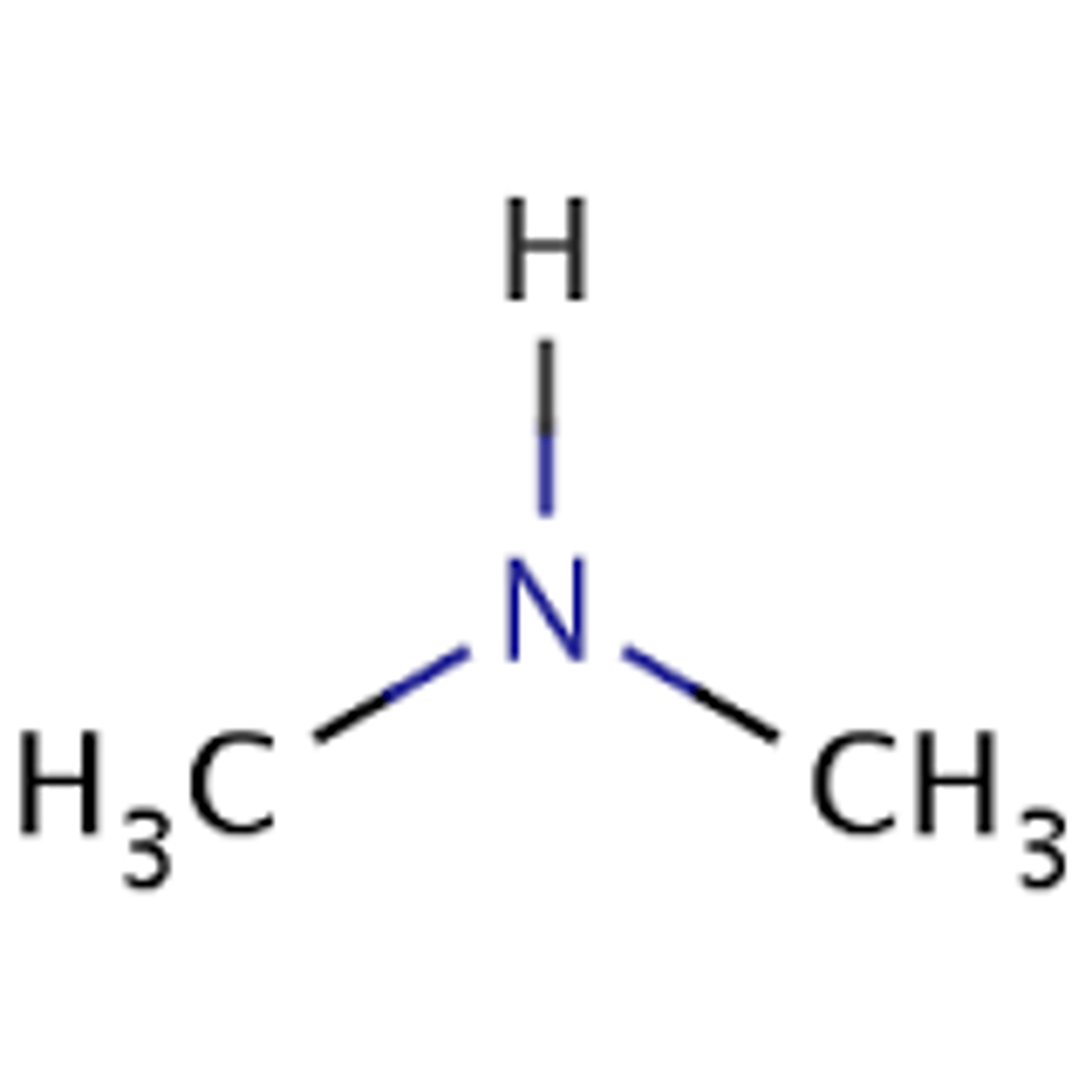
Draw N-methylpropylamine.
Explain why it is named this way.
The longest alkyl chain has three carbons (propyl).
The secondary amine also has a methyl group. It is attached to the nitrogen (not to the propyl), so an N- is used to show this.
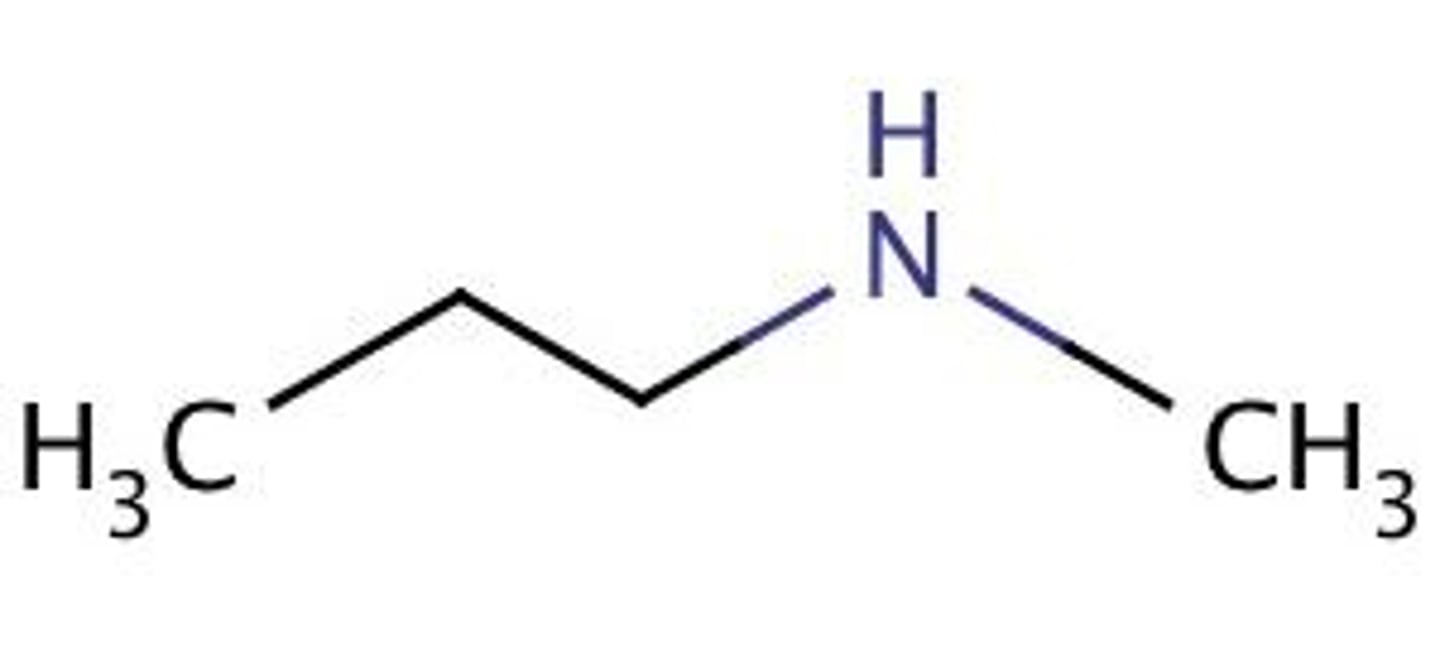
Draw N,N-diethylpropylamine.
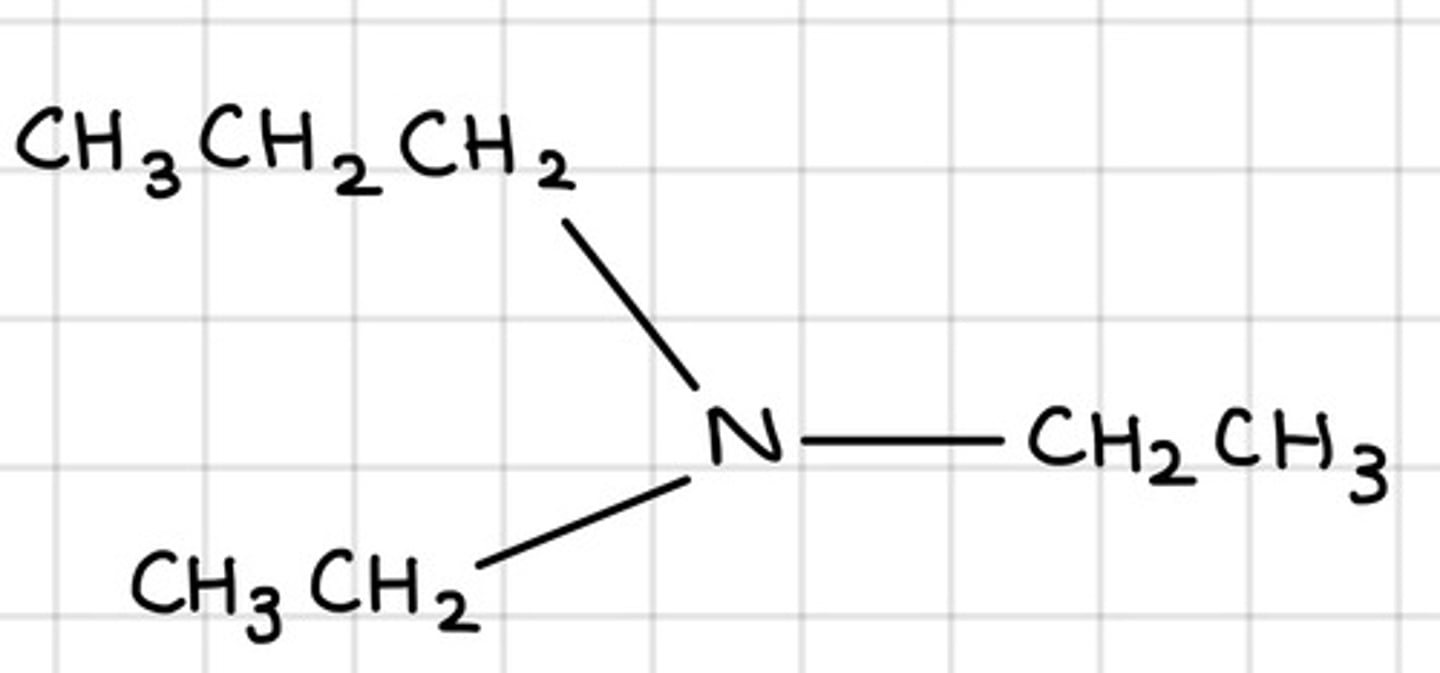
Draw N-ethyl-N-methylpropylamine.
Central N with methyl, ethyl and propyl groups attached.
What is the functional group hierarchy?
Carboxyl, aldehyde, ketone, hydroxyl, amine, alkene.
What are the IUPAC rules for naming substituents?
Use the lowest numbers possible for the substituents.
Name in alphabetical order (bromo, chloro, ethyl, fluoro, iodo, methyl, phenyl, propyl, nitro).
Explain two ways that a primary amine can be prepared, stating the mechanisms and conditions.
The reaction of ammonia with a halogenoalkane requires heat in a sealed flask with excess ammonia in ethanol. Nucleophilic substitution.
The reduction of nitriles, either by using hydrogen gas in the presence of a nickel catalyst, or using LiAlH4 as a reducing agent.
Explain how aromatic amines are formed.
By the reduction of nitro compounds.
Nitrobenzene can be reduced by heating under reflux with tin and excess concentrated hydrochloric acid as a reducing agent.
Since excess acid is used, the phenylammonium ion forms (C6H5NH3+).
The addition of concentrated sodium hydroxide removes the hydrogen ion to form the amine group and water.
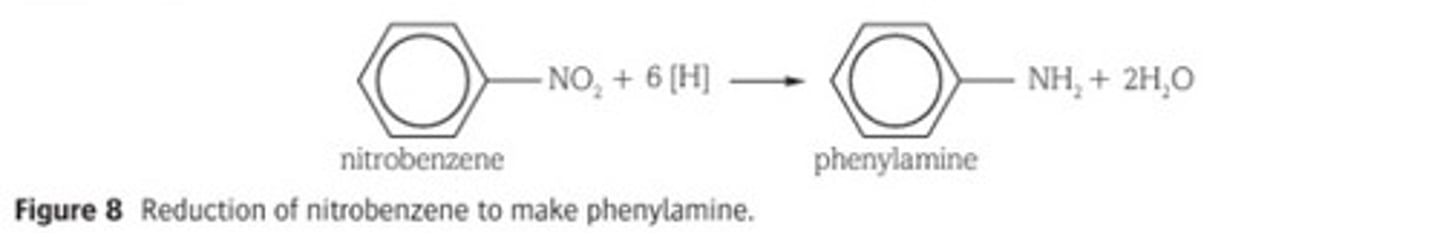
Describe a use of aromatic amines.
Aromatic amines, prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds, are used in the manufacture of dyes. These dyes include the food and textile industries.
Amines are weak bases. Define a base.
Proton acceptor
Explain why primary aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
The alkyl group attached to the nitrogen is electron donating. It releases electrons, so there is slightly more electron density on the N, making the lone pair more available so can accept a proton more easily.
Explain the trend in basicity of an amine when:
The chain length of the alkyl group increases,
The number of alkyl groups on the N increases.
An increase in chain length increases basicity due to a greater inductive effect.
Same reasoning for primary amines < secondary amines < tertiary amines.
Explain why primary aromatic amines are weaker bases than ammonia.
The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen can overlap with the delocalised pi electrons in the benzene ring. The lone pair is delocalised into the pi system, decreasing the electron density on N and the lone pair is less available for accepting a proton.
Amines are nucleophiles or electrophiles?
Nucleophiles, because they are an electron pair donor.
Draw the nucleophilic substitution for the reaction of excess ammonia and 1-bromoethane.
Suggest the effect of excess ammonia or excess haloalkane.
Excess ammonia favours the production of primary amines, as it is less likely that another haloalkane will react with the same amine due to a large number of ammonia to react with.
Excess haloalkane favours the production of quaternary ammonium salts, as each ammonia will react with four halogenoalkane molecules.
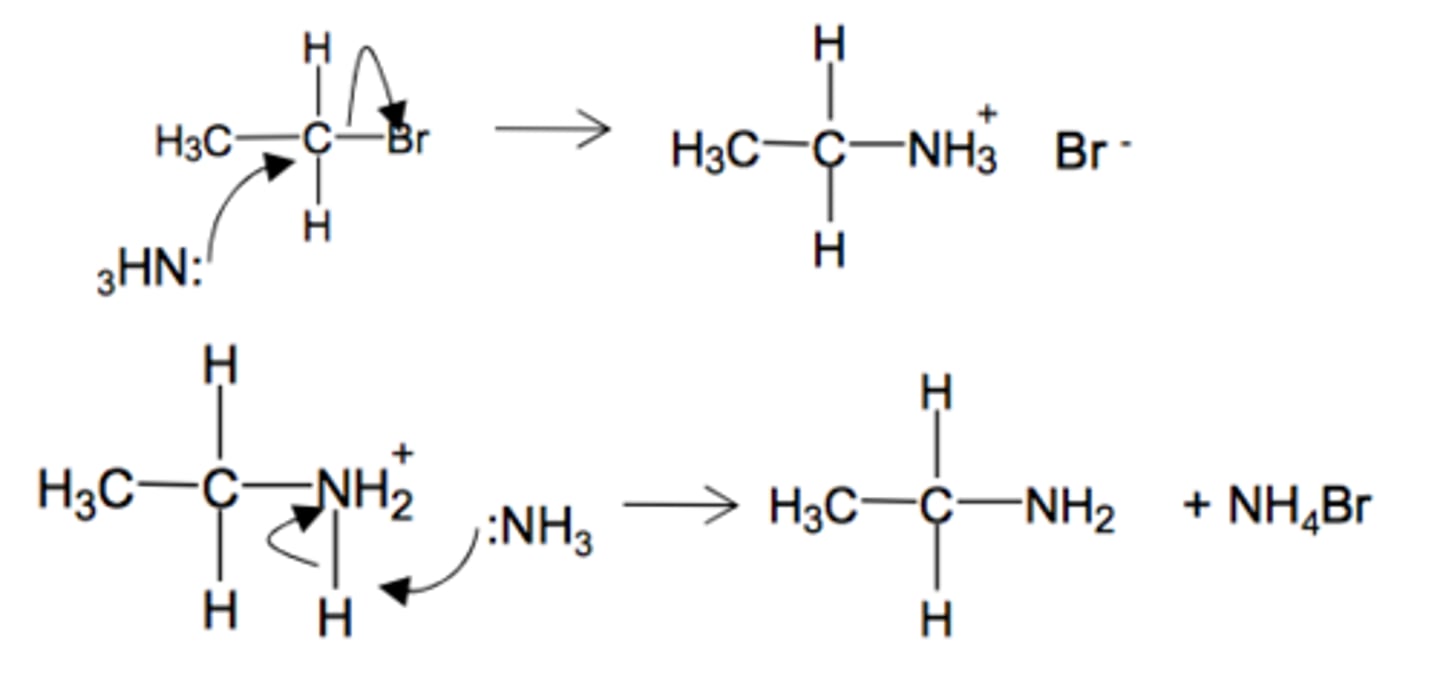
Explain why primary amines are not usually produced by the reaction of ammonia and a halogenoalkane.
It leads to a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary amines as well as quaternary ammonium salts.
Describe the uses of quaternary ammonium salts.
Used in the production of cationic surfactants (that are found in detergents, fabric softener, hair conditioners).
They coat the surface of the cloth with positive charges and reduce the static from negatively charged electrons.
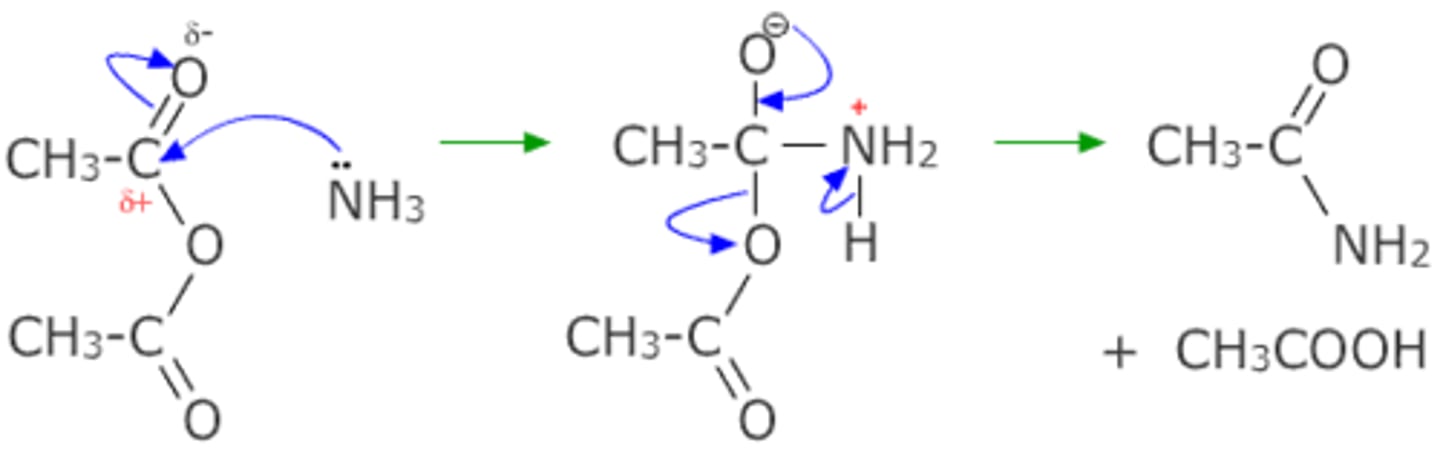
Draw the nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction of ammonia and ethanoic anhydride.
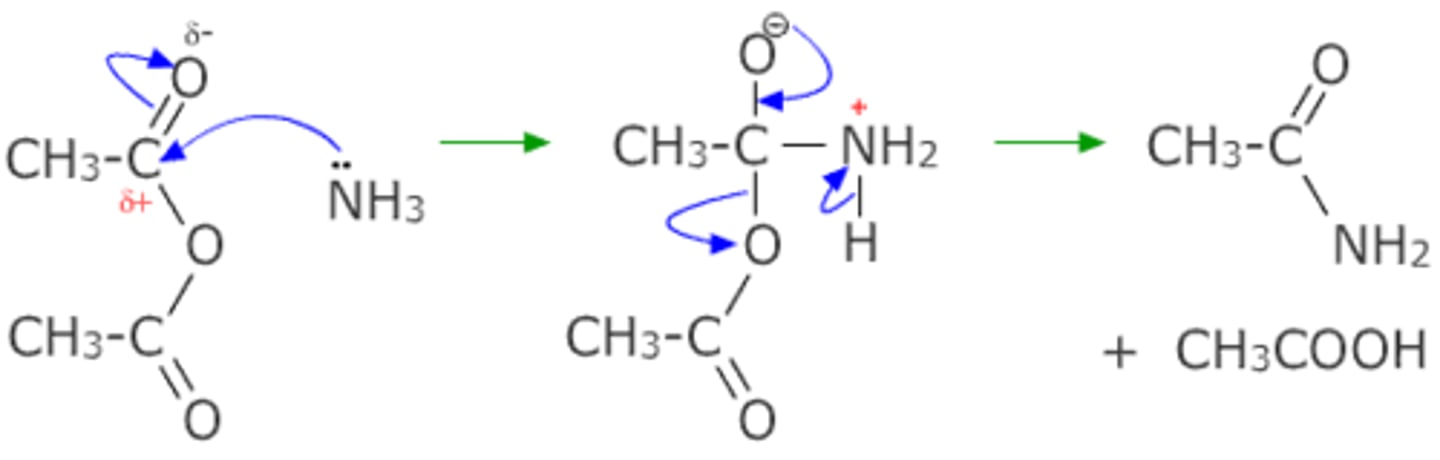
Draw the nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction of methylamine and ethanoic anhydride.
NH3 replaced by CH3NH2