DNA cell test
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
Phases of Mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
2
New cards
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
3
New cards
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes and Nucleolus disappears.
4
New cards
Metaphase
chromosomes line up along metaphase plate
5
New cards
Anaphase
Chromosomes break at centrosomes and sister chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell
6
New cards
Telophase and Cytokinesis
Nuclear membrane reforms and nucleoli reappear and chromosomes unwind into chromatin.
7
New cards
What cells do not preform mitosis
Sex Cells
8
New cards
Which cell splits from the inside
Plant cell
9
New cards
telophase under microscope
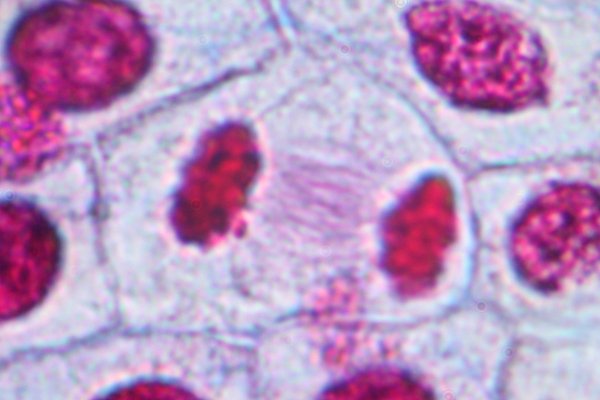
10
New cards
Which cell forms a cleavage and splits from the outside
Animal cell
11
New cards
anaphase under microscope
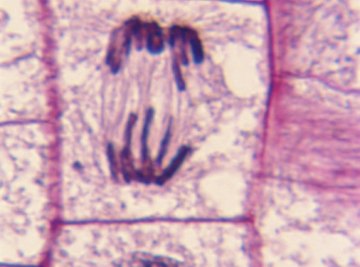
12
New cards
metaphase under microscope
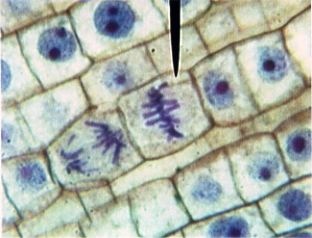
13
New cards
prophase under microscope
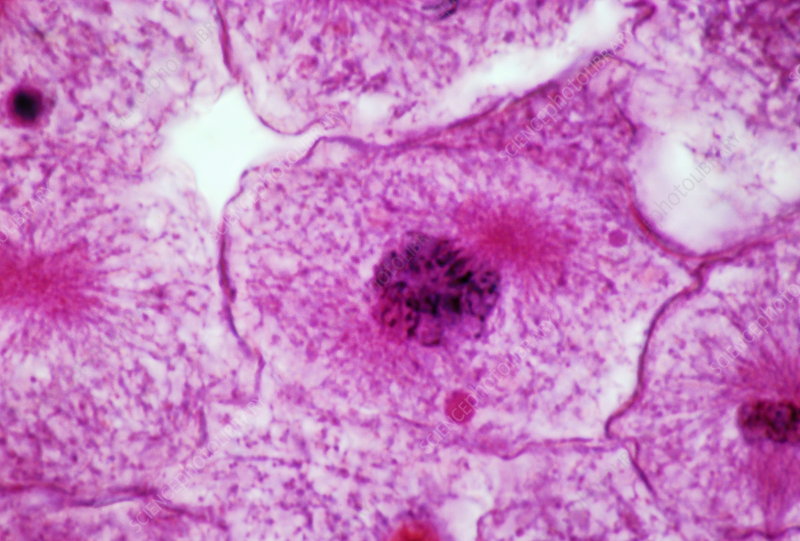
14
New cards
Base parring
(A-T C-G) This guarantees that a copied strand of DNA always end up being the same as the original.
15
New cards
DNA structure
* 2 deoxyribose (sugar) backbone strands
* Bases held together by \n hydrogen bonds
* DNA shape is a double helix
* Bases held together by \n hydrogen bonds
* DNA shape is a double helix
16
New cards
How is DNA fit in a Chromosome
DNA wraps around a Histone to from a Nucleosome
Nucleosomes come together to form Chromatine
Chromatine then from loops
The Chromatine loops condense to form a Chromosome
Nucleosomes come together to form Chromatine
Chromatine then from loops
The Chromatine loops condense to form a Chromosome
17
New cards
Helicase
* “Unzips” or unwinds the DNA double helix.
* Binds at the location called the replication fork
* Exposes the leading strand to the next enzyme
* Separates bases from each other
* Binds at the location called the replication fork
* Exposes the leading strand to the next enzyme
* Separates bases from each other
18
New cards
DNA Polymerase
* Synthesizes free nucleotides onto the template DNA
* Matches the right nucleotide with the exposed bases
* Creates the complementary strand
* Matches the right nucleotide with the exposed bases
* Creates the complementary strand
19
New cards
DNA Ligase
* An enzyme that puts things together
* Glues together Okazaki fragments after matching
* Glues together Okazaki fragments after matching
20
New cards
Primase
* Enzyme that makes a primer
* The primer is the starting point for polymerase on the lagging strand
* The primer is the starting point for polymerase on the lagging strand
21
New cards
Leading strand
* replicated (copied) in 3’-5’ direction
* copied straight off, no fragments made.
* copied straight off, no fragments made.
22
New cards
Lagging strand
* replicated in 5’-3’ direction
* replicated in small pieces, known as Okazaki fragments, starting at a primer
* The polymerase has to jump back and make a small section
* Ligase glues the Okazaki fragments together
* replicated in small pieces, known as Okazaki fragments, starting at a primer
* The polymerase has to jump back and make a small section
* Ligase glues the Okazaki fragments together
23
New cards
Prophase I
* The DNA is already replicated forming two pairs of chromosomes
* The homologous sister chromatids pair up 2 and 2
* Chromosomes form tetrad
* Sometimes parts of the chromosomes are exchanged between the maternal and paternal chromosomes: crossing over or recombination
* In meiosis
* The homologous sister chromatids pair up 2 and 2
* Chromosomes form tetrad
* Sometimes parts of the chromosomes are exchanged between the maternal and paternal chromosomes: crossing over or recombination
* In meiosis
24
New cards
tetrad
two homologous chromosomes that have each already replicated into a pair of sister chromatids
25
New cards
Metaphase I
The chromosomes are moved to the metaphase plate (the middle) they line up randomly
* In meiosis
* In meiosis
26
New cards
Anaphase I
* The paired homologous chromosomes start to separate from each other
* The whole sister chromatid is being moved to either pole
* Pulled apart by the mitotic spindle
* In meiosis
* The whole sister chromatid is being moved to either pole
* Pulled apart by the mitotic spindle
* In meiosis
27
New cards
Telophase I
* Cell starts cytokinesis, dividing the cells completely
* The cells are now haploid
* In meiosis
* The cells are now haploid
* In meiosis
28
New cards
Haploid
having a single set of __unpaired__ __chromosomes__.
29
New cards
Diploid
containing two complete sets of __chromosomes__, one from each parent
30
New cards
Prophase II
* Very short phase
* Centrioles start migrating
* Nucleolus dissolves
* Mitotic spindle forms
* In meiosis
* Centrioles start migrating
* Nucleolus dissolves
* Mitotic spindle forms
* In meiosis
31
New cards
Metaphase II
* Sister chromatids line up at metaphase plate
* In a line this time
* Spindle fibers attach to the centromere (middle of chromatid)
* In meiosis
* In a line this time
* Spindle fibers attach to the centromere (middle of chromatid)
* In meiosis
32
New cards
Anaphase II
* Sister chromatids are being pulled to opposite sides of the cell
* Sister chromatids break down the middle
* Chromatids become separate chromosomes
* In meiosis
* Sister chromatids break down the middle
* Chromatids become separate chromosomes
* In meiosis
33
New cards
Telophase II
* The chromosomes have completely moved to their cells
* Membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
* The cells bud off to become individual haploid cells
* In meiosis
* Membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
* The cells bud off to become individual haploid cells
* In meiosis
34
New cards
cytokinesis
bringing about the separation into two daughter cells