part 9: LIQUIDS
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Mercury
Bromine
Periodic table elements that are liquid in room temperature
Possess less kinetic energy than gases
Occupy a definite volume
Takes the shape of the container that holds it
Are considered more denser and less compressible than gases
Characteristics of Liquids
Noyes Whitney Equation
Equation used to determine Rate of Dissolution
Dissolution
The process where a solute in gaseous, liquid, or solid phase dissolves in a solvent to form a solution
Solubility
The measure of ability of a solute to get dissolved in a solvent
moles/L.soln
g/L, g/mL
Units of solubility: ______________ or ________________
Pharmacopeial Expression of Solubility
It is the number of milliliters of solvent in which 1 gram of solute will dissolve to make a saturated solution
Very soluble
< 1 part
Freely soluble
1 to 10 parts
Soluble
10 to 30 parts
Sparingly soluble
30 to 100 parts
Slightly soluble
30 to 100 parts
Very slightly soluble
1000 to 10,000 parts
Practically insoluble
> 10,000 parts
Nature of solute and solvent
Particle size
Particle size
Pressure
Presence of Salts (mostly for proteins)
pH
Factors affecting Solubility
Like dissolves like
The greater the similarity between the solute and the solvent the greater the solubility
Low particle size = High Surface area = High Solubility
In particle size:
Low particle size = ____ Surface area = ____ Solubility
Endothermic: High Temperature = High Solubility
In temperature of Solid and Liquid:
Endothermic: ____ Temperature = ____ Solubility
Exothermic: Low Temperature = High Solubility
In temperature of Solid and Liquid:
Exothermic: ____ Temperature = ____ Solubility
Low Temperature = High Solubility
In temperature of Gas:
Low Temperature = ____ Solubility
negligible
Solids and Liquids: The effects of pressure changes on the solubility of solids and liquids are __________
Pressure
Most important factor influencing solubility of a gas in a liquid (Henry’s Law)
High Pressure = High Solubility
In Gas, High Pressure = ____ Solubility
High Solubility
Salting in: + salt = __ Solubility
Low Solubility
Salting out: + salt= __ Solubility
Weak acids or bases
Many drugs are _____ acids or bases
Aqueous solution
The ionized form of a compound will be most soluble in an ____________________
Acidic
WB + __________ aqueous solution = ionized form
Basic
WA + __________ aqueous solution= ionized form
Equilibrium Vapor Pressure (VP)
The pressure of the saturated vapor above the liquid
Equilibrium
Evaporation rate = Condensation rate
mmHg
Unit of Vapor Pressure
23.8 mmHg
Vapor Pressure of Water at 25°C
355.1 mmHg
Vapor Pressure of Water at 80°C
4.61 mmHg
Vapor Pressure of Water at 0°C
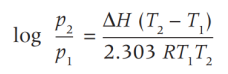
Clausius Clapeyron Equation
Cohesion
Attraction between similar molecules
Adhesion
Attraction between unlike molecules
Interfaces
Boundaries of solids, liquids and gases with other solids, liquids or gases
Surface
Used when referring to either a gas-solid or gas-liquid interface
Surface Tension
The “tension” in the surface
Force per unit length that must be applied parallel to the surface so as to counterbalance the net inward pull
Liquid-Gas or Solid-Gas
SI: N/m
CGS: dyne/cm
Unit of Surface Tension
Interfacial Tension
Force per unit length existing at the interface between two immiscible phases
Liquid-Liquid
Solid-Solid
Liquid-Solid
N/m (SI) or dyne/cm (CGS)
Unit of Interfacial Tension
Capillary Rise Method
Dropweight method
Du Nouy Ring method
Methods of Surface Tension and Interfacial Tension Determination
Capillary Rise Method
Oldest method for surface tension determination
Most accurate method (the surface is undisturbed during the measurement)
Not suitable for interfacial tension measurement
Higher rise = Lower surface tension= concave meniscus
Adhesion > Cohesion =
Lower rise = Higher surface tension = convex meniscus
Cohesion > Adhesion =
Stalagmometric method
Dropweight method is also known as?
Stalagmometer
Instrument used in Dropweight method
Tensiometer
Instrument used in Du Nouy Ring method
Platimum or Iridium ring
Du Nouy Ring method uses what?
Du Nouy Ring method
Measures both surface and interfacial tension
Surfactants or Amphiphiles
Surface Active Agent is also known as?
Surface Active Agent
Molecules or ions that causes reduction of surface and interfacial tension
Griffin Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance System
Number system to establish an HLB range of optimum efficiency for each class of surfactant
Polarity
Each agent is assigned an HLB value or number indicating the substance’s _____________
1-40 (1-20 usual range)
Range of Griffin Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance System
Hydrophilic
Higher HLB = ____________
Lipophilic
Low HLB= ____________
1-3
Antifoaming
3-6
w/o emulsifiers
7-9
Wetting agents
8-18
o/w emulsifiers
13-16
Detergents
Solubilizers
15-20
Absorption
The liquid or gas being absorbed penetrates into the capillary spaces of the absorbing medium
Example: Sponge and Water
Adsorption
Adsorption is the process in which materials of one phase (Adsorbate) accumulate or concentrate at the interfacial surface of the other phase (Adsorbent)
Attraction on the surface
Example: Activated Charcoal
Positive adsorption
Negative adsorption
Physical adsorption
Chemical adsorption
Types of Adsorption
Positive adsorption
When the molecules or ions are partitioned in favor of the SURFACE or INTERFACE
Negative adsorption
Some molecules or ions are partitioned in favor of the BULK of liquid
Physiosorption
Physical adsorption is also known as?
Physical adsorption
The force of attraction between adsorbate and adsorbent is weak (Van Der Waals)
Reversible (by increasing Temperature or reducing Pressure)
Desorption
The process by which a physically adsorbed gas is removed
Chemisorption
Chemical adsorption is also known as?
Chemical adsorption
The force of attraction between adsorbate and adsorbent is chemical bonds
Irreversible
Solid-Gas Adsorption
Solid-Liquid Adsorption
Adsorption at Solid Interfaces
Removal of objectionable odors (from rooms and food)
Operation of gas masks
Measurement of the dimensions of particles in a powder
Solid-Gas Adsorption
Decolorizing solutions
Adsorption chromatography
Detergency
Wetting
Solid-Liquid Adsorption
Wetting
Detergency
Adsorption at solid surfaces is involved in the phenomena of __________ and __________
Wetting
An adsorption process in which an intimate contact of the solids with liquid phase is achieved
Low contact angle
_____ contact angle: Adhesive>Cohesive
High contact angle
_____ contact angle: Cohesive>Adhesive
Complete wetting
0° = __________ wetting
No wetting
180° = __________ wetting
7-9
Wetting agents are surfactants with HLB values of ___ - ___
Wetting agents
aid in attaining intimate contact between solid particles and liquids
Detergency
A phenomenon in which surfactants are used to remove foreign materials from solid surfaces
Detergents
will reduce the surface tension and aid in wetting the surface and the dirt