Blood bank exam 2 review
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
organize D, C,E, d, c, e in order of percentage in the populations
e=98%
D=85%
C=70%
c= 80%
E=30%
d= 15%
Ce in fisher race is equal to what in weiner (D and d)
D= R1
d= r’
cE in fisher race is equal to what in weiner (D and d)
D= R2
d= r”
ce in fisher race is equal to what in weiner (D and d)
D= R0
d=r
CE in fisher race is equal to what in weiner (D and d)
D= Rz
d= ry
D+ C+ E- c- e+, possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner
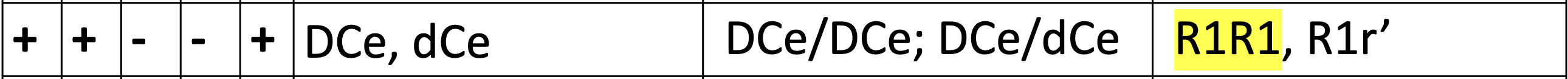
D-, C-, E-, c+, e+, possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner
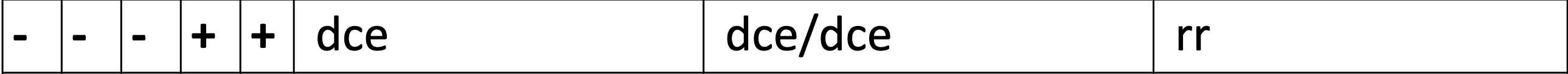
D+, C-, E+, c+, e+, possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner
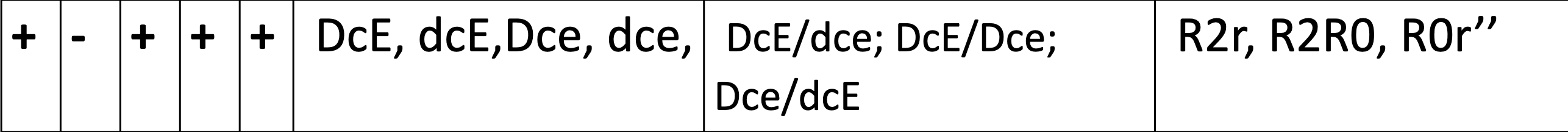
D-, C-, E+, c+, e+ possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

D+, C+, E-, c+, e+ possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

D-, C+, E-, c-, e+ possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

D-, C-, E+, c+, e- possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

D+, C+, E+, c-, e+ possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

D-, C+, E+, c+, e- possible haplotype, fisher race, Weiner

what is the f antigen and is it clinically significant
antigen is expressed on the RBC when both c and e are present
on the same haplotype. Antibodies against ce or anti-f have been
called compound antibodies
yes, although its not common
if a transfusion is needed what kind of units in the D, C, E world would be given if F antigen is a worry?
c negative units
What antigen is found on all C + cells withD+
G antigen (DC)
Someone with antigen G should receive units that are
negative for D and C antigens
Normal RHD gene →
normal Rhd protein
Normal RHCE gene →
Normal RHCE protein
Amino acid point mutations in the gene RHCE make?
C or c and E or e
What causes variation in D antigen expression?
Deletion & suppression
• Weak expression
• Weak-D
• Del
• Partial expression or partial d
If there is a mutation in RHAG but normal RHD/RHCE gene then it is said to be regulated by
the regulator pathway
deletion of RH antigen is said to be conrolled by the
amorph pathway
When there is Rh null the RBC has:
osmotic fragility
decreased anion transport
decreased lifespan
RBC structure=stomatocyte
How are weak D antigens detected
monoclonal anti-D reagents at IS
AHG
C in the trans position→ steric hinderance of D →
weak expression of the D antigen
What is Del
IS type as Rh negative, takes adsorption or elution to determine if he D antigen is present
Partial d uses altered D epitopes and can form
anti-D
Weak D has a decreased number of RhD on the surface and
does not typically form anti-D
Wen is weak D testing required
Donors
Pregnant females- RhIg
Neonate cord samples

invalid/ no control

invalid/ control is positive

weak D positive
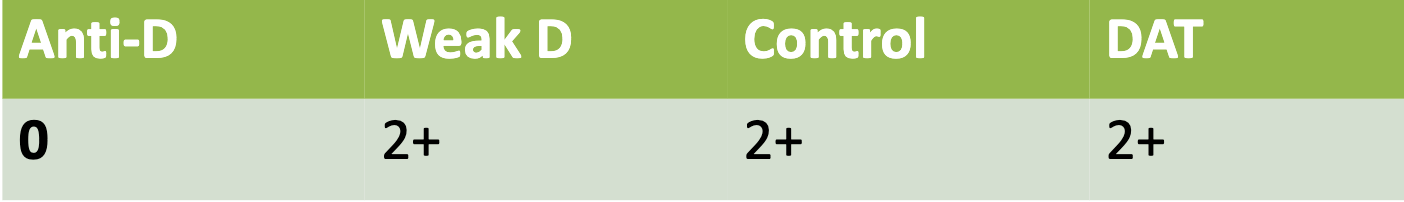
Invalid control and DAT positive

invalid/ control is positive
What IgM is cold agglutinating
M,N, Lewis Lea Leb, I i, Lua
Which antibodies and other blood groups make IgG
Rh (D,d,C,c,E,e)
Kidd (Jka, Jkb)
Duffy(Fya, Fyb)
Kell (K, k), Lub
What antigens show dosage?
Kidds
Duffy
Rh-except D
MNS
Kmod
weak expression of Kell BGS antigens due to point mutation(s) in the KEL gene
Another way for weaker Kell antigen
expression is due to the presence of Kpa
in the cis position
K null
lack of Kell BGS antigens
• Can form anti-Ku (Kell Universal) and will
only not react with RBCs from another K0
individual
McLeod phenotype
weak expression of Kell BGS antigens due to the lack of Xk protein
What is AHG
anti-human globulin
what is the purpose of AHG
a probe for the Fc portion of human igG and other globulins such as complement (C3)
What causes a false positive DAT
contaminated sample
over-centrifugation
inadequate shaking
over reading tubes
in vitro binding of C3 due to cold antibody
What can cause a false negative DAT
inadequate washing
delayed washing
AHG was not added or had a delay
delay in reading
contaminated AHG
Over shaking
under reading
DAT detects
in-vivo
IAT detects
in vitro
What are screen cells
O positive cells used in antibody screen
Duffy null or fyfy means what for the patient
they will be resistant to plasmodium vivax
in the duffy system what antibodies are rare
Fy3 and Fy5
What groups are destroyed by enzymes
M, N, Duffy
What are high frequency antigens
e
k
Jsb
Kpb
Lub
blood group antigen P1 uses what neutralizing agent
pigeon eggs
blood group antigen Sda uses what neutralizing agent
pooled urine
blood group antigen Lewis uses what neutralizing agent
Saliva
blood group antigen Chido and rogers uses what neutralizing agent
Plasma
what is required with a pre-analytical sample
pts full name
at least one unique identifying factor
EDTA or clot tube without gel
date/ time of collection and phlebotomist
tube much match the req
if an individual is Rh null the expression of the Fy5 antigen will be affected how
it will be weakend
what is the most clinically significant of the three isotopes of duffy
IgG 3
they cause HTR and HDN
What enzyme is duffy resistant to
DTT
anyone who is Rh + can recieve what blood type regardless of ABO
O+
O- is the
universal blood donor of red cells
AB+ is the
universal receiver of Donor red cells
O+ and O- is the universal
Plasma receivers
AB people receiving plasma can receive what type of plasma
AB
lectin
protein capable of binding to a carbohydrate
Anti-H lectin derived from seeds of Ulex europaeus plant will agglutinate type O cells but not
Oh cells
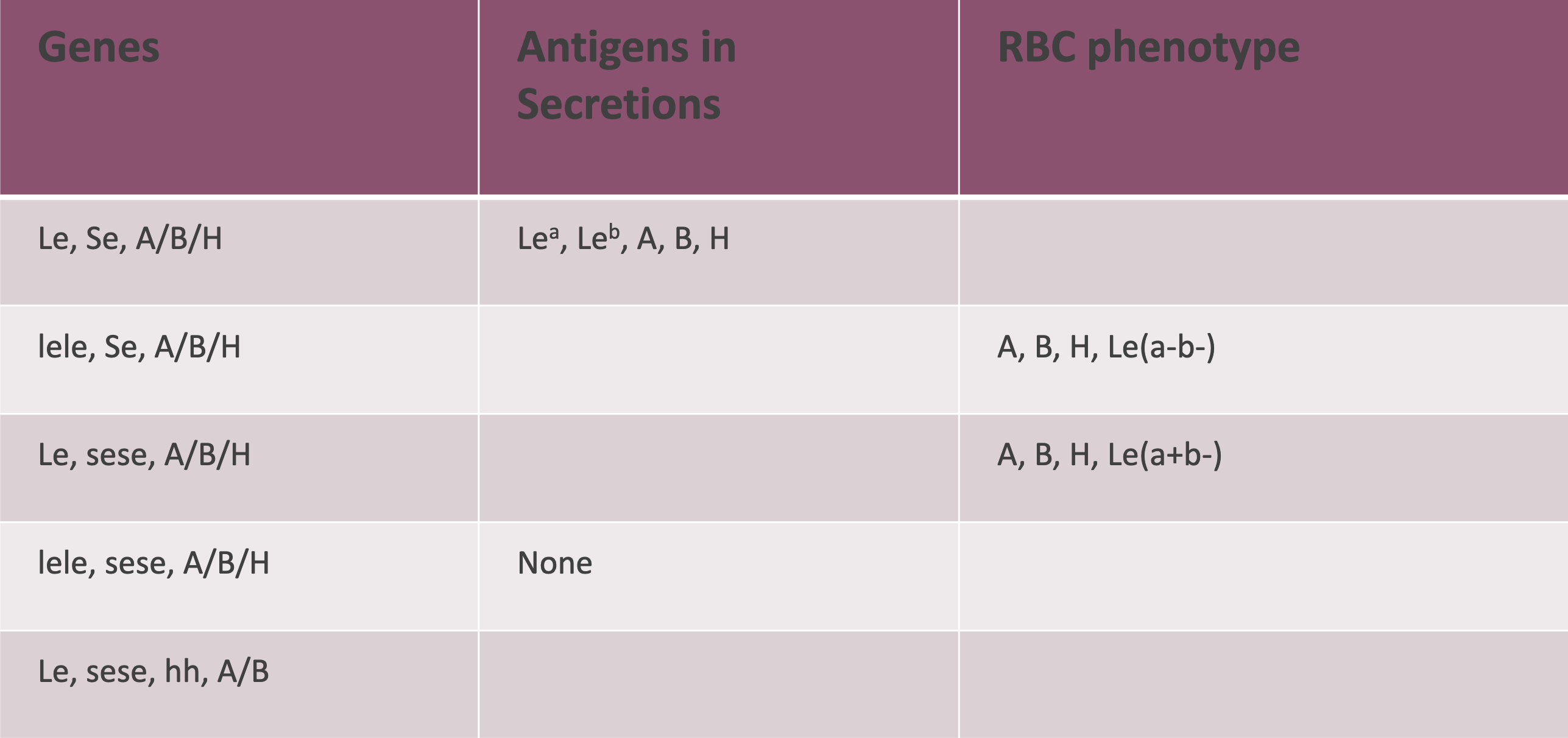
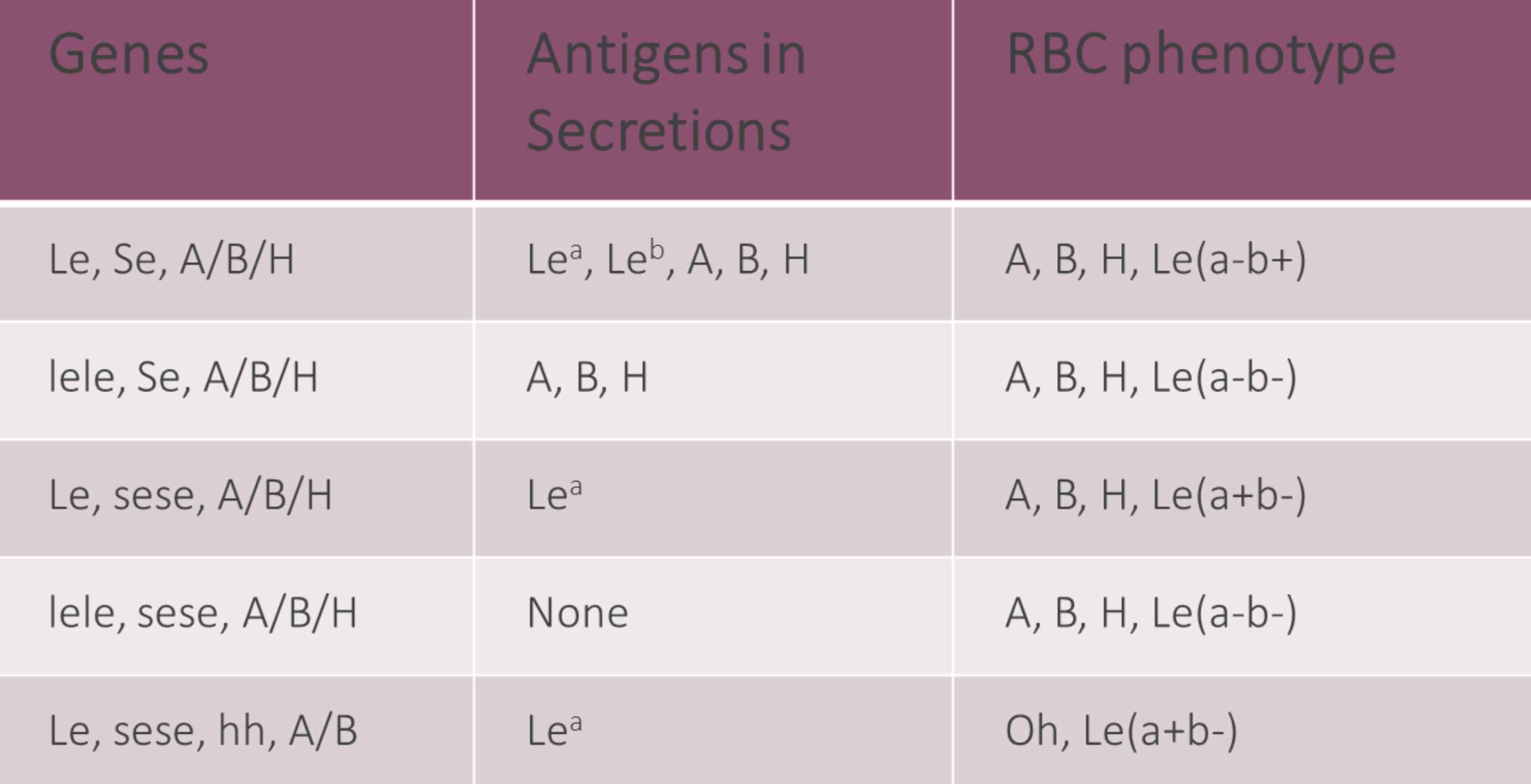
Se and Le attach sugars to
PS1
H and ABO genes attatch terminal sugars to
PS2 and ABO
Lewis system with a secretor gene is
Leb
Lewis system with no secretor gene is
Lea
Fill in this chart