PSIO Final Exam (BLOCK 5 ONLY)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is membrane potential?
The difference in charge across a membrane
Limb generation/regeneration is caused by…
Bioelectric memory
0-7 year olds slightly capable
Lost over time
What does membrane potential have control of?
anatomical plan
Excitable tissues
Cell cycle
Proliferation
Cell volume
Wound healing
Hormone release
What are the two parameters that membrane potential relies on?
Transmembrane ion gradients
Membrane permeability to those ions
What happens during depolarization?
Positively charged ions (K+, Na+) come inside the cell, making the charge less negative/more positive
For every ___ Na+ ions exiting the cell, ___ K+ ions enter the cell
3;2
What happens during polarization?
Positively charged ions leave the cell, making the cell’s interior more negative
What are the chemical forces as it comes to movement across a membrane?
Concentration differences → chemical gradient
i.e. Na+ is higher in concentration on the extracellular side of the membrane, therefore it ‘wants’ to move inside
What are the electrical forces as it comes to movement across a membrane?
Electric attractions across a membrane; electrical gradient
i.e. Na+ is electrically attracted to the cell’s interior because it is negatively charged at rest
What is equilibrium potential?
When electrical and chemical forces are equal
around -90mV for K+
around +55mV for Na+
What are the equilibrium potentials for…
Na+
K+
Cl-
Positive
Negative
Negative
Glutamate is an example of a(n) ____ neurotransmitter
Excitatory
GABA is an example of a(n) ____ neurotransmitter
Inhibitory
GABA Channels are an example of what kind of transport protein?
Ligand-gated ion channel
____ leads to electrical signals
Change in membrane permeability
The membrane potential will move toward the equilibrium potential the membrane is ___ permeable to
Most!
What is graded potential?
Small, localized changes in membrane potential
size varies with stimulus
Can trigger action potentials if graded potential helps reach threshold for excitability
Inhibitory signals…
Makes the membrane potential more negative (polarizing/hyperpolarizing)
Excitatory signals…
Makes the membrane potential less negative/positive (depolarizing)
Absolute Refractory Period
During the most depolarized moment in the action potential; another action potential cannot be fired
Relative Refractory Period
During the most hyperpolarized moment in the action potential; another action potential could be fired, but it would require more energy
Dendrites have which two protein channels?
Ligand-gated ion channels
Mechanically-gated ion channels
What are two types of graded potentials?
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential (IPSP)
Hyperpolarizing
Excitatory Post-Synatic Potential
Depolarizing
What does spatial summation look like in graded potentials?
Post-synaptic neurons recieving inputs from multiple different pre-synaptic neurons
Where is the action potential “decision” (whether to or not to fire) made?
Axon hillock
What are the steps of generating an action potential?
Local changes in the membrane potential (graded potentials)
IPSPs and EPSPs
Depolarization to threshold
Opens v-gated Na+ channels
v-gated ion channels spontaneously close (inactivate)
Repolarization
K+ channels open (“brakes”)
What happens to the neuron when Na+ ion channels close?
The neuron enters the refractory period (think repolarization)
What does the refractory period establish for a neuron?
The rate at which it can fire an action potential
What do refractory periods prevent?
Backward movement of action potentials
What is propagation with respect to the nervous system?
How an action potential travels down an axon
What two factors determine the velocity of propagation?
Size of diameter (axial resistance)
larger diameter = lower resistance
Myelination
Insulation → prevent ion leakage
How do unmyelinated neurons propagate their action potentials?
Continuous Conduction: depolarization and repolarization down the length of an axon
Slower
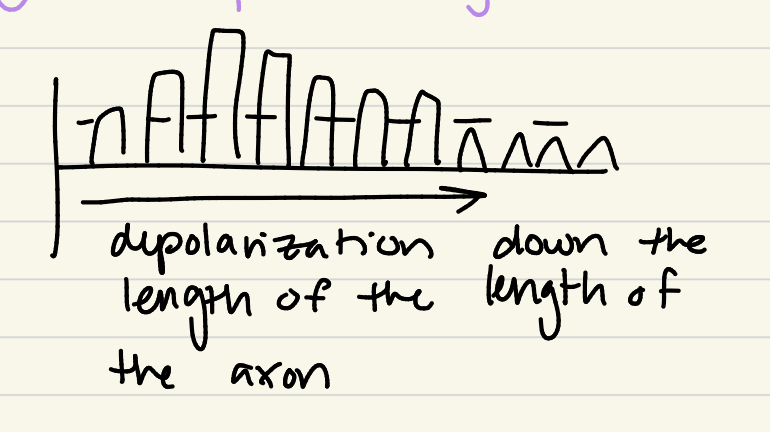
How do myelinated neurons propagate their action potentials
SALTATORY Conduction: v-gated ion channels at the Nodes of Ranvier ONLY
Goes both TOWARD next node and BACK to original node
Quicker
Describe the process of action potentials firing beginning with Ca+ v-gated ion channels
Activate Ca+ V-gated ion channel @ presynaptic cleft
Release neurotransmitters
Graded potentials
Action potentials!
Name the two different type of receptors we are looking at in this unit
Ionotropic receptors
Metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors
The receptor is an ion channel
Fast, short effects
Changes in Vm
Metabotropic receptors
Receptor = G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
Slower, long-lasting effects
What are modalities?
Types of sensory information
(i.e. light, smell, somatic (pressure, stretch), temperature, etc.)
What is sensory transduction? Where does it occur?
Sensing a stimuli and turning it into a electrical signal via the change in Vm
Occurs on sensory receptors
Sensory discrimination
Different receptors detecting specific stimuli
Receptive field
An area around dendrites of a neuron that allows discrimination between stimuli
What is sensory resolution?
How well you detect stimuli
Why is the name mechanoreceptor misleading?
Because the ‘receptor’ itself is not a receptor, they are cells (neurons) with receptors on them
What is a receptor?
A special type of cell that can detect different changes via sensory transduction
Describe the steps of sensory transduction
Stimulus → receptor → changes in membrane potential
Receptor influences rate of action potential production (graded potentials)
Action potentials travel to CNS along afferent pathway
CNS interprets/processes incoming signals
Neural coding
The principle that different stimuli are conveyed by defining frequencies and patterns
What are special senses?
Receptors collected in specialized ‘sense organs’
i.e. smell (olfaction) - nose
taste (gustation) - tongue
sound/equilibrium - ear
Where are olfactory receptors located?
Inside olfactory epithelial cells
Which secrete mucus
What type of neurons are found here? (nose)
Bipolar sensory neurons
T/F: The substance being smelled has to dissolve in the nose mucus
True
Where are action potentials sent to in the nose?
Glomeruli in the cribiform plate
What is the function of each glomerulus?
Collect specific parts of a scent; all glomeruli together = scent
On what do glomeruli synapse?
Mitral cells
What is the function of mitral cells?
Their axons make up the olfactory tract
Odorant molecule
Activated by olfactory receptor
Activates g-proteins
What do the g-proteins do once activated by the odorant molecule?
Activate adenylate cyclase, which turns ATP to cAMP
cAMP opens Na+ ion channels
What is the evolutionary/physiological purpose of our sense of smell?
Allows us to detect changes in the environment
Describe how light passes through the eye
Cornea → aqueous humor → pupil → lens → vitreous humor → retina
Where are photoreceptors at the highest density?
Fovea (on retina)
Describe the path of visual information as it comes in the brain
Optic nerves → Optic chiasm → thalamus → primary visual cortex
What two types of smooth muscles make up the iris?
Circular (sphincter pupillae)
Radial (dilator pupillae)
Circular (sphincter pupillae)
*PARASYMPATHETIC control
Constricts the pupil
Radial (dilator pupillae)
*SYMPATHETIC control
Dilates the pupil
What happens to water as it passes through mediums with different densities?
It refracts
What is accommodation as it comes to the eye?
Change of lens shape (for focusing)
Rounder = focused
When the eye is unfocused, the suspensory ligaments are ____ and the ciliary muscles are _____
Tight
Relaxed
(focus on ciliary muscles, which control shape of lens directly)
When the eye is focused, the suspensory ligaments are ____ and the ciliary muscles are _____
Relaxed
Tight
What are the two types of photoreceptor layers?
Rods: monochromatic, dim lights
Cones: color vision, bright lights
What other types of layers are there in the retina?
Neuron processing layers (contrast, etc.)
Melanopsin
Detecting the intensity of light
Sends to hypothalamus for circadian rhythm
Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Tissue that comprises the blood-retinal barrier
Contains melanin to absorb light
Absorbed light = better vision
Prevents oxidative damage
Müller Glial Cells
Like astrocytes, but in the retina
Guide photons to photoreceptors
Reuptake NTs
Describe the path of light info as it comes in the retina to the optic nerve
Rods & Cones → Bipolar cells → Ganglion cells → optic nerve II
Where are the receptors for oderant molecules located?
Embedded in cilia in on the olfactory receptor neurons
T/F: We have a lot more CONES than RODS
False; we have more rods than cones
Rods
Important for monochromatic, dull light vision
On the periphery of the retina
Permit the detection of movement
What are the membranous discs of rods?
Receptors that detect light
What is rhodopsin? What is it comprised of?
Light receptors embedded in the membranous discs
Comprised of opsin + retinal
G-coupled protein receptor
What does rhodopsin couple with a G-protein to activate? What does that become?
Beta-carotene (vitamin A) → 11-cis retinal
What happens when 11-cis retinal is struck by a photon?
It becomes trans-retinal
This is detection of light
Cones
Color vision, bright light vision
Located in the center of the retina (fovea)
What are the vision steps of transduction in the DARK?
High production of cGMP
cGMP opens Na+ channels
Depolarizes cell (“dark current”
Cells release NT (glutamate)
NT changes action potential frequency of bipolar cells
T/F: There are more action potentials in the dark with regards to vision
TRUE
What are the vision steps of transduction in the LIGHT?
Rhodopsin’s retinal absorbs the photons, activating opsin
Enzymes break down cGMP
Decrease in cGMP closes Na+ channels
Hyperpolarization, decrease in glutamate
What type of hearing loss is associated with the middle ear? And the inner ear?
Middle: Conductive
Inner: Sensorineural
The movement of the stapes increases pressue in the cochlea for hearing. What structure regulates that pressure?
Round window
Basilar membrane
Found along the organ of Corti
Vibrates in response to sound waves;
Different frequencies determine which part of the basilar membrane will move
What structures in the basilar membrane are directly responsible for triggering action potentials? How? What are they connected by?
Stereocilia
Stereocilia move with the cochlear fluid’s direction
Whenever stereocilia bend, they open mechanically-gated ion channels
Ca++ channels (not Na+!!!)
Connected via tip links
In the case of hearing, what causes depolarization?
K+ ions
Endolymph is very high in K+
How is frequency and loudness determined on the basilar membrane?
Frequency: precise location on the basilar membrane
Loudness: How high/low is the movement of the basilar membrane
What might cause sensorineural hearing loss?
Inner ear damage; hair cell damage (cannot detect changes in frequency)
What is equilibrium? Balance?
Equilibrium: No change in speed
Balance: Process of stabilizing the body in response to changes in speed/gravity
What structures make up the vestibule?
Semicircular canals
Utricle
Saccule
What type of movements do the semicircular canals detect?
Movement on X,Y, and Z axes
Rotational movements of the head or side to side
What is the ampulla?
Base of each semicircular canal
Has stereocilia that project into crista
Bends in response to movement
What is the vestibulocular reflex?
Keeping the eye focused on a fixed point even if your head moves
In the utricle and saccule, what membrane do the hair cells project into?
The otolithic membrane
How do hair cells move in the saccule and utricle?
Saccule: Up/down in response to gravity
Utricle: Left/right in response to acclerations