Chemistry Chapter 5 Electromagnetic Radiation
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Which of the following orbitals are possible in an atom: 4d, 1p, 3g, and 5d?
4d & 5d
Which of the following orbitals are possible in an atom: 3s
2s, 5s or 3f?
3s, 2s & 5s
An ________ is the region around the nucleus where electrons of a certain energy are most likely to be found.
orbital
An _________ contains all the electrons with similar energy.
energy level
A ________ contains all the electrons with the same energy.
sublevel
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He
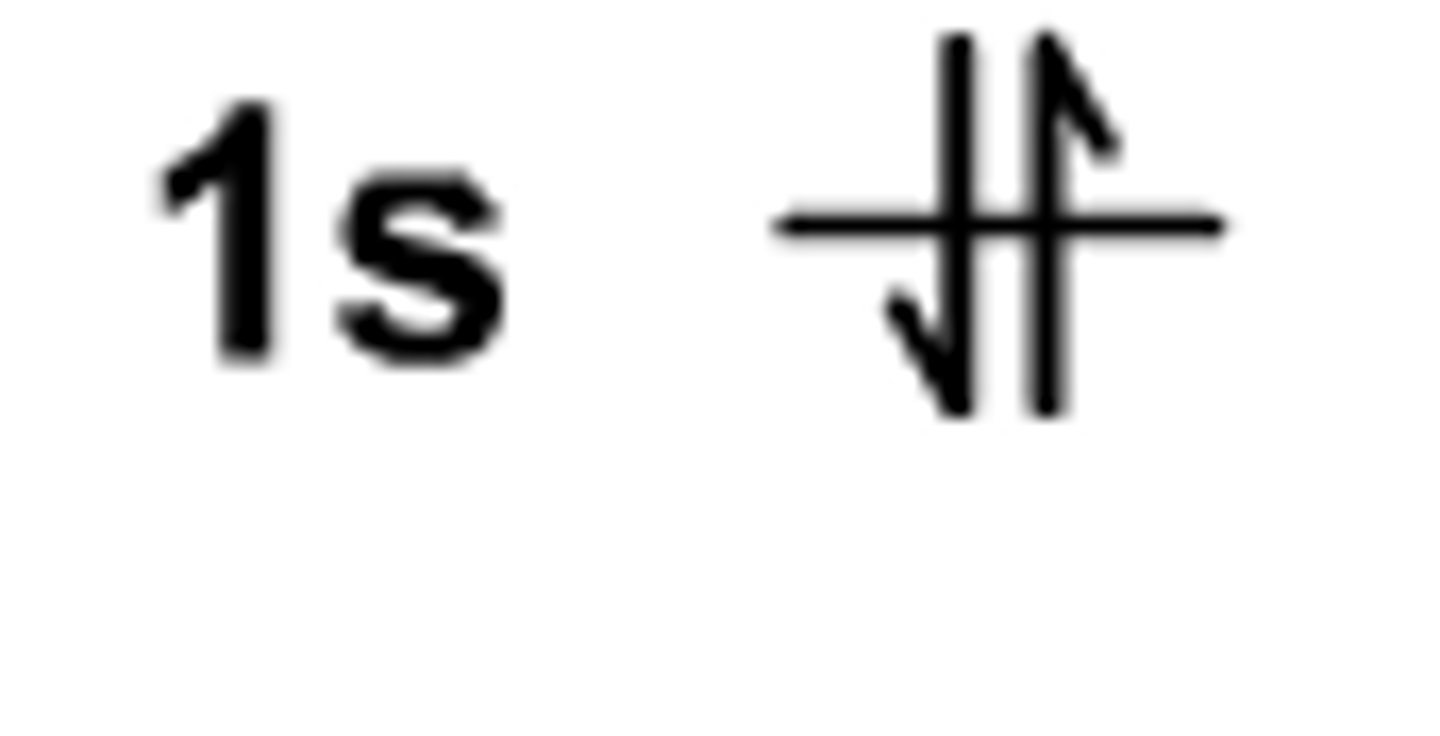
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of oxygen, O.

Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of gallium, Ga.
Which of the following is the correct electron configuration for nitrogen?
1s 2s2 3p3
1s 22s 22p 3
1s 22s 21p 3
1s 22s 22p 4
1s 2s2 3p3
Which element fits the following description: an element that has 2 electrons in the n = 3 energy level?
Mg (Magnesium)
Express your answer as a chemical symbol.
1s2 2s2 2p4
O
[Ne]3s2 3p2
Express your answer as a chemical symbol.
Si
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
Express your answer as a chemical symbol.
Ar
[He]2s2 2p5
Express your answer as a chemical symbol.
F
Enter an abbreviated electron configuration for sodium:
Express your answer in complete form, in order of increasing energy
[Ne] 3s1
Enter an abbreviated electron configuration for beryllium:
Express your answer in complete form, in order of increasing energy.
[He] 2s2
Enter an abbreviated electron configuration for phosphorus:
Express your answer in complete form, in order of increasing energy.
[Ne] 3s2 3p3
Enter an abbreviated electron configuration for arsenic:
Express your answer in complete form, in order of increasing energy.
[Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p3
Which element has three electrons in the 3p sublevel
P
Which element has three 2p electrons
N
Which element completes the 5s sublevel
Sr
Which element has one electron in the 4s sublevel
K
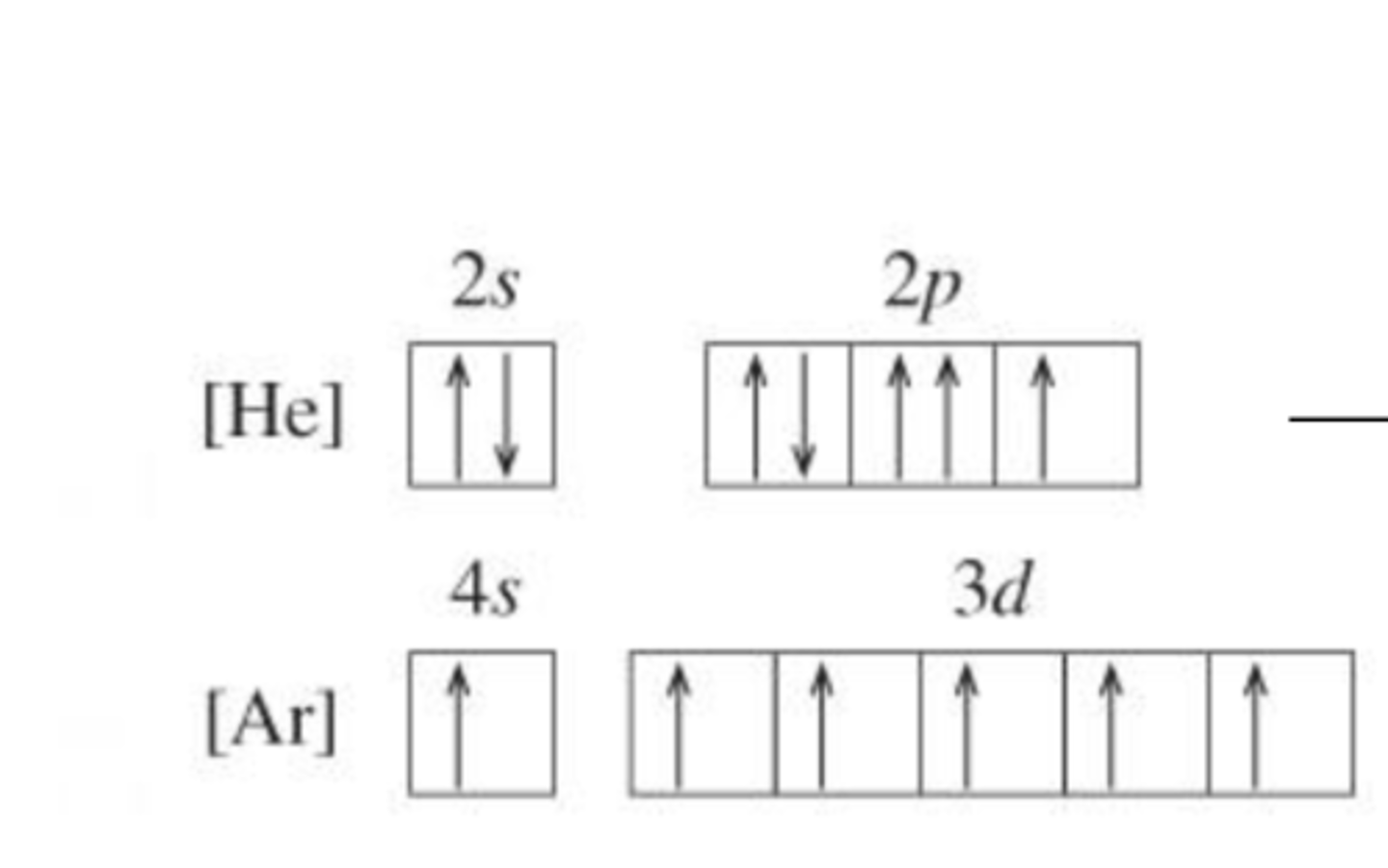
Indicate if the following abbreviated orbital diagrams are possible or not. Which element does the correct one represent?
Bottom one because typically, lower-energy orbitals are first filled before placing electrons in higher-energy orbitals, with the exception of CrCr and CuCu. With CrCr, the valence electrons are close to being a half-filled sublevel. Thus, there is only one electron in the 4s sublevel and five electrons in the 3d sublevel to give more stability throughout the half-filled d sublevel.
It is Cr.
Which block of the periodic table has six elements in each period?
p block
How many electrons are in the 3d sublevel for manganese?
Manganese has 5 electrons in its 3d sublevel.
How many electrons are in the 3p sublevel for phosphorous?
Phosphorous has 3 electrons in its 3p sublevel
How many electrons are in the 6p sublevel for lead?
Lead has 2 electrons in its 6p sublevel.
How many electrons are in the 3s sublevel for magnesium?
Magnesium has 2 electrons in its 3s sublevel.
How many valence electrons does oxygen have?
6 valence electrons
Rank the following elements by atomic radius from largest to smallest:
Al
Si
Ar
Na
Cl
Na
Al
Si
Cl
Ar
In general, as you move left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases.
Rank the following atoms by most to fewest valence electrons:
In
K
Br
Xe
As
Xe
Br
As
In
K
The number of valence electrons increases within a period from left to right for the main group elements.
Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing atomic size (largest to smallest):
P
Al
Ar
Cl
K
K
Al
P
Cl
Ar
Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing ionization energy (high to low):
germanium
strontium
phosphorus
silver
molybdenum
phosphorus
germanium
silver
molybdenum
strontium
Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing metallic character (high to low):
Cl
Cs
Sr
Rh
Se
Mo
As
Cd
Cs
Sr
Mo
Rh
Cd
As
Se
Cl
Which of the following atoms has the largest atomic radius?
Rb (atomic size increases going down and from right to left)
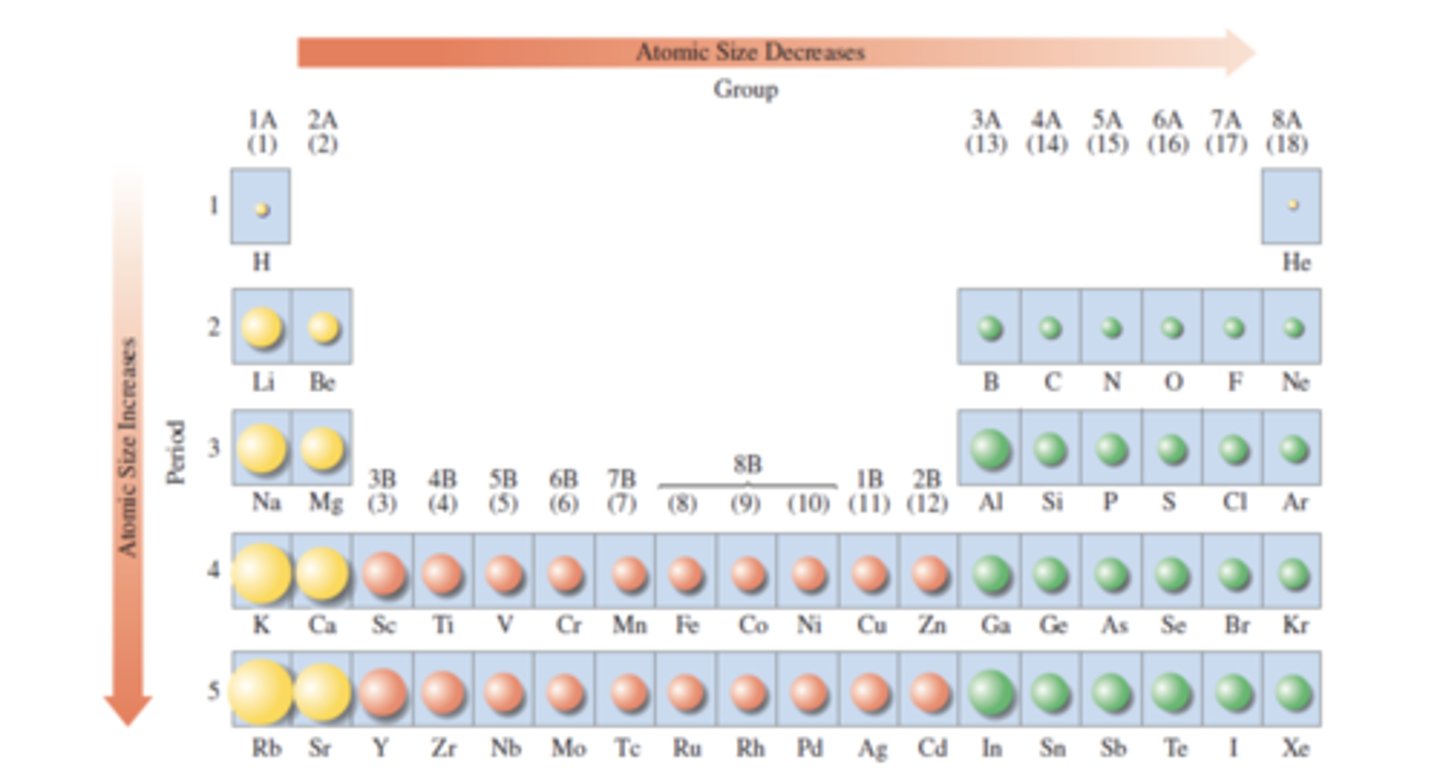
What is similar and what is different about the valence electrons of the elements in a group?
1)approximately the same distance from the valence electrons to the nucleus. As you go down the group, the number of valence electrons increases.
2)the same number of valence electrons. As you go down the group, the valence electrons are closer to the nucleus.
3)approximately the same distance from the valence electrons to the nucleus. As you go down the group, the number of valence electrons decreases.the same number of valence electrons.
4)As you go down the group, the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus.
(4)
For a group of representative elements, the size of the atom increases going from top to bottom due to the increased distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons occupying the outermost, highest energy level. The elements in a group all have the same number of valence electrons, which explains why elements in the same group often have common characteristics and reactivity.
Indicate the number of valence electrons in each of the following:
B, Al, Ga, In, and Tl
As
O, S, Se, Te, and Po
group 4A
3
5
6
4
Select the larger atom in each pair:
Kr or As
As or P
Se or Rb
Se or Ca
As
As
Rb
Ca
Select the element in each pair with the higher ionization energy:
S or Ar
Na or Cl
Na or Rb
N or Ne
Ar
Cl
Na
Ne
Place the following in order of increasing metallic character (smallest to largest):
Li, O, B, Ne
Ne, O, B, Li
energy level
specific energy of each electron (n=1,n=2,n=3) and contains electrons of similar energy.
sublevel
Contains all the orbitals of a given shape and electrons with identical energy (s,p,d,f blocks).
orbitals
regions around the nucleus in which given electron or electron pair is likely to be found (1,2,3 etc).
Which orbitals can be modeled as dumbbell shaped?
p orbitals
Which orbitals are spherical
S orbitals
Which orbitals can be modeled as 4 leaf clovers
D orbitals
their shapes are even more complex than s, p, or d orbitals; can hold a total of 14 electrons in 7 sub-shells
F block
What do periods represent?
energy levels
What is the lowest energy level
1s or n=1
Pauli exclusion principle
states that a maximum of two electrons can occupy a single atomic orbital but only if the electrons have opposite spins
Orbital diagram
Explains where the electrons are