Ap world unit 1-2 (1200-1450)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
key takeaways
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms

china
government: bureaucracy, civil service exams, neo-confucianism
contributions: champa rice, civil service exam, paper money, textiles, gunpowder
social: women facing oppression , filial piety
religion: buddhism , hinduism
maintaining rule: bureaucracy, civil service exams, neo-confucianism
China developed a complex government system characterized by a bureaucracy supported by civil service exams and neo-Confucianist philosophy. It made significant contributions in agriculture, economy, and culture, while women's roles were often constrained by societal norms.
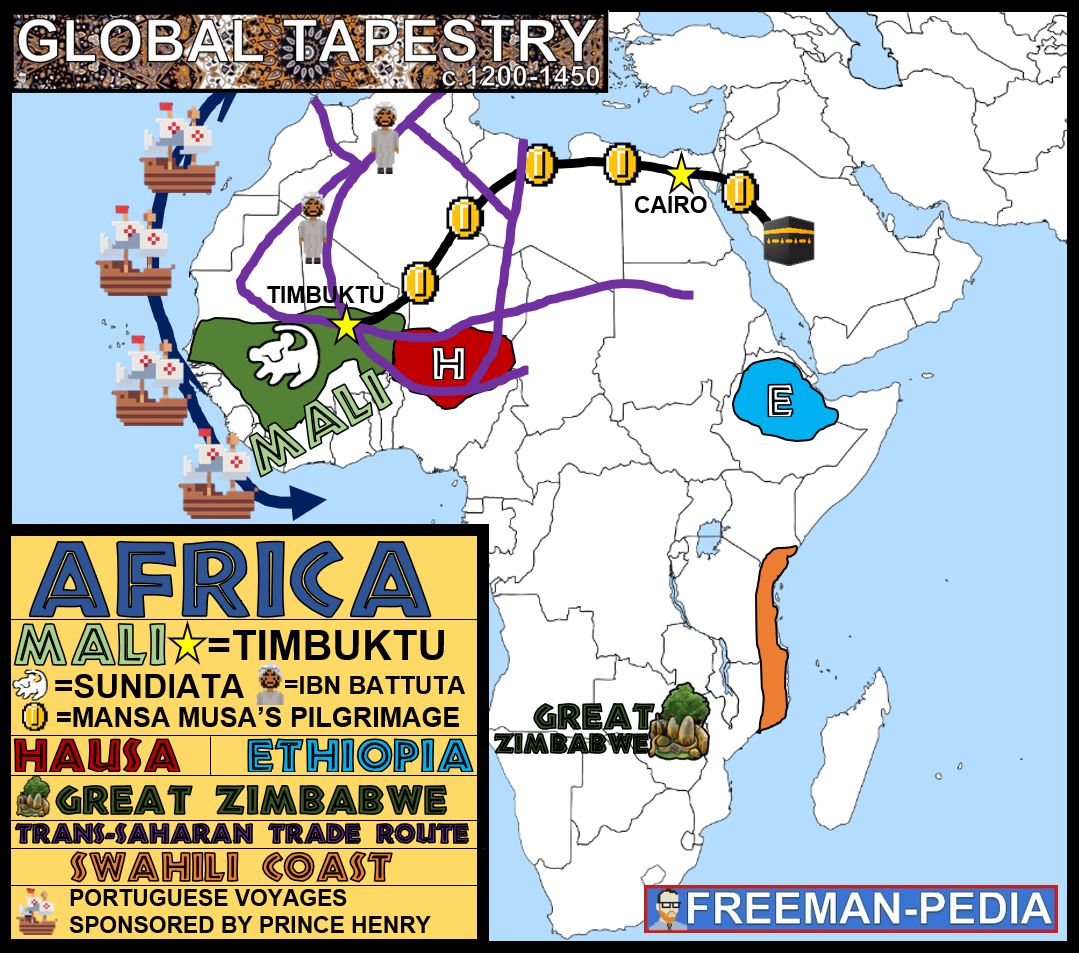
africa - mail,ghana,ethiopia
major states: mali, ghana, ethiopia
government: monarchies, theocratic (islam or muslim)
maintaining rule: religious legitimacy control of trade route
state building: wealth from trade and neighboring trade cities
contributions: textiles, gold, slaves
environment : caravan trade- savanna zones
Africa saw the rise of major states such as Mali, Ghana, and Ethiopia, characterized by monarchies and theocratic governance often legitimated through religion. The control of trade routes contributed to state wealth, while significant contributions included textiles, gold, and slaves, facilitated by caravan trade in savanna zones.

the americas - Maya, Mexica (aztec, Inca)
Government : city states (maya) theocratic (aztec) bureaucratic (inca)
Contributions: agriculture, architecture, calendars, and writing systems
Social: class divisions, human sacrifice, matrilineal and patrilineal societies
Religion: polytheistic beliefs, rituals, and priesthood
maintaining rule: centralized governments, tribute systems, and religious authority.
economy: agriculture, trade, tribute systems including precious metals and goods.
The Americas, particularly the Maya, Mexica (Aztec), and Inca civilizations, were marked by distinct government structures such as city-states (Maya), theocratic rule (Aztec), and bureaucratic systems (Inca). They made notable contributions in agriculture, architecture, and writing, while their societies were characterized by rigid class divisions, human sacrifice practices, and a mix of matrilineal and patrilineal kinship. Religion played a crucial role, as polytheistic beliefs and rituals were integral to governance, reinforced by centralized authorities and tribute systems that facilitated economic trade and wealth.

Japan - Heian and Kamakura
major states: heian and Kamakura
Government: decentralized feudalism
statebuilding: tributes, mandate of heaven
economy: pro industrialization, grand canal
contribution: printing , porcelain, The Heian period (794-1185) is characterized by courtly culture, poetry, and refined aesthetics, while the Kamakura period (1185-1333) introduced samurai rule and the establishment of a feudal system.
environment : terraced farming
social: bushido, feudalism
religion: shinto Buddhism, Shintoism
were significant periods in Japanese history, marked by cultural and political developments. The Heian period is noted for its advances in art and literature, while the Kamakura period saw the rise of the samurai and military governance.
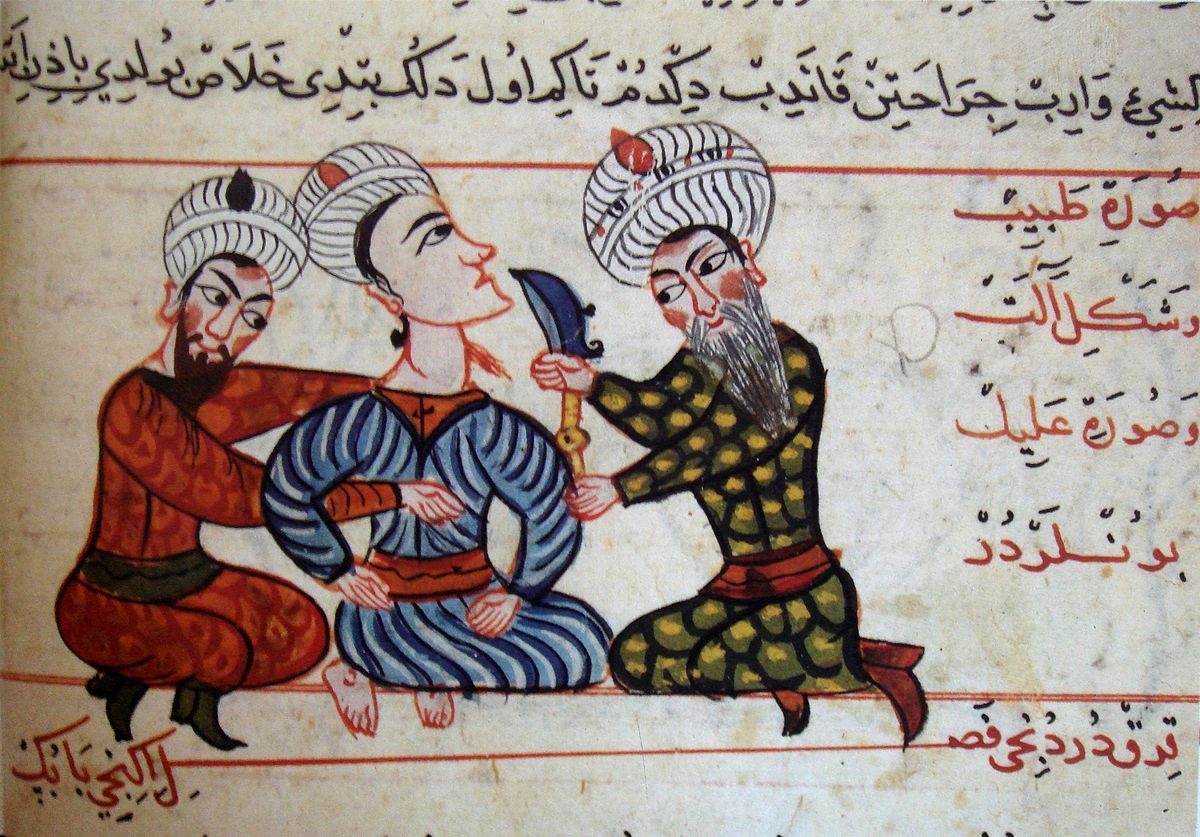
Muslim Word
major states: Abbasid Caliphate , Delhi Sultanate , Mamluk Sultanate
government: caliphates and sultanates unified under Islam
state-building : spread through trade and conquest
maintaining rule: military, islamic law, islamic scholars
economy: agriculture, trade, and taxes.
contributions: mathematics, medicine, architecture, and philosophy.
environment: agricultural advancements helping growth
The Muslim world during this period saw major states such as the Abbasid Caliphate, Delhi Sultanate, and Mamluk Sultanate, which were unified under Islam through caliphates and sultanates. This era was characterized by significant contributions to mathematics, medicine, architecture, and philosophy, driven by advancements in agriculture and a robust trade economy.

Europe - holy roman empire, france, england
major states : France, England, Roman Empire
Government: Feudal monarchies, decentralized
State-building: christianity, crusades , centralized monarchy
maintaining rule: divine right , church authority
economy: largely agricultural society dependent on free and coerced labor including serfdom
contribution : architecture
environment: deforestation
transportation: viking boats

Mongols - nomadic empires
major state : mongol empire
government: Khanates
state building : conquest, religious tolerance
maintaining rule: military prowess, tribute system
economy: trade networks, taxation
contribution: cultural exchange, technology diffusion
environment: adaptation to diverse climates
social: steppe culture, hierarchy
religion: varied beliefs, including shamanism and Buddhism

south and southeast Asia - Sirvjaya , vijayanagara, Khmer
major states: Sirvjaya , vijayanagara,Khmer
Government: hindu and buddhist monarchies
State-building: maritime trade and agriculture
maintaining rule: religious legitimacy
economy: spices, gold, textiles, highly commercial
contributions: cultural diffusion from trade
environment : monsoon winds
The major states in South and Southeast Asia include Srivijaya, Vijayanagara, and the Khmer Empire, characterized by Hindu and Buddhist monarchies. Their state-building processes relied on maritime trade and agriculture, while they maintained rule through religious legitimacy, with economies based on spices, gold, textiles, and vibrant commercial activity. Cultural diffusion was fostered through trade, and the region's environment was significantly influenced by monsoon winds.

Themes (1200-1450)
Major themes during this period include state-building and expansion, cultural interactions, and the rise of trade networks across regions like Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Common strategies to build and maintain power: religion as legitimacy (divine right, christianity, mandate of heaven)
Bureaucracy and legal codes (confucian exams, islamic law, civil service)
Military force and conquest
Tribute systems (China and Aztecs)
Economies based on trade, agriculture, and tribute systems. (Indian ocean, Silk roads, Trans-Saharan)
agricultural innovations ( champa rice)
states taxed trade or control
summary: This period is characterized by the development of complex governmental structures, the use of religion to justify authority, and the expansion of trade routes, all of which facilitated cultural exchange and economic growth.
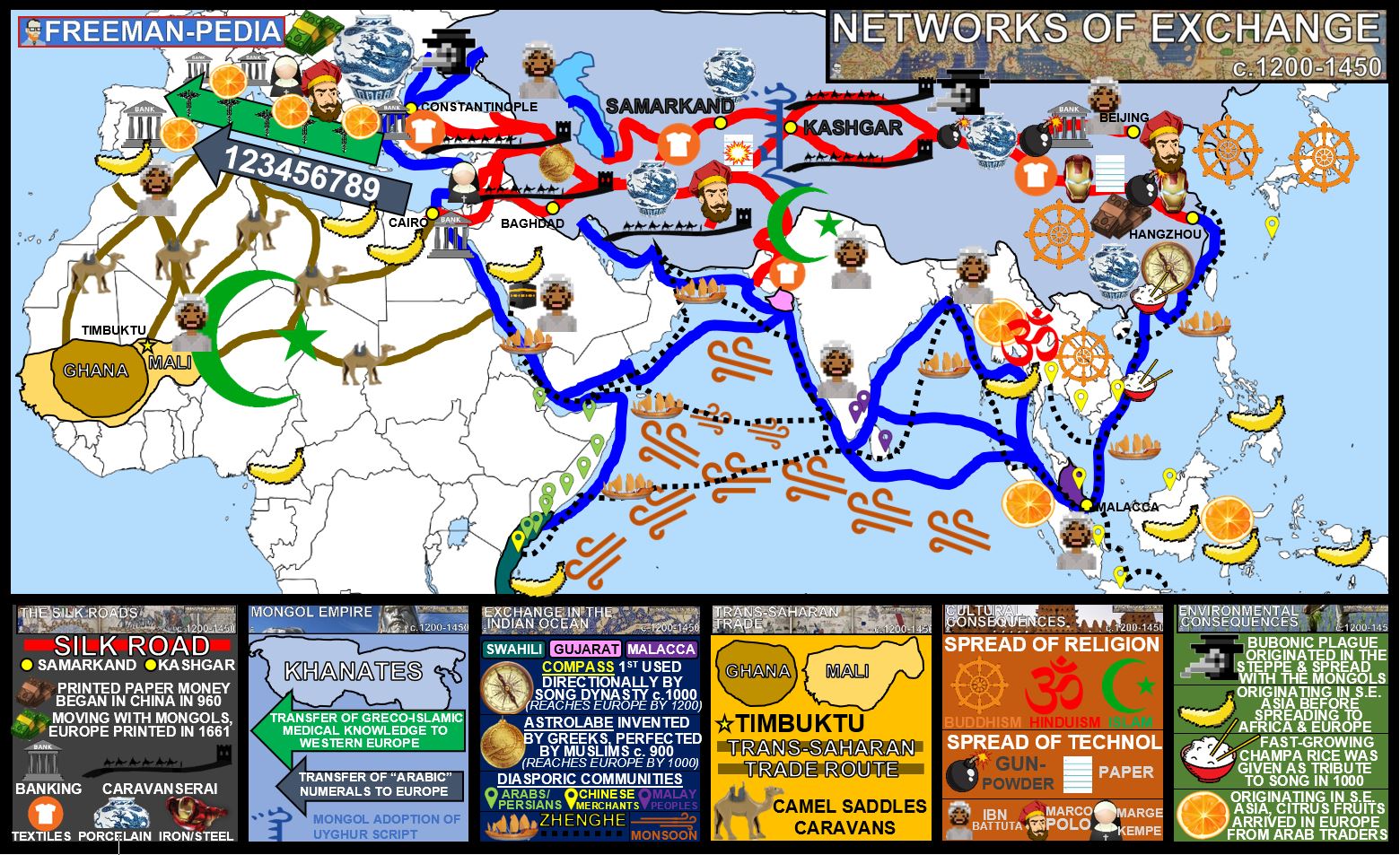
Vocab / Definitions
neo-confucianism (used by china/ Song Dynasty) - rid of confucian of the prior thought of buddhism which had influenced prior centuries
Mitá system- a labor system established by the Incas that required communities to provide a certain number of workers for public projects.
centralization- the process of consolidating power and authority within a central government, leading to increased control over political, economic, and social matters.
bureaucracies- administrative systems governing large organizations, ensuring efficient management and implementation of policies.
sultanates- political entities ruled by a sultan, characterized by Muslim governance and often influencing trade and culture in their regions.
feudalism- a social and economic system in medieval Europe where land was exchanged for military service and loyalty, creating a hierarchy of lords, vassals, and serfs.
bhakti movement - a devotional trend in Hinduism emphasizing individual connection to God through personal devotion and love, promoting equality and rejecting caste distinctions.
tribute system-an economic and political framework in which tribute is paid by subordinate states to a dominant power, often involving the exchange of goods for political protection or recognition.
bushido: code of honor in Japanese samurai culture emphasizing loyalty, bravery, and moral principles.
crusades -military campaigns initiated by European Christians in the Middle Ages to reclaim Jerusalem and other holy lands from Muslim rule, leading to significant cultural and political impacts.
religion
buddhism:
hinduism:
christianity: