KHAN respiratory 2 exam
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Traits of asthma
Airway obstruction
Mucous secretion
Inflammation
Th2 help cell
Eosinophil involvement
Bronchial hypersensitivity
How is asthma treated?
Bronchodialators and anti-inflammatroy’s
Traits of COPD
Airway obstruction
Mucous secretion
Inflammation
Cytotoxic T-Lymphocytes
Neutrophil involvement
What are the causes of COPD
-Smoking and old age
-Deficiency of alpha-1 antipyresis
What is the treatment of COPD
Beta 2 agonists and anticholinergics
What is Bronchial hyperactivity?
The bronchial is sensitive to stimulants (Pollen, animal dander, and irritant chemicals) which causes bronchoconstriction
What is the MOA of theophylline?
-Inhibits PDE → Increase in cAMP
-Adenosine antagonist
Why can’t Theophylline be used in asthma?
Has low therapeutic window
Names of the Short Acting Beta Agonists (SABA)?
Albuterol and Levabuterol
What are the names of the Long Acting Beta Agonits (LABA)?
Salmeterol
Formoterol
MOA of Beta-2 agonists?
Activating adenylyl cyclase → Increasing cAMP production
-cAMP mediates bronchodialatory effect
ADR’s of Beta-2 Agonists
1) Tachycardia
2) Skeletal muscle tremors
3) Hypokalemia
4) restlessness, apprehension, anxiety
Boxed warning of LABA
Asthma related death
Advantages of steroid and LABA combination
Reduces inflammation and increases Beta-2 expression
Can LABA be used alone in COPD?
YES
How can you ensure beta 2 selectivity?
-Catechol group
-Large R group
-resorcinol / hydroxymethol
What are the names of the three endogenous hormones secreted from the adrenal cortex?
-Glucocorticoids
-Mineralcorticoids
-Adrenal Androgen
What is the precursor of Cortical hormones?
Cholesterol
What is the rate limiting step for cortical hormone synthesis?
•cholesterol (C-27) →pregnenolone (C-21) conversion
What occurs during prolonged GC therapy?
HPA suppression
MOA of steroids
• Steroid in circulation bound to CBG (costicosteroid binding protein →carrier protein)
• Enters cell interact with receptor (cytosol)
• Receptor confirmation changed
• Steroid-receptor complex →Nuclear translocation
• Receptor dimerization → Binds to GRE (glucocorticoid response elements) and regulate transcription
• Glucocorticoids increase, or decrease in transcription (for example-decrease transcription of genes coding for pro-inflammatory cytokines)
Cortisol (steroids) decrease which blood cells? (immune system 1)
-Monocytes
-Basophils
-Eosinophils
-Lymphocytes
Do steroids (cortisol) increase or decrease expression of lipocortin? (immune system 2)
Increases
What is the MOA of Lipocortin?
Inhibits PLA2
A decreased expression of COX-2 leads to….
Decreased PG
Cortisol (steroids) alter expression of cytokines, which are decreased and which are increased? (immune system 3)
Increased
-Anti-inflammatory proteins (IL-10)
Decreased
-certain cytokines involved in inflammation (IL-1, TNF-alpha)
Explain Cortisol on immune system 4
Inhibition of Mast cell and basophil degranulation. decrease in IgE mediated Histamine, and LT release
Explain Cortisol on immune system 5
Decreased expression of adhesion molecules. This is helpgul because luekocytes binjd to endolthelial cells through these molecyles and move to the inflamation. —> reduced influx of luekocytes
Names of Systemic glucocorticoids
•Cortisone
•Methylprednisolone (MEDROL)
•Prednisolone (MILLIPRED, ORAPRED)
•Prednisone (RAYOS)
•Dexamethasone (DECADRON)
•Hydrocortisone (CORTEF)
•Triamcinolone (ARISTOPAN)
ADR’s of systemic glucocorticoids
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects following short-term systemic therapy:
•Mood disturbances
•Increased appetite
•Loss of glucose control (b/c decrease glucose uptake in tissues, increased gluconeogenesis)
•Weight gain
•Fluid retention (cause: mineralocorticoid effects® aldosterone mediated water and sodium retention)
•Hypertension (cause-as above)
•Peptic ulcer
• Long-term systemic use: HPA suppression® taper dose to restore endogenous hormone (cortisol) production
What is significant of positions 1-2,6,9,11,16 on systemic glucocorticoids?
Most changes occur in these positions
Structure of cortisol
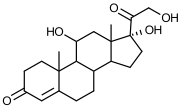
Structure of cortisone
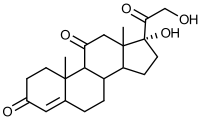
Structure of Prednisone
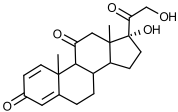
Structure of Prednisolone
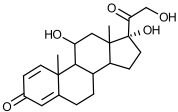
Which systemic glucocorticoids are active?
-Cortisol
-Prednisolone
What are the positions on Triamcinolone and what do they effect?
F at position 9= Increases GCC and MCC
OH at position 16= decrease in MCC
Names of the inhaled glucocorticoids
•Beclomethasone (BECLOVENT)
•Triamcinolone (AZMACORT)
• Flunisolide (AEROBID)
• Budesonide (PULMICORT)
• Fluticasone (FLOVENT)
ADRs of inhaled glucocorticoids
•Oropharyngeal candidiasis (b/c of localized immunosuppression and allowing opportunistic infections)
•Hoarseness of the voice
On an inhaled glucocorticoid, Budenoside, what does Acetal group on 16,17 do?
-Increase lipophiliocity
-Decreased mineralcorticoid activity
Inhaled glucocorticoid, Beclomethasone, 9 alpha chloro, 16 beta methyl results into what?
9 alpha chloro increases GCC and MCC
16 Beta methyl Decreases MCC activity
What is the Cromolyn effect?
Its a mast cell stabalizer
BUT has bad taste
How is LTA4 synthesized?
Arachidonic acid is converted to LTA4 through 5-lipoxygenase
What are the names of the luekotriene modifiers?
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
•Zafirlukast
•Montelukast (SINGULAIR)
Leukotriene Synthesis Inhibitor
•Zileuton
MOA of Leukotriene modifiers ANTAGONISTS
•Selective, high-affinity, competitive antagonists of CysLT1 (cysteinyl leukotriene 1) receptor
ADR’s of Leukotriene modifiers ANTAGONISTS
•Hepatotoxicity (hepatitis, enzyme elevation)
•Neuropsychiatric events
MOA of Leukotriene modifiers INHIBITION
•Inhibits 5-lipoxygenase
•Leukotrienes results from the action of 5-lipoxygenase on arachidonic acid and are synthesized by a variety of inflammatory cells in the airways
ADR’s of Leukotriene modifiers INHIBITION
•Hepatotoxicity
•Neuropsychiatric events
MOA of Omalizumab
•The anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (targeted against the portion of IgE that binds to its receptors on inflammatory cells)
•Clears unbound, circulating IgE from the circulation
•IgE-Anti-IgE complexes are cleared from the blood
•Does not activate IgE already bound to cells
•Does not provoke mast cell degranulation
ADR’s of Omalizumab
•Anaphylaxis can occur during tx or at a later time
•Malignancy
What are the muscarinic receptor names?
•Ipratropium (Atrovent)
•Tiotropium (Spiriva)
MOA of Muscarinic antagonists
–Decreases mucous secretion
–Decreases bronchoconstriction® bronchodilation
Do muscarrinic receptor antagonists have CNS effect?
NO
What is the most common ADR of Muscarinic antagonists?
DRY MOUTH
Are Muscarinic antagonists? used in Asthma or COPD
COPD
Why do Muscarinic antagonists have no systemic effect?
Low systemic absorption
MOA, Metabolite, of Roflumilast
MOA:•PDE4 inhibitor → increases cAMP levels in the lungs
Metabolite: roflumilast N-oxide, it is pharmacologically active