B2: Cell division
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is in the nucleus of cells?
Chromosomes
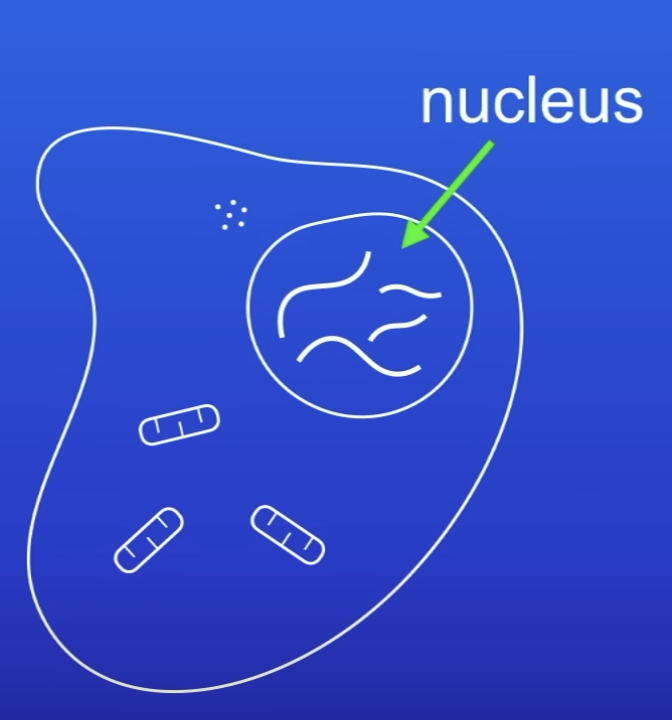
What molecule are chromosomes made up of?
DNA
How many of each chromosome do body cells contain?
2
Paired
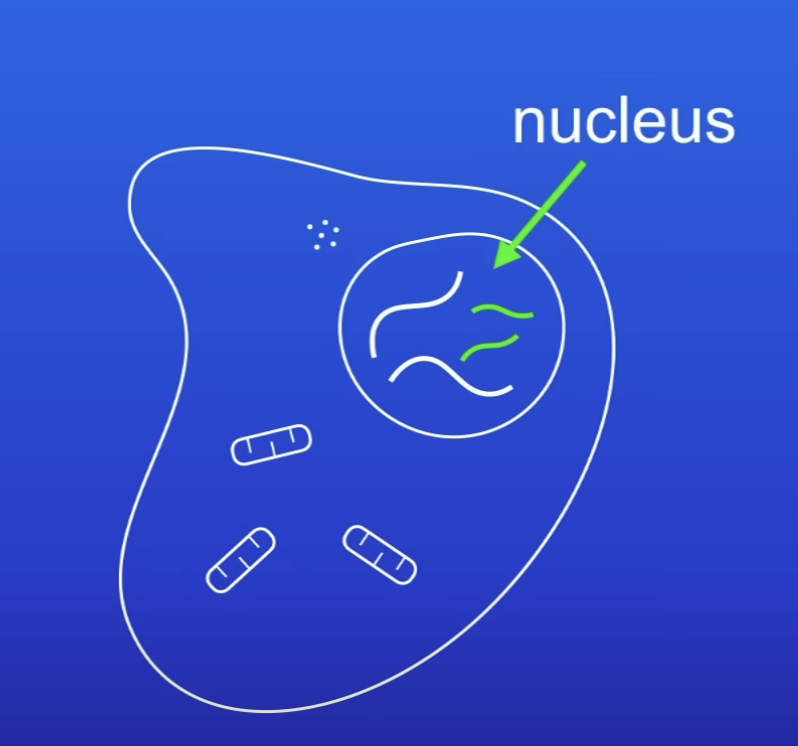
Are chromosomes in body cells single or paired?
Paired
What is special about the chromosomes in gametes?
Not paired
How many chromosomes do human gametes have?
23 single chromosomes
What do chromosomes carry?
Large no. of genes
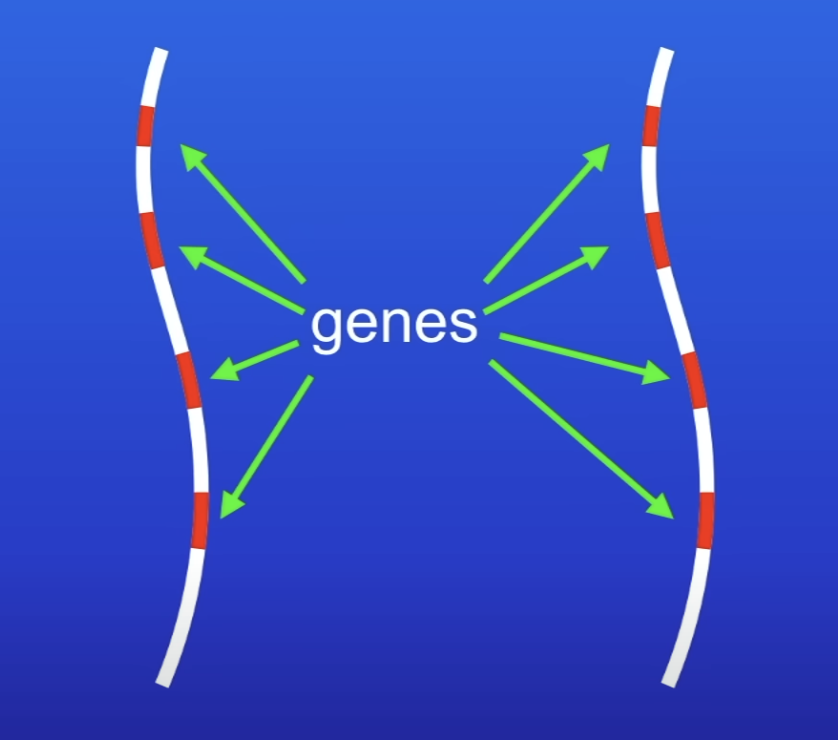
What do genes do?
Determine many of our features
Cell cycle
Series of stages in which cells divide
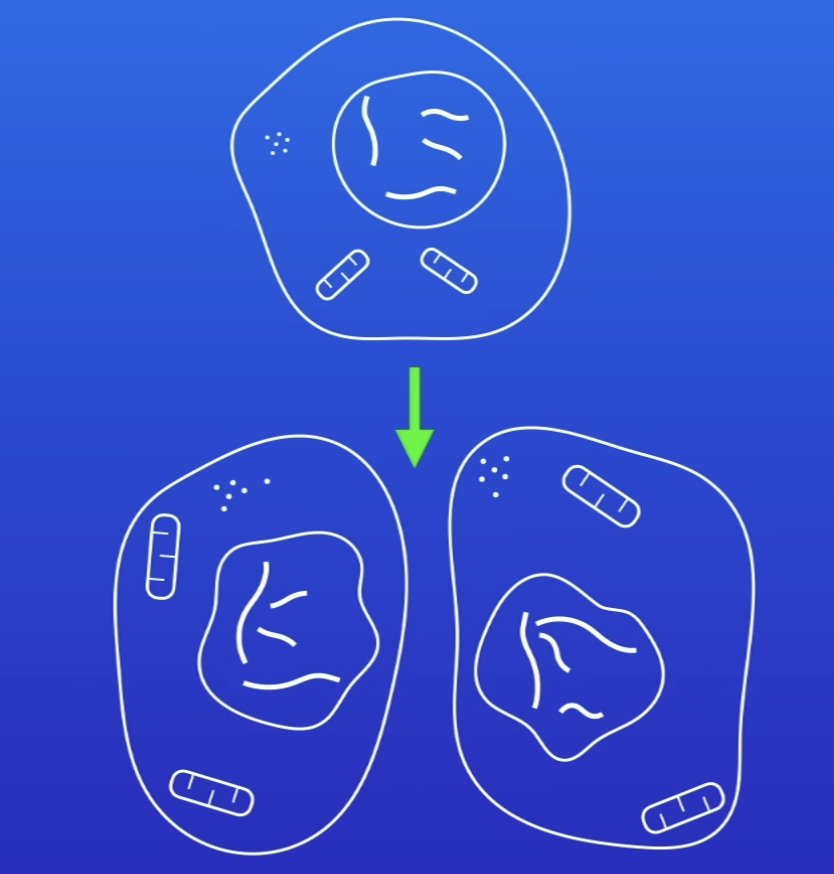
How can cells divide?
Mitosis
Meiosis
How many stages of the cell cycle are there?
3
What happens in the cell cycle in terms of genetic material?
GM doubled
Then divided into 2 identical cells
Stage 1 of the cell cycle
DNA replicates (to form 2 copies of each chromosome)
Cell grows + increases no. of sub-cellular structures (mitochondria, ribosomes)
Stage 2 of the cell cycle
Mitosis
1 set of chromosomes pulled to each end of cell
Nucleus divides
Stage 3 of the cell cycle
Cytoplasm + cell membrane divide to form 2 identical cells
What does mitosis do?
Copy 1 cell into 2
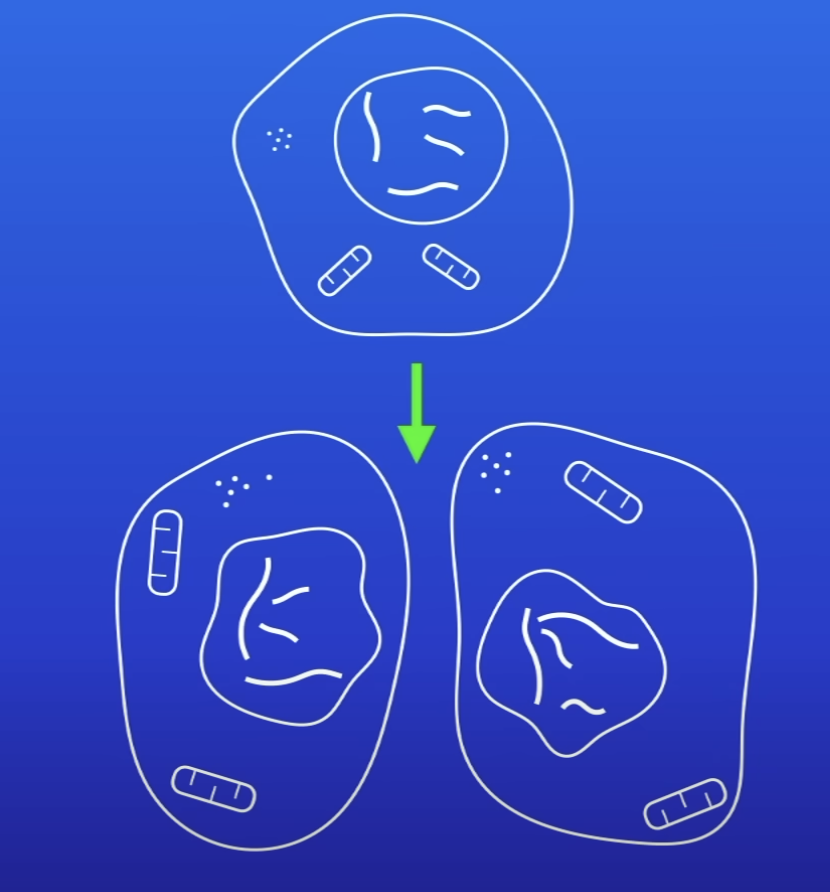
What happens during mitosis?
1 set of chromosomes pulled to each end of cell
Nucleus divides
Are the cells produced by mitosis gentically identical?
Yes
What is cell division by mitosis important for?
Growth + development of multicellular organisms
When does mitosis occur?
When an organism repairs itself
Asexual reproduction
What happens to cells as an organism develops?
Cells differentiate to form different types of cells
When do most types of animal cells differentiate?
Early stage
What is special about a plant cells ability to differentiate?
Most retain the ability to differentiate throughout life
In mature animals, what is cell division restricted to?
Repair
Replacement
A cell differentiates to become?
A specialised cell
What happens as a cell differentiates to become a specialised cell?
Acquires diff sub-cellular structures to enable it to carry out a certain function
Fertilisation
Sperm cell joins with egg cell (ovum)
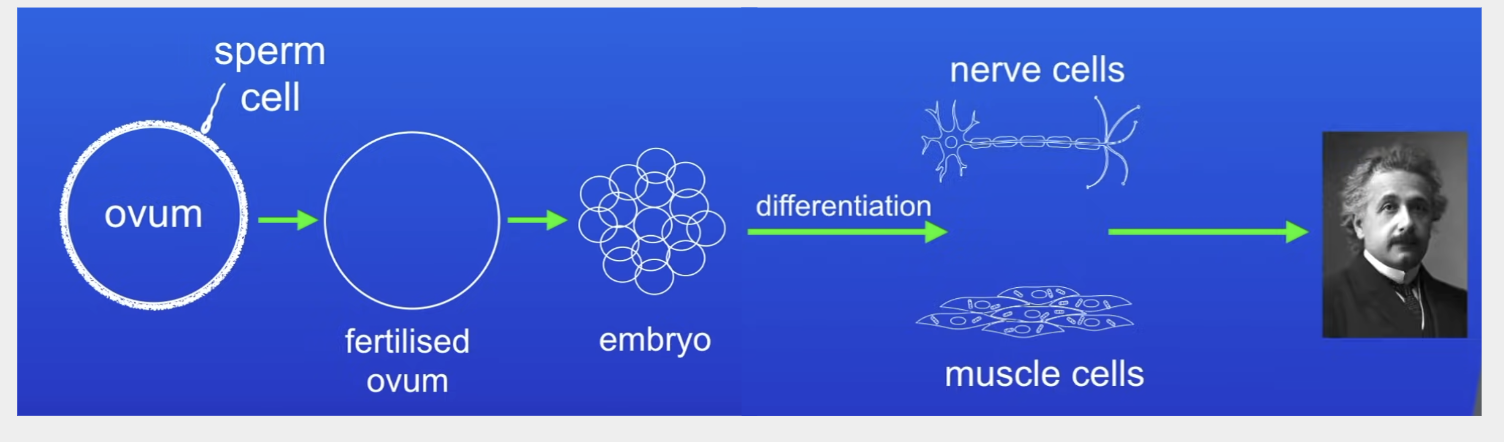
How do humans start?
Fertilisation- sperm cell joins with egg cell = fertilised ovum
Fertilised ovum undergoes mitosis = embryo
Overtime, these cell continue to undergo mitosis + change to form specialised cells
Embryo
Ball of cells
Differentiation
Process of cells becoming specialised
Stem cell
An undifferentiated cell of an organism which can give rise to more cells of the same type + can differentiate to form other types of cells
Where are embryonic stem cells found?
Early stage embryo
Cells are undifferentiated
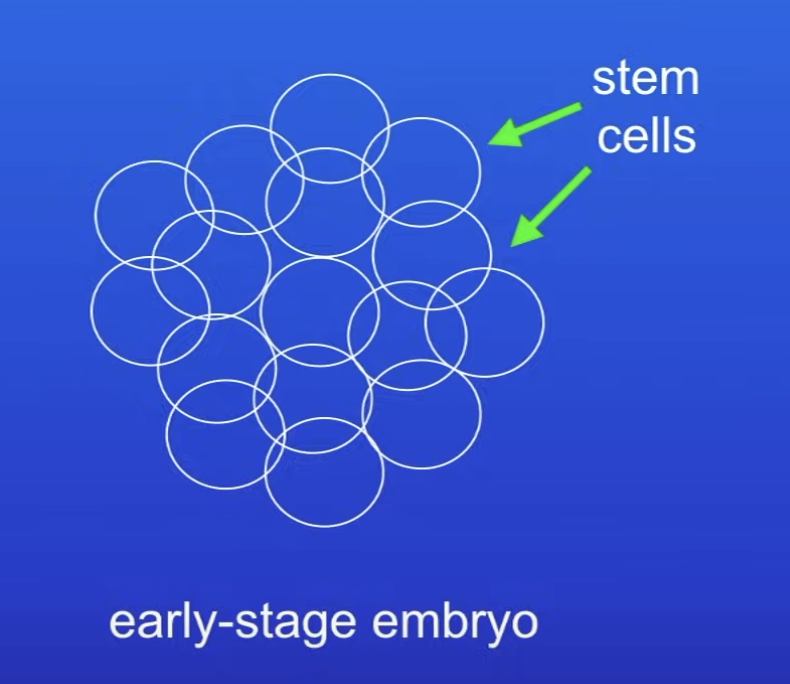
What does it mean if a cell is undifferentiated?
Any cell is capable of differentiating into any type of body cell
Embryonic
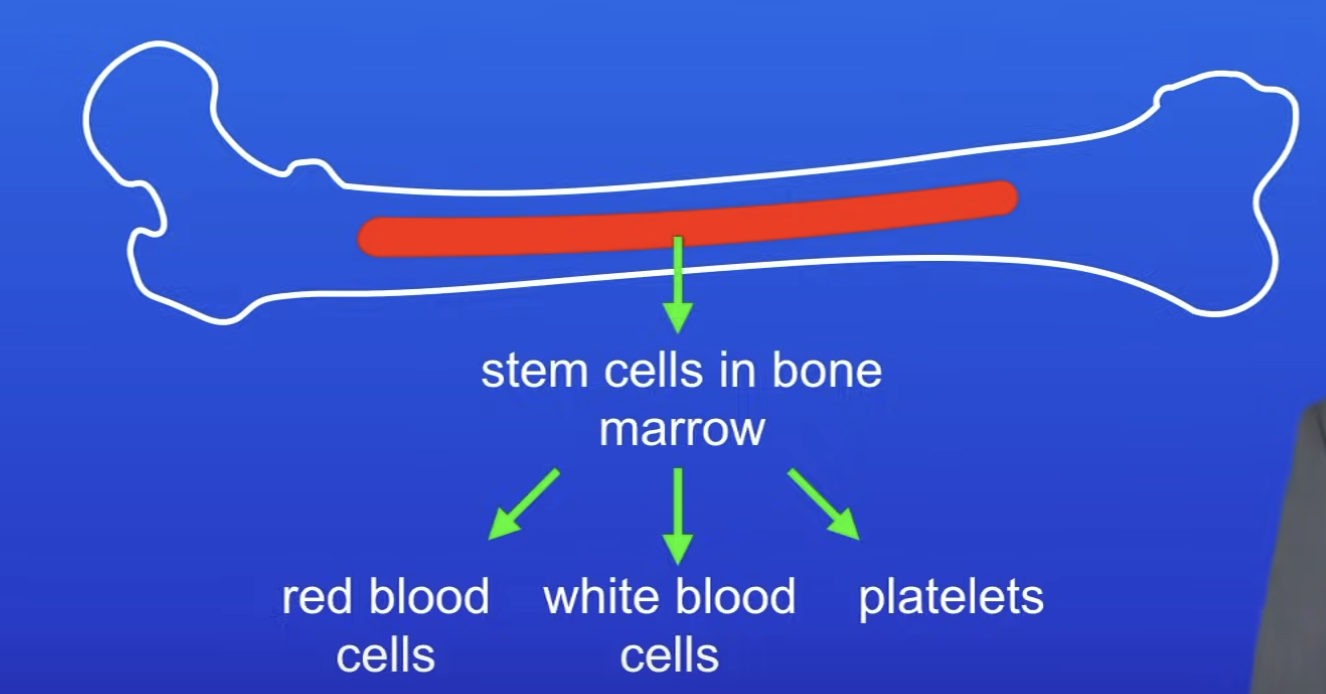
Where are adult stem cells found?
Bone marrow
Adult vs embryonic stem cells
ASC can’t differentiate into any other cell type
What types of body cells can stem cells in adult bone marrow differentiate to form?
Cells found in blood
RBC
WBC
Platelets
What are stem cells used for in medicine?
Bone marrow transplant
Therapeutic cloning
What parts of a plant contain meristem tissue?
Roots
Buds
What is special about the stem cells in meristem tissue in plants?
Can differentiate into any type of plant cell, throughout the life of the plant
What can stem cells from meristems in plants be used to produce?
Clones of plants quickly + economically
What types of plants would farmers want to clone?
Rare plants- prevent from going extinct
Crop plants w special features (disease resistance)
Cloning plants
Producing a large no. of identical plants for farmers by asexual reproduction
Leukaemia
Cancer of bone marrow
Steps of how is leukaemia treated?
Bone marrow transplants
Patient’s existing BM destroyed using radiation
Patient receives BM transplant from donor
Stem cells in BM divide + form new BM
+ they differentiate + form blood cells
Issues with bone marrow transplants
Donor must be compatible with patient
Otherwise WBC produced by donated BM could attack the patient’s body
Risk that viruses can be passed from donor to patient
Why must the donor be compatible with the patient in a bone marrow transplant?
If not, WBC produced by donated BM could attack the patient’s body
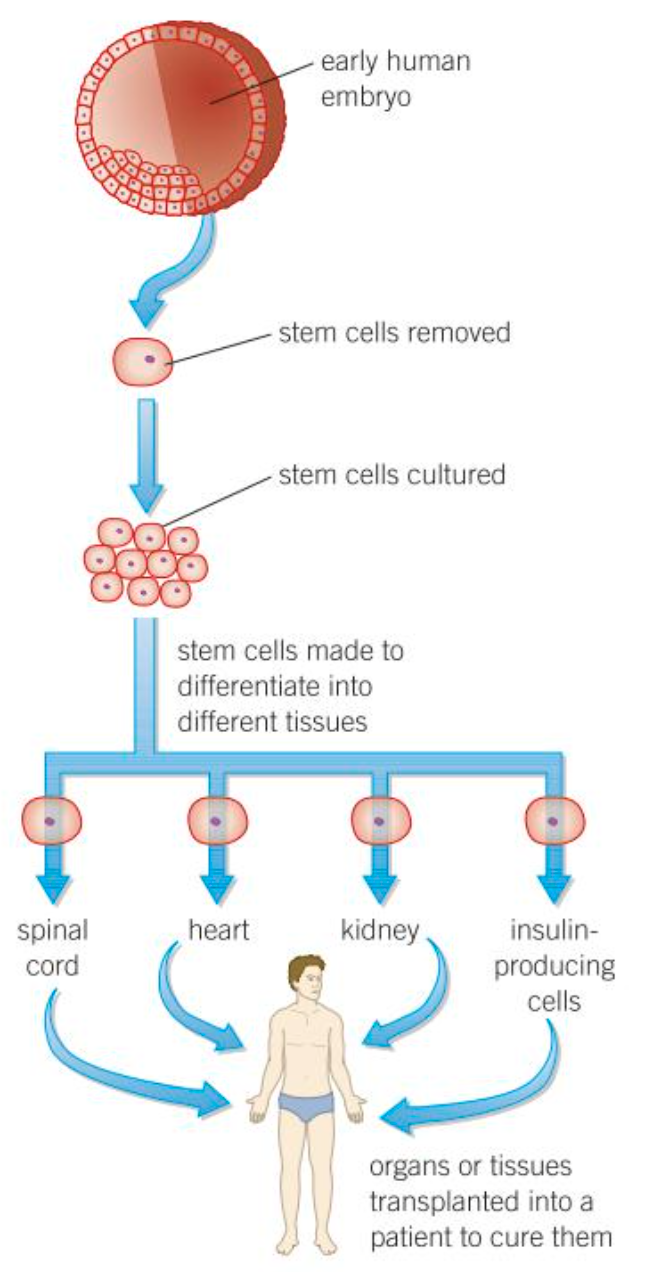
What is produced in therapeutic cloning?
Embryo with same genes as patient
Why is it a pro that therapeutic cloning produced an embryo with the same genes as the patient?
Stem cells from the embryo can be transplanted into the patient w/o being rejected by the patient’s immune system
Embryos produced by therapeutic cloning have the same genes as the patients so…
SC fm the embryo produced aren’t rejected + can be used for medical treatment
What happens after an embryo with same genes as patient is produced in therapeutic cloning?
Once inside the patient, SC differentiate to replace cells that have stopped working correctly
What medical conditions could therapeutic cloning be used to treat?
Diabetes
Paralysis
Cons of the use of stem cells
Potential risks- eg transfer of viral infection
People have ethical / religious objections to the procedure
Cloning
Producing identical offspring
How do bacteria divide?
Binary fission (simple cell division)
What conditions do bacteria need to divide quickly
Enough nutrients
Suitable temp
How often can bacteria divide if they have enough nutrients + a suitable temp?
Once every 20 minutes
What can bacteria be grown in?
A nutrient broth solution
As colonies on an agar gel plate
What is needed for investigating the action of disinfectants + antibiotics?
Uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms
What type of microorganism is bacteria and what does this mean?
Prokaryotes
Genetic info not enclosed in nucleus
What happens in binary fission?
1 bacterial cell splits into 2 bacterial cells
Equation to calculate the no. of bacteria after a given time
2n

Why do scientists need to grow lots of microorganisms in a lab to study them?
MO are v small
What does a nutrient broth solution contain?
All nutrients bacteria need to grow + divide

Why is the nutrient broth cloudy?
Contains large no. of bacteria
What do agar gel plates contain?
Nutrient broth set into a jelly using agar
Poured into petri dish + set
How do bacteria grow in agar gel plates?
In divisible colonies
How to avoid contamination when making nutrient broth solution? Aseptic techniques
Sterilise all Petri dishes, bacterial nutrient broth, agar, inoculating loop → kills unwanted MO + prevents contamination
Transfer bacteria onto dish + attach lid of Petri dish using adhesive tape → stops lid falling of + unwanted MO from entering
Place agar plate upside down into an incubator → stops moisture from dripping down onto bacteria + disrupting colonies
In school labs, cultures should be incubated at 25°C
Why we have to avoid contamination when making nutrient broth solution?
Lots of MO (bacteria, fungi) naturally in environment → could contaminate our culture
Inoculating loop
Used to transfer bacteria into the culture
How do you sterilise an inoculating loop?
Pass it thru a Bunsen burner flame
In school labs, what temp should bacteria cultures should be incubated at?
25°C
In school labs, why are bacteria cultures incubated at 25°C?
Reduces chances that harmful bacteria will grow
Zone of inhibition
Region around antibiotic discs where bacteria haven’t growth