Newton's Laws and Forces
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
force
a push or pull upon an object
balanced force
when forces on an object are of equal magnitude and in opposite directions; no acceleration

unbalanced force
when forces on an object do not cancel out; causes acceleration

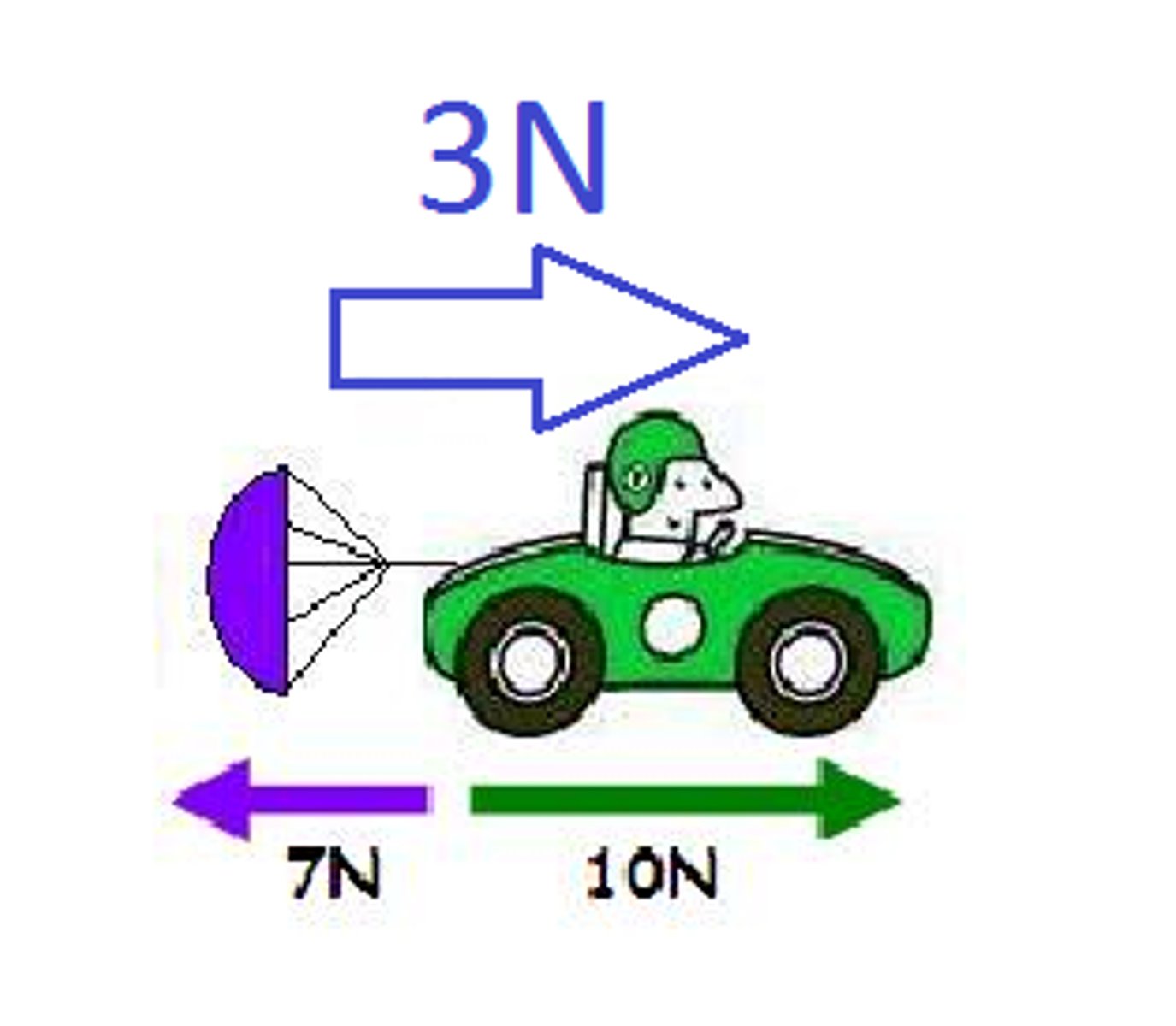
net force
the sum of all the forces acting on an object
friction
a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact

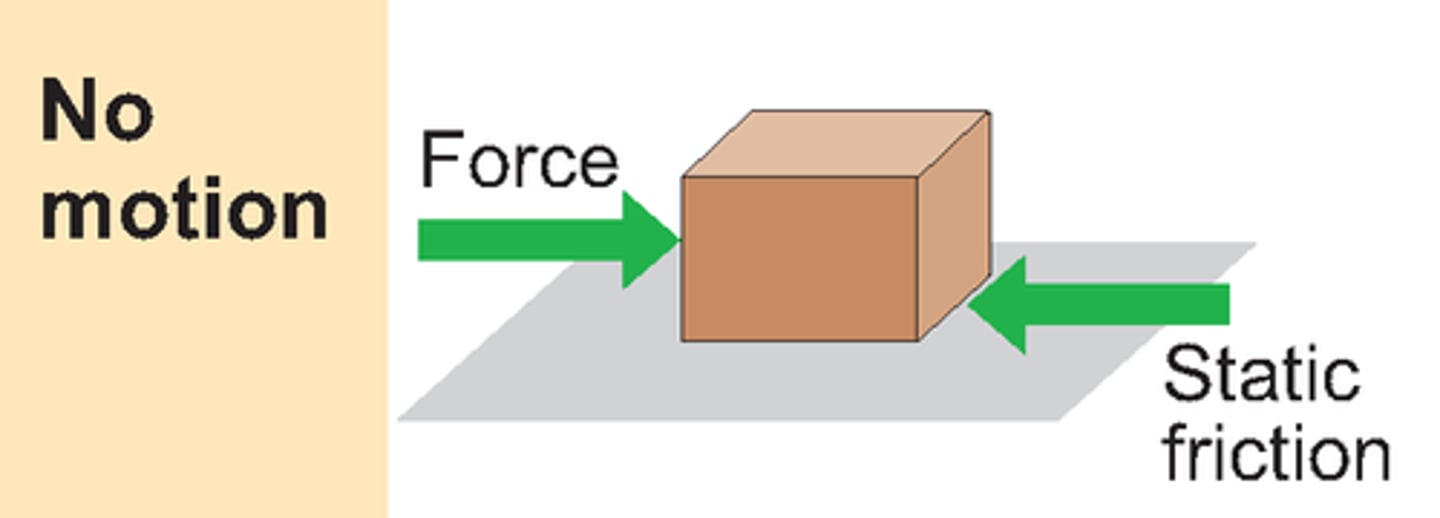
static friction
the force that resists the initiation of sliding motion between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest
inertia
the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion unless an outside force acts on it

weight
the measure of the force of gravity on an object

gravitational force
the attractive force existing between any two objects that have mass

free fall
the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body

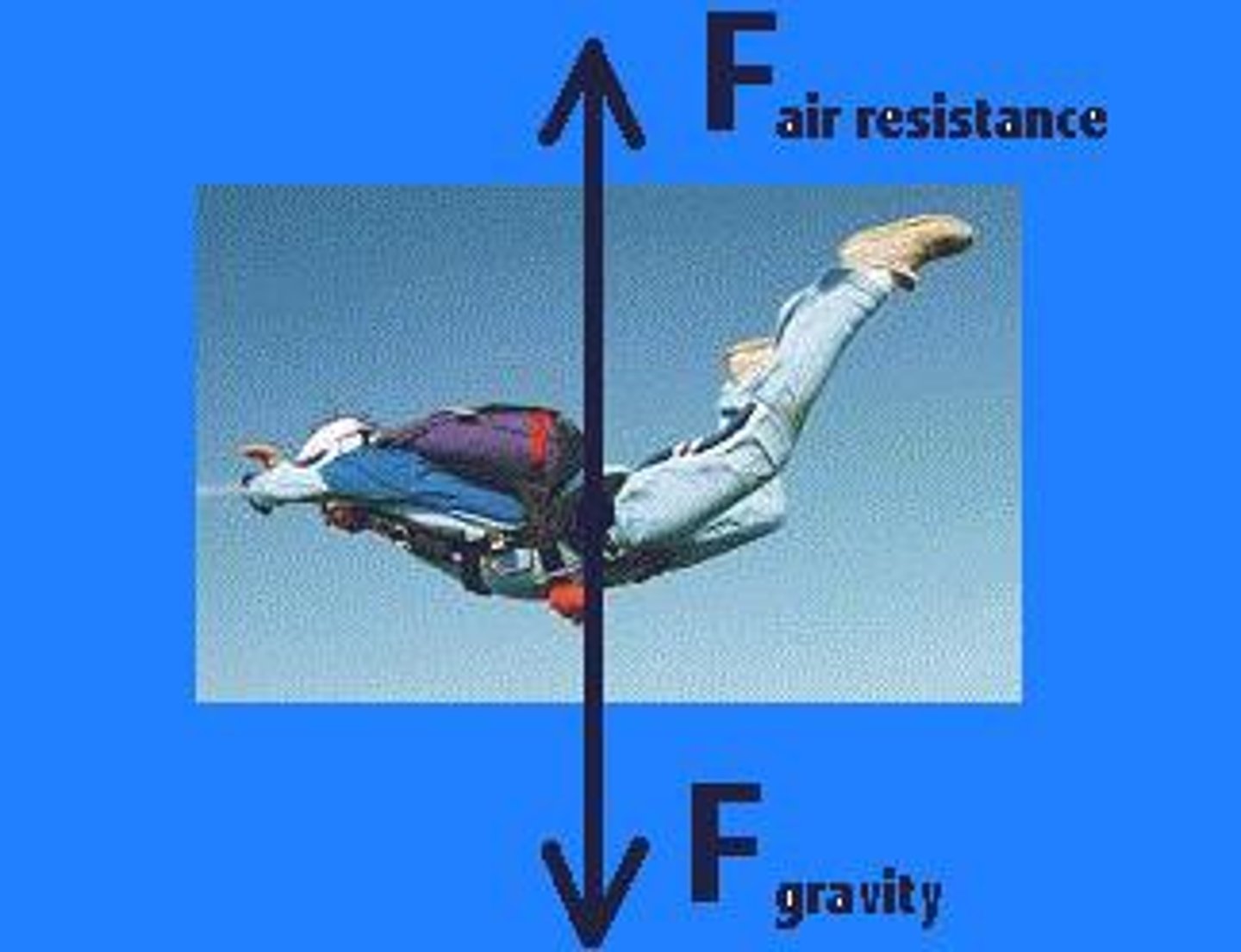
terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity.The maximum velocity a falling object can achieve
Mass
The amount of matter in an object

Newton
A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second

Friction
The force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other

Sliding Friction
Friction that occurs when one solid surface slides over another

Rolling Friction
Friction that occurs when an object rolls over a surface

Momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity

Fluid Friction
Friction that occurs as an object moves through a fluid
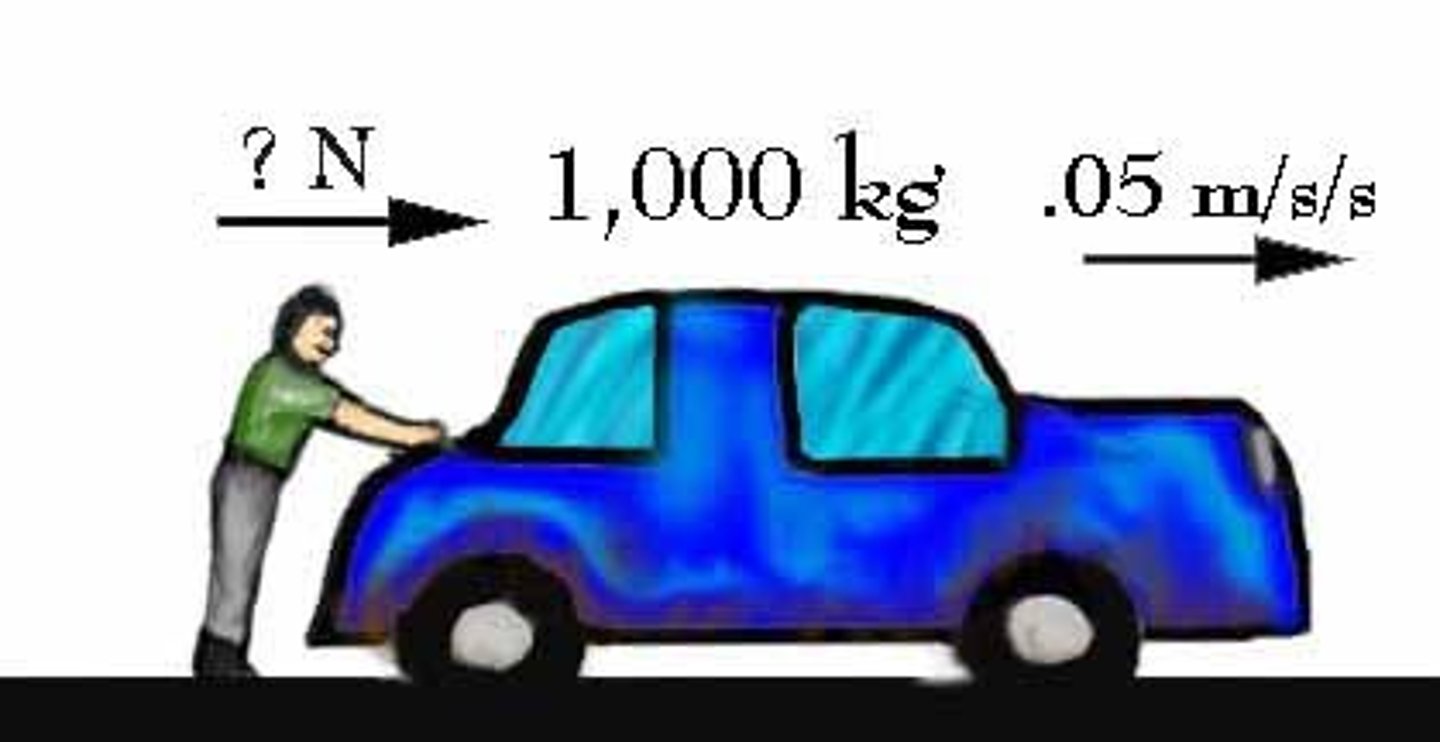
Acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes
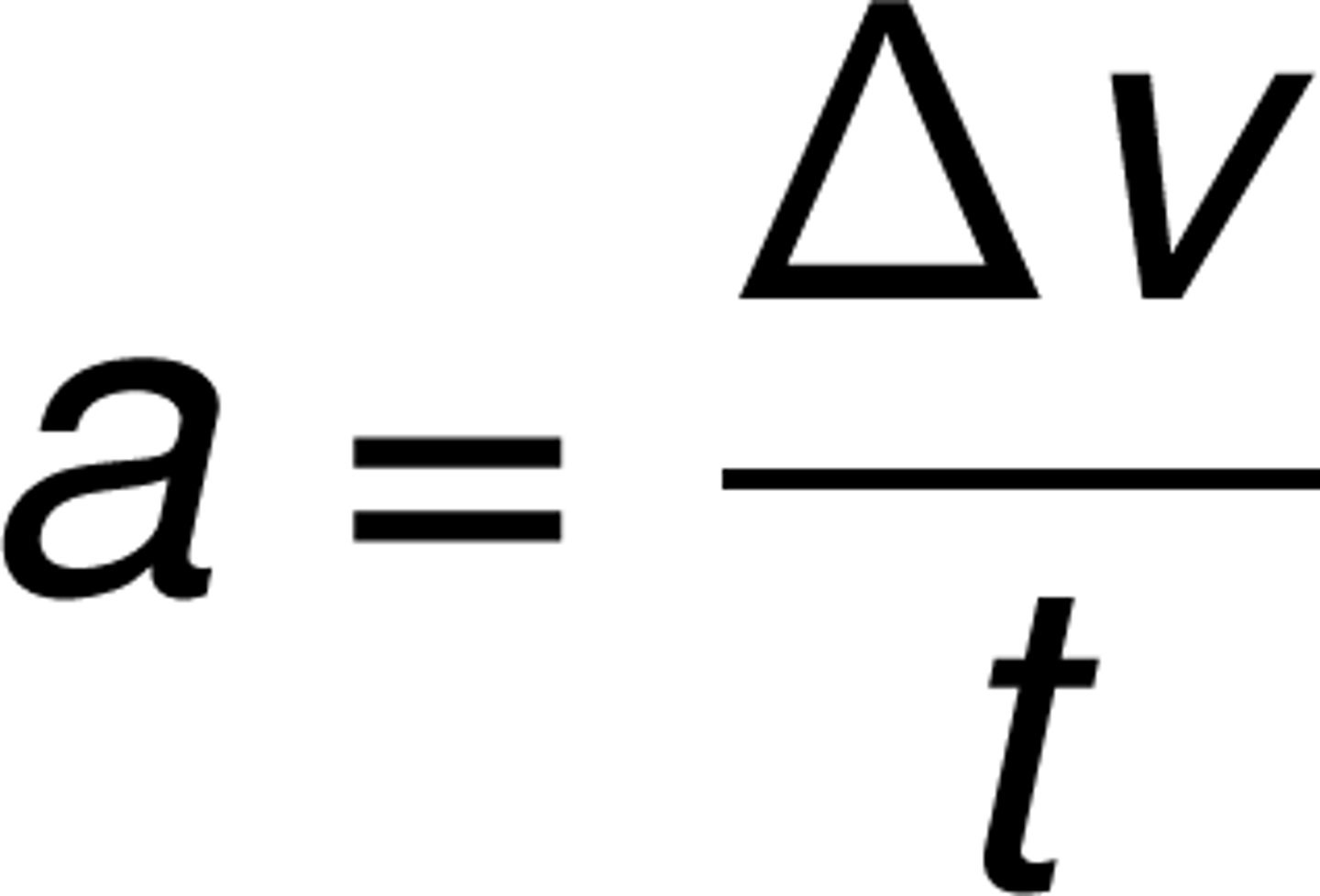
You are riding a bike, you hit a rock and you fly off the bike into the mud in front of the bike.
1st Law
It is harder to stop a train than a car if both are going 50 miles per hour.
2nd Law
A rocket is pushed into space by the burning fuel.
3rd Law
Brian, age 5, and his dad are skipping pebbles on the pond. The pebbles that Brian's dad throws goes farther and faster than his.
2nd Law
As the bus makes a sharp right turn you lean to the left.
1st Law
A gun recoils (moves backward) when fired.
3rd Law
The harder you hit a golf ball the faster it moves.
2nd Law
It takes more force to lift and carry your backpack than just your notebook.
2nd Law
Friction between the sand and a surfboard stops the surfboard.
1st Law
You are riding a horse and it stops suddenly causing you to fly off the front of the horse.
1st Law
The air from a balloon pushes out one way causing the balloon to go the opposite way.
3rd Law
After you start up your motorbike, as you give it more gas, it goes faster.
2nd Law
As an ice skater pushes harder with his leg muscles, he begins to move faster.
2nd Law
When you paddle a canoe, the canoe goes forward.
3rd Law
A child pulling a sled stopped to pull on her hat. The sled kept moving and hit her in the back of her legs.
1st Law
Baylee falls off his skateboard. He comes to a crashing stop against the sidewalk, but his skateboard rolls on.
1st Law
When you walk, you push on the floor and the floor pushes back.
3rd Law
Jessica's little sister isn't swinging very high, so she gives her a huge push to get her higher.
2nd Law
An athlete can throw a baseball farther than a shot put.
2nd Law
Christian's science book sits on his desk until he opens it.
1st Law
When Grace throws a basketball it is pulled down into the basket by gravity instead of travelling in a straight line.
1st Law
An astronaut in the Space Shuttle pushes against the wall and this forces him backwards.
3rd Law
When a tablecloth is pulled out from underneath a set of dishes, the dishes remain on the table.
1st Law
A swimmer pushes water back with her arm, but her body moves forward.
3rd Law
Vector
A quantity that has magnitude and direction
Resultant Force
The sum of vectors
Normal Force (Fn)
for that is always perpendicular to the surface that applies it
Tension (Ft)
the pull exerted by a string, rope, or cable when attached to a body and pulled taut
Newton's First Law (Law of Inertia)-Definition
An object in motion (or at rest) will tend to stay in motion (or at rest) until it is acted upon by an outside force.
Newton's Second Law of Motion-Definition
The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied.
Newton's Third Law-Definition
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Free Body Diagram (FBD)
a simple drawing of an object showing all the forces that are acting on it
Vector
A quantity that has magnitude and direction
Applied Force (Fa)
A force that results when one object makes contact with another and pushes or pulls on it
centripetal force
A force that causes an object to move in a circle
magnitude
Greatness of size or strength
Gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.

weightlessness
Free from the effects of gravity. An object's apparent weight of zero results when there are no contact forces pushing up on the object.

air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air

force pair
The action and reaction pair of forces that occur in an interaction. They do NOT cancel out.