Appendicular Skeleton
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANP1106A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
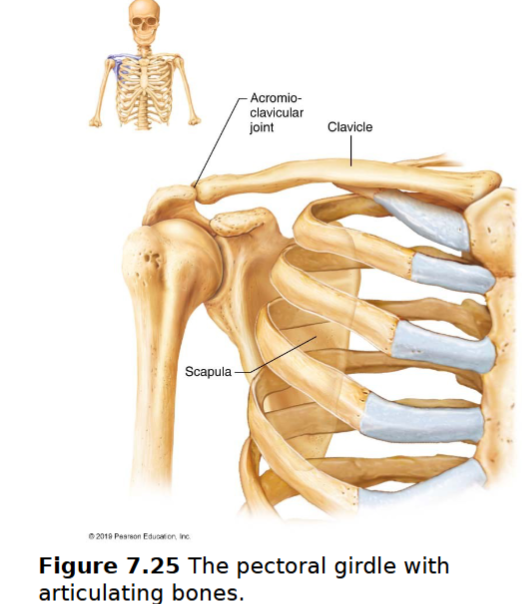
Pectoral girdle
2 pairs of bones: clavicles & scapulae almost a complete circle around upper trunk
bones are light & very movable- because scapulae only attached laterally- not attached to the axial skeleton
socket of shoulder joint (glenoid cavity) is shallow & poorly reinforced
attachment points of muscles that move upper limbs
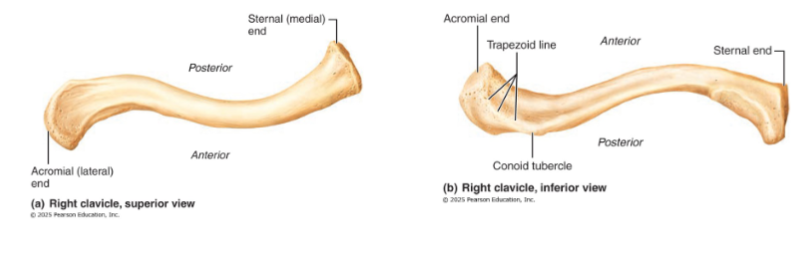
Clavicles
collarbones
mildly S-shaped sternal end articulates with the sternum (curvature ensures outward fracture, away from subclavian artery)
Flattened acromial end articulates laterally with scapula
sternal end articulates with manubrium
insertion points for muscles, also a brace to push arms laterally
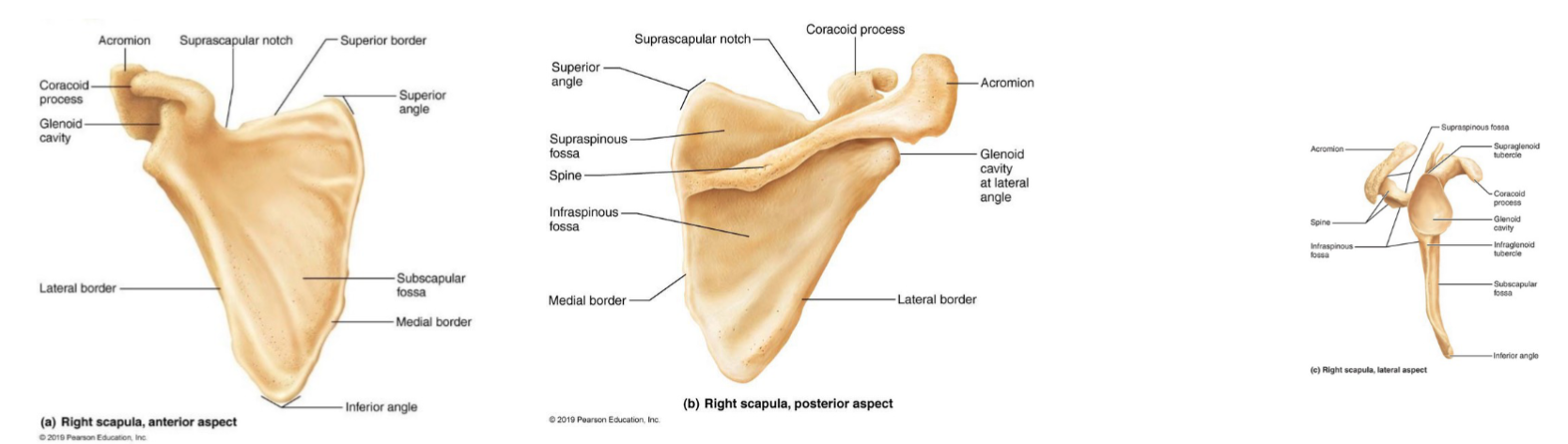
Scapulae
shoulder blades
thin, triangular, irregular bones
dorsally, between ribs 2 & 7
Each has 3 borders:
superior
medial
lateral - near armpit, ends superiorly in glenoid cavity fossa (shoulder joint)
Several large fossae, named according to location
spine
acromion
lateral projection that articulates with acromial end of clavicle
number of muscles attach here as well
coracoid process
For biceps muscle
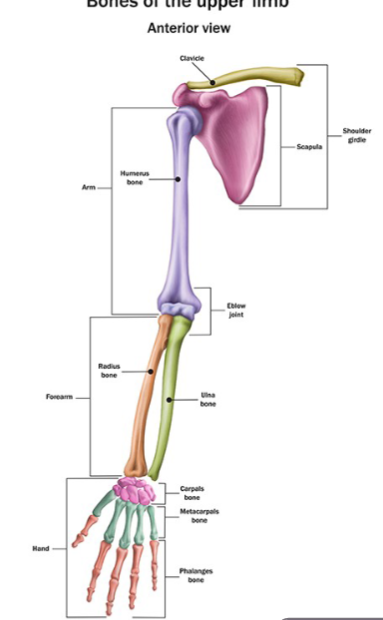
Upper Limb
30 bones form skeletal framework of each upper limb
Arm
Humerus
Forearm
Radius and ulna
Hand
8 carpal bones in the wrist
5 metacarpal bones in the palm
14 phalanges in the fingers
Upper Limb
Humerus
Forearm
Ulna
Radius
Humerus
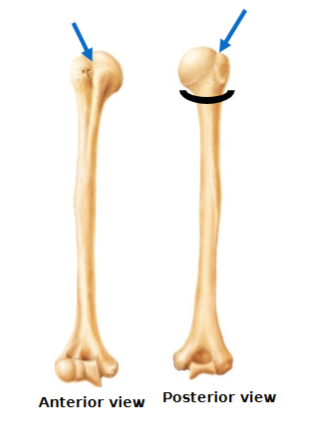
longest, largest bone of upper limb and the only bone of the arm articulates with scapula, radius & ulna
Head - inserts into the glenoid cavity
Anatomical neck vs surgical neck
surgical neck (black semicircle) is below the greater and lesser tubercle and it more commonly fractured
Greater & lesser tubercle separated by the intertubercular sulcus (groove)
Deltoid tuberosity
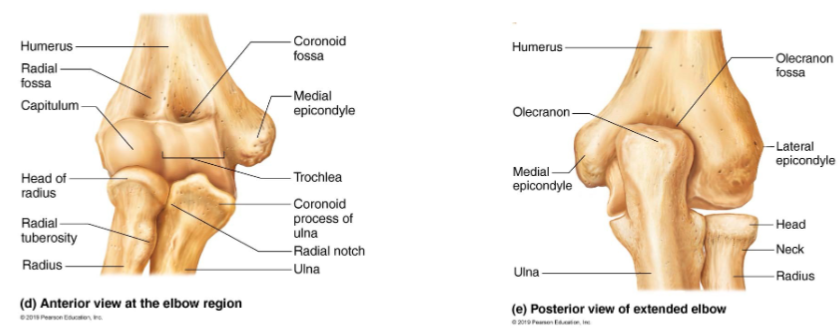
Fossae: olecranon (elbow bone), coronoid and radial
Two condyles:
Trochlea articulates with the ulna
Capitulum articulate with the radius
Two epicondyles
point of attachment for muscles to allow movement of fingers
Medial and lateral
Note: the ulnar nerve behind medial epicondyle (nerve that gets irritated when you hit the ‘funny bone’)
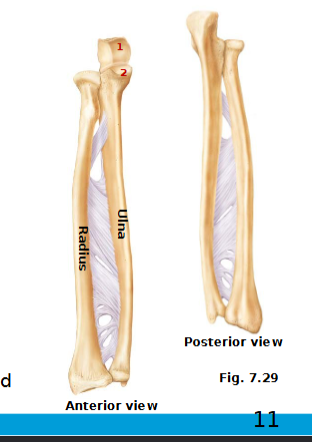
Forearm
parallel long bones: radius & ulna
Articulates with
Humerus (proximal) & wrist bones (distal)
with each other at superior & inferior radio-ulnar joints
What is the interosseous membrane
white structure, a fibrous sheath of CT that spans length of the bones. It holds them together, limiting their movement
Ulna (elbow joint)
slightly longer than radius
olecranon & coronoid processes
locking of olecranon prevents elbow hyperextension
radial notch on coronoid process
Styloid process: ligaments to the wrist
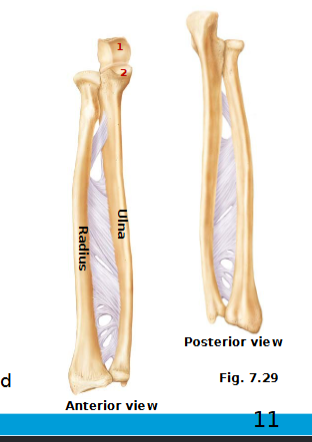
Radius(Wrist joint)
head at proximal end
distal end at the wider end
distal end has medial ulnar notch & lateral styloid process
Articulation at the elbow
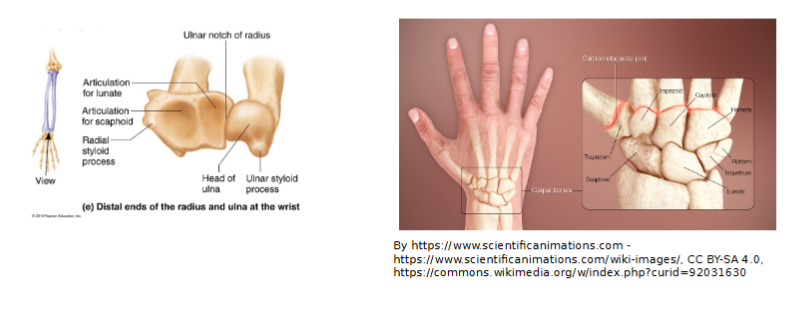
Hand
27 bones
includes bones of carpus, metacarpus and phalanges
Carpus (wrist)
8 carpal bones in two rows
Proximal row:
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform (“So Long To Pittsburgh” )
Distal Row
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
(“Time To Call Home” )
Only scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum form the wrist join
(“Sally Left The Party To Take Cathy Home)
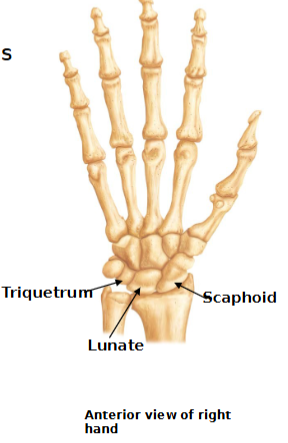
Carpus
wrist
8 carpal bones in two rows
Proximal row:
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform (“So Long To Pittsburgh” )
Distal Row
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
(“Time To Call Home” )
Only scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum form the wrist join
(“Sally Left The Party To Take Cathy Home)
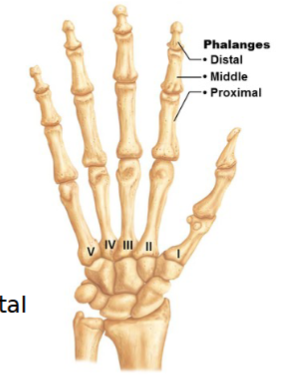
Metacarpals
5 long bones - distal ends are knuckles
numbered I - V from thumb to little finger
Bases articulate with carpals, and heads articulate with proximal phalanges
Phalanges (fingers)
numbered I-V from thumb to little finger
Miniature long bones - phalanges
Digits II to V has 3 bones: proximal, middle & distal phalanx
Digit I (pollex) has 2 bones
Pelvic girdle
Two hip bones (each also called coxal bone or os coxae); form a complete circle
left & right coxal bones unite with each other anteriorly & with sacrum posteriorly
attach the lower limbs, transmits weight of upper body to lower limbs; support pelvic organs
Each os coxa consists of 3 bones that fuse at puberty: ilium, ischium, pubis
Acetabulum is area where all 3 bones join »» forms socket of hip joint
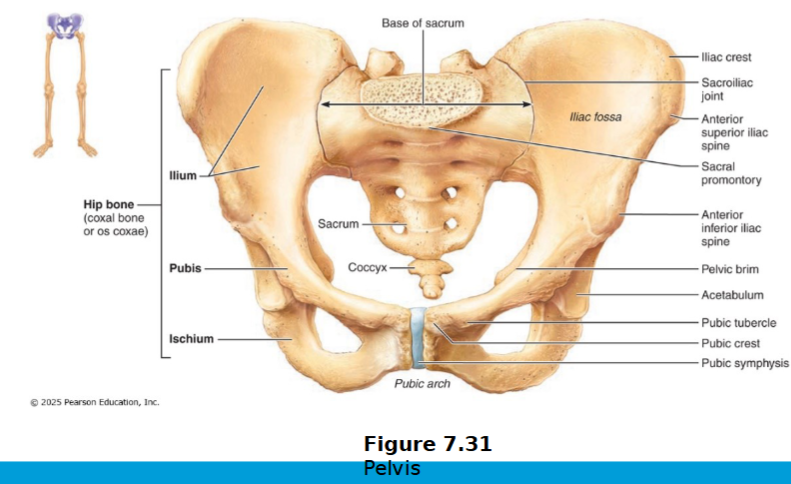
Pelvic girdle: ilium
large flaring bone that forms most of os coxa
iliac crest (superior border); iliac spines (attachment of muscles)
Greater sciatic notch
Auricular surface: connects to sacrum to make sacral ilium
anteriorly, the body of the ilium joins the ischium and the pubis
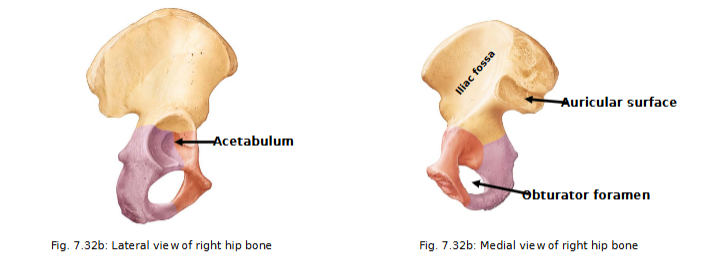
Ischium
postero-inferior part of hip bone
thicker superior body joining ilium and thinner, inferior ramus (joins the pubis)
ramus= bar of bone
What is Ischial tuberosity?
supports your weight while sitting and is supported by ischial tuberosity
Pubis
anterior part of ox cosa
Consists of the body and superior and inferior pubic rami
2 pubic bones unite at pubis symphysis
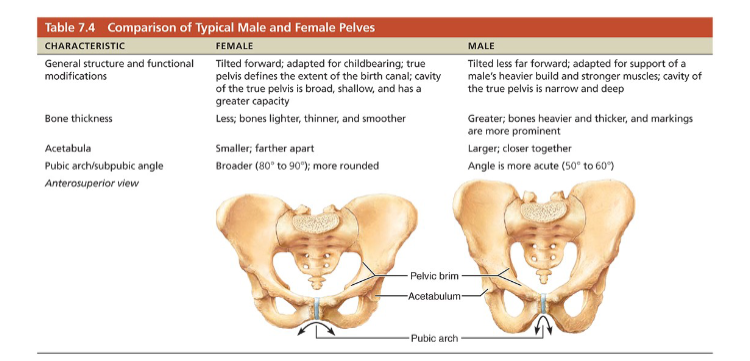
Pelvic structure and childbearing
Female pelvis tends to be wider, shallower, lighter, and rounder than male’s
Adapted for childbearing
Pelvic brim
the bony rim (pelvic inlet) that separates the upper "false pelvis" (part of the abdomen) from the lower "true pelvis" (the actual pelvic cavity)
True pelvis: inferior to pelvic brim; defines birth canal
Pelvic outlet: inferior margin of true pelvis
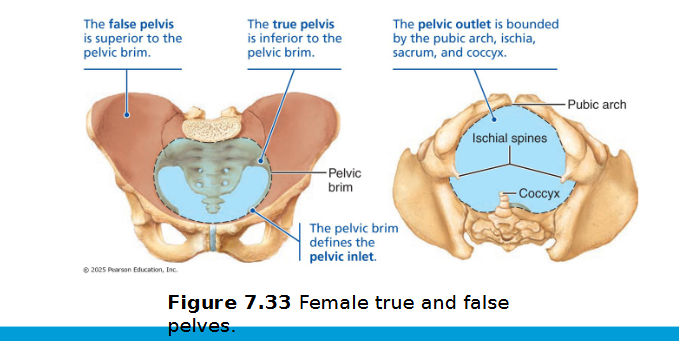
Comparison of male and female pelvis
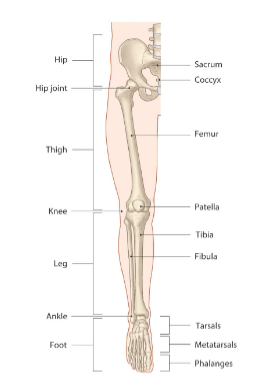
Lower limb
Carries entire weight of erect body
Subjected to exceptional forces during jumping or running
Three segments of lower limb
Thigh
Leg
Foot
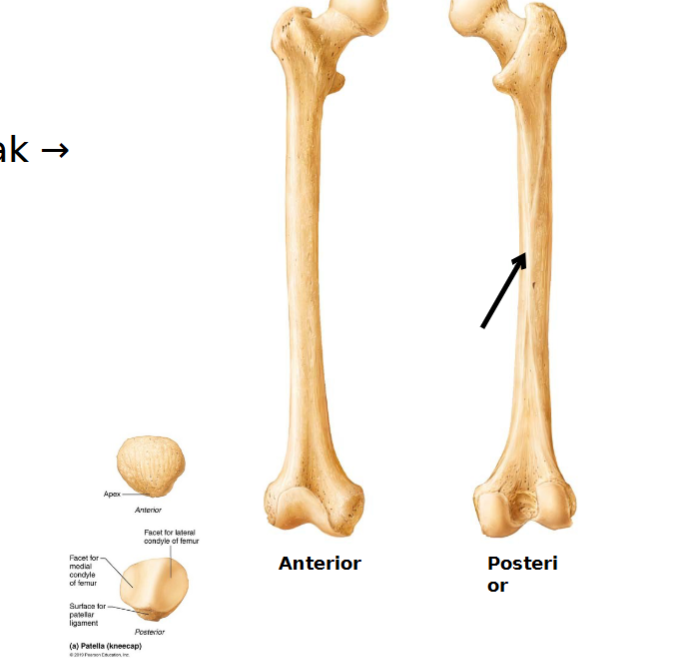
Thigh
Femur is the largest, strongest and longest bone in the body making up about ¼ of a person’s height.
Articulates proximally with acetabulum of hip and distally with tibia and patella
Fovea capitis
Head and neck
neck (angles laterally to shaft; weak → fractures)
Greater and lesser trochanters: site for muscle attachment
Linea aspera: roughened ridge on surface of femoral shaft; site for muscle attachment
Distally
Lateral & medial condyles (attachment site for joint)
articulate with tibia
Lateral & medial epicondyles
Sites of muscle attachment
Patellar surface (between condyles)
patella site in between it
Lower limb: leg
2 parallel bones: tibia & fibula connected by interosseus membrane and proximal & distal tibiofibular joints (rigid)
fibula not contributor to knee join
Tibia
next largest & strongest bone
receives weight from femur & transfers it to foot
medial bone of the leg
medial & lateral condyles
tibial tuberosity (patellar ligament): insertion point for tendons of quadricep muscles
Medial malleolus
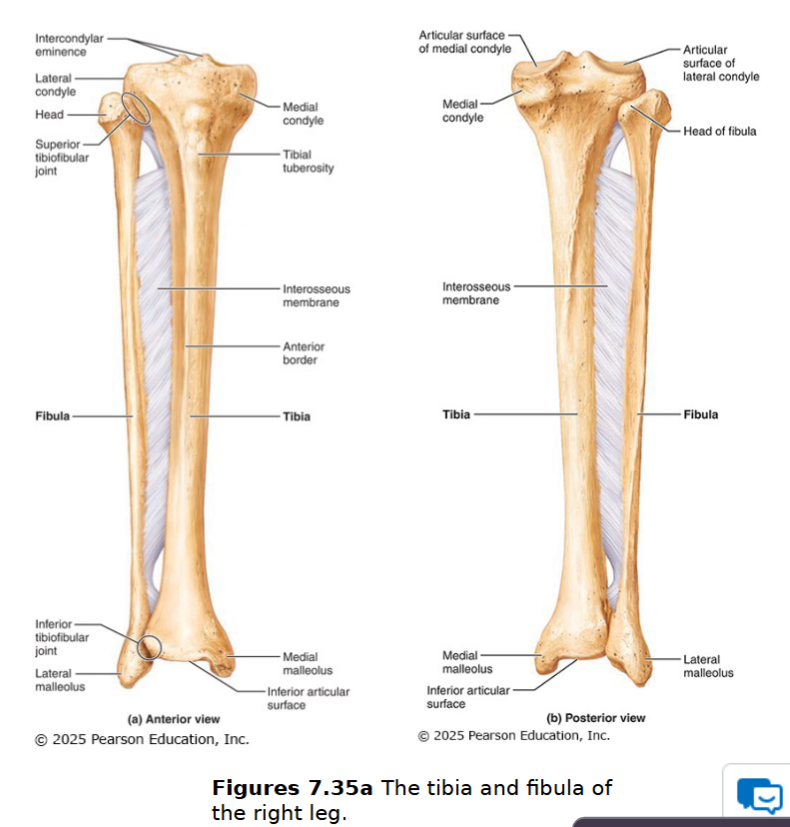
Fibula
not weight bearing/no articulation with femur
head
lateral bone of leg
Lateral malleolus
Lower limb: foot
total of 26 bones: tarsus (ankle bone), metatarsus & phalanges
Tarsus
7 tarsal bones
cuboid, navicular, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform, talus and calcaneus
largest is the calcaneus (heel bone) and second largest is the talus (part of ankle joint).
talus connects to tibia, which is weight of upper body is transferred
these two primarily carry the weight of the body
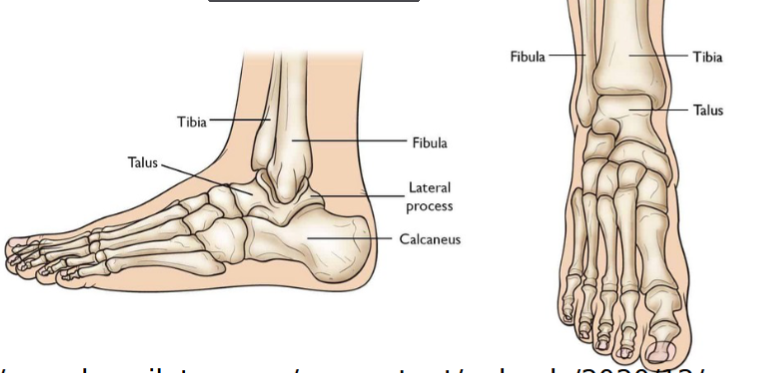
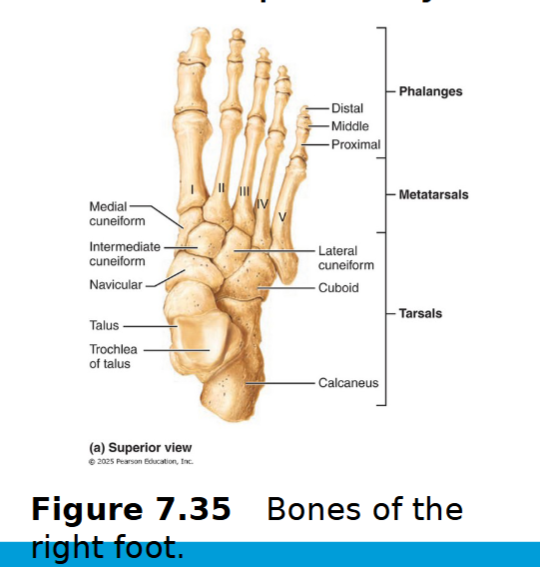
Metatarsus
5 miniature long bones numbered I-V from the hallux to the little toe
hallux: has only proximal and distal end
Phalanx~single, phalanges~ plural
naming a bone: position AND what toe or finger it is
in numbering of phalanges of upper limb, number from pinky to pollex (medial to lateral)
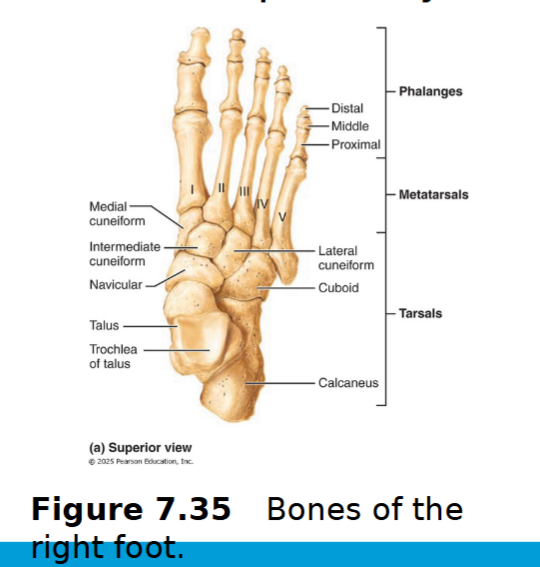
Phalanges of lower limb
14 bones of toes
Digit I (hallux) has two
Digits II to V have 3 bones - proximal, middle & distal phalanx
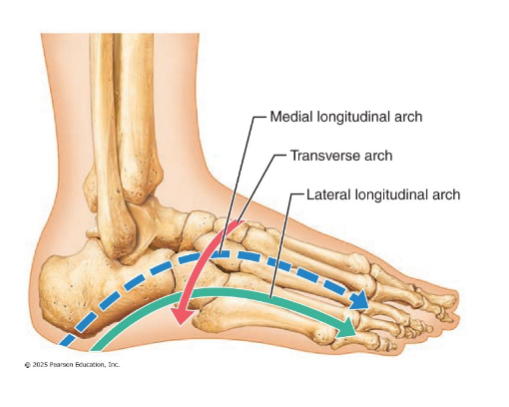
Arches of the foot
Maintained by interlocking foot bones, ligaments, and tendons
Allow foot to bear weight
Three arches
flat foot= collapse of medial and longitudinal arche, walking = overpronation=foot rolls inward too much
arches too high cause stress on lateral structures
plantar fasciitis: band of tissue runs along
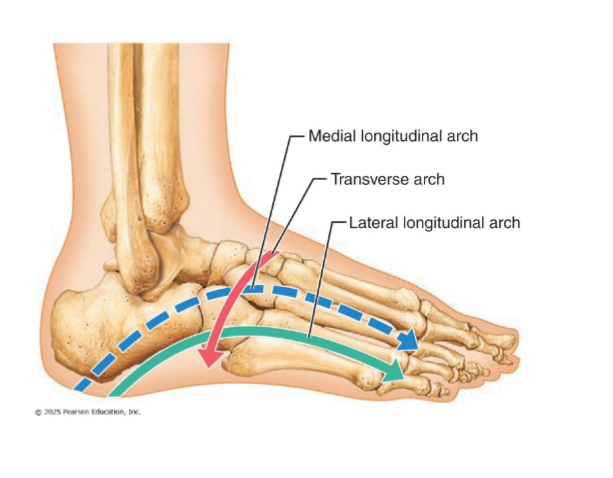
3 arches of the foot
Lateral longitudinal: low curve that elevates lateral part of foot
Medial longitudinal: arch curves upward
Transverse: runs obliquely from one side of foot to other