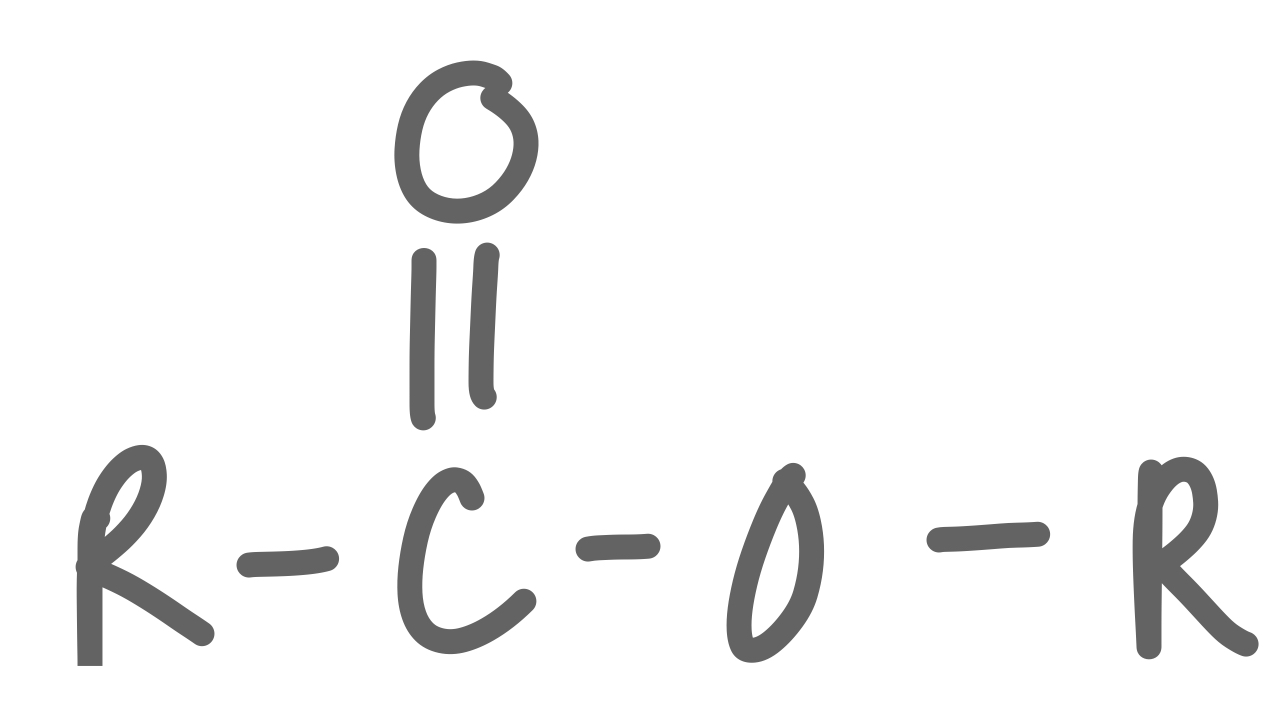GENCHEM 2: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:51 AM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
5 branches of Chemistry
Physical, Analytical, Inorganic, Organic, Biochemistry
2
New cards
Inorganic Chemistry
A chemical compound that **lacks** carbon–hydrogen bonds
3
New cards
Organic Chemistry
* Has **at least one** carbon to hydrogen bond
* Study of carbon and its compounds
* Study of organic compounds
* Study of carbon and its compounds
* Study of organic compounds
4
New cards
Vitalism Theory
* Organic compounds can only be synthesized by organic matter
* Debunked by Friedrich Wohler
* Debunked by Friedrich Wohler
5
New cards
Friedrich Wohler
* Created Urea
* first to synthesize an organic compound from an inorganic substance
* first to synthesize an organic compound from an inorganic substance
6
New cards
Properties of Carbon
Tetravalency and Catenation
7
New cards
Tetravalent
Property of carbon that states that carbon should always have 4 bonds
8
New cards
Catenation
Property of carbon that states that an element can bond with the same element
9
New cards
Carbon
* most stable element
* can form a chain/cyclic structure
* has 2 properties: tetravalent and catenation
* can form a chain/cyclic structure
* has 2 properties: tetravalent and catenation
10
New cards
Isomers
* Compound with same molecular formula but different structure
* not ideal for organic chemistry
* not ideal for organic chemistry
11
New cards
Types of Chemical Structures
Skeletal structure, Condensed structure, Line-bond structure
12
New cards
Functional Groups
Group of atoms that give chemical properties to an organic compound
13
New cards
Hydrocarbon
* hydrogen and carbon only
* can be saturated (ALKANE) or unsaturated (ALKENE & ALKYNE)
* can be saturated (ALKANE) or unsaturated (ALKENE & ALKYNE)
14
New cards
Meth-
1 carbon
15
New cards
Eth-
2 carbon
16
New cards
Prop-
3 carbon
17
New cards
But-
4 carbon
18
New cards
Pent-
5 carbon
19
New cards
Hex-
6 carbon
20
New cards
Hept-
7 carbon
21
New cards
Oct-
8 carbon
22
New cards
Non-
9 carbon
23
New cards
Dec-
10 carbon
24
New cards
Alkyl Halide
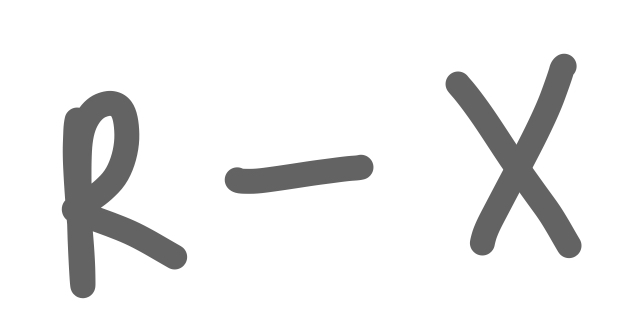
25
New cards
Alcohol
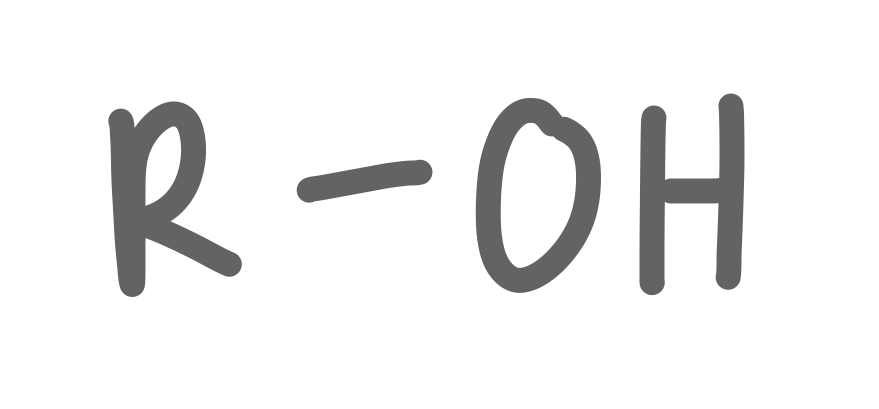
26
New cards
Ether
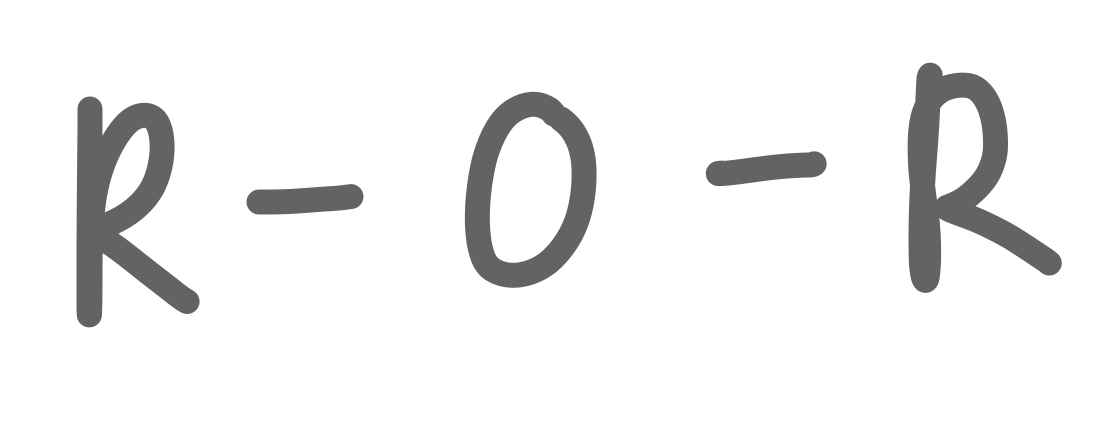
27
New cards
Amine

28
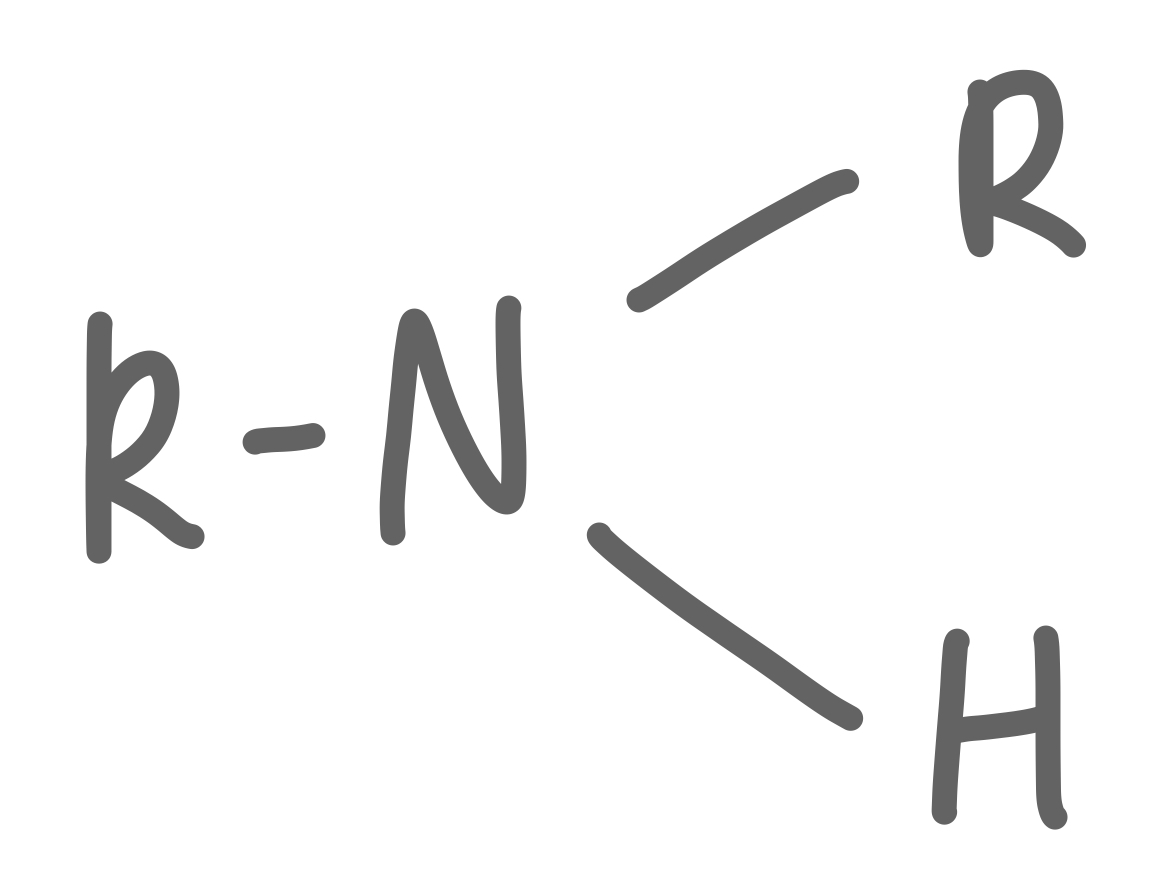
New cards
Secondary Amine
29
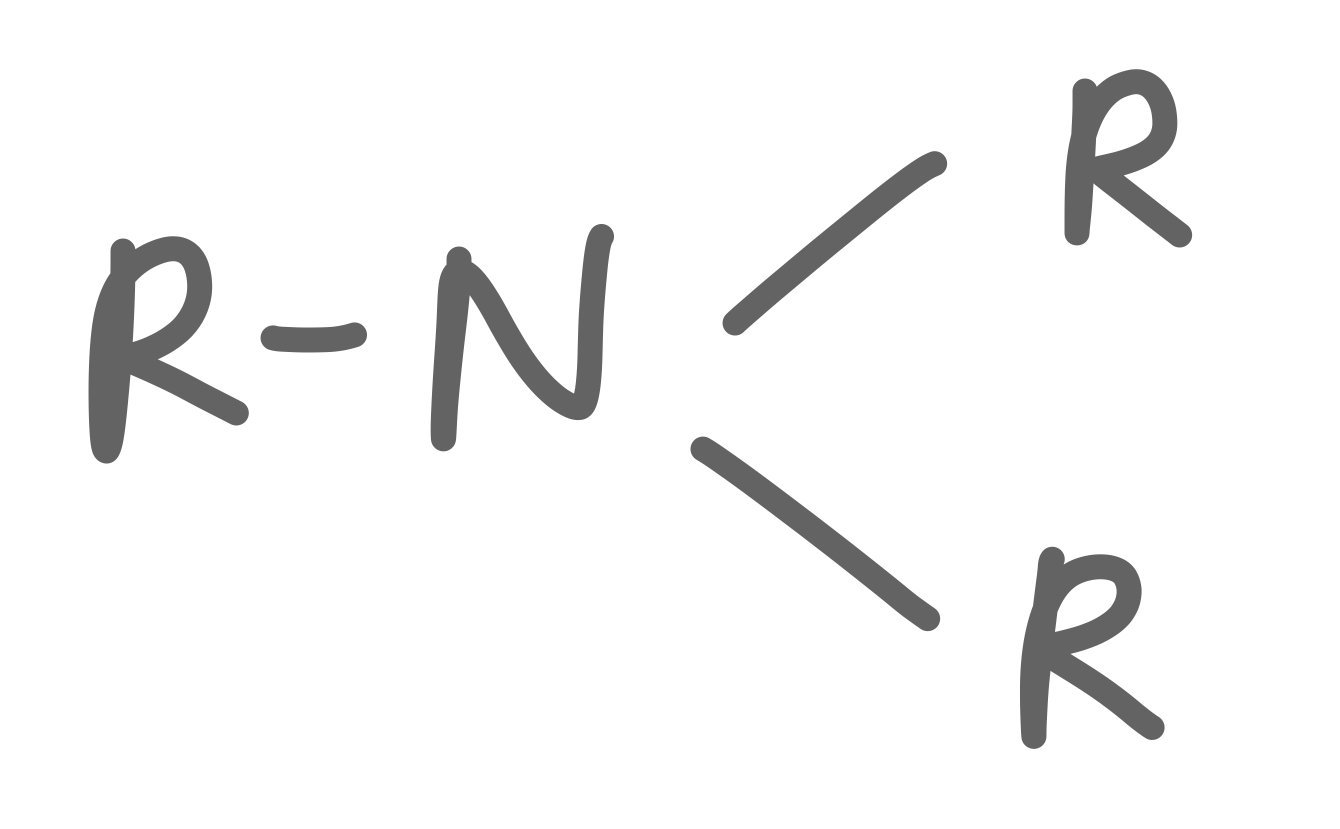
New cards
Tertiary Amine
30
New cards
Amide
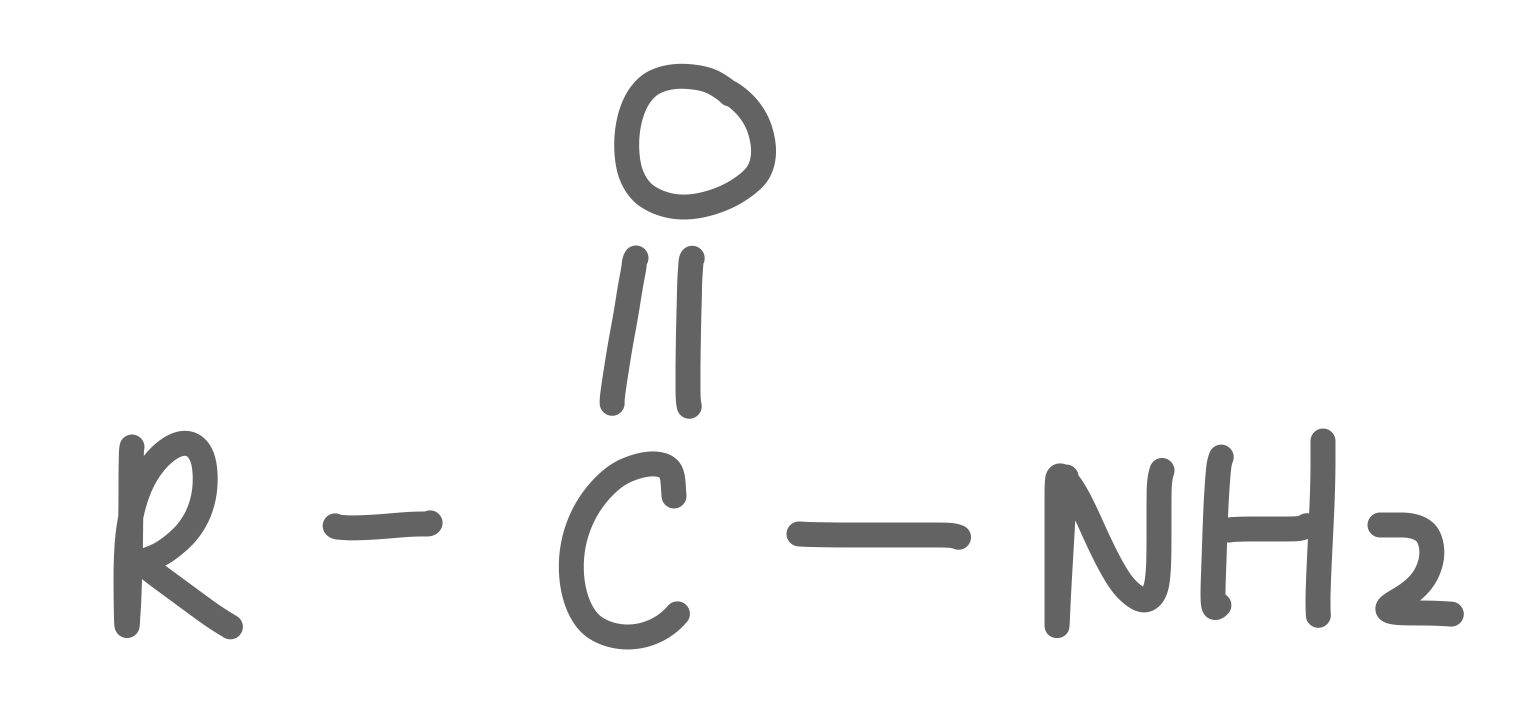
31
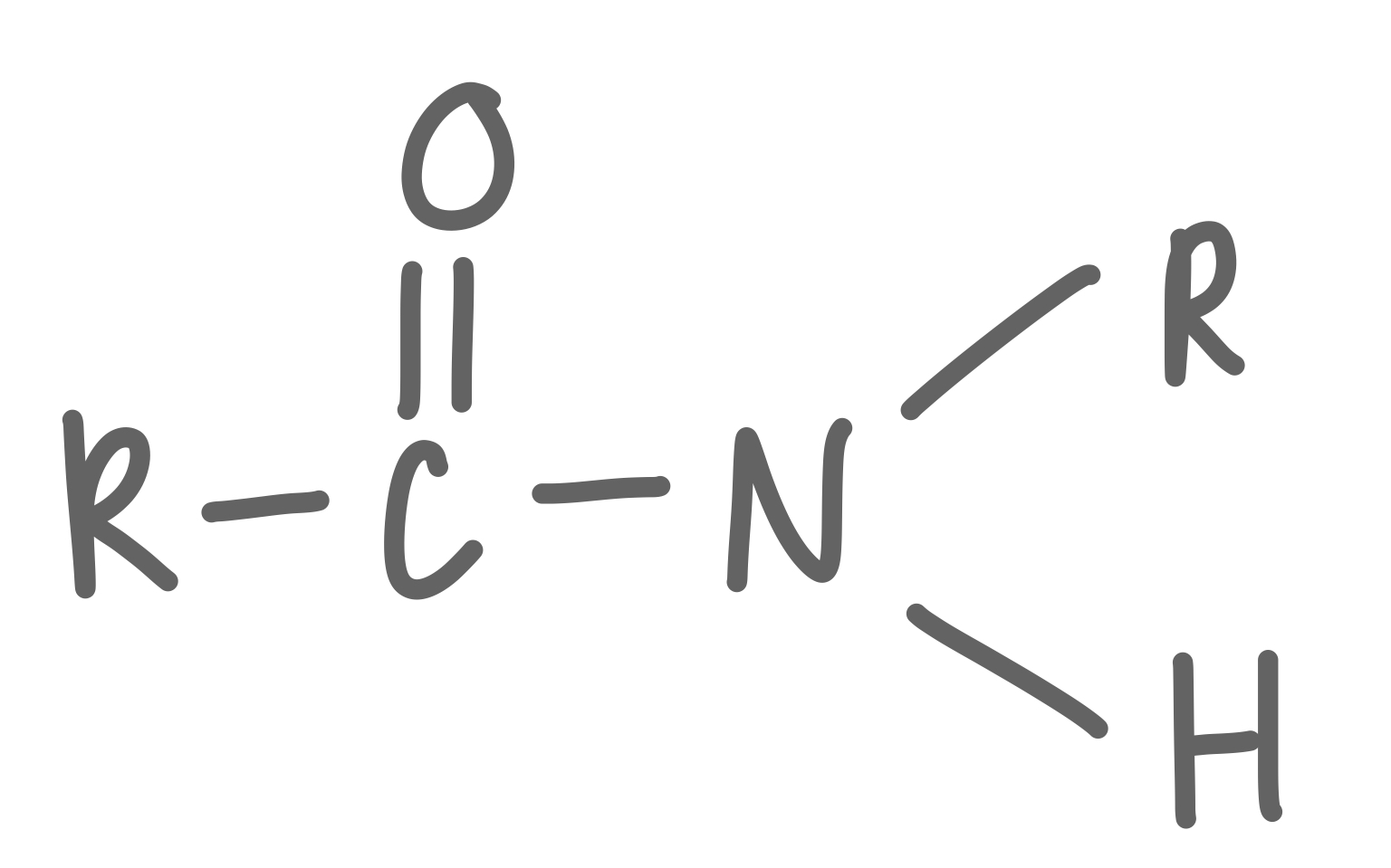
New cards
Secondary Amide
32
New cards
Tertiary Amide
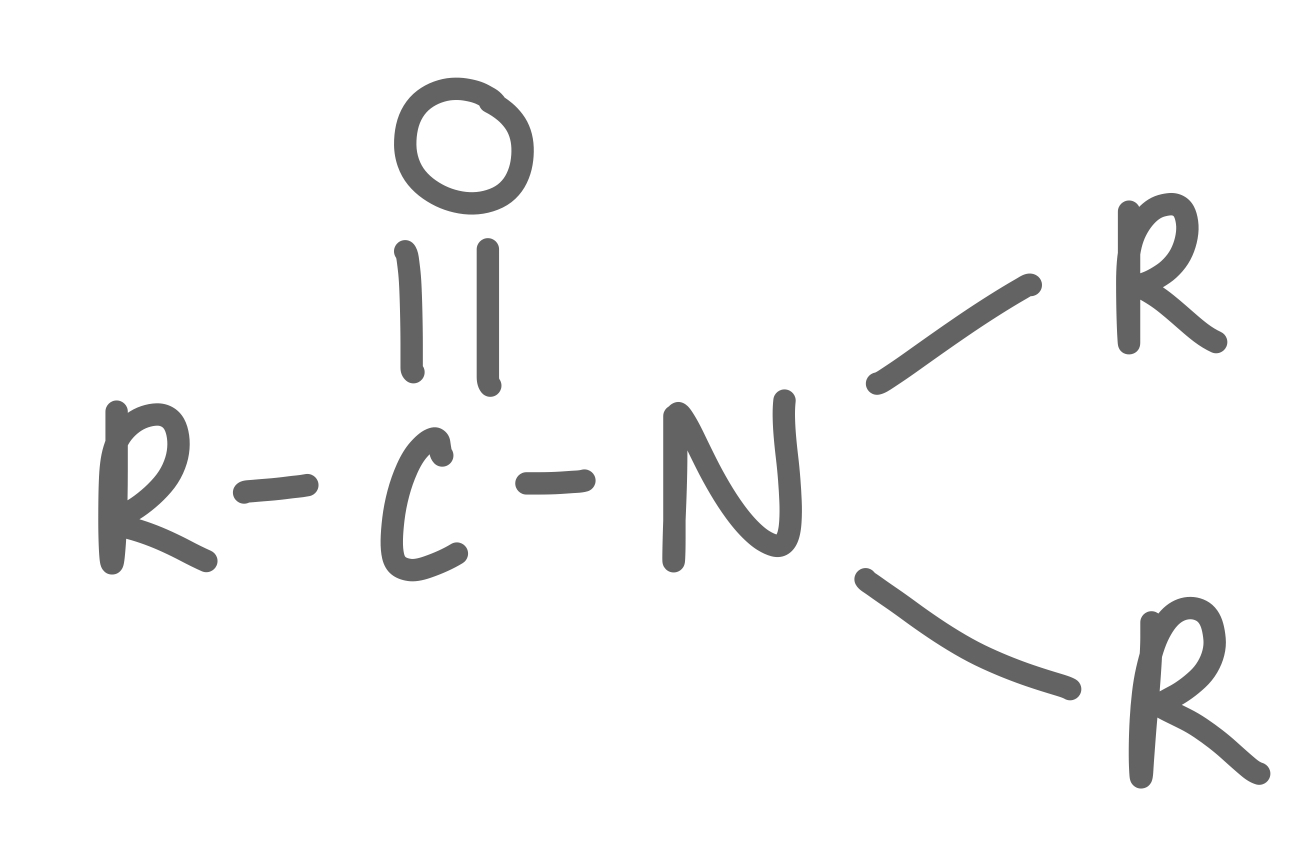
33
New cards
Thiol
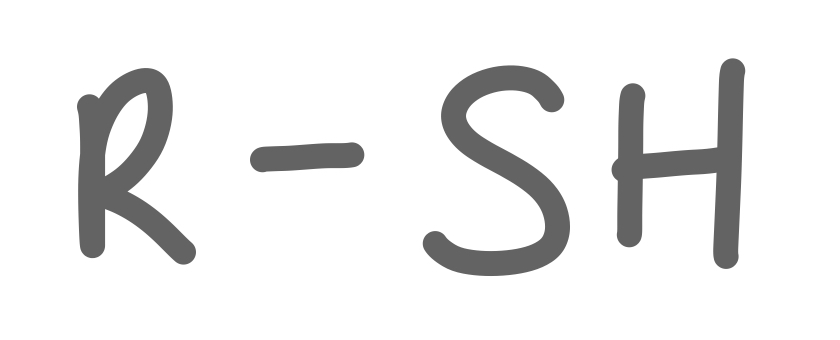
34
New cards
Sulfide
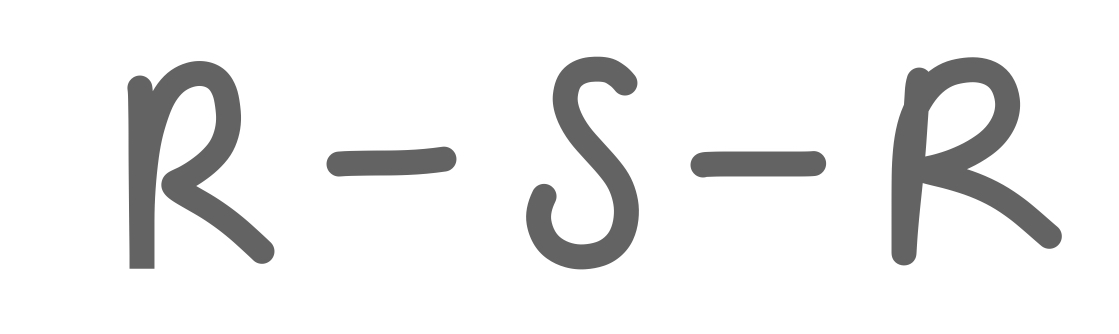
35
New cards
Aldehyde
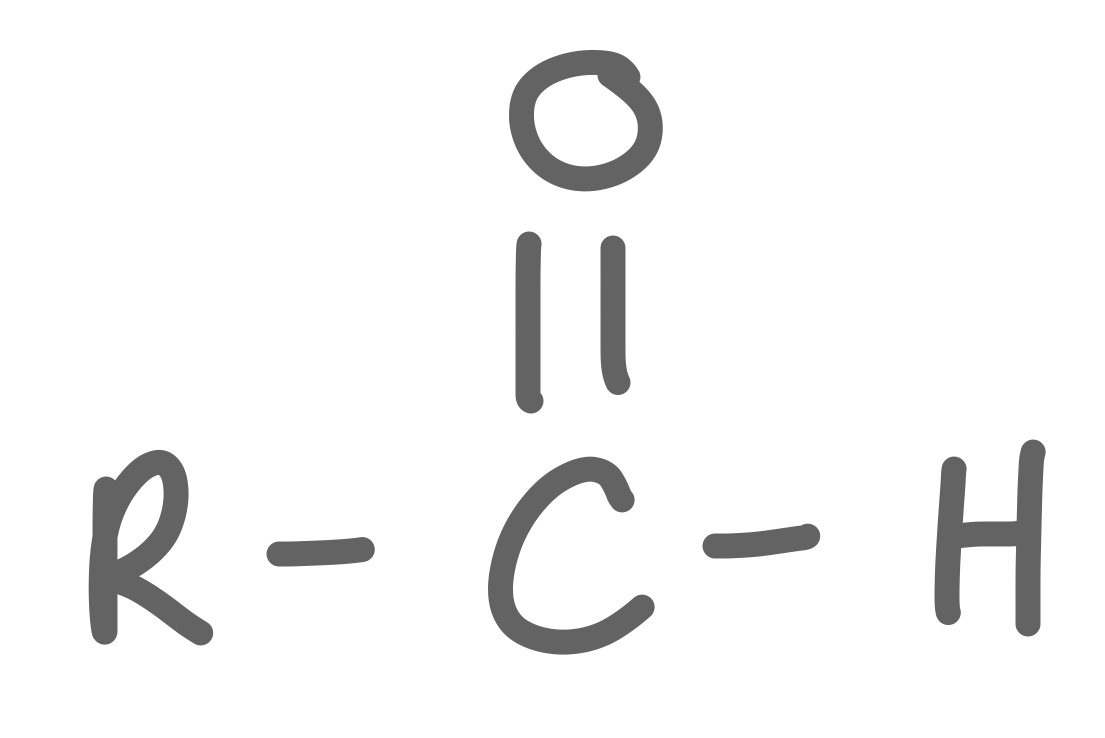
36
New cards
Ketone
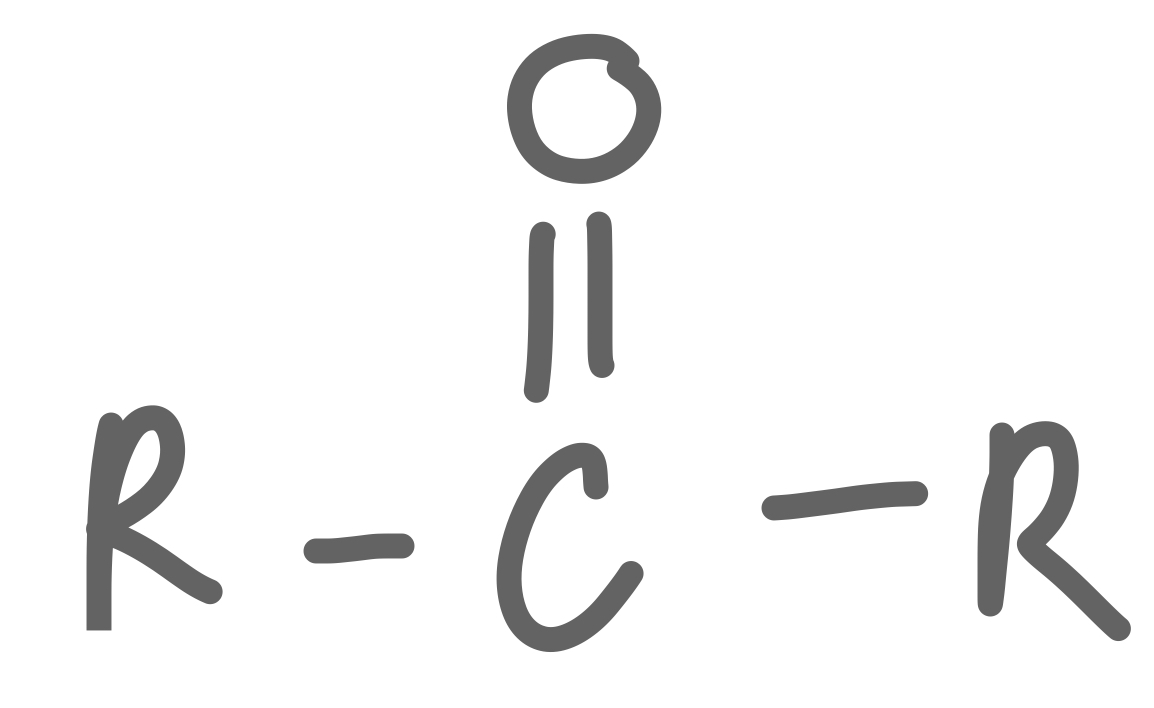
37
New cards
Carboxylic Acid
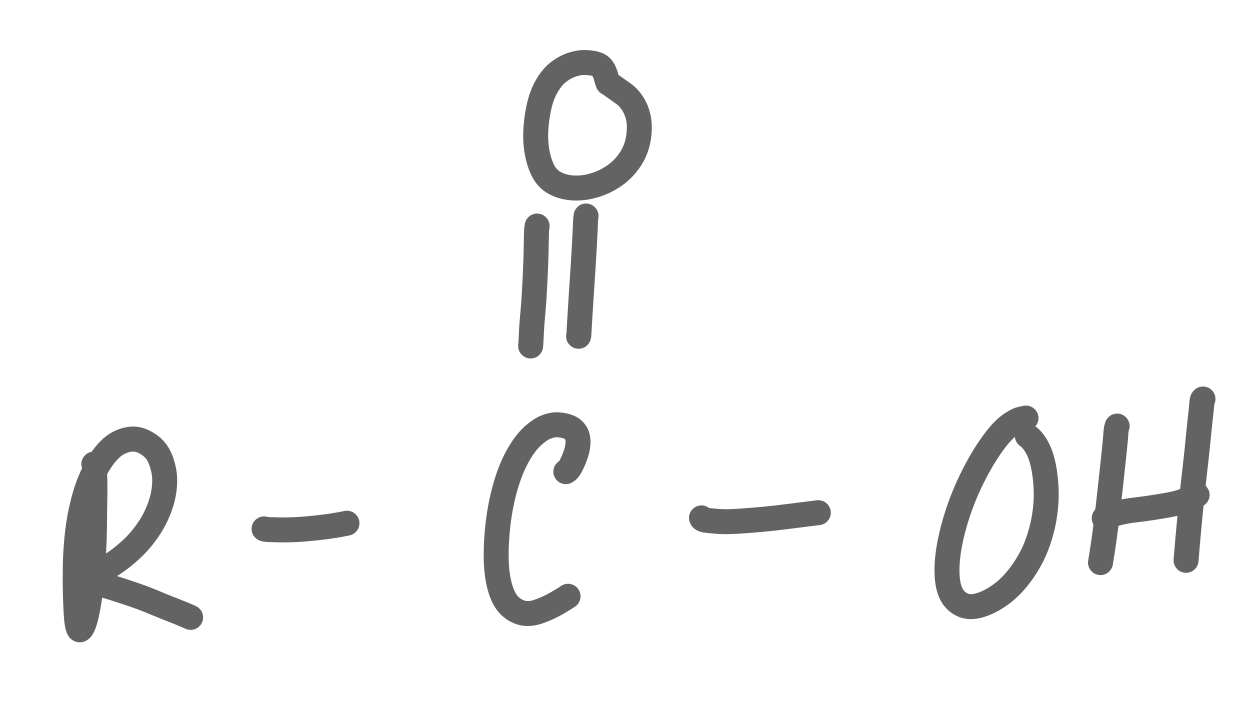
38
New cards
Ester