Ch 6: Atmospheric systems and societies
6.1: Introduction to the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a dynamic with input, outputs, storages, and flows
- Heat and pollutants are carried across the earth by air currents in the atmosphere
- The composition of the atmosphere has changed over time, these changes have significant effect on the ecosystem
Composition of Air: 20.9% oxygen, 78.1% nitrogen, 0.038% carbon dioxide, 0.93% argon, 0% other gases
The stratosphere and troposphere are where most reactions affecting life occur
Factors influencing climate:
- Biotic Factors: plants and animals
- Abiotic factors: mainly temperature and precipitation
The greenhouse effect is a natural and necessary phenomenon which maintains suitable temperatures for living systems, which is a good thing for life on earth
- Effect is caused by gases in the atmosphere reducing heat losses by radiation back into space
- Greenhouse traps heat by reducing convention which removes the heat more than by radiation
- This heat is removed by the atmosphere as it reduces loss of heat by radiation
Incoming solar radiation is mostly made up of visible light, ultraviolet light and infrared heat
- Passes through the atmosphere of the earth unaffected
If we didn’t have greenhouse gases, the heat would go straight back into space and the temperature on earth would fall drastically every night
- Some of the heat is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere which re-emits it as heat energy back to the earth
Gases: water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane which are the main greenhouse gases
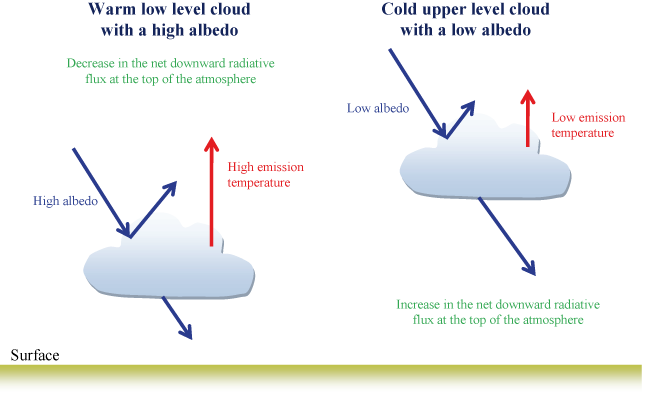
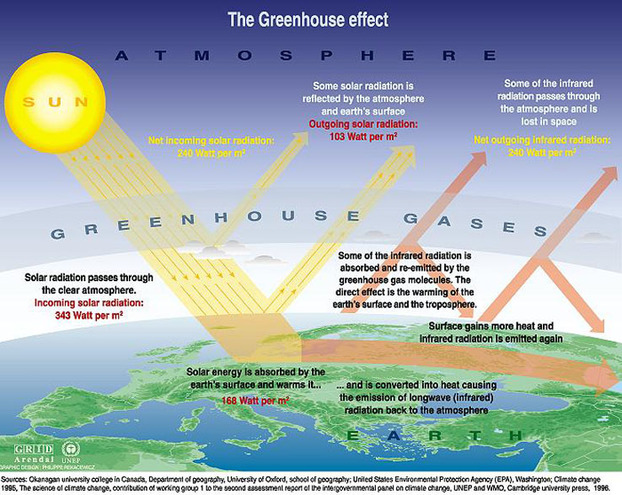
Most clouds form in the troposphere and play an important role in the albedo effect for the planet
Incoming solar radiation is mostly made up of visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared heat
Nearly 50% of this is absorbed, scattered or reflected by the atmosphere and clouds before it reaches the surface of the earth
5% is absorbed, this is used in several processes including photosynthesis, heating the ground and seas, evaporation
6.2: Stratospheric Ozone
Stratospheric Ozone: key component of the atmospheric system because it protects living systems from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation from the sun
- Human activities have disturbed the dynamic equilibrium of stratospheric ozone formation
- Pollution management strategies are being employed to conserve stratospheric ozone
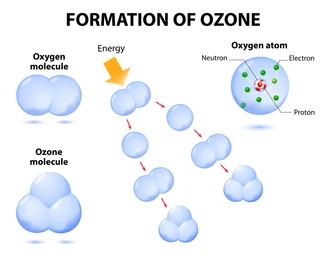
Ozone: is found in two layers in the atmospheric. Ozone is a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms.
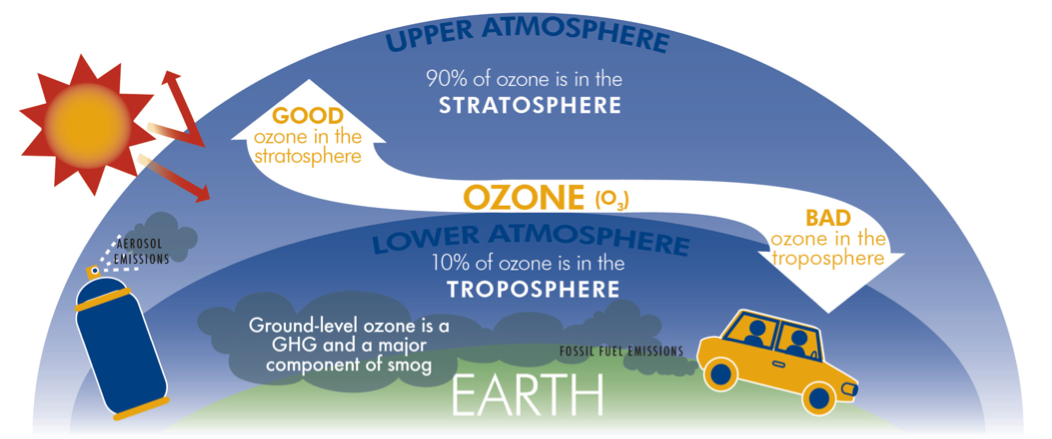
- Ozone is a reactive gas mostly found in the ozone layer in the lower stratosphere
- Ozone layer is an example of a dynamic equilibrium because ozone is contributing made from oxygen atoms and is converted back to oxygen
- Some ultraviolet radiation from the sun is absorbed by stratospheric ozone causing molecules to break apart
- Ozone destruction and reformation is an example of dynamic equilibrium
Atmosphere Ozone:
- Troposphere ozone (lower atmosphere): where it is produced as a local air pollutant and has negative impacts for humans respiratory health
- Stratospheric Ozone (in the upper atmosphere): where it is essential in reflecting ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and protecting humans from dangerous levels of UV exposure
- Formed by chemical reactions involving solar ultraviolet radiation and oxygen molecules, which make up 21% of the atmosphere.
- This breaks apart one oxygen molecule (O2) to produce oxygen atoms (2O)
- Highly reactive with oxygen molecules to produce ozone molecules
Ozone-depleting substances: including halogenated organic gases, are used in aerosis, plastics, and such to cause halogen atoms from these pollutants to increase destruction of ozone in a repetitive cycle so allowing more ultraviolet to reach the earth
Halogenated organic gases can liberate halogen atoms when exposed to ultraviolet radiation in the stratosphere
- Pollutants enhance the destruction of ozone re-formation
- This distributes the equilibrium of the ozone production system
Oxygen-depleting substances (ODS):
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs or freons) - propellants in spray cans
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbons
- Methyl bromide-pesticides
- Nitrogen oxides: bacterial breakdown of nitrates, and nitrates of soil
- Cleaning substances
Harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation:
- Genetic mutation and health defects
- Damage to living tissues
- Eye Problems (blindness or glaucoma)
- suppression of the immune system
- Damage to consumers of photosynthetic organisms
Benefits of ultraviolet radiation:
- Stimulates the production of vitamin D in animals
- Used to treat psoriasis and vitiligo
- Used as a steriliser
- Industrial uses in lasers
One chlorine atom can destroy many molecules of ozone in a chain reaction with positive feedback
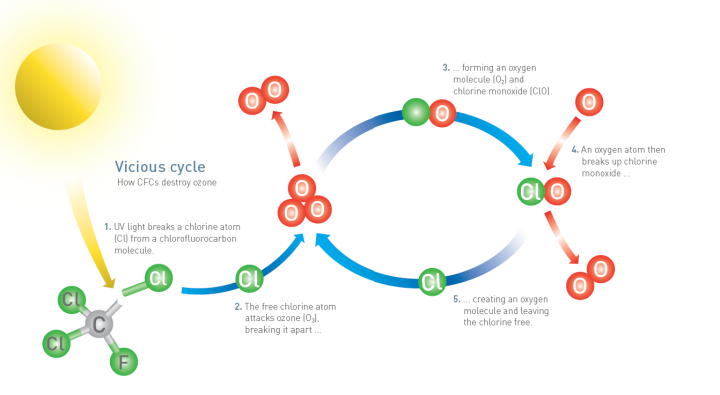
The montreal project: Is an international agreement to phase out the production of ozone depleting substances
- Made between MEDC’s and LEDC’s. The LEDC’s got more time to implement
6.3 - Photochemical Smog
Combustion of fossil fuels produces primary pollutants which may generate secondary pollutants and lead to photochemical smog, whose levels can vary by topography, population density and climate
- Photochemical smog has significant impacts on societies and living systems
- Photochemical smog can be reduced by decreasing human reliance on fossil fuels
Primary Pollutants: from the combustion of fossil fuels include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, black carbon/soot, unburned hydrocarbons, oxides of nitrogen, and oxides of sulfur
In the presence of sunlight, secondary pollutants are formed when primary pollutants undergo a variety of reactions with other chemicals already present in the atmosphere.
- Tropospheric Ozone is an example of a secondary pollutant, formed when oxygen molecules react with oxygen atoms that are released from nitrogen dioxide in the presence of sunlight
- The nitrogen dioxide released into the atmosphere is highly reactive and damages crops, which creates respiratory illness and damages fabrics and rubber materials
The ozone is found at ground level where it is naturally released by plants and soil where hydrocarbons can be found along with stratospheric ozone. This occasionally migrates down to the earth’s surface. However, these contributions to the ozone are not considered to be harmful to the health of humans or the environment
- More ozone and harmful substances are present in the lower atmosphere due to pollution and human activities.
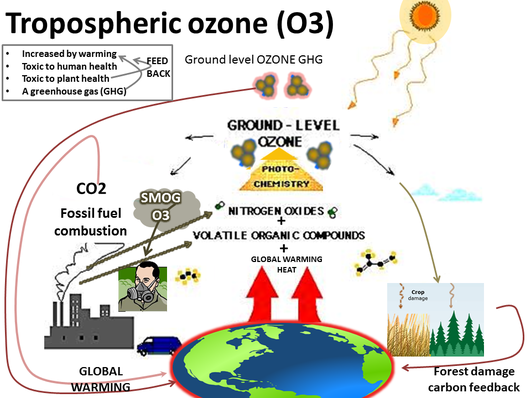
Smog: is a complex mixture of primary and secondary, of which tropospheric ozone is the main pollutant
- The frequency and severity of smog in an area depends on local topography, climate, population density and fossil fuel use.
- The ozone and smog are very toxic
Thermal Inversions: occur due to a lack of air movement when a layer of dense, cool air is trapped underneath a layer of dense, warm air
- Deforestation of largely populated forests contributes to smog
Pollution management strategies: include altering human activities to consume less. This will help decrease harmful emissions released into the environment
- This is for regulating and reducing pollutants at point of emission
- The pollution management is supported by government regulations and taxations
- Taxation of people within the country helps the government distribute the money to different functions
- Using catalytic converters to clean CO2 exhaust
- Adopting clean-up measures such as deforestation, re-greening and conservation of areas
6.4 - Acid deposition
Acid deposition: general term for acid coming down from the air
- Acid comes down in the form of rain or snow: wet deposition
- Acid comes down as ash or dry pollutants: dry deposition
- Dry and wet deposition are forms of converted secondary pollutants
The combustion of fossil fuels produces sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxides as primary pollutants
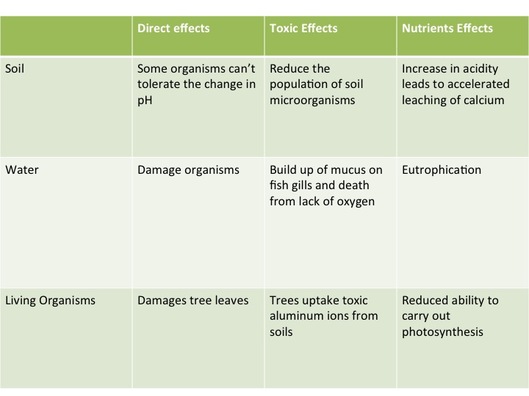
Effects of acid deposition:
- Direct effect: acid on aquatic organisms and coniferous forests
- Indirect toxic effect: increased solubility of metal on fish
- Indirect nutrient effect: leaking of plant nutrients
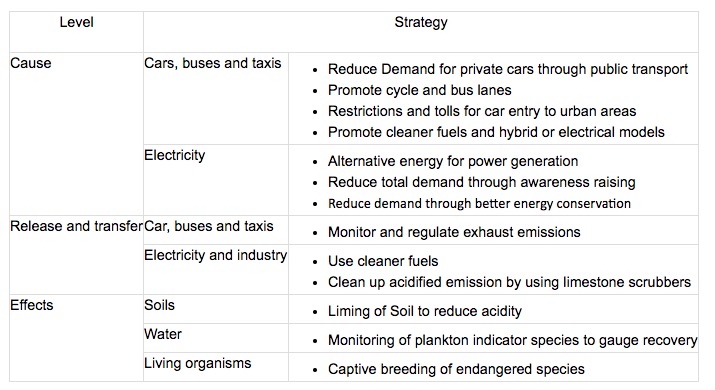
Pollution Management strategies for acid deposition:
- Altering human activities to reduce the use of fossil fuels
- Regulating and monitoring the release of pollutants through catalytic converters
- Replacing: switching to the use of renewable energy (reducing the use of fossil fuels), use less automobiles and more public transportation, increase energy efficiency
- Regulate: install catalytic converters to reduce carbon emissions produced by factories and automobiles
- Restoring: add lime to forestry plantations to increase the use of natural resources and forests (decreases the need to export and import which is harmful for the environment)
- Cleanup and restoration measure includes recolonisation of damaged systems
In the atmosphere, acid deposition travels with wind and water vapour
- Adopting a sustainable way of living helps the environment and aids in the preservation of natural resources as well.
- A greener lifestyle can be implemented by intergovernmental agreements which aids in the mission of the 17 SDG Goals
The impacts of acid deposition may be limited to areas downwind of major industrial regions but these areas may not be in the same country as the source of emissions.