Lecture 40: Mass spectrometry
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what is spectroscopy?
how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation
the theory
what is spectrometry?
application of spectroscopy to produce results
practical
what is a spectrometer?
the instrument used to measure
expensive but useful
what is mass spec?
an analytical technique used to measure the mass of a charged ion
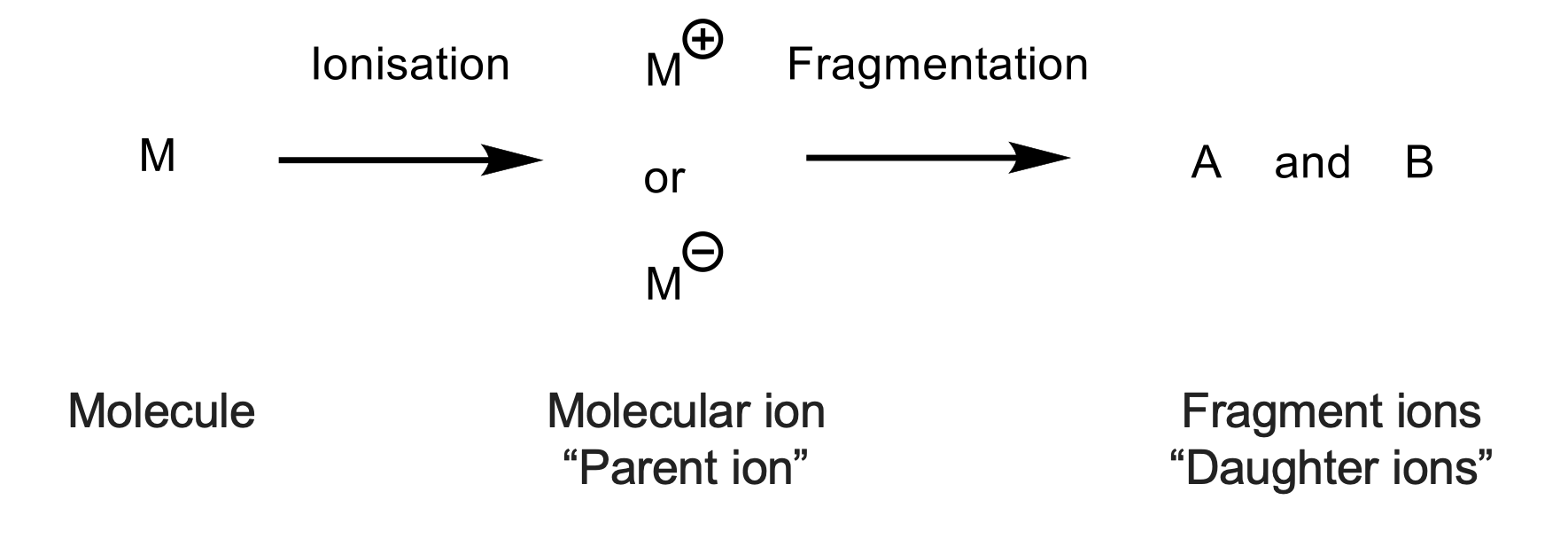
what are the 2 components of mass spec?
ionisation
separation of charged ions
what is the main process of ionisation?
molecules need to be charged
sample goes in, gets charged(hit with something) and is then sent through to the analyser
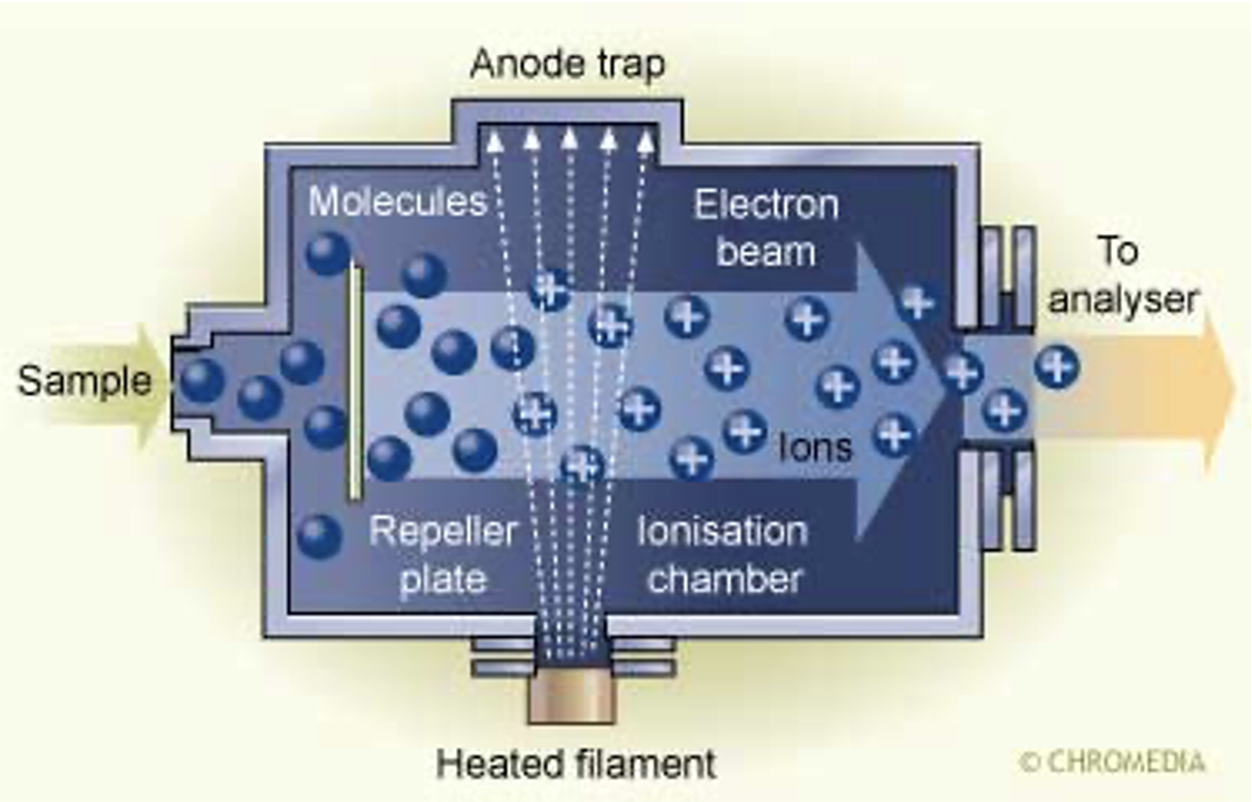
mass to charge ratio is:
m= mass of ion
z= charge of ion
mass to charge ratio m/z but since z=1usually, we just consider mass of ion
what are the different ways of achieving ionisation?
electron ionisation(electron impact)
chemical ionisation(stream of protons)
what is electron ionisation(electron impact)?
hard technique
generates a radical cation M+ in the +ve mode, or a radical anion M- in -ve mode
results in lots of fragmentation
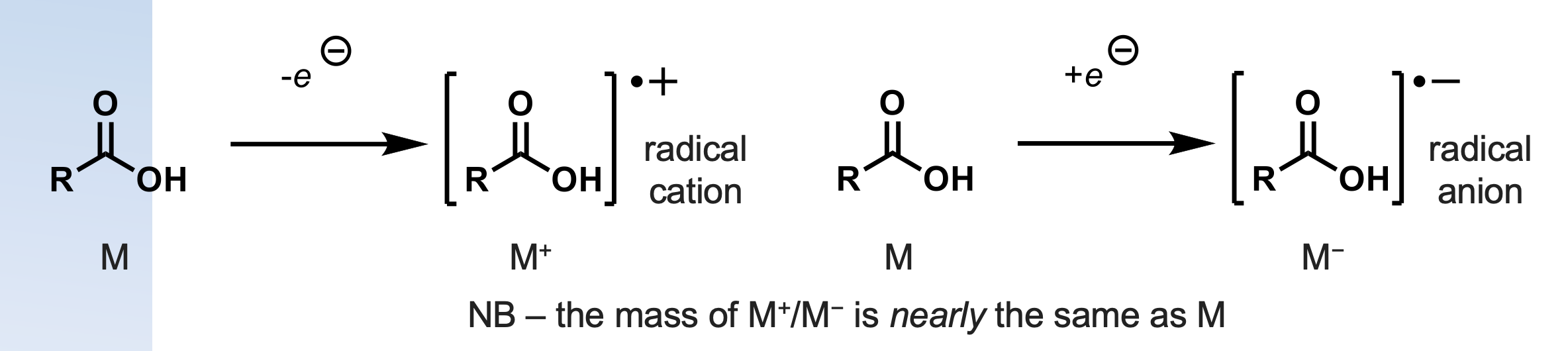
what is chemical ionisation(stream of protons)?
soft technique
generates ions through protonation to give MH+ or deprotonation to give MH-
less fragmentation

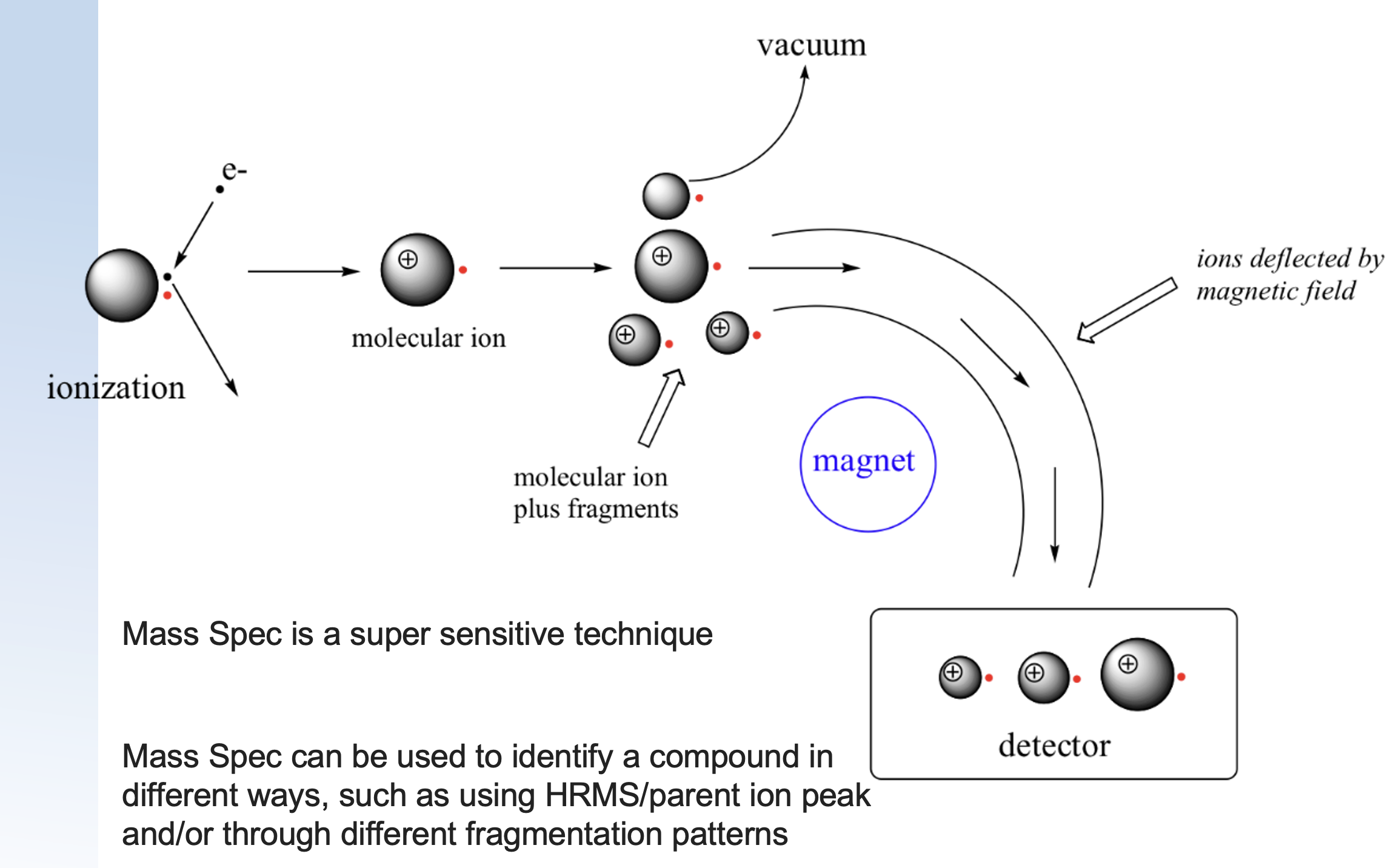
how are charged ions separated?
ionised: picks up or loses e-
starts to fragment and is charged in a vacuum
smaller particles are more displaced by magnet so are foiund on the left side, large particles are not as displaced so found on the right
how can high resolution mass spec be used?(HRMS)
mass spec can differentiate between these 2 molecules
since the exact masses will differ, high res mass spec is used to predict molecular formula but not arrangement
powerful technique used to determine specific compounds at very low concentrations
same parent ion, different molecules will fragment differently
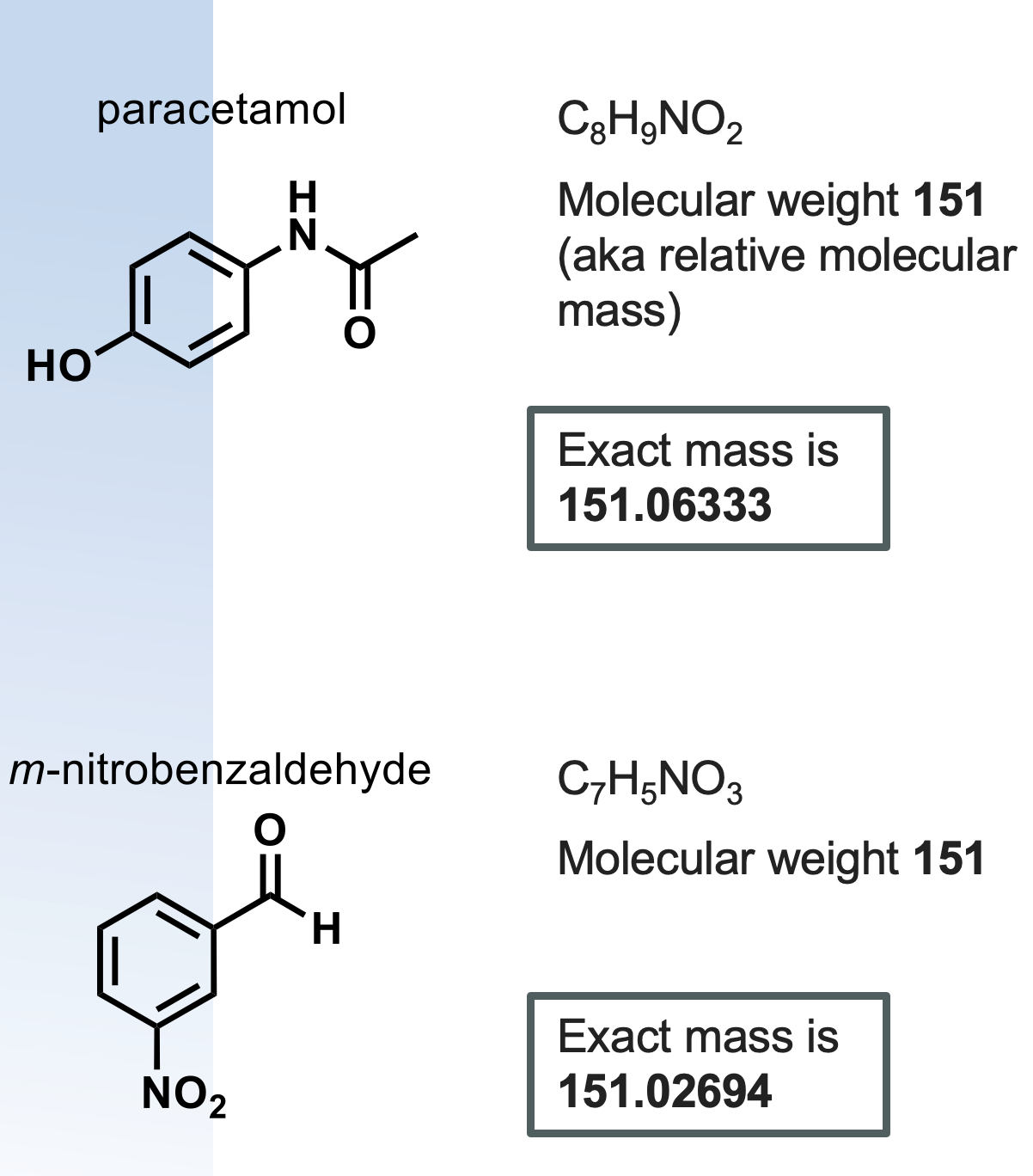
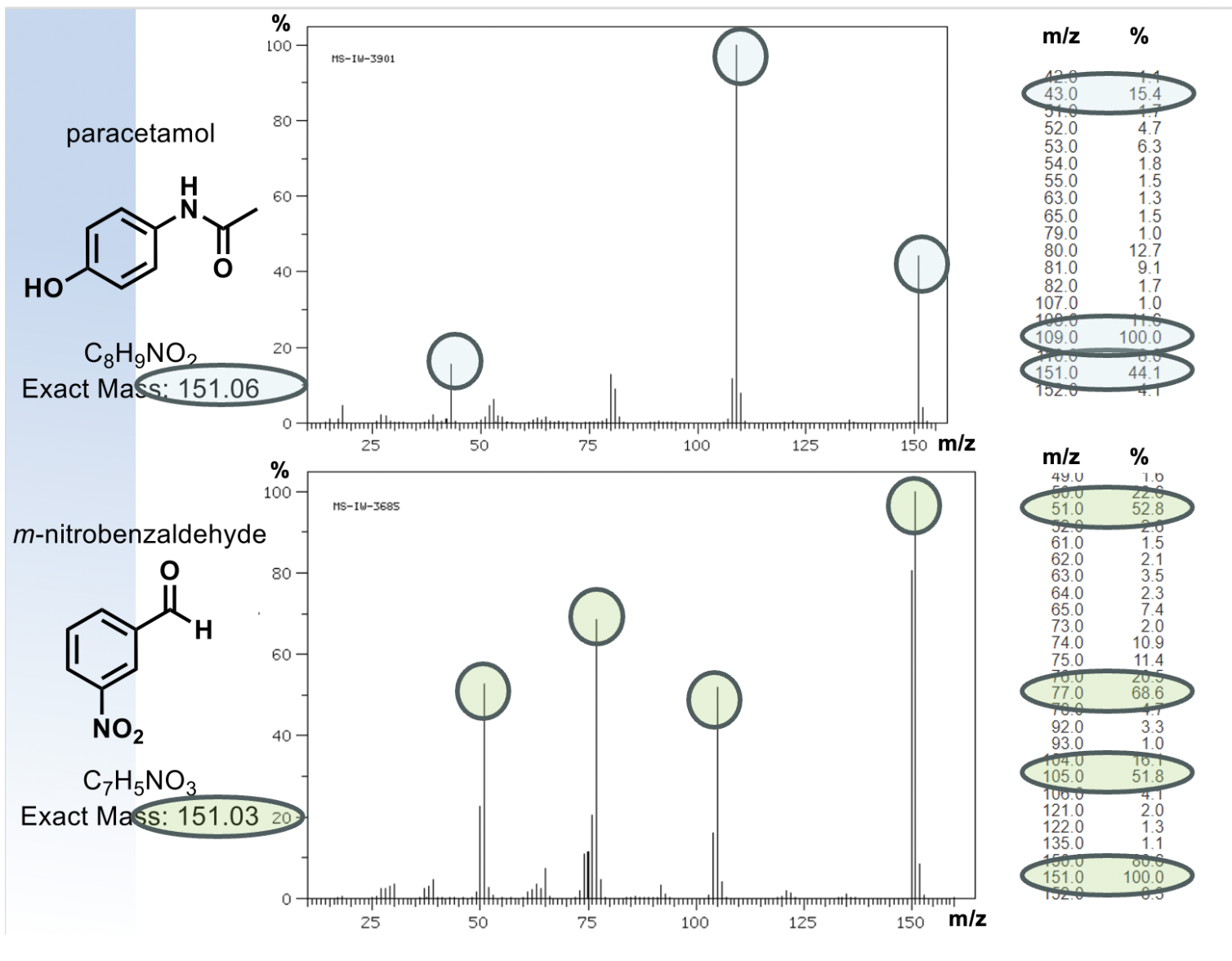
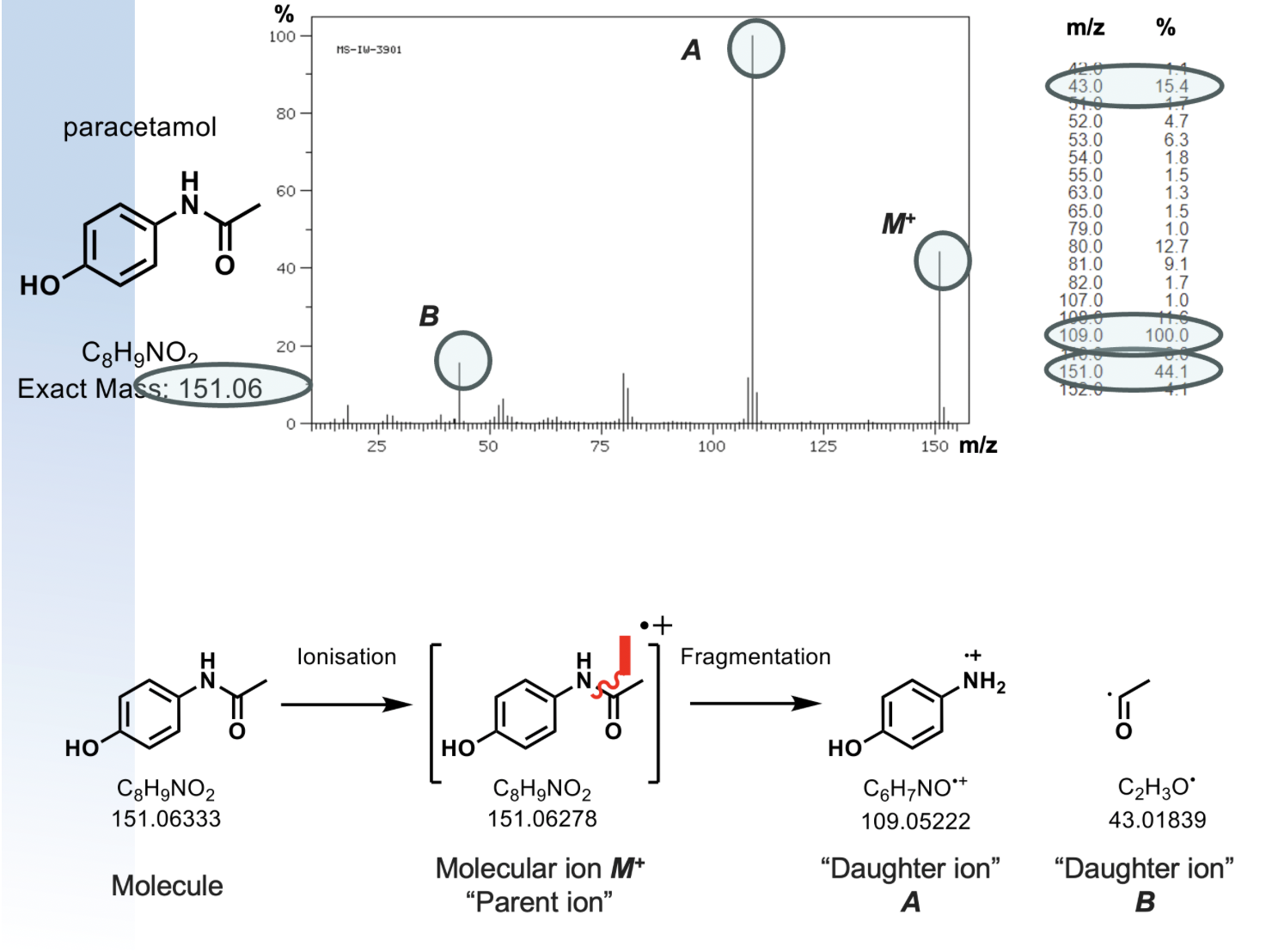
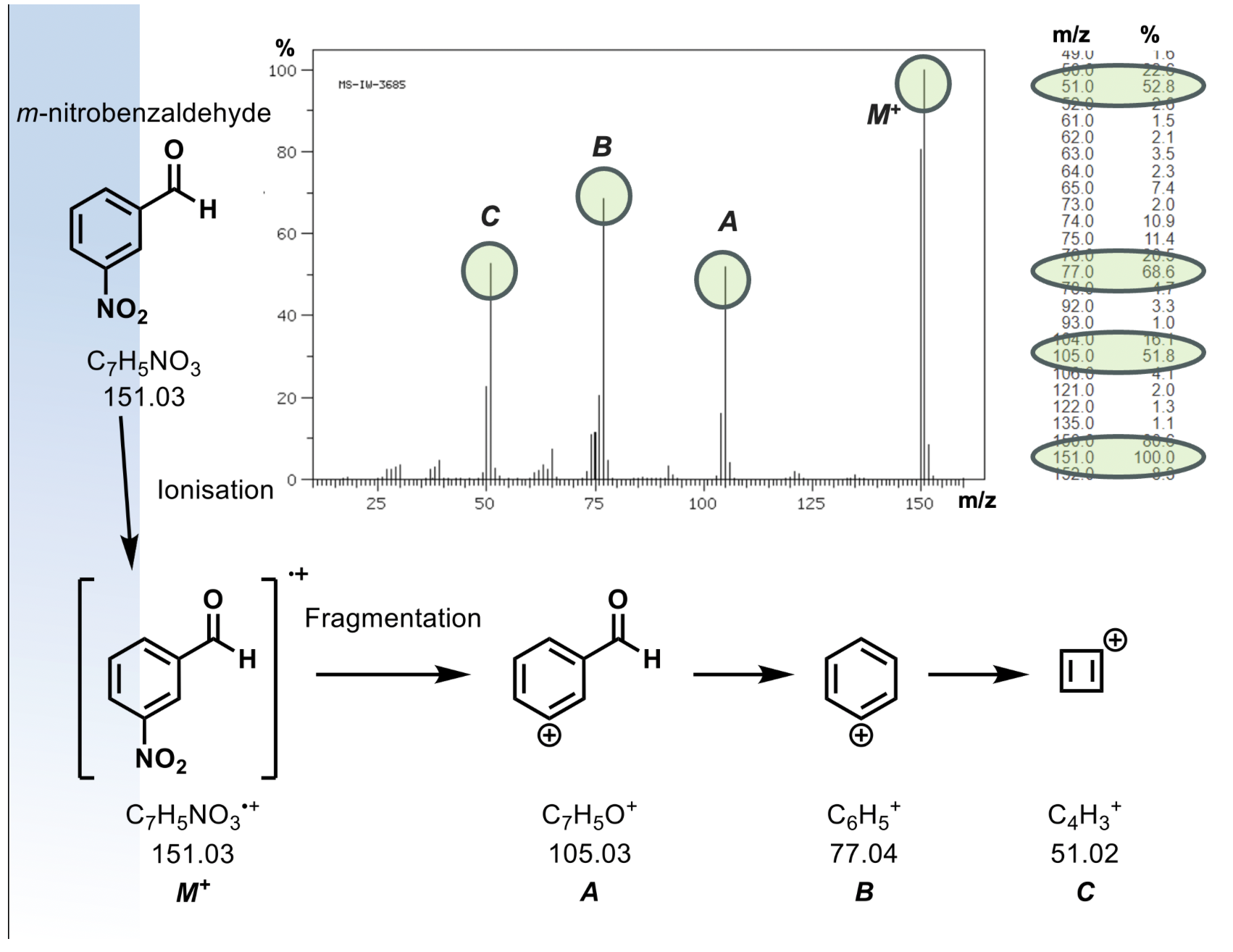
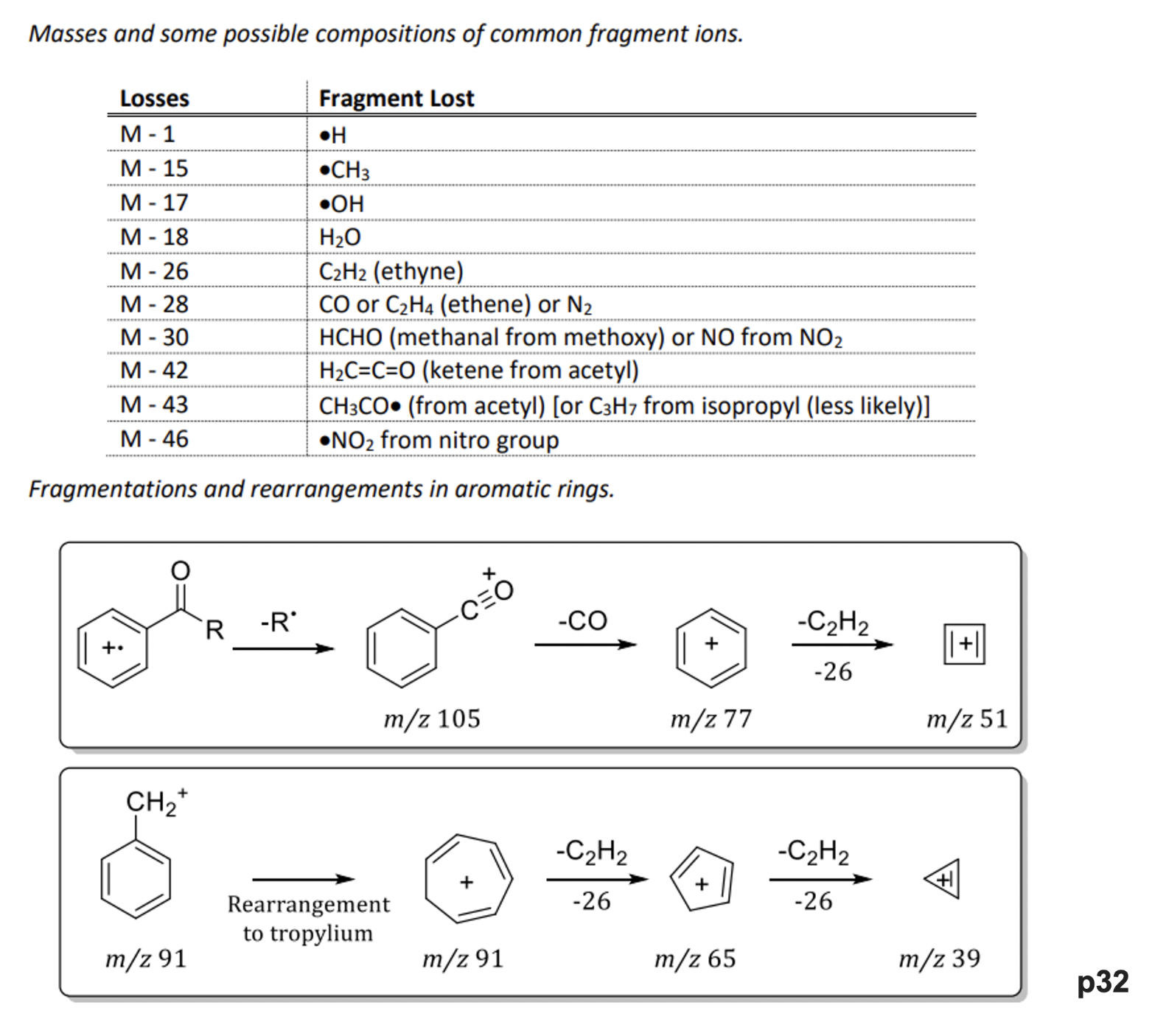
what is exact mass used for?
what is molecular weight used for?
for mass spec/analysis of single molecules
for yeild calculations- its calculated using average of isotopes
what is the nitrogen rule?
applies to neutral molecules
compounds containing C,H,N,O,S and the halogens have even molecular weights
compounds containing an odd number of N atoms are odd