10. Surgical diseases of the salivary glands and ducts. Symptoms, diagnosis and therapy.
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
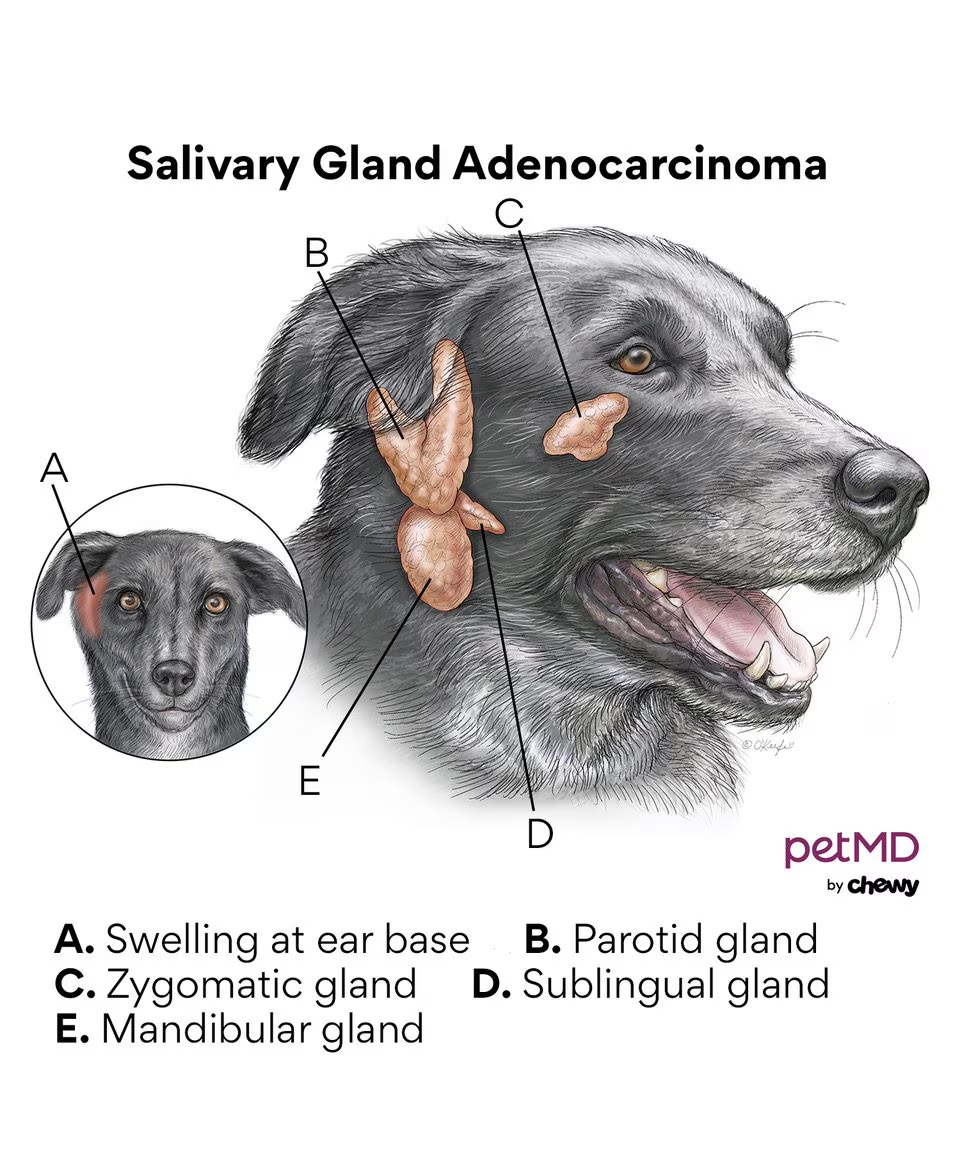
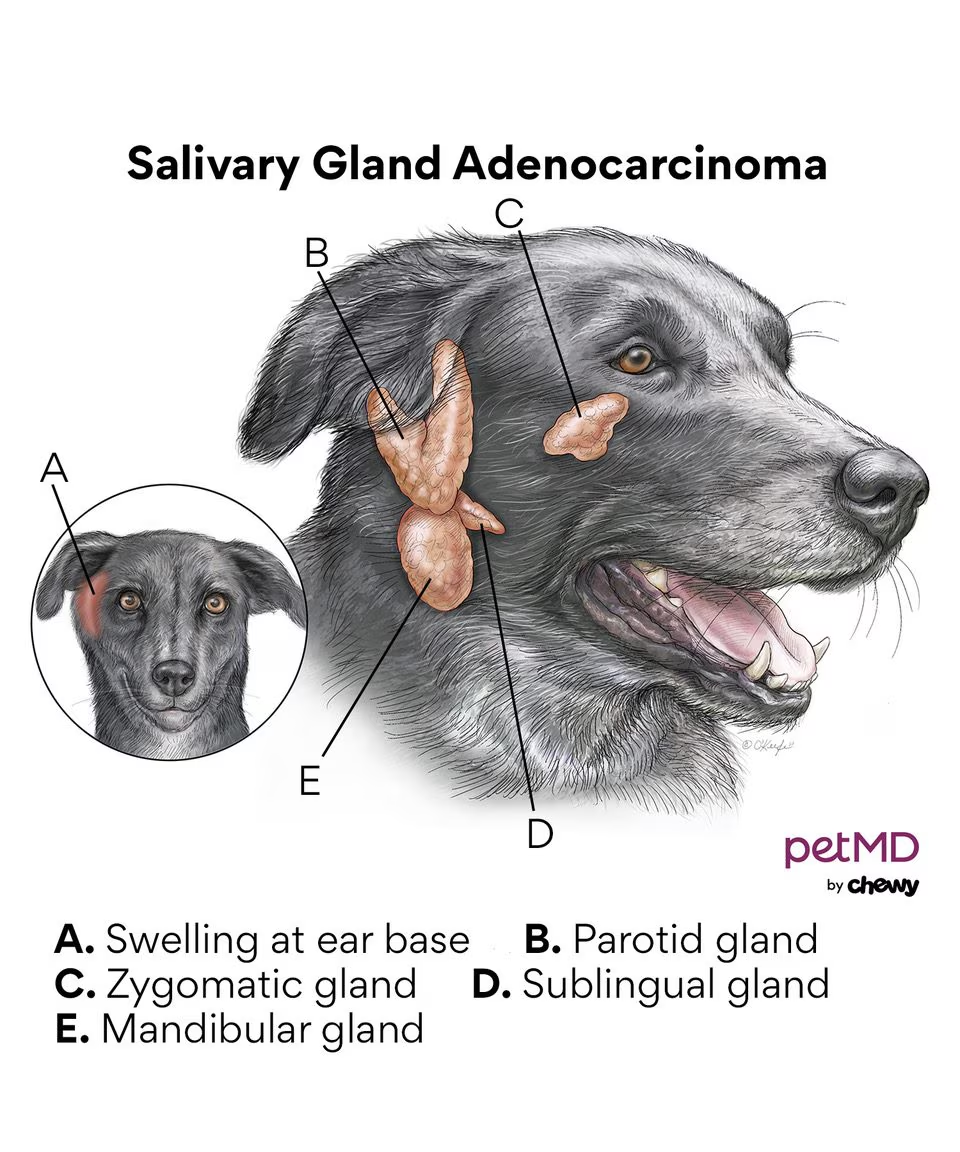
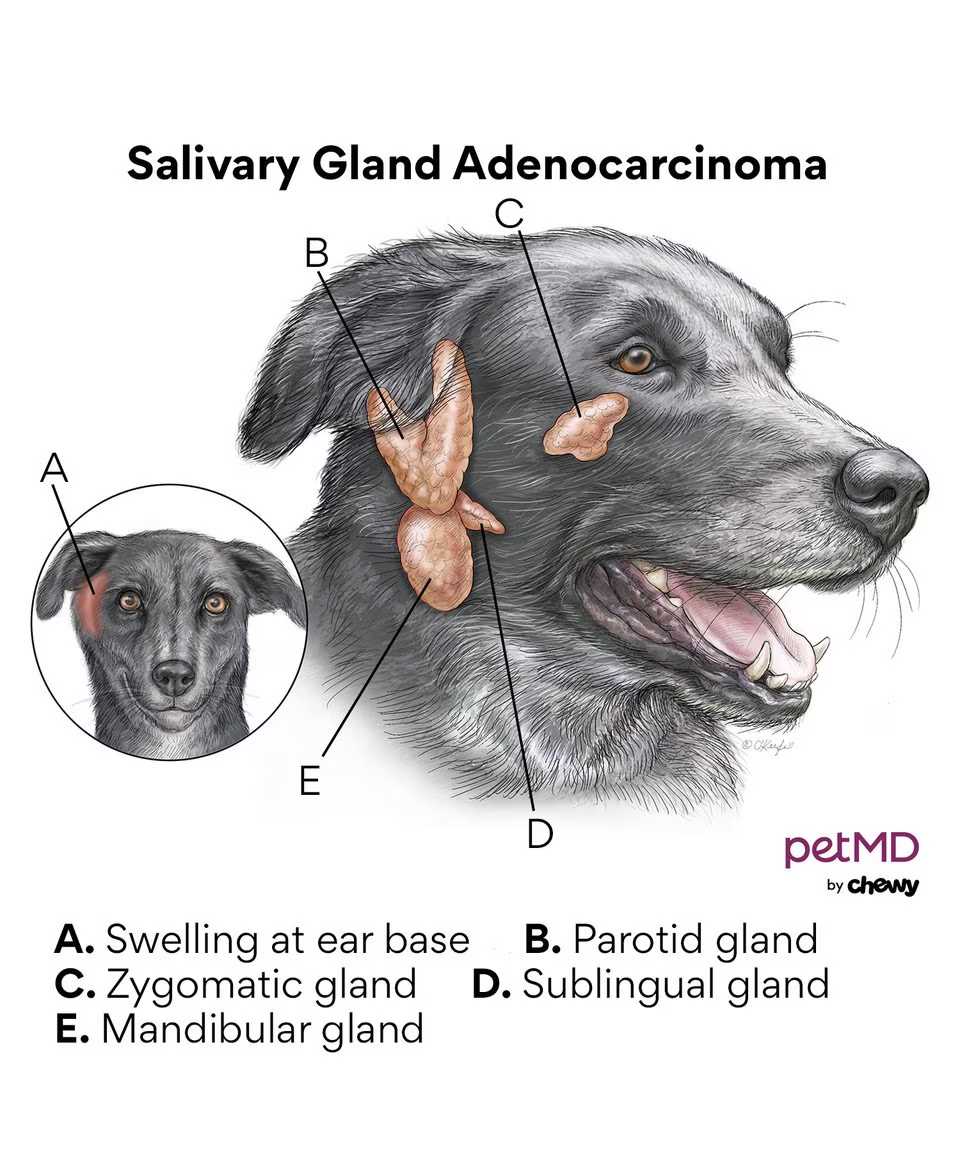
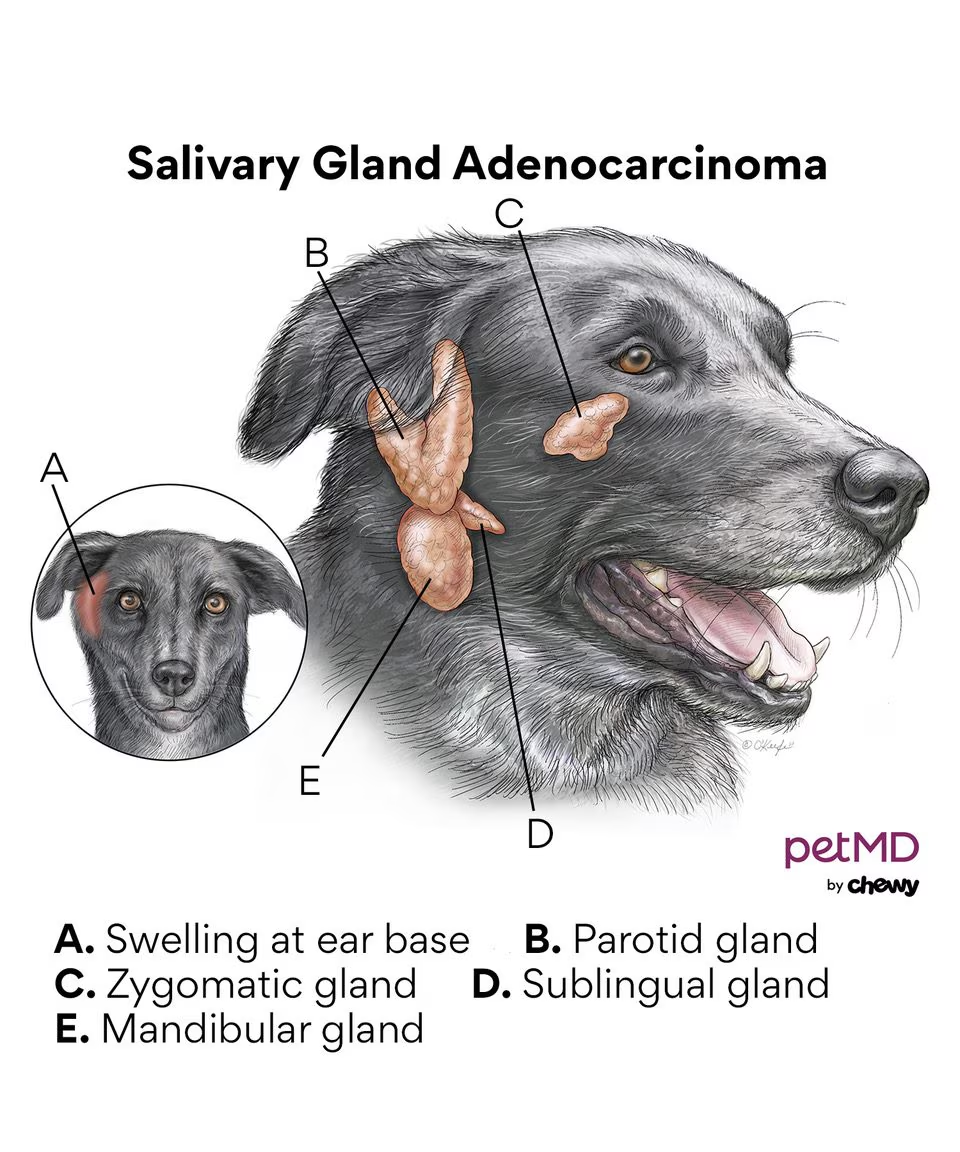
The monostomatic duct opens with the mandibular duct at the sublingual caruncle.
The polystomatic ducts have multiple small openings along the sublingual mucosa.
What effect does parasympathetic stimulation have on saliva production?
Increases saliva production.
What are examples of surgical diseases of the salivary glands and ducts?
Sialadenosis
Sialadenitis and necrotising sialometaplasia
Sialocele
Sialoliths
Rupture or fistula of salivary ducts
Salivary gland neoplasia
Salivary production disorders
What is the aetiology of sialadenosis?
Unknown
Phenobarbital (1-2 mg/kg PO every 12 hours). Surgery alone is ineffective.
What are clinical signs of sialadenitis and necrotising sialometaplasia?
Fever, depression, painful and swollen SG on palpation, vomiting.
Rupture of abscessed gland discharges pus into the surrounding tissue or the mouth. Rupture through the skin may form a salivary fistula.
How is sialadenitis diagnosed?
Clinical exam, histopathology
Cervical mucocele
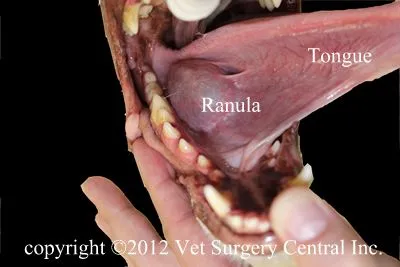
Ranula (sublingual mucocele)
Zygomatic mucocele
Pharyngeal mucocele


Aspiration of saliva, cytology, sialography, biopsy, USG, MRI, and CT
Sialadenectomy of the affected gland
Removal of saliva by incision or aspiration (often recurs)
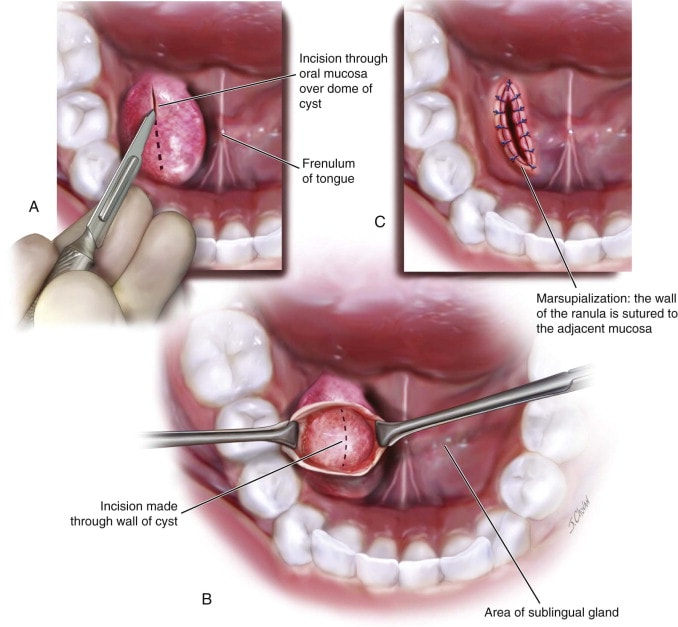
Ranulas are treated by marsupialisation.
Calcified masses (salivary stones) that form in salivary glands (calcium, oxalate, phosphate, etc.)
Palpation, radiography, USG, and CT scan
Depends on location, infection, and recurrence risk. Options include:
Surgical removal of the affected duct-gland complex if easily accessible.
For stones near the oral papilla, mucosal incision and removal, healing by second intention.
Duct ligation, resection and anastomosis, or primary repair for complex cases.
Marsupialization into the oral cavity for cases with duct dilation
Trauma to the mandibular, zygomatic, or sublingual salivary glands.
Injury such as bite wound, abscess drainage, or prior surgery causes iatrogenic rupture
Draining sinuses caused by foreign bodies or endodontic disease of a mandibular tooth.
Mass and lymph node sampling (biopsy), three-view thoracic radiographs for metastases, and CT/MRI for surgical planning.
Sialadenectomy (removal of the affected gland with tumour). Radiotherapy.
What are examples of salivary production disorders?
Ptyalism
Hypoptyalism
Drugs, toxins or poisons (organophosphates)
Local irritation or inflammation associated with stomatitis, glossitis (especially in cat), oral foreign bodies, neoplasms, injuries or mucosal defects
Infectious diseases (Rabies), nervous form of distemper, or other convulsive disorders
Motion sickness, fear, nervousness, excitement
Reluctance to swallow or interference of swallowing (esophageal irritation, obstruction)
Sublingual lesions
Tonsillitis
Administration of medicine
Conformational defects
Metabolic disorders (hepatic encephalopathy)
Abscess or other inflammatory blockage conditions of the salivary gland
What is important before examining an animal with ptyalism?
Eliminate possibility of rabies (vaccine, history of dog/fox bites)
Treating the underlying cause.
Glycopyrrolate reduces production of saliva
Treating the underlying cause.
Pilocarpine stimulates saliva production. Encourage drinking water.
What are examples of surgeries of the salivary glands?
Sialadenectomy (extirpation)
Marsulialisation
Blunt and sharp dissection to expose and decompress sialocele.
Identify and dissect glands from surrounding tissues.
Ligate blood vessels and continue blunt dissection rostrally along ducts.
Ligate or carefully dissect ducts, avoiding the lingual branch of the trigeminal nerve (V → V3 n. mandibularis → n. lingualis).
Transect ducts and glands near the oral cavity if necessary.
Incise platysma to expose external jugular bifurcation.
Blunt dissection to expose salivary glands (differentiate from mandibular lymph nodes).
Incise capsule, ligate vessels, and retract glands caudally.
Bluntly dissect sublingual gland under the digastricus muscle, clamp ducts, and excise glands.
If ranula is present, extend dissection past lingual nerve to sublingual caruncle, ligate and transect duct.
Closure: Use absorbable monofilament to close tissues, optional drainage for sialocele.
What is the procedure for marsupialisation?
Drain mucocele (usually ranulas) by excising an elliptical, full-thickness section of the mucocele wall.
Suture the granulation tissue lining to the sublingual mucosa to encourage draining for several days.
Marsupialised ranulas contract and heal quickly by secondary intention
What type of tumour can be seen in the salivary glands?
Adenoma/adenocarcinoma