5_Isolation of Mitochondria and Nucleus
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Chloroplasts
are the organelles in plant cells and algae responsible for photosynthesis
photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are the organelles in plant cells and algae responsible for
Palisade and spongy mesophyll cells
The ___ of the epidermal layers of leaves are the structures where most of the chloroplasts are located.
mitochondria
are another membrane-bound organelles described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
mitochondria are another membrane-bound organelles described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of ____, used as a source of chemical energy.
centrifugation
In studying the features of subcellular components like mitochondria,___ becomes a popular concept.
It is one of the techniques used in isolating various organelles and components of the cell. It is based on the principle that every cell’s organelles have various densities and sedimentation coefficient and therefore subjecting the organelles to varying centrifugal forces, the selected organelle can be precipitated and therefore be separated.
Papaya (Spinach in module)
What source was used to isolate the chloroplasts from its leaves?
Cauliflower
What source was used to isolate mitochondria?
Composition
Studying subcellular components:
the native structure of the cell organelles
Function
Studying subcellular components:
the activity of their components
Morphological, Biochemical, Biophysical, Physiological
Studying subcellular components:
Where components structures differ
to lyse/break open the cells
Methods of cell disruption is to?
MM. SD. CM.
(Mechanical method, Structural Damage, Chemical Methods)
Methods of cell disruption are:
Homogenization, Pressure, Sonication, Grinding
Methods of cell disruption - Mechanical Method:
Osmotic shock, Freeze/Thaw
Methods of cell disruption - Structural Damage:
Detergents, organic solvents, Enzymes
Methods of cell disruption - Chemical Method:
Methods of Cell Disruption
All of these methods allow receiving a mixture of subcellular organelles, which is very convenient for further separation
Mammalian tissues
In Homogenization, these are easy to homogenize
Plant tissues
In Homogenization, these are tougher (because of the cell wall)
Mortar and pestle, Mixers, Rotating knives/razor blades, Juice extractors, Ball mills
Standard Homogenizers:
Osmoticum, Buffer, Metal ion chelators, Antioxidants, Bovine serum albumin (BSA), Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)
Homogenization mediums:
broken cells
The resulting homogenate is composed of ____ with subcellular components released in a buffered medium
Debris
must be separated by standing the homogenate for some time or by filtration
Supernate or filtrate
is subjected to Centrifugation
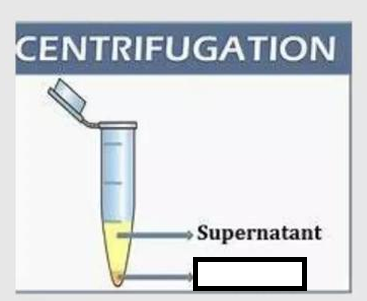
Solution (Supernantant)
To more rapidly and completely cause the precipitate (pellet) to gather on the bottom of the tube. The _______ is then either decanted or used in other step.
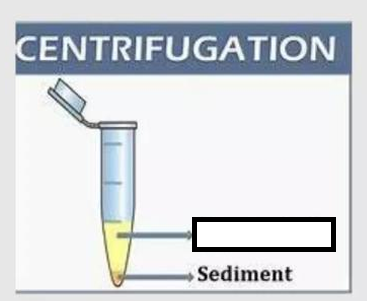
Sediment/Precipitate (Pellet)
So as to more rapidly and completely cause the _____ to gather on the bottom of the tube. The solution (supernatant) is then either decanted or used in other step.
Centrifugation
a process that involves the use of the centrifugal force for the separation of mixtures used in laboratory, increasing the effective gravitational force on a test tube
used for the isolation and purification of organelles and macromolecules.
RPM or g
The rate of centrifugation is specified by the acceleration applied to the sample, typically measure in ___
rate of movement of the particle through a specific solution
In centrifugation, when a particle is subjected to centrifugal force by spinning a cellular extract at extremely rapid rates in a laboratory centrifuge, the ___ depends on its size and density, as well as the solution's density and viscosity.
size and density, as well as the solution's density and viscosity.
In centrifugation, when a particle is subjected to centrifugal force by spinning a cellular extract at extremely rapid rates in a laboratory centrifuge, the rate of movement of the particle through a specific solution depends on its___
different densities (mg/mL)
Cell organelles usually have ___
LSC. HSC. UC. DC. DGC.
(Low-speed centrifuge, High-speed centrifuge, Ultracentrifuge, Differential centrifugation, Density gradient Centrifugation)
Types of Centrifuges:
Low-speed centrifuge
What type of centrifuge?
Table centrifuge
typical maximum speed is 6000 rpm
room temp.
cell, nucleus, etc. (easily precipitated material)
High-speed centrifuge
What type of centrifuge?
max. speed 20,000 - 25,000 rpm (60,000 X g)
temp. control
cell, nucleus, organelle, etc.

Ultracentrifuge
What type of centrifuge?
max speed 98,000 (1,000,000 X g)
temp control and vacuum system
cell, nucleus, organelle, components of membrane, polysome, macromolecule, etc.

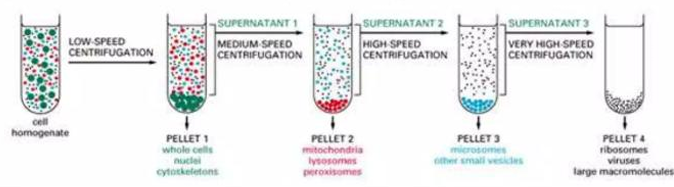
Differential centrifugation
What type of centrifuge?
is a procedure in which the homogenate is subjected to repeated centrifugations each time increasing the centrifugal force
is used for the first steps in cell fractionation because it rapidly separates large membrane organelles from smaller one. It is based on differences in speed at which organelles sediment to the bottom of a centrifuge tube.
Density gradient centrifugation
What type of centrifuge?
is a procedure for separating particles in which a sample is placed in a preformed gradient such as sucrose. Upon contrifugation, the particles are “banded” in the gradient and can be collected as a pure fraction
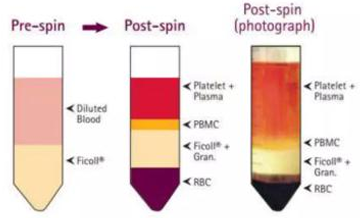
pure fraction
Density gradient centrifugation is a procedure for separating particles in which a sample is placed in a preformed gradient such as sucrose. Upon contrifugation, the particles are “banded” in the gradient and can be collected as a ____
Light Microscopy
Isolating and purifying organelles is to use ____ for the use of cytochemical methods and immunofluorescence methods
Electron microscopy
Isolating and purifying organelles is to use ____ for the observation of morphology and the use electron microscopy methods
Microscopy (LM)
for some fractions (including nuclear and nucleolar)
Both phase-contrast and interference microscopy are based on the amplification of phase differences, caused by differences in refractive index, within various structures of the observed specimens
Phase optic
allows estimation of unstained native cell organelles, without harming them
additional specific staining
For others, ____ (using dyes that selectively stain the required structures or compartments of the cell) should be applied in order to increase the contrast
Cytochemical methods
Observations under the LM are made after fixation, to preserve the organization of the cell and cellular organelles as natural state as possible.
Janus Green
A blue-green dye for staining mitochondria
Redox indicator sensitive to active mitochondria
stains mitochondria by undergoing oxidation in active mitochondria, producing a blue-green color. This highlights functional mitochondria due to their oxidative metabolism.
Janus green B for vital and staining
Mitochondria stains greenish blue - due to the action of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase system, which maintains the dye in the colored form.
Janus Green for Reduction-Oxidation indicator
• It accepts H+ that are used in ATP at the mitochondria.
• When the dye accepts the H+, it causes the dye to become pink or colorless
• This is REDOX reaction
pink or colorless
Janus Green for Reduction-Oxidation indicator
• It accepts H+ that are used in ATP at the mitochondria.
• When the dye accepts the H+, it causes the dye to becomes ____
• This is REDOX reaction
greenish blue
In using Janus green B for vital staining, Mitochondria stains ___ - due to the action of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase system, which maintains the dye in the colored form.
Leaves of spinach and lettuce
are commonly used for the isolation of chloroplasts
Intact chloroplasts
are the best source for studying the processes like carbon assimilation, electron flow, and phosphorylation
A 650 × 100/36
Formula for mg/ml chlorophyll concentration:
Spectrophotometer
an instrument which measures the absorption or transmission of light by a solution at any wavelength(s) selected by the experimenter
Lacto-aceto-orcein
Stain used for nuclear fraction
Binds DNA and chromatin proteins
stains nuclei by binding strongly to DNA and chromatin proteins. The acidic dye highlights the chromosomes for clear visualization under a microscope, showing deep red or purple coloration.
Deep red or purple
Subcellular fractions
___that are smaller than these which are suspended in the supernatant would require higher speed and longer time of centrifugation.
Percoll
is a colloidal substance made up of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silica particles which is used with success for cells and organelle separation.